PVC pipe for electrical wiring is an effective means of protecting communications from external influences. In accordance with the requirements of SNiP, open installation of power cables is prohibited in buildings made of solid wood and panels. In addition, houses are subject to shrinkage, there is a possibility of the walls getting wet, which can cause a short circuit. The use of electrical PVC pipes allows you to reduce the risk of damage and destruction of communications to a minimum, which ensures the safe operation of the building.
Scope of use
Open laying of cables and wires on the surface of walls and ceilings, behind false walls and inside plasterboard partitions and behind suspended ceilings in accordance with regulatory documents is not allowed. In such cases, electrical wiring should be additionally insulated and protected from mechanical damage, exposure to aggressive environments, ultraviolet radiation, and precipitation. The most versatile and practical way to insulate and protect wires is to use pipes. The variety of their types helps you choose the necessary pipe for any situation that arises during the construction and renovation of your home.
But the favorite of all types of pipes for electrical wiring are PVC products - durable, non-conductive, non-flammable, aesthetic, and easy to install.
Scope of application of PVC pipes:
- Installation of electrical wiring indoors and outdoors, underground.
- Installation of telephone lines.
- Installation of telecommunication cables, fiber optic communications.
- Installation of alarm systems, including fire alarm systems.
- Installation of all kinds of local communication systems, computer networks, etc.
Characteristics of electrical PVC pipes
Polyvinyl chloride as a material for pipes used for laying wires is an almost ideal material:
- PVC does not conduct electricity.
- Does not spark, does not support combustion - protected wires can be laid over structures made of flammable materials.
- If necessary, the wires can be sealed inside the pipe.
- Pipes can be straight and strong, or flexible and corrugated.
- To install pipe systems, many fittings, boxes, components, connections, and brackets are produced - there is no need to reinvent the wheel during installation.
- Pipes are light in weight, easy to cut, and easy to install.
Construction of the trench
Arranging a trench is an important aspect of installing a power line into the ground. Many people turn a blind eye to this, however, the rules should still be followed. Let's consider the basic requirements that underground cable installation must meet:
- the pipeline must have a depth in the soil of no less than 70 cm. If installation is carried out in non-standard climatic conditions, this figure will be correspondingly higher;
- It is important to remember that the distance of the communication being laid to the foundation must be at least 60 cm. It is strictly forbidden to lay a route under the foundation ;
- The width of the trench is determined by the diameter of the pipe. In turn, the diameter of the pipeline must correspond to the number of cables. If several conductors are placed in the channel, the distance between them must be at least 10 cm;
- Before arranging a ditch, it is necessary to study the plan of a specific site. This is necessary in order to select the correct location of the trench. According to the PUE, the cable is laid in the pipe at appropriate distances from other communications (the route must be at least 2 m from the gas pipeline, and also no closer than 1 m from the water supply);
Construction of trenches must be carried out in accordance with the PUE; laying of warning tape is mandatory
Helpful information! In some cases, to strengthen such communication when the soil subsides, owners use ordinary bricks. It is not recommended to use hollow bricks for these purposes.
- It is imperative to put a tape on top of the route, which will warn that a power cable is laid here. After this, it is necessary to again fill in a layer of sand and earth (with a slide of 10–15 cm).
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Durability - the first products have already worked for more than 50 years and are approaching 60 (although the service life of the wires is half as long).
- Low cost.
- Non-flammability is especially important for electrical networks; PVC also has self-extinguishing property.
- Easy installation - easy to cut, there are many types of connecting elements; there is no need for complex expensive equipment for installation.
- No corrosion.
- Strength and at the same time high impact strength - pipes resist mechanical damage well; Products are not fragile and can be restored after deformation.
- Frost resistance - withstands freezing and thawing and returns to its original shape.
- Flexibility - plastic is easy to bend when heated even with your hands, corrugation generally bends easily;
- Harmless to humans and animals.
- Chemical inertness, resistance to acids and alkalis;
- Smooth walls make it easier to tighten wires;
- No need for regular maintenance (cleaning, anti-corrosion, environmental friendliness - fairly harmless production, easy disposal.
- Aesthetic qualities.
- Easy care - the stainless steel surface is easy to wash and remove dirt.
- Light weight and lack of fragility facilitate transportation and storage.
- Polyvinyl chloride is UV resistant.
Flaws:
- Low heat resistance of polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride - their operating temperatures are practically limited to 60 ° C. However, such temperatures practically never occur when laying wires in a residential building (only near heating systems).
- Fragility in the cold.
- The strength of plastic is still lower than that of metal.
Advantages of PVC pipes over metal ones
The most significant drawback of common steel pipes is their susceptibility to corrosion. Pipes made of copper and stainless steel do not rust, but their price for installing wiring under normal conditions is simply unacceptable. Yes, steel pipes are more expensive than PVC pipes.
The second advantage of PVC is its light weight and easy installation - PVC is easy to cut, weighs less, and is easier to attach to walls and ceilings.
The third advantage is that PVC does not conduct electricity. Fourth, PVC systems do not require grounding.
Advantages of laying in the soil
Installation of cables in the soil is carried out using various types of pipes: metal, metal-plastic, low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE). This type of gasket has a number of advantages over the air method:
- laying the cable in a pipe ensures its protection from adverse weather conditions and will also reduce the likelihood of mechanical damage;
Helpful information! The cable laid underground is very easy to replace if necessary. To do this, you just need to dig out the communication and remove the old cable from the line, replacing it with a new one.
- this method eliminates the possibility of fire, which is a very important advantage, especially for houses made of flammable materials (for example, wood);
- additional protection of the wiring in the form of a pipe eliminates the possibility of damage to the cable by rodents;
- such communication (unlike air communication) is not visible and does not spoil the aesthetics of the site;
- in most cases, the cost of such cable installation is lower than with open installation.
Requirements for PVC pipes for wiring
PVC pipes used for laying electrical networks must have the following qualities:
- Sufficient strength.
- Durability.
- Extinction upon fire.
- Chemical inertness.
GOST standards
In the production of polyvinyl chloride pipes, the following GOST standards are used:
- GOST 32415-2013 Pressure pipes made of thermoplastics and connecting parts for them for water supply and heating systems. General technical conditions.
- GOST R 54475-2011 Polymer pipes with a structured wall and fittings for them for external sewage systems. Technical conditions.
Special standards for PVC pipes used for laying electrical systems have not been developed.
Types and range of polyvinyl chloride pipes (and not only)
In practice, PVC pipes for laying electrical networks are divided into two types: smooth and corrugated. In addition, it should be noted that steel and copper pipes and products made from other types of plastic: low-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene are used for electrical installation work. High-density polyethylene is not usually used: it is more expensive, too flexible for smooth pipes and too hard and inflexible compared to corrugated pipes.
Smooth
Smooth pipes have a constant cross-section along their length and wall thickness. Thick walls provide the greatest strength among PVC pipes. For electrical installation work, pipes with an outer diameter of 10 to 50 mm, very rarely 63 mm, are used. But installing such structures is not always convenient, and flexible corrugated hoses are often used.
Smooth-walled products are supplied in lengths from 4 to 12 m with a multiplicity of 0.25 m. Typically, lengths of 3, 6, 12 m are found. Length 12 m is usually for diameters 50 and 63 mm.
PVC products are usually painted gray. For their installation, all kinds of distribution boxes, couplings, angles, tees, clips are used, and for large diameters - metal clamps. Couplings are usually used in rooms with high humidity.
Corrugated
A corrugated pipe is a flexible pipe that has a structurally variable cross-section along its length and a textured surface. Thanks to this, it bends easily, but retains its strength under numerous cycles of compression, stretching and bending. The starting material (sheet) is bent at a certain equal distance; the pipe manufacturing technology is a little more complicated. This processing of the source material helps to increase the strength of the material and increases the resistance to deformation during bending. Plastic corrugations can be single-layer or double-layer, reinforced with steel wire.
Corrugated hoses for electrical installation work are made of steel and plastics, copper, rubber and some other materials.
The division of corrugated hoses into types depending on strength is given in the table:
Table 1
| Type of corrugated hose | Withstand loads in N/5 cm² | Application |
| Lungs | 320 | They have thin walls, are very flexible, and are used for laying wires behind wall and ceiling cladding |
| Average | 750 | For laying wires in wall grooves |
| Heavy | 1250 | Durable, rigid, with a thick wall, laid in walls and screeds, poured with concrete |
| Extra heavy reinforced | 4000 | The corrugation has a reinforcement made of a wire spiral; it is needed for laying cables underground and for installation outdoors |
Plastic corrugations are usually painted in different colors: PVC in gray, polyethylene in black, polypropylene in blue. Double-layer corrugation for laying in the ground is often painted red or red-orange. There are no strict requirements for painting corrugations, but there is an international standard for painting plastic corrugations depending on the purpose of the cable or wire. White products are used for computer networks, green - for telephones, red - for outdoor installation. Gray and black (and brown) corrugations are intended for general purpose wires.
When carrying out work in an unfamiliar building, these international painting standards should be kept in mind, but it should be borne in mind that the electricians during installation may not have followed generally accepted rules, but simply “cobbled together from what was available.”
Be careful! The diameters of corrugated hoses for electrical wiring range from 16 to 50 mm, rarely with a large cross-section.
Metal corrugation for electrical installation work is divided into the following types:
- RZ-Ts, RZ-TsKh, RZ-TsA – made of galvanized steel;
- RZ-SL and RZ-SL-X - made of tinned steel tape (tin plate with tin coating);
- RZ-TsP – with PVC insulation.
The letter “X” in the first two options indicates the presence of a cotton seal, and the “A” indicates an asbestos-cement seal. The "P" in the latter type of corrugation indicates the outer layer of PVC. Also, metal hoses for wires exist with flanges at the ends and welded ends. Plus, there are corrugated hoses in explosion-proof versions and for high pressure. This corrugation is used in industry.
Conventional metal hoses are made from steel tape. It is wound in a spiral; such a sleeve is not airtight. When pressed hard, the tape strips move apart and the hose simply falls apart. The metal hose is suitable for installing electrical networks on a wooden base and outdoors in the open air - its non-flammability and resistance to ultraviolet radiation will come in handy.
For tightness, a metal corrugated hose with an inner tube made of PVC or coated with PVC is produced. In this case, the layer seals the contents of the sleeve well. There are also stainless steel corrugations. Sealed corrugations are used in wet rooms (bathrooms, bathhouses) for safety.
Hard
All smooth-walled pipes are rigid. Hard covers are needed when pouring communications into concrete - walls or screed, sometimes when laying through a wall or when laying wires in industrial premises or warehouses.
Steel
Steel pipes are also used to protect electrical cables and wires. Despite their disadvantages, they are much more durable than plastic. At home, such protection for wires is rarely needed, but when installed in production, in public buildings, in apartment buildings, boxes with reliable protection for cables can come in handy. Steel will cost much more than plastic.
Wiring using stainless steel is very rarely used. It is expensive. If you need a compact case (the minimum outer diameter of stainless steel products is 9.8 mm), or it is very important to protect the wires with a durable stainless case.
Plastic
It is impossible not to mention other types of plastic pipes - polypropylene and low-density polyethylene. Smooth-walled products are often used from polyethylene, and corrugated and ordinary tubes are used from polypropylene. The strength of these plastics is lower than that of PVC; They are not resistant to ultraviolet radiation, so they are usually used for indoor installation work.
Copper
Copper conduits for laying wires are a great idea, but very expensive. The quality and durability of copper products is beyond praise - they can last a hundred years (but wires will not last that long). A wide variety of fittings are available for them; connecting the pipeline will not be a problem. This type of installation has not become widespread due to the high cost of copper and products made from it. In addition, it should be taken into account that the length of wires in any room and the house as a whole is much greater than the heating or water supply systems.
Sometimes copper is used as a decorative element in the design of a room. The range of copper tubes includes very small diameters, and they are sometimes used where compact protection is needed for fine wiring - for example, in lamps, decorative lighting or lighting systems.
Nowadays, decorative open installation of electrical networks from copper pipes and boxes is becoming fashionable. At the height of fashion are artificially aged copper products for retro interiors.
uPVC
Unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVC-U, vinyl plastic) does not contain plasticizers and has greater strength than plasticized ones. Actually, pipes are made from unplasticized polyvinyl chloride. It is this type of PVC that is non-flammable and self-extinguishing.
Corrugated
For electrical wiring, corrugated PVC pipes are most often used - products that have a variable cross-section.
Corrugation for cable laying
Thanks to the thickening, the pipe is given rigidity; areas with thin walls make it possible to stretch and bend the pipe at different angles.
PVC is a common rigid material. Considering the shorter length of sections with thin walls, such a product will not be able to stretch much. At the same time, the flexible properties are very high, especially for small diameters.
Recommendation: if you buy a corrugated product, remember that the diameter in the catalogs is indicated as external. Therefore, it must be chosen larger than the diameter of the cable bundle.
Why do you need corrugation?
Corrugation is a fairly flexible and long tube. Its main advantage is that it can be bent many times without the help of components and with minimal labor costs.
Due to its design, the corrugation is quite compact and at the same time quite resistant to mechanical damage.
Using long tubes allows you to save on connecting elements and even seal the wire inside the corrugation.
Modern technologies for finishing rooms with plasterboard and suspended ceilings require laying communications in covers, while at the same time, corrugation is very easy to place behind a false wall or ceiling without extra costs for fittings. The corrugation can be easily fixed to the frame of suspended ceilings and plasterboard sheathing - this significantly saves effort, and the corrugation is simply irreplaceable for such installation.
A corrugated hose is also indispensable when laying wires and cables in the ground - the corrugated hose is not afraid of small soil subsidence, a long tube can be easily sealed and protect the cable from soil moisture.
Subtleties of laying a corrugated pipeline
Inside all corrugated pipes there is a thin steel wire, the so-called broach. Since this wire is installed with some tension, when cutting the pipe you need to carefully cut it with side cutters, holding it so that it does not slip away.
Next, you can stretch the wires inside the pipe and install it in the planned places - the ceiling or walls. Clips made of aluminum or plastic are suitable for this.
Completion
So, you are convinced that PVC pipes can be an ideal option for laying electrical cables. At the same time, they are able to protect wires from moisture, dirt and mechanical damage.
Tips for choosing pipes for installation in different conditions
The most important parameter taken into account when choosing a method for protecting electrical wiring is the location: indoors on the wall, behind a suspended ceiling, plasterboard false wall; at a height of up to 2 m, at the level of the floor or baseboard, above 2 m; in a damp room, in the open air or in the ground. The second parameter is the required degree of protection, which directly depends on the location of the electrical networks.
For laying wires and cables outdoors, smooth and corrugated steel pipelines are often used. They are somewhat stronger than PVC structures. In addition, although PVC is considered resistant to ultraviolet radiation, PVC corrugation will not last very long under direct sunlight - 15-20 years. PVC pipe will last a little longer. But it all depends on the purpose of laying the wire and the potential service life of the entire structure - if it is a power cable, then it is laid reliably and for a long time, and if it is wiring to a lamp, then in 15-20 years the time will come to update both the lamp and the wiring.
It is advisable to ensure the tightness of laying wires outdoors - both for the safety of wires and insulation, and for the safety of pipes - when water freezes in them, they can break or become deformed. When using metal corrugation, you should choose a corrugation with an inner layer of plastic. It is advisable to coat the joints of pipes and hoses with boxes or fittings with sealant or seal them with sealants.
HDPE and polypropylene are not UV resistant, so they are not used outdoors. Although they will last 2-3 years, they are suitable for temporary installation of electrical networks.
Communications are laid in the ground using HDPE and double-layer PVC corrugation. The gasket in metal is almost a thing of the past due to the tendency of steel to corrosion.
Any type of casing for electrical wiring can be used indoors, taking into account the strength requirements.
To pour into screeds and concrete walls and floors, and to pass through walls, it is necessary to use strong, smooth steel or plastic pipes or reinforced heavy corrugation. Manufacturing and storage areas also require durable, smooth cable ducts. In public buildings, entrances and some other places, it will also be necessary to use smooth, durable pipes, based on considerations of human safety (or vandal resistance).
In wet rooms, a two-layer corrugation is used, which reliably seals the wires.
The thinnest and lightest corrugated hoses are used when laying electrical networks under wall and ceiling cladding, suspended ceilings, and in plasterboard partitions.
When laying open, the location of the wiring should be taken into account - if there is a possibility of damage by objects, bags, arms, legs and other parts of the body, you should choose either smooth pipes or durable corrugated pipes with a thick wall. This danger should be especially taken into account when laying the wire near the floor and above the baseboard, at hip height (0.8-1.2 m)
When purchasing corrugations, you should choose products with a probe (wire) for pulling the cable. The absence of a probe will complicate your work and raises doubts about the quality of the corrugated hose.
It is advisable to buy in large stores and hypermarkets. When purchasing, you should definitely ask for a receipt and a certificate, especially for plastic products. For internal wiring, the plastic must be self-extinguishing! If possible, it is advisable to buy a small piece of pipe and check it - try to set it on fire.
Dimensions and approximate prices
When choosing pipes, it is necessary to choose the correct diameter. For lighting networks, telephone or computer networks, a pipe with a diameter of 16 mm is sufficient. For supplying wires to switches and sockets, a diameter of 20 mm is suitable. For small cables (for example, for connecting powerful equipment in the kitchen), a diameter of 25 mm is suitable. It is better to lay power cables in pipes with a diameter of 25-50 mm.
Prices for PVC corrugation:
- Diameter 16 mm – from 4.7 to 9 rubles. and higher.
- Diameter 20 mm – from 6.5 to 11 rubles. and higher.
- Diameter 25 mm – from 10.8 to 18 rubles. and higher.
Prices for smooth PVC products:
- Diameter 16 mm – from 12 rub. and higher.
- Diameter 20 mm – from 18 rub. and higher.
- Diameter 25 mm – from 35 rub. and higher.
The price varies greatly among different manufacturers.
Selection of metal pipes for cable laying
The electric cable can be laid in almost any pipes.
The minimum requirement for the casing is the absence of rust, burrs and internal irregularities.
Metal pipes are selected according to various parameters: price, decorativeness. Pay attention to the resistance of the pipes against corrosion, as well as how easy it is to install the system.
- The most decorative are copper and brass pipes; they cope better than others with the task of decorating electrical wiring laid in an open way and do not require painting. At the same time, thin-walled pipes allow the casing to be given any necessary shape without the use of shaped elements, while thick-walled pipes can further emphasize the deliberate roughness of the communication by assembling the pipeline using fittings.
- Stainless steel pipes are the most expensive, but reliable and easy to install: they do not need to be painted, they are smooth inside and out, do not corrode and are suitable for laying cables in any way.
- Galvanized ones have the same advantages as stainless steel ones, but their price is lower, so galvanizing is often preferred. However, the service life of galvanized pipes is half as long.
- Steel pipes that do not have a protective coating and aluminum pipes will need to be painted inside and out before installation to prevent oxidation. If an electrical cable in a steel casing is laid in a cement screed, the outer surface of the pipe does not need to be painted.
- Corrugated pipes are easy to install as they easily take on the required shape. Their disadvantage is a weak level of cable protection from compression and impact, so corrugation should not be used for underground communications and in rooms where the risk of strong physical impact is high.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: Spiral-wound air duct designs
In construction stores you can choose consumables for laying electrical cables to suit every taste. But pipes remaining after the dismantling of a gas or water supply system are also suitable.
It is important to first inspect the future casing and assess its condition: if the pipes do not have cracks, internal seams or other irregularities, they can be used.
It is important! Before installation, it is necessary to clean the internal surface of any deposits that have formed by pulling the steel brush through with a cable.
If the pipe does not have a protective coating, it must be painted. Painting from the inside is done by pulling a sponge with paint or pouring paint into a vertically located pipe.
Rules for installing PVC pipes for electrical wiring with your own hands
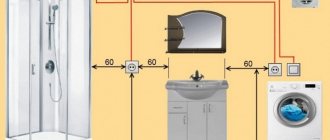
Laying out an electrical network begins with a layout of sockets, automatic machines, lamps, switches, and connection points for stationary electrical equipment (stove, boiler, electric oven). All power supply lines must run either vertically or horizontally, at a distance of 20 cm from the ceiling, floor, door, and distribution boxes must be installed at branching points.
Regardless of the wiring installation method (behind a false wall, in grooves), there must be access to the boxes. Connecting wires is allowed only in junction boxes and under no circumstances inside the shell pipe.
When installing pipes for pouring into a screed or concrete wall, you must first securely secure the structure using metal clamps. When installing a pipeline in a groove in a brick wall, you can fix it with quick-setting plaster (alabaster) and then plaster it.
To install the pipe shell outdoors, metal clamps are used; inside the building, plastic clips are used.
During installation, any pipes must fit into the opening of boxes, sockets, switches; gaps between the box and the pipe are not allowed.
In damp rooms, outdoors and in the ground, sealed pipes are used for installing electrical wiring. At the joints of pipes and distribution boxes, special seals are used (you can additionally coat them with sealant, for example, silicone). When laying open communications in dry rooms, the use of seals is not necessary.
If the electrical wiring is installed near the heating system, then when crossing, the distance from the heating should be at least 5 cm, and if the pipes run parallel, then the distance should be at least 10 cm.
You cannot bend pipes with a small turning radius; when bending, you must comply with the standard radius and use a pipe bender or templates. There should be no cracks, folds, or creases at the bend site.
Required tools and materials
Tools required to perform work with corrugated hoses:
- Grinder with cutting disc.
- Hammer.
- Drill and screwdriver.
- Metal scissors.
- Construction knife.
Materials:
- Corrugated sleeve
- Clips or clamps.
- Dowels.
- Distribution boxes, boxes for sockets and switches.
- Electrical tape, scotch tape.
- Sealing gaskets, sealant.
- Perhaps a hard thin wire or a special broach.
Installation technology
The installation technology is quite simple:
- Cut the pipes or corrugation into pieces of the required length; when cutting the corrugation, you must ensure that the probe does not go inside the pipe.
- Securely attach the cable to the probe using tape or tape. The bent tip of the probe must be bitten off, otherwise when the cable is retracted it will damage the inner surface of the corrugation.
- Pull the cable into the tube. If several wires are pulled in, you need to tape them together several times with electrical tape.
- Mark the location of the cable in the casing and the places of fastenings.
- If necessary, punch a hole, secure the tube using clamps, clips, or alabaster. Fasteners must be installed at intervals of at least 50 cm and always near the boxes, at a distance of no more than 20 cm. The system can only be filled after the pipelines have been securely fastened.
- Mount boxes, tees, bends, connect to pipes, seal if necessary (install seals, lubricate with silicone).
Features of corrugated pipe installation
The corrugated pipe has very great flexibility - after installation it will sag slightly; it is necessary to frequently place clips or clamps. Do not tighten the corrugation too much during installation - this weakens its strength. When installing behind plasterboard or other facing materials, you cannot lay the corrugation obliquely - only vertically and horizontally. You can attach the corrugated hose to the frame structures for cladding. Do not lay corrugation through sharp corners on structures - it will quickly become damaged.
Installation features
During installation, it is important to follow the installation rules:
- It is advisable to minimize the number of pipe turns, since each angle complicates cable pulling.
- At network nodes - turns, branches and places where electrical appliances are connected - distribution and wiring boxes are installed. This will simplify cable pulling after pipeline assembly and maintenance of the electrical network during operation.
- To pull electrical cables, a steel string is used: first, it is pulled through the resulting cable channel, the string is connected to the cable and pulled out from the opposite side. Thus, cables are gradually laid throughout the pipeline and the sections of wires in boxes are connected, forming a single electrical network.
- Plastic bushings are fixed at the ends of the pipes, the purpose of which is to prevent chafing of the cable braid.
- It is better to connect pipes using threaded fittings - special connecting elements, and not by welding. This will simplify installation and further repairs.
- The pipeline is secured using clamps and brackets, the distance between which depends on the internal diameter of the pipes.
| Pipe internal diameter, mm | Distance between fastening elements no more than, m |
| 15-20 | 2,5 |
| 25-32 | 3 |
| 40-80 | 4 |
| 100 | 6 |
- Boxes - distribution and traction - are placed at such a distance to ensure ease of pulling cables and simplify their replacement in the future. This distance depends on the number of turns of the electrical cable.
We recommend that you read: Is it possible to wall up polypropylene pipes when laying a pipeline into a wall?
| Number of corners | Distance between boxes no more, m |
| 1 | 50 |
| 2 | 40 |
| 3 | 20 |
- If it is necessary to rotate the cable more than 90 degrees, an additional cable duct will have to be installed at the turning point. Otherwise, when pulling the electric cable, it will be caught in the bend of the pipe and it will not be possible to pull it out.