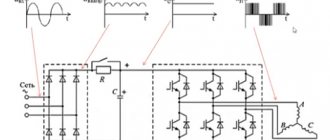
Changing the speed and direction of rotation of an asynchronous motor is a problem that has to be solved in a number of problems. For this you can use a frequency converter. This is a power converter to which asynchronous motors are connected; as a result of changing the frequency of the output voltage, the speed of rotation of the motor rotor also changes. Proper control of the electric drive allows you to increase the efficiency of its use. In this article we will tell you how to choose a frequency converter for an electric motor based on power, current and other parameters.
What is a frequency converter and in what cases is it used?
The frequency converter is designed to control the rotation speed of a three-phase asynchronous electric motor with a squirrel-cage rotor.
Appearance of frequency converters
Frequency converters are used in the following cases:
- if necessary, change the rotation speed of the electric motor;
- if it is necessary to maintain the value of a process parameter (for example, pressure) by changing the rotation speed of the electric motor;
- no 380V power supply. Frequency converters with 220V power supply are supplied with power up to 2.2 kW inclusive. The engine power is not lost in this case (If the engine has the ability to switch “ star-delta
” 380/220, then it can be turned on from a single-phase 220V network); - connection to an industrial network of motors with a “non-standard” supply voltage and frequency is required.
In addition to the main functions, the inverter provides
- the ability to turn on reverse without additional equipment;
- motor starting current limitation;
- motor current control;
- smooth acceleration and braking (time adjustable);
- additional engine protection;
- possibility of skipping resonant frequencies;
- stabilization of motor torque even with fluctuations in input voltage;
- possibility of stopping with deceleration;
- the ability to save energy with a partially loaded engine (even without a feedback sensor);
- work with built-in timer and counter;
- transition to “sleep mode” with the pump turned off in the absence of water consumption;
- Possibility of automatic restart when power is restored.
All listed parameters (functionality) are supported by ELHART frequency converters of the EMD-MINI and EMD-PUMP series.
Criterias of choice
Unfortunately, there is no clear list of criteria for choosing a frequency converter. This is explained by the specifics of different types of industrial equipment. Each piece of equipment used in factories, factories, and small businesses has its own conditions and restrictions. Therefore, the choice of technical parameters of the frequency converter is individual in each case.
The key criterion is the type of actuator. The universal recommendations given below will help you navigate the remaining parameters.
Selection of frequency converter
2.1 Frequency converter for single-phase motor
It is worth noting that standard frequency converters are not designed to work with single-phase motors. Almost all frequency converters on the market are designed to control the rotation speed of a three-phase squirrel-cage induction motor.
More often, when they say “single-phase frequency converter,” they mean a frequency converter powered by a single-phase 220V network. Such a converter has 3 phases of 220V at the output and is also designed to control a three-phase asynchronous motor.
However, frequency converters for single-phase motors exist, but are extremely rare.
Figure 1 - Inverter for a three-phase motor
2.2 Selection of frequency converter by power
When selecting a converter, you first need to focus on the current and supply voltage of the electric motor. This information is indicated on the engine nameplate.
Figure 2 - Engine nameplate
1. Voltage on the windings. The motor, the nameplate of which is shown in Figure 2, is capable of operating at a three-phase voltage of 220V (the windings must be connected in a delta circuit)
) and at a three-phase voltage of 380V (
star
). If the nameplate indicates 380/660, then such a motor can be connected to an inverter with a 220V power supply, but in this case the rated characteristics of the motor will not be ensured.
2. Rated linear current of the motor. This motor consumes 1.44A when connected in a delta (220V power supply) and 0.83A when connected in a star (380V power supply).
The rest of the information given on the motor nameplate does not affect the choice of inverter.
Despite the current indicated on the motor nameplate, the most correct method for determining the operating current is to directly measure it while the motor is running. This will avoid problems if the motor operates at high current. The actual continuous operating current of the motor should not exceed the rated output current of the inverter.
It is not correct to buy a frequency converter based on engine power, since engine power depends on efficiency and power factor ( cosφ
), and the power indicated on the electric motor refers to the mechanical power of the motor on the shaft, and not to the active power consumed from the power source, as is customary for other consumers of electricity.
For example, let’s compare the currents of 1.5 kW motors with the current of inverters of the same power ELHART EMD-MINI – 015 T (1.5 kW, 4A, 380V), ELHART EMD-MINI – 015 S (1.5 kW, 7A, 220V).
Table 1 – Electrical characteristics of motors
| Engine | power, kWt | RPM | Current at Δ220/Y380 V | Efficiency, % | Coef. Power | IP/IN |
| AIR 80 A2 | 1,5 | 3000 | 6,2 / 3,6 | 78,5 | 0,85 | 6,5 |
| AIR 80 B4 | 1500 | 6,8 / 3,9 | 78,5 | 0,80 | 5,3 | |
| AIR 90 L6 | 1000 | 7,3 / 4,2 | 76 | 0,70 | 5,0 |
The AIR 90 L6 engine (1000 rpm), with the same power as the frequency converter, consumes a current of 4.2 A in rated mode with a supply of 380 V, and the converter has a rated output current of 4.0 A.
When connecting the same motor in a triangle
"With a 220 V power supply, the rated current will be 7.3A, and the frequency converter is designed for 7.0A. Therefore, both with a 380V and 220V power supply, the specified motor must be connected to a frequency converter with a power level one step higher (2.2 kW):
- Frequency converter ELHART EMD-MINI – 022 T (2.2 kW, 5 A, 380 V)
- Frequency converter ELHART EMD-MINI – 022 S (2.2 kW, 11 A, 220 V)
Thanks to the frequency converter, it is possible to connect motors with “non-standard” power supply to an industrial network of 220 or 380V. In this case, the main thing is that the rated motor supply voltage does not exceed the inverter power supply, and the rated frequency is maintained by the inverter.
For example, the MSU-200 sheep clipper is powered by an alternating voltage of 36V with a frequency of 200Hz. To work with such a machine, the rated motor supply voltage is set in the settings of the frequency converter - 36V and the rated motor frequency - 200Hz.
Despite the electric motor power of 115W, the operating current is about 3A. In addition to the rated motor current, it is necessary to take into account the amplitude, frequency and duration of possible overloads. In moments of overload, the current of the specified machine can reach up to 7A.
The ELHART EMD-MINI frequency converter can withstand an overload of 150% of the rated current for 60 seconds; EMD-PUMP – 120% for 60 seconds.
Therefore, the rated current of the inverter must be at least 7 ÷ 150% = 4.7A. To connect to a 220V network, select the ELHART EMD-MINI – 007S frequency converter (0.75 kW, 5A, 220V). To connect to a 380V network, select the ELHART EMD-MINI – 022T inverter (2.2 kW, 5A, 380V).
Please note: with a small current margin in this example, the power of the inverter is 6 and 20 times greater than the power of the corresponding motor!
2.3 Choosing between vector and volt-frequency control modes
According to the control mode, frequency converters can be divided into volt-frequency and vector. Let's look at the operating features of these modes.
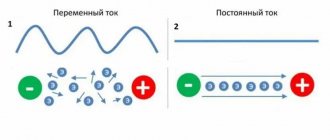
Volt-frequency (or scalar) control mode of the inverter
- Maintains a constant value of the stator magnetic field at a given frequency (the ratio of supply voltage to frequency is constant). This means that at different speeds the rated torque on the motor shaft will remain unchanged. There are features of operation at low frequencies. Details are described in the section “ Possible range of engine speed adjustment using an inverter”;
- The engine rotation speed depends on the applied load: when the load increases, the engine slows down, when it decreases, it speeds up. With a constant load, the rotation speed does not change;
- Allows you to operate multiple motors simultaneously (to operate multiple motors, additional current protection must be provided for each motor).
Vector control mode of the inverter:
- maintains a constant rotation speed under changing loads (due to automatic adjustment of the output voltage);
- operates more stably at low frequencies (by compensating for the voltage drop in the motor windings).
Features of vector mode:
- it is possible to change the rotation speed at a constant load within 2Hz (due to the search for the optimal voltage). This is normal and not a malfunction;
- Can only work with one motor (does not support multi-motor mode);
- works correctly if the engine's passport data is entered correctly and its autotest has successfully passed.
Both volt-frequency and vector control modes, in the presence of a built-in PID controller, are capable of accurately maintaining a process parameter based on a feedback sensor (speed, pressure, humidity, temperature, and others).
As a rule, for most applications, using the voltage-frequency mode is sufficient. Such applications include pumps, fans, conveyors, woodworking machines, high-speed milling machine spindles, simple cutters, presses, packaging machines, filling machines, dispensers, compressors and other equipment.
Vector mode is usually used when working with lifting and transport mechanisms, crushers, drilling equipment and other loads where high torque is required in the low frequency range and at startup, and there is no clear dependence of the load torque on the rotation speed.
2.4 Supported frequency converter control methods
Since the frequency converter is usually installed in a control cabinet, to access the built-in panel it is necessary to open the cabinet door each time (if you work in a dusty industry - flour, dust, cement - frequent opening of the door is unacceptable). In addition, often the inverter is installed next to the engine, and the operator's console is located to the side.
Using the EMD-Mini remote control panel - RCP (not included in the delivery package), you can implement remote control of the EMD-Mini frequency converter at a distance of up to 2 meters. The remote control has exactly the same functions and capabilities as the control panel on the frequency converter itself.
In ELHART frequency converters of the EMD-PUMP series, the built-in remote control is removable and can be removed using the included two-meter cable.
To remotely control engine starting and stopping using buttons and switches, discrete inputs are required.
The presence of an analog input allows you to remotely smoothly adjust the speed using a potentiometer or an analog signal 0...10V/4...20mA
. Together with the built-in PID controller, the analog input allows you to continuously maintain the value of the process parameter (pressure, flow, temperature, etc.)
RS-485 interface
or
RS-232
allows you to connect to the upper level of the process control system.
Program mode allows you to change the speed and direction of rotation according to a predetermined program.
2.5 Selection of frequency converter for the pump
Special attention should be paid to frequency converters of the pump series. What distinguishes them from other converters is the inherent algorithm for working with several motors. Namely: alternating engines and cascade mode. The alternation mode is used to ensure uniform wear of the engines. Cascade mode is used when it is necessary to control several pumps using one frequency controller. The peculiarity of the cascade mode is that a low-power frequency converter is capable of regulating productivity or pressure over a wide range, including the minimum required number of pumps. ELHART EMD-PUMP frequency converters can control a group of 2 to 7 pumps
. It is possible to work with pumps of different powers; in this case, the power of the inverter is determined by the most powerful pump.
2.6 Additional equipment
In some cases, when using a frequency converter, it may be necessary to install additional equipment:
- A braking resistor is needed to dissipate the energy supplied to the inverter from the motor, which operates in generator mode. The braking resistor is used to ensure a quick stop or deceleration of the engine (especially with high-inertia loads), when working with lifting and transport mechanisms (cranes, elevators, inclined conveyors, elevators), high-inertia applications (smoke exhausters, centrifuges, roller tables, draft mechanisms, transport carts) , in applications where positioning accuracy is important.
- The motor choke is installed when the distance between the motor and the converter is more than 30m; protects the motor from pulse currents, reduces interference, limits the amplitude of short-circuit current, reduces the rate of rise of short-circuit current and, as a result, improves the protection of the converter from short-circuit.
- The mains choke is connected to the input of the converter and is a two-way buffer between the power supply network and the frequency converter. Protects against peak voltage surges in the network. Installation of a network choke is recommended in case of unstable network parameters (ripple, voltage dips), when phase imbalance is more than 3%, if the power of the power source (distribution transformer) is more than 500 kVA and exceeds the power of the converter by six or more times, or if the cable length between the power source and IF less than 10m. The use of network chokes significantly increases the service life and reliability of frequency converters.
Changes to the privacy policy
We have the discretion to update this privacy policy at any time. In this case, we will post a notice on the home page of our site. We encourage users to frequently check this page to stay informed of any changes to how we protect the user information we collect. By using the site, you agree to accept responsibility for periodically reviewing the privacy policy and changes to it.
Motor speed control range when using a frequency converter
3.1 Using an inverter to reduce motor speed
To operate at low frequencies (below 10-15 Hz), special attention must be paid to motor cooling and shaft torque.
Enclosed fan cooled motor ( TEFC)
) has cooling only due to the built-in fan. The performance of the cooling fan decreases in proportion to the engine speed. When engine speed is reduced, cooling efficiency decreases, which leads to engine overheating and possible failure.
There are several options for cooling the electric motor when operating at low frequencies:
- reduce the period of continuous operation of the engine at low frequency
- organize additional cooling;
- reduce the load on the motor shaft;
- install a reduction gearbox, which will increase engine speed;
- use a larger motor.
The volt-frequency control method allows you to maintain a constant torque on the motor shaft at different speeds. When operating at low frequencies (below 5-10 Hz), the torque on the shaft will depend on the characteristics of the specific motor (active resistance of the windings). To maintain torque at frequencies below 5-10 Hz, it may be necessary to adjust the minimum voltage of the U/f
. Increasing the voltage value will cause an increase in starting torque, but will also lead to an increase in current consumption, and in proportion to the increase in flowing current, heating increases. Recommended frequency control range for voltage-frequency control: 5-50 Hz. The ELHART EMD-MINI frequency converter supports frequency adjustment from 0.5 to 999.9 Hz.
The vector control method is able to more accurately maintain torque at low frequencies (especially with changing loads). The range of possible adjustment is wider than that of the volt-frequency mode and depends on the specific model (company, series) of the inverter. For vector control, it is recommended to use Delta Electronics frequency converters of the VFD-E and VFD-C series.
To increase the starting torque, it is recommended to use a frequency converter of higher power (since the converter can only provide the motor with one and a half times the current (rated current × overload capacity of the inverter).
Providing data to third parties
We do not disclose users' personal information to companies, organizations or individuals not affiliated with us. The exceptions are the cases listed below.
User data is publicly available
The user’s personal data may be published publicly in accordance with the functionality of the site, for example, when leaving reviews, the name specified by the user may be published; such activity on the site is voluntary, and the user, by his actions, consents to such publication.
As required by law
Information may be disclosed to prevent fraud or other illegal activities; as required by law and in other cases provided for by law.
To provide services and fulfill obligations
The user agrees that personal information may be transferred to third parties in order to provide services ordered on the site and fulfill other obligations to the user. Such persons, for example, include courier services, postal services, cargo transportation services and others.
Third party services installed on the site
The site may contain forms that collect personal information from other organizations; in this case, the collection, storage and protection of the user’s personal information is carried out by third parties in accordance with their privacy policy.
The collection, storage and protection of information received from a third party is carried out in accordance with this privacy policy.