DRL lamps, which are still actively used today, belong to gas-discharge lighting devices. Their distinctive feature is rich luminous flux and durability. Due to the mercury content, these products are used to organize artificial lighting of streets and industrial areas. But certain technical and operational nuances do not allow them to be used in domestic conditions. In the article we will look at what a DRL gas-discharge lamp is, how it works, the principle of its operation and where it is used.
DRL lamps.
The DRL lamp is an electric gas-discharge lighting device for artificial lighting. The abbreviation stands for Mercury Arc Lamps. The term “mercury lamp” or “RL” is generally recognized. It is used in technical documentation.
- D – arc.
- R – mercury.
- L – phosphor (light source).
The physical principle of operation is an electrical discharge in mercury vapor.
The marking also includes a number indicating power. For example, DRL-250 - 250 Watt, Mercury Arc Lamp.
In the USSR and Russia, there are regulatory documents for the manufacture of mercury illuminators GOST 27682-88 and 53074-2008.
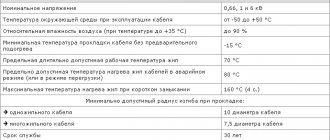
Specifications
All arc discharge light sources have the following characteristics:
- Power ranges from 80 W to 1 kW. In reality, low- and high-power lamps are used much less frequently. The most common is the DRL 250 lamp.
- Base standard E27 for low power and E40 for high power.
- The value of the starting current for different powers ranges from 2 to 16 amperes, the operating current - from 1.5 to 7 A.
- The luminous flux, in other words, the light intensity emitted by such devices, ranges from 3.2 thousand to 52 thousand lumens.
- The service life of any DRL lamp according to the passport is more than 10,000 hours. For powerful models, this figure increases to 20-25 thousand hours. In practice, most light bulbs burn out long before this period expires.
When using gas-discharge mercury lamps, it should be taken into account that their luminosity decreases over time. A lamp that has served for a year will be almost 30% dimmer than a new one!
Types of DRL lamps
This type of illuminant is classified by the vapor pressure inside the burner:
- Low pressure - RLND, no more than 100 Pa.
- High pressure - RLVD, about 100 kPa.
- Ultra-high pressure - RLSVP, about 1 MPa.
DRL has several varieties:
- DRI – Arc Mercury with radiating additives. The only difference is in the materials used and gas filling.
- DRIZ – DRI with the addition of a mirror layer.
- DRSh – Arc Mercury Ball.
- DRT – Arc Mercury Tubular.
- PRK – Direct Mercury-Quartz.
Western markings are different from Russian ones. This type is marked as QE (if you follow ILCOS - generally accepted international marking), by the following part you can recognize the manufacturer:
HSB\HSL – Sylvania,
HPL – Philips,
HRL – Radium,
MBF – GE,
HQL - Osram.
Design
The design includes the following elements:
- glass container;
- threaded base;
- mercury-quartz burner filled with argon. Additionally, a drop of mercury is added;
- main cathodes;
- additional electrodes;
- additional carbon resistor.
Helpful information! The purpose of the additional electrodes is to facilitate lighting of the lamp. They are also responsible for stable operation.
The elements are discussed in more detail below:
- base It receives electricity from the network as a result of contact of the current-carrying parts of the lamp with the contacts of the lamp socket. As a result, electricity is transferred to the burner electrodes;
- quartz burner. It looks like a flask with two electrodes on each side (two are main, two are additional). The burner is filled with argon and a drop of mercury;
- glass flask. This is the outer part of the light bulb. Inside there is a burner with connected electrical conductors coming from the contact base. To pump nitrogen into the flask, all the air is first pumped out of it.
You might be interested in: Features of Edison lamps
The first models of DRL lamps had only two electrodes. Such lamps were more difficult to light - an additional starting device was required. The modern, throttle version is equipped with four electrodes.
Device
Operating principle and connection diagrams of DRL
The connection diagram for a two-electrode DRL is not discussed in the article, since this type of lamp is obsolete and is no longer produced.
The schematic diagram shows:
EL – DRL.
C – capacitor (not a mandatory element).
LL – choke (inductor).
FU – fuse.
When voltage is applied, gas ionization occurs between pairs of main and ignition electrodes. Since they are located in close proximity, ionization of the gas occurs easily between them. After ionization of the gas, a breakdown occurs between the main electrodes - an arc discharge is formed. The light from the discharge itself has a blue or violet tint.
The phosphor itself gives a reddish tint, thus mixing primary colors and producing cool white light. The visible shade may vary slightly depending on the applied voltage.
The discharge in the burner gains brightness within seven to eight minutes. This is due to the fact that initially mercury is in the form of a ball in a liquid state. As the temperature rises, the mercury gradually evaporates and the discharge improves. As soon as the liquid metal completely transforms into a vapor state, the brightness will reach its maximum. At the same time, the pressure also increases. Maximum brightness is achieved in ten to fifteen minutes. The ambient temperature affects the time it takes for the light source to return to normal mode.
The choke is necessary, it is the simplest ballast - ballast. It also limits the current passing through the electrodes. If a DRL lamp is connected directly to the network, then its failure is inevitable. Usually this happens instantly. The polarity of the inductor connection does not play any role. Its main purpose is to stabilize the operation of the illuminator.
The selection of a choke for a specific DRL lamp is discussed in the table
| DRL 125 W | DRL 250 W | DRL 400 W | DRL 700 W | |
| Rated choke current (ballast) | In=1.15 A | In = 2.15 A | In = 3.25 A | In = 5.45 A |
Selection of a specific inductor by current
You can study the design and operating principle of the throttle in detail here
The capacitor used is selected based on the power of the lamp. Recommendations are presented in the table.
| DRL lamp type | Capacitor capacity |
| DRL-125 1.15 A | 12uF |
| DRL-250 2.15 A | 18uF |
| DRL-400 3.25 A | 25uF |
| DRL-700 5.25 A | 40uF |
With the current development of electronics, the choke is an archaic element. Electronic arc stabilization units can now be found on sale. These devices can withstand the precise power conditions required to start and maintain combustion, regardless of changes in voltage in the lighting network.
If you cannot purchase electronic ballast, you can make it yourself. Here Ф is phase, 0 is zero.
What is a throttle for?
The choke for DRL lamps is used for starting; there are different types of lighting devices on the market in which it is used:
- Fluorescent and ultraviolet lamps.
Ultraviolet lamp Various types of mercury arc lighting devices: DRT, DRL, DRIZ, DRSh, DRI.
Arc mercury lamps Arc sodium lamps: DNaMT, DNaS, DNaT. Arc sodium lamp All lighting devices have differences in the principle of obtaining light flux, there are other differences:
- different materials are used in their design;
- differ in the presence of chemical elements;
- inside the flasks there is pressure according to the own parameters of each lighting device;
- they differ in power and brightness of the light flux.
These types of lamps are united by the variable value of the starting current and resistance during the start-up process and further operation.
In order to limit the amount of operating current, different types of ballast are used in lighting devices of this type: electronic ballasts, ballasts and ballasts, which are inductor coils (chokes). At the moment of startup, each device of this type has a high resistance value; when the lighting device is ignited, a process of electrical breakdown occurs in the inert gas environment with which the lamp is filled (mercury or sodium vapor), and an arc discharge occurs.
During the process when the lamp is ignited, the ionized gas loses resistance from the arc discharge several tens of times, and for this reason the current increases and heat is released. If you do not limit the amount of current, it will instantly create a superheated gas environment, which will lead to breakdown of the lighting device and damage from the inside. To prevent this, a resistance (choke) is included in the lighting device circuit.
Physical parameters and connection diagram of the inductor
A DRL inductor connected in series has a reactance, the value of which depends on the inductor: one Henry passes one ampere of current when the voltage is one volt.
Throttle
The parameters of the inductor include:
- square of copper wire used;
- number of turns;
- what is the core and cross-sectional size of the magnetic circuit;
- what electromagnetic saturation.
The inductor has an active resistance, which is always taken into account when calculating the ballast for each type of lighting device of this type, taking into account its power; the overall dimensions of the inductor depend on this.
Let's consider a simple circuit for switching on the ballast, when the design of the DRL lamp provides (additional) electrodes for the process of occurrence of a glow discharge that turns into an electric arc.
DRL lamp connection diagram
In this case, inductance limits the amount of operating current in the lighting device.
Ballast for fluorescent lamps
Structurally, a fluorescent lighting device uses a ballast choke for starting; new types of this lighting device use electronic ballasts, this is an electronic type of ballast. The purpose of this device is to contain the increasing current value at one level, which maintains the required voltage on the electrodes inside the lighting fixture.
Scope of application
DRLs are designed for lighting large areas. They are usually used in street lighting, gas stations, and roads. They are often used in warehouses. Those. where high quality color rendering is not needed.
They are not used for permanent use in residential premises. This is explained by the low color rendering coefficient and the long time to reach normal mode. At home, at a minimum, it is inconvenient to wait about ten minutes after clicking the switch.
Very often they are found in lighting installations for exhibition complexes. Here their advantages are fully revealed - the maximum power can be 1 kW, while the luminous flux reaches 52,000 lumens. Their glow is usually the same color - 5500 Kelvin.
Product details
DRL lamps (mercury arc lamp) are a light source that operates on the principle of optical radiation, which is generated by a gas discharge from mercury vapor. Today this is a fairly common lamp that has become widely used in a variety of fields. Today, such lamps are used to create lighting:
- at industrial facilities. These are excellent industrial lamps that create a good luminous flux and can work in various conditions;
- for outdoor lighting. Such lamps are placed on poles located along roads, pedestrian paths in parks and squares. Outdoor type lamps can withstand various climatic conditions and even sudden temperature changes;
- creating the required level of illumination in public premises;
- for home, etc.
Note! The most widespread are DRL type lamps (250 lamps are more often used than 400 lamps), as well as DNaT lamps, which are used for street lighting.
Street lamp
DRL lamps have an elongated shape, making them very similar to ordinary incandescent light bulbs. The product consists of the following components:
- metal base;
- glass flask;
- a tube containing mercury vapor. In the tube, mercury vapor is always under pressure. The tube is made of quartz glass.
This structure determines the special operating principle of such devices.
Disposal
The lighting devices in question are classified as hazard class 1. Therefore, the number of places where these are prohibited for use is now growing. It is possible that in a few years mercury lamps will be phased out everywhere, as government policies are aimed at reducing the amount of equipment containing mercury. In compliance with government orders, utilities are reducing their use of DRLs.
Unfortunately, not everyone thinks about the issues of decommissioning such light sources. By doing this, they harm not only themselves, but also those around them .
Soon their sale will be completely stopped. Devices containing mercury will be left only in medical equipment until a safe analogue is found.
Currently, recycling of mercury lamps is a licensed service. On September 3, 2010, a corresponding decree of the Russian government was adopted. The document describes the requirements for the disposal process and contains information on the procedure for dealing with mercury contamination. The process of demercurization - removal of mercury is described.
Now all legal entities of the Russian Federation are required to create a waste passport for fluorescent lamps and keep strict records of mercury-containing waste. The presence of mercury is already a potential danger .
Recycling and recycling refers to the recovery of used metals from devices containing them. Including mercury. A damaged flask will allow liquid metal to escape into the environment.
In Russia, the Federal Law No. 187 is in force (Article 139). According to it, a fine will be collected for improper disposal or placement of a hazardous waste container in an inappropriate place. Unauthorized removal from the storage area is also punishable.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any light source, DRLs have their positive sides. But, unfortunately, there are more negative sides.
pros
- Great light output.
- Great power (the main plus).
- Small body dimensions.
- Low price (compared to LED products).
- Low power consumption.
- Service life – up to 12 thousand hours. This parameter is determined by the quality of workmanship. Not all manufacturing companies carefully control the process. This is especially true for new Chinese firms.
Minuses
- Presence of mercury.
- Long time to reach the regime.
- Do not start a heated lamp until it cools down. It's about fifteen minutes.
- Sensitivity to voltage surges (a voltage deviation of 15 percent causes a change in brightness of up to 30 percent).
- Sensitivity to ambient temperature. The colder it is, the longer it takes to return to normal operation.
- Light pulsation and low color rendering (Ra no more than 50, comfortable from 80).
- Very high heat.
- The need for special heat-resistant wires and cartridges.
- The need for control gear.
- The DRL illuminator makes a buzzing sound.
- Ozone is formed during operation. According to sanitary standards, ventilation must be present.
- All arc lamps are incompatible with dimers - devices for continuously adjusting illumination.
- During operation, the phosphor layer degrades, the luminous flux weakens, and the emission spectrum deviates from the reference one. By the end of their service life, up to fifty percent of the luminous flux is lost.
- Flickering may occur during operation.
- Operation on direct current is not possible.
If you still plan to use DRL for lighting, then it is advisable to refrain from purchasing cheap lamps of unknown origin.
In European countries, Osram and Philips still hold the leading positions in the quality of manufacturing of lighting devices.
Technology development
Technology has also improved. Metal halide lamps are now available. They have added iodine and other metal compounds to improve visible emission and color.
A new variety was created - DRV. This is a hybrid of a classic incandescent lamp and DRL. They have a tungsten filament added to them. It plays the role of a limiting resistor and a radiation source at the same time. The resistor is usually carbon. Here it is made of refractory tungsten. This design solution made it possible to abandon the use of a throttle. This lamp is connected like a regular incandescent lamp - it does not require additional ballasts.
Device types
Lamps operating according to the principle described above are of the following types:
FRL – fluorescent mercury arc lamp;
Model HPL-N (Philips)
DRL lamps differ from DRL lamps in that they use a tungsten filament, which performs two functions: a light source and an electric current voltage limiter. To operate a device of this type, no special ballasts are required (throttleless electric lamp);
High pressure DRV devices (HQL), manufacturers Osram and Philips
conclusions
Since DRL will soon be banned everywhere, the time has come to choose an alternative to them.
These lamps have been used for quite a long time, but their history is already coming to an end.
Currently, they are actively being replaced by LED products. Economically, LED lighting pays for itself in the first year of operation. The use of DRL can only be justified by dubious economic feasibility - low price at the time of purchase.
On September 24, 2014, the Russian Federation signed the Minamata Convention on Mercury. Since 2022, the import and export of mercury-containing devices is prohibited by law. Mercury vapor lamps are covered by this document.
- Related Posts
- Lamps with e40 base: the most powerful, advantages and disadvantages, circuit diagram of LED lamps
- Heating with an infrared lamp (reviews, conclusions, operating rules)
- What is an LED (device, parameters, markings)
Discussion: 2 comments
- Vitaly:
Thank you for the clarification, it became clear what DRL is, how they are structured, how they work, what are the types.Answer
AdminVF:
Hello, Vitaly. I am very glad that you found this article useful.
Answer