In a modern car, the leading role at the moment the engine starts is played by the battery. The operation of the entire on-board electrical system depends on the good condition of the power source and its operational characteristics. It is also necessary that all output parameters, including capacity, voltage and number of amperes, are within normal limits.
What is current strength
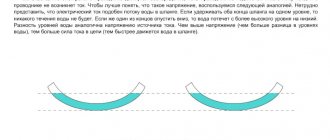
Electricity in batteries is generated through chemical reactions during the interaction of an electrolyte (an acidic or alkaline solution of a certain density) and lead plates that act as electrodes. As a result, a current is formed - the ordered movement of charged particles. Current strength is usually called the amount of electricity moving in the cross section of a conductor per unit of time (second).
The classic version, under ideal conditions, assumes that the current strength throughout the entire circuit is constant. Practice proves that the final value is influenced by various external factors:
- ambient temperature;
- possible sources of electromagnetic radiation located nearby;
- complexity of the electrical circuit, etc.
For a car battery, an important parameter is the starting current, which in some sources is also called cold cranking current (Cold Cranking Amps - CCA).
In Russia, state standards have been established for manufacturers of automotive power supplies according to CCA. The lower threshold values of batteries are limited in GOST 53165-2008. According to the current standard, without landing, the battery is required to output below 9 V at the terminals for 30 seconds at an ambient temperature of -180 C.
A parameter such as the battery capacity is related to the amount of electricity. The value is measured in ampere hours. During normal operation, motorists are not recommended to discharge the battery below the minimum limit values. This will negatively affect the further operation of the device.
The capacity value helps to calculate the approximate period for the battery to return its charge. The capacity is directly dependent on the current strength, so during testing the discharge conditions are standardized. For most batteries, the capacity is 60 Ah, respectively, for a twenty-hour discharge the amperage will be 3 A, and for a ten-hour operation - 6 A. For a discharge current of 25 A, the typical battery capacity will be 40 A, providing power to the on-board system for 96 minutes.
Battery types
Before we find out how many amperes are usually in a classic 12-volt car battery, let's look at the types of power sources. There are the most popular battery options, such as acid and alkaline. In the first case, metal plates (electrodes) are immersed in a solution of sulfuric acid, and in the second case, the liquid is an alkaline solution.
For northern regions, it is not recommended to use alkaline power sources, as they do not perform well at low temperatures.
Regardless of how many amperes there really are in an alkaline car battery, they are available in two versions: nickel and lithium. The former may contain cadmium or metal hydroxide in combination. Due to their large dimensions, such devices are more in demand on electric forklifts or trucks, since there is more space for the placement of cells with a lower specific current compared to acid analogues.
Lithium power supplies are cheaper to manufacture, but in practice they are very sensitive to low temperatures. This equipment has proven to be in demand in electric vehicles.
Acid batteries are available in the following types:
- Antimony. Lead plates include more than 5% antimony. Although such a battery is capable of withstanding a significant number of discharges/charges, due to other disadvantages it is not used in modern cars.
- Low antimony. They are manufactured using a similar technology as antimony batteries, but with a lower percentage of antimony. They have better practical characteristics.
- Calcium. The plates in them are made with the addition of calcium compounds (without antimony). In some models, the electrodes include silver alloys. Power supplies are quite sensitive to frequent deep discharges, but have stable operating parameters.
- Gel or AGM batteries. This technology assumes that the electrolyte is in a jelly-like (gel) state. Such models are significantly higher in price than liquid analogues - 2–3 times. Their advantages are high resistance to frequent deep discharges and good output parameters, but their disadvantages are the need for a high-quality charger with reduced current parameters and stable consumers.
How to check the battery charge using the indicator
Many maintenance-free batteries have charge indicators that allow you to visually determine the condition of the battery. This option first appeared on Japanese products and quickly gained popularity due to its convenience and accessibility.
The hydrometer, as the indicator is called, is a transparent window on the battery cover. The color of the window changes depending on the condition of the battery:
- Green —full charge.
- Gray or white - need to be charged.
For some indicators, the window turns red when capacity is lost.
The principle of operation of the device is based on changes in the density of the electrolyte at different charge levels. It works like this:
A tube with a green float is attached to the window.
- When charging the battery, the density of the electrolyte increases and the float rises, approaching the window.
- If the battery is discharged, the density drops and the ball sinks in the electrolyte. As a result, the indicator window changes color to gray or black.
Some indicator models have a red ball that floats up when the density of the electrolyte decreases. This provides a red indication of the discharge.
When the electrolyte level drops, not the ball, but the electrolyte itself will be visible through the window. To prevent the destruction of the plates, you need to add distilled water to the jars and charge the battery.
The advantage of the indicator is that the device allows you to determine the condition of the battery without the use of special instruments. This is convenient when purchasing a battery or in road conditions when you need to quickly check the condition of the battery. However, indication using a float does not always allow one to draw accurate conclusions about the performance of the battery. Therefore, when in doubt, you should use a multimeter or a load fork. They are also useful when you need to check a battery that is not equipped with an indicator.
Number of amperes in a charged car battery
The battery capacity is indicated on the battery case or in the operating instructions (passport). Let's look at how to independently check the indicated amps on your battery. Capacity is important for a motorist, since it can be used to find out how much charge the battery will have time to deliver over a certain period of time. The parameter is measured in ampere hours.
Monitoring is carried out under load and without it. The readings are given by a multimeter, and a regular lamp serves as the load. A charged battery should show good performance when the light stays on for a long time, but if it quickly starts to go out, then the battery is faulty. In such testing, we recommend taking a 35–40 W lamp and holding it for about 2 minutes.
A car battery that was charged before measurements and after loading produced a voltage above 12.4 V can be considered serviceable. If the values are reduced, you should consider purchasing a new power source.
Most power sources located in the engine compartment of passenger cars have a capacity of 55–65 Ah. This is quite enough to start the engine in any weather. However, it is worth considering that a car parked in a garage or parking lot gradually consumes current for small needs, for example, a clock on the dashboard, alarm system, central locking, injection controller, etc. If the total volume of consumers does not exceed 50–70 mA, then this will not prove critical. Otherwise, you need to think about reducing current consumption or buying a more powerful battery that can produce more energy.
What parameters can be checked?
Using a multimeter, you can measure voltage with high accuracy. By the magnitude of the electrical voltage, you can determine whether the battery is charged or the element needs to be charged with direct current.
Using a multimeter, you can check the voltage not only of acid batteries, but also of cell phone batteries. To check the mobile phone's battery charge level, the device is switched to the mode for measuring direct current up to 20 V. In this mode, the digital device allows you to measure voltage with an accuracy of hundredths of a volt.
The screwdriver battery can also be easily checked with a multimeter. The rated voltage of the device, in this case, can be found out from the documentation of the power tool, and if the voltage is less than this value, then the battery must be charged.
The battery capacity can also be checked with a multimeter. For this purpose, you can use several methods.
You can check current leakage using a multimeter. If it is necessary to measure this parameter on a car, then in addition to the current leakage on the body, the leakage in the vehicle’s on-board network is also checked.
In this way, you can prevent rapid discharge of the battery and increase its service life.
How to check battery charge with a multimeter?
Determining the condition of a lithium-ion (the most common type of modern battery) battery is quite simple if you follow these instructions:
- Disconnect the energy storage device from the car and wait 5-6 hours.
- The multimeter should operate in the “voltage” mode (voltage test).
- A standard lithium battery produces current in the range of 12.7–13.2 volts. The switch is set to 20 or closest to it. This is how the voltage is measured from this value and below.
- The wires coming from the device are connected to the battery: red to the positive terminal, black to the negative terminal. If the wires are the same color, then you should focus on their markings and connect them to opposite charges, minus to plus and vice versa.
How to charge a car battery
There are several ways to charge the battery in a car. In the first case, you can make do with the built-in equipment in the car. It is enough to start the engine without removing the battery and drive it at high speeds for about 10–15 minutes. It is necessary to carry out such an operation not in garages or closed boxes, but in the open air, so as not to be poisoned by toxic exhausts.
We recommend that the event be carried out during the daytime to avoid the use of electric lighting devices. You also need to turn off the audio system, heated windows, mirrors, steering wheel, seats and other electricity consumers.
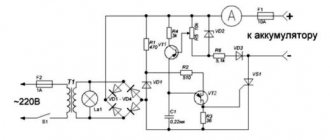
In the second case, you will need an external charger. It is preferable to remove the battery from the car and charge the battery by placing it on a flat horizontal surface. Next we carry out the following actions:
- in serviced batteries, we slightly unscrew the plugs to ensure gas escape, and in unserviced batteries, we check the gas outlet holes;
- connect the positive contact of the charger to the positive terminal, and the negative contact to the negative terminal;
- turn on the device and set the current on it to 1/10 of the capacity, for example, a 55 Ah power source requires a current of 5.5 A, and a 60 Ah unit requires a current of 6 A;
- we leave the connected battery for about 9 hours, monitoring the degree of charge, since the exact time depends on the performance characteristics of the battery and the output parameters of the charger;
- After turning off, you need to let the battery stand for 15–20 minutes so that all the gas comes out, and only then tighten the plugs until they stop.
A fully charged battery gives, after measurements with a multimeter at the terminals, 12.6–12.7 V without a connected load. For a regularly used battery, normal values are in the range of 12.3–12.2 V. You should not allow acidic devices to significantly discharge, as this will negatively affect their service life.