Prikupets L.B., Ph.D., Head of Lab. All-Russian Scientific Research Institute (VNISI) named after. S. I. Vavilova, leading consultant of BL TRADE LLC.
Industrial floriculture using light culture technology has made a qualitative leap over the past 10 years. More than a dozen new greenhouse complexes with modern high-tech greenhouses with a total area of more than 100 hectares have been built. As a result, by 2015, about 180 hectares of floricultural greenhouses (CVGs) with light culture technology are operating in Russia, which is approximately 1.25 times greater than the area under light culture of vegetable plants. The digital lighting sector is one of the most energy-intensive (in specific terms) and, at the same time, the most energy-efficient among consumers of electric lighting devices and light sources. Illumination levels in greenhouses reach 15 klx (in traditional lighting installations in buildings more than an order of magnitude lower), the daily photoperiod can last up to 20 hours in the darkest months of the year, the duration of lighting per year is about 5000 hours, the specific installed power is at level 100–120 W/m2.
The importance of light for plants
The main conditions for the development of any vegetation are warmth, light and water. Due to these biological characteristics, vegetative processes are impossible during short winter days. The fact is that natural or artificial light gives the stems energy for growth.
Thus, entire chains of organic reactions arise from the simplest molecules. When photons of rays hit the surface of the foliage, they trigger the biochemical interaction of its components, resulting in the growth of the root system and above-ground biomass of the crop, that is, photosynthesis.
Did you know? The color of plant biomass is due to the fact that during the growth process they reflect green light and absorb rays of other colors for photosynthesis. If you place a growing stem under a green lamp, it will wither.
The consequences of light deficiency for plants can be:
- thinning and stretching of cuttings;
- fragility and fragility;
- leaf deformation;
- growth inhibition;
- yellowing of the root layers of biomass.
After all, without it, the laying of buds and fruits is impossible. In this case, it is important to focus on the light type of the crops being grown. They are:
- Short daylight hours. These are plants that came to our latitudes from the tropics and subtropics. For the formation of their flower stalks, it is important that the night lasts at least 12 hours. This type includes: cucumbers, beans, eggplants, bell peppers, zucchini, melons, tomatoes, basil, pumpkin, sesame seeds, etc.
- Long daylight hours. Representatives of flora characteristic of northern and temperate latitudes were included here. They can develop fully only with daily illumination lasting at least 13-14 hours - otherwise there will be an intensive increase in biomass without flowering and fruiting. We are talking about celery, rutabaga, beets, carrots, potatoes, cabbage, onions, radishes and radishes, lettuce, spinach, dill, parsley, parsnips, etc.
- Neutral. They are distinguished by active budding and ovary formation without a pronounced dependence of the duration of day and night. This group includes: the majority of varietal and hybrid crops zoned for mid-latitudes.
Did you know? A century-old lamp in a California fire station has been burning continuously since 1901 and is considered the longest-lasting in the world.
Goodbye "Ilyich's light bulb"
It should be noted right away that the usual incandescent lamps are not suitable for lighting greenhouses, which is well known to experienced gardeners, but not all beginners know this. The fact is that an ordinary incandescent lamp is a source of excessive thermal radiation, which provokes incorrect proportions of stems and leaves in plants, which negatively affects the formation of fruits. However, following Europe, our country has banned them, and in the near future they will become history, so we will not consider them. This paragraph was published just in case, because it is possible that in rural areas their reserves are still being sold.
Greenhouse lighting requirements
The lighting needs of each crop are different and may vary depending on external factors affecting the process of its growing season. To correctly determine how much to illuminate a greenhouse bed, experts advise following the main principle: all plants that are cultivated for flowers and fruits require much more light than those intended to produce edible greens.
The intensity of artificial illumination is also influenced by the seasonal characteristics of greenhouses, as well as photoperiodicity, which is characteristic of all plants without exception. It has been noticed that flower and vegetable crops develop better under blue and red lamps. But at the same time, they cannot completely replace sunlight, since such an experiment can result in a bountiful but inedible harvest.
Stable violet light is recommended for decorative flowering plants. In such conditions, the richness of their petals becomes brighter, and the culture’s resistance to cold is also developed. Orange rays promote intensive growth of crops and seedlings, but in excess they can lead to the death of plant cells, so it is advisable to limit such light in time.
Yellow lamps are generally not recommended for illuminating greenhouses, as they contribute to the deformation of cuttings and leaves. Seedlings grown under such light will be characterized by thin and fragile stems and underdevelopment.
Did you know? Thanks to metabolic reactions, people are bioluminescent. But this glow is a thousand times weaker than what is visible to the naked eye.
To properly install artificial lighting in a greenhouse, consider the following rules:
- Alternate the color of the lamps to highlight the beds. If this is not done, the same color of rays (especially if we are talking about infrared or ultraviolet) can reduce the quantity and quality of the expected harvest.
- It is advisable to place the light source at a distance of half a meter from the upper foliage. If the plant does not grow well, experiment by determining the desired level for the lamp.
What you need to know
Before you start organizing greenhouse lighting, you need to remember that the need for light is also different for different plants. Cucumbers, tomatoes, green onions, bell peppers, lettuce and other greens are considered the most light-loving. They need special care and light 10 hours a day and, of course, in winter they will have to provide additional lighting to preserve the harvest.
What kind of lighting should be in the greenhouse? There are quite a few options, but we immediately warn you that ordinary incandescent lamps are absolutely not suitable for these purposes. They heat up quickly, are short-lived, and also lack the blue color necessary for plants in their spectrum. Fluorescent, gas-discharge and LED lamps are best suited for an indoor garden in a country house or in a private house.
We recommend watching a video that discusses this issue in detail:
Expert opinion
Types and characteristics of lamps for lighting in a greenhouse
When choosing a lamp to illuminate a greenhouse, it is important to consider its material, power, amount of emitted energy and light spectrum. Only then will you be able to make accurate calculations of the required amount of light and its sources. You should trust only trusted manufacturers whose products comply with Gosstandart and are provided with warranty service.
Options made of corrosion-resistant metal are preferred, since the humidity level under the shelter must meet the requirements of the vegetation. Although experts advise additional protection of all lamps.
Luminescent
They are advantageous due to the variability of vertical and horizontal installation, as well as economical energy consumption. Because of this, they are also called energy-saving. Very suitable for growing seedlings and flowers.
When choosing, you need to consider that:
- cool white glow is recommended to be used for the background, and not as a spot;
- warm white rays are more valuable and will cost more (they contain red photons useful for plants);
- a combination of warm and cold light will save on energy consumption and at the same time provide the plants with the necessary lighting.
The disadvantage of luminescent products is the dependence of the brightness and the number of generated rays on voltage.
If it is deficient, the lamp may not turn on at all. Important! When installing artificial light in a greenhouse, make sure that its sources do not shade the sun, since without it the plants will not be able to develop. In this regard, it is recommended to periodically wash glass and film fragments of the structure.
Gas discharge
This type of lamps is intended specifically for greenhouse use. It is advantageous due to its decent imitation of sunlight, but loses due to the lack of blue spectrum radiation.
- The advantageous characteristics of such lamps are:
- high light output (especially for models equipped with mirror elements);
- low energy consumption;
- spectral predominance of orange and red colors, which stimulates budding and fruiting of plants;
- durability (one lamp can continuously operate for about 20 thousand hours);
- additional heating of the room, which allows you to save on heating costs;
- satisfactory efficiency (equal to 39%);
- affordability.
The disadvantage of gas-discharge lamps is considered by many to be their tendency to overheat.
LED
The peculiarity of lighting a greenhouse with LED lamps is their environmental friendliness, safety, efficiency in terms of electricity consumption (the most advantageous option among all existing lamps), as well as the ability to choose blue, red or combined emission spectra. The owner of such an installation has the opportunity to adjust the intensity and spectrum of radiation.
When using LED lamps, you can save 40% of electricity consumption. Such lamps provide a lot of bright diffused light even at low voltage. They are designed to last 15–20 years with 15 hours of daily operation, even in conditions of high dampness and sudden changes in temperature.
LED strips and spotlights do not burn plants even if accidentally touched, since they are characterized by low heat transfer. Among the disadvantages of LED lamps, many cite their high cost and suitability only to a certain type of base.
Important! Transparent glass and film greenhouses need less lighting compared to opaque ones.
Incandescent lamp
This is not the best choice for illuminating flowers and garden crops, especially when it comes to polycarbonate greenhouses. The fact is that such lamps are characterized only by a red spectrum of light, which is not suitable for constant use. Experts advise turning on incandescent lamps for a short time only to force out greenery. The only advantage of incandescent lamps is their low cost.
- Among the disadvantages are:
- lack of a blue spectrum of light (infrared, bright orange and red predominate);
- risks of burns on the foliage, as well as deformation, thinning of the stems and suspension of the growing season in case of long-term use;
- tendency to excessive heating, which is unsafe for cultivated plants;
- high energy costs.
Important! To determine the comfort level of plants under the lamp, just place your hand over the tops of the cuttings. If you feel hot, you need to reduce the heating intensity.
Sodium lamps
They are favorably distinguished by their high efficiency, since with a power of 400 W they are able to provide high heat and light output. Their warm spectra promote seedling growth. However, the predominant yellow-red rays lack a blue glow, without which the full growth of any vegetation is impossible.
Mercury vapor lamps
Such lamps are characterized by powerful ultraviolet radiation, which is very important when the seedlings have become elongated or overgrown.
- The advantages of this type of lamp can be considered:
- high light output;
- low power consumption;
- ease of installation.
- Users call the disadvantages:
- mercury toxicity, which complicates the disposal of used electrical appliances;
- tendency to overheat.
Metal halide lamps
These models are considered the most suitable for heating greenhouse plants. They are characterized by an ideal spectrum and a satisfactory ratio of the amount of radiation to power consumption.
- Among their disadvantages are:
- fragility (the more often you turn on the lamp, the faster its service life will shorten);
- high cost (they cost much more than other light bulbs);
- the spectrum of emitted light is affected by electrical voltage (even minor changes are noticeable);
- unsafe (there is a high probability of explosion at high voltage).
SOURCES OF LIGHT
The main issues related to the characteristics of high-pressure sodium lamps (HPS) used in CVT are discussed in [1]. Without repeating ourselves, we will touch upon some additional issues related to the operation of light sources (lamps).
Among them is the issue of economically viable service life, requiring group replacement of lamps. The physical service life of modern phyto-NLVDs reaches 40 thousand hours, however, during operation, their luminous flux, which determines the measure of efficiency, gradually decreases. As shown by our direct tests conducted on PlantaStar 600W/400V f. Ozgat (Germany) (Fig. 3), by 20 thousand hours, which corresponds to approximately 4 years of operation, the decline reaches 20%. In a modern CVT with an initial illumination level of 12 klx, this means a reduction to 9.6 klx.
Let's try to assess how this will affect the output of rose greenhouses. To do this, we will use the “light curve” of Dutch origin, which describes the dependence of productivity on the level of illumination during rose light culture (Fig. 4). The curve, of course, can be considered as indicative, having a “methodological” meaning, since productivity depends on many factors, including the plant variety. However, we consider it quite possible to use this dependence to quantitatively assess the impact of the decline in the luminous flux of lamps and, accordingly, illumination in the greenhouse and the loss of flower yield.
From Fig. 4 it is easy to see that a 20% decrease in illumination from the initial level of 12 klx to a level of 9.6 klx can lead to a decrease in flower yield from 190 to 160 pcs/m2.
With the average wholesale price of a flower in 2015 at 45 rubles. this will lead to a loss of revenue from 1 ha of about 13.5 million rubles. The corresponding estimate of the cost of replacing 1600 lamps with a power of 600 W, providing an initial illumination of 12 kLx per 1 hectare, in 2015 prices will be: Se = 1600 x 1600 rubles = 2.56 million rubles.
Obviously, timely replacement of 600 W lamps after 4 years of operation will provide an income of about 11 million rubles per 1 hectare.
Thus, 4 years can be considered an economically feasible service life for a 600 W LLVD in a CVT, after which the lamps should be replaced
.
The issue of replacing 1000 W lamps requires additional research. Currently, we do not have data on the decline in luminous flux of lamps of this type in real conditions. At the same time, in this case, one should not expect noticeable differences from the decline in luminous flux for 600 W lamps. Taking into account the 40% smaller required number of 1000 W lamps, even taking into account the noticeably higher cost of this light source, the saved revenue when replacing lamps after 4 years of operation will be at the level of 10 million rubles/ha.
Features of greenhouse lighting
The subtleties of installing artificial lighting for plants largely depend on the material of the covering structures, the season and time of day. The slightest violation of agrotechnical and biological norms will negatively affect the number of inflorescences and ovaries. The following recommendations will help you avoid this.
Important! It is advisable to hang the cables combined into trunks inside the greenhouse by air or on a wooden crossbar. Be sure to check the integrity of the insulating layer, since its violation in conditions of high humidity can cause a short circuit and fire.
Polycarbonate greenhouse lighting
To create maximum comfort for plants, a gardener needs:
- When installing a polycarbonate structure, take into account the possibilities of maximizing the use of sunlight by orienting it to the southeast.
- Every six months in the fall and spring, thoroughly wash the external and internal surfaces of the greenhouse with disinfectant soap solutions. These measures will allow natural light to freely reach the foliage of the seedlings. After all, every month the amount of solar ultraviolet radiation indoors decreases by 15–20%.
- Plan planting of vegetation in such a way that opaque structural elements do not cast a shadow. It is advisable to paint them with white paint, which will improve light scattering. Also, in places where more sun hits, reflectors will not be amiss (even homemade options made from polycarbonate or plywood covered with foil are possible).
Industrial greenhouse lighting
Artificial light sources are simply irreplaceable in the industrial production of flowering or fruiting plants. After all, they allow the use of greenhouses year-round, increasing the yield of grown crops. Such large-scale structures may have infrared lighting systems and additional blue lighting. The main mechanisms in them are installations for heating, watering, shading and ventilation.
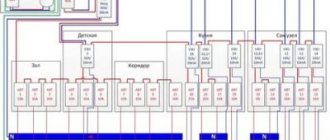
The distribution and power network consists of cables, the laying of which involves special trays embedded in the material of the structure. Control of additional lamps, which are assigned the function of short-term illumination at a certain time, is carried out automatically.
Find out more about how to choose the best greenhouse.
The number and layout of the required light sources is determined based on the design parameters of the greenhouse (span width, length, height of tray attachment), as well as the specific characteristics of the plants. The level of electric lighting in industrial structures can correspond to 6–24 thousand lux. It depends on the light type of the crop.
It is characteristic that 95% of modern greenhouses prefer to use sodium lamps, as well as their mirror variations with a power of 600 to 1000 W. In addition, in such structures, lamps are required in the central passages and along the perimeter of the complex for illumination at night.
Greenhouse lighting in winter
Taking into account the short daylight hours in the cold season, owners of functioning greenhouses should provide their plants with 12-hour lighting. At the same time, a natural light source cannot be excluded. The operating time of additional light sources is calculated depending on the characteristics of the cultivated seedlings.
Eg:
- Nightshades, pumpkin crops, cucumbers and sweet peppers can grow in short daylight conditions. If they are illuminated daily for 12 hours a day, the ripening period of the crop will accelerate by 2 weeks.
- Greens, carrots, beets, onions and tomato varieties zoned for the northern regions can bear fruit only when illuminated for 13-14 hours a day.
You will be interested to know how to choose or make a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands.
Lighting in a greenhouse at night
Greenhouse lamps should not be allowed to operate around the clock in winter. They should be turned on for no more than 16 hours. This limitation is due to the biological characteristics of plants. For convenience, it is advisable to equip the room with an automatic on and off system.
Lighting mode
The lighting regime for greenhouse plants deserves special mention. For some reason, many gardeners believe, quite unfoundedly, that the longer the light is on in the greenhouse, the better. This is absolutely not true. Any plants, like any other living, growing and developing organism, need a certain time, both for wakefulness and for rest. It must be remembered that an excess of light contributes to “fatigue” of plants and reduces their growth rate, especially in winter and spring. Therefore, additional lighting should be organized in such a way that it simulates the average length of a summer day in a given region. That is, in the late evening, the backlight must be turned off all night.
How to make artificial lighting for a greenhouse with your own hands: step-by-step instructions
Homemade electrification of a greenhouse is a very risky business, since mistakes made can result in an electric shock or a short circuit in the wiring. Moreover, it must work for a long time in conditions of increased dampness. Therefore, it is advisable to invite a qualified electrician to carry out the necessary calculations and prepare diagrams.
If you still decide to take on such a responsible job, follow the instructions below:
- Before installing the wiring, decide on the number of lamps needed (it is calculated based on the norm of 3 thousand lux per 1 m² of area) and draw a plan for their placement. Also at the preparatory stage you need to select wires of a certain power, fuses and heating devices (preferably microwave).
- Connect power to the room. This can be done by stretching the cable over the greenhouse supports through the air or by hiding it in waterproof grooves running along the frame slats. Their approximate depth should be 4-5 cm. If you plan to deepen the wiring into underground trenches, calculate their height at 80 cm and do not allow intersections with drainage channels. Be sure to cover the top of the cable with tiles, protecting it from damage when plowing the soil.
- Lead the cable to the shield, from which you will route the wires to sockets and switches.
- If the frame of the greenhouse structure is made of wooden slats and beams, then to attach artificial light sources it is enough to screw in the mounting hooks for lamps. You will have to drill special holes in the metal frame rods to mount the lamps.
- Connect the required number of lamps.
You will be interested to know about the optimal sizes of polycarbonate greenhouses.
With the greenhouse method of growing plants, even when they are in a passive state of stagnation, additional lighting is extremely important. It is installed not only in large industrial greenhouse complexes, but also on window sill “beds”. A wide range of electric lamps allows us to satisfy the needs of even the most demanding gardeners and gardeners.
Lighting in a greenhouse: we conduct electricity
Any person can handle electrical wiring; there is no difficulty, there are only certain nuances.
We draw the wire from the electrical panel, and you can stretch it:
- It's safer underground.
- At altitude - faster.
It can be installed at a height without effort; we simply connect it to each device separately. We recommend that you consider a switch near the greenhouse; it will simplify the work.
If you decide to run the cable underground, read the article on how to do it. Do not forget to calculate the cable diameter, so all the lamps will burn with the same light and not overheat.