The cable is heating up: causes of heating, solutions
Heating of power wires is a common cause of fires not only in production, but also in apartments.
The high temperature of the conductor leads to melted insulation, and as a result, to an open source of fire. If you notice that the cable is heating up, then the cause of its heating should be eliminated immediately.
This article will help in determining such a reason and bringing a household appliance to the appropriate level of electrical safety.
The main reasons for heating cables and wires
To understand the reason for the heating of electrical wiring, you need to remember the basics of electrical engineering. Electric current is the ordered movement of free electrons, in the path of which other atoms of a substance appear. A certain number of such atoms is called electrical resistance. If the resistance is too high, the temperature of the material increases.
An example of securely tightened wires
This principle is successfully applied, for example, in water heaters. In other household appliances or the electrical network, it is necessary, on the contrary, to reduce the heating of the conductors - to bring it to the nominal level.
The main reasons for heating cables and wires:
- The reason why the wire heats up is the choice of its wrong cross-section. When choosing a small cross-section of wires, which haunts almost all would-be electricians, and a constant current strength, a rapid increase in the temperature of the cable occurs. The same principle applies to water pipes - the larger the diameter, the greater the water pressure.
- Overheating of the line occurs due to improper installation. For example, a minor short circuit that does not respond to an overrated circuit breaker. The machine does not open the line - the cable continues to heat up, and after a while it burns out.
- Poor quality connection or oxidation of contacts. Aluminum wires oxidize very quickly, the connections of which should be checked more often than copper wires. In order not to worry about the quality of twisting, it is better to use special terminal blocks or carefully solder the cables.
- Using a low quality cable or wire. Now the electrical equipment market is rapidly filling with products from Korea and China, the quality of which leaves much to be desired. Such a cable, even if installed correctly, can itself cause heating and fire.
Solutions to the problem
If you notice a heating cable, then you need to know how to solve this problem. There are several popular ways to determine the problem and fix it.
What if the neutral wire gets hot?
It is a rare case when the neutral wire in the electrical panel begins to heat up. For example, when recently laying a resistive cable for floor heating in an apartment. You should know that there is no life-threatening potential on the neutral conductor, and its temperature should be within room temperature, but not higher.
What could cause this heating?
- With uneven distribution of currents. This means that at the working zero the current strength exceeds the current that passes through the phases. Self-regulating cables, which are used to heat pipes, lead to this result due to their power. In this case, the zero can not only overheat, but also burn out.
- Poor contact of the neutral wire with the neutral bus. Accompanied by an unpleasant crackling sound and sparking. It is enough to tighten the contact or check the nearest place of twisting and the problem will be eliminated.
- Connecting electrical devices that directly affect the frequency. These are: induction furnaces, pulse consumers, heating cables, LED-based lighting sources, etc.
Consequences of poor-quality neutral wire contact
Conclusion
The above malfunctions are often a consequence of one problem - poor contact. Of course, there are other reasons: poor cable quality, inappropriate circuit breaker, old wiring and much more. But the most common is a contact that interferes with the electrical energy passing through the conductor.
To avoid the consequences of excessive heating of the cable, it is necessary to periodically check the connections in electrical panels and distribution boxes, and, as necessary, tighten or tighten the twists or terminal blocks.
How hot does the cable get?
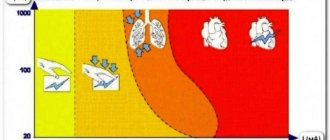
The collision accompanying the passage of current is an endless source of kinetic energy, which increases the vibration of the conductor and increases its temperature. If the electricity is turned off at any point, this energy will be released into the environment in the form of heat. But what if the current passes for many hours? According to Joule's law, the amount of heat accumulated in a conductor must increase over time. Is there a limit?
The release of energy into the environment is possible due to particles in the surrounding air. They receive thermal energy during the cooling process. In physics, air is considered a rather poor conductor of heat, but there is a property that helps it conduct this. Namely, the higher the temperature difference between the heated object and the environment, the faster the heat dissipation occurs.
What does this mean for the wire? As soon as the power is turned on, while the wire is still cold, it begins to heat up very quickly. But over time, when the temperature reaches several tens of degrees, the cable begins to release more and more heat into the environment, which slows down its further heating. Eventually, it comes to the point that the rate of energy release coincides with the rate of heating, and the increase in temperature of the conductor stops. The cable then reaches the so-called limit temperature, as can be seen in the graph:
Useful tips
When performing repair work on an electrical circuit, it is important to follow a few tips. Let's highlight the main ones:
Let's highlight the main ones:
- Always check the voltage level before carrying out repairs.
- If possible, call a specialist for electrical repairs.
- Install high quality machines. This requirement also applies to wires, sockets and switches.
- For safety, use cotton tape (it provides better insulation).
- The appearance of visual damage or thinning of the metal indicates the need to replace the socket.
Please note that electricity is deadly and should not be trifled with. If any problems arise with the outlet, junction box or input panel, it is better to fix the problem immediately.
Delaying repairs often leads to aggravation of the situation, damage to household appliances and even a fire.
Additionally, working on an electrical circuit without the proper knowledge may result in exposure to voltage, serious internal injury, or death.
What are the dangers of poor connections and connections?
Poor contact of current-carrying wires when connecting to each other and at the points of connection to devices leads to heating of the contact points. Why do the contacts get hot?
The physics of heating of poorly made contacts is explained by a simple law of two physicists, Joule and Lorentz. Let me remind you:
The heat generated is proportional to the square of the current, the resistance of the conductor and the flow time.
With good contact between two metal wiring elements, the heat generated by the current has a very specific value, which is calculated and taken into account when choosing the cross-section of conductors and the ratings of circuit breakers.
When the contact is broken, at short distances of such a violation, or, more simply put, when the contact is weakened, the resistance begins to increase, more heat is released, and the contacts begin to heat up.
The heating of the contacts further enhances the thermal expansion of the connection points, as a result the contact weakens even more. As a result, the contact resistance tends to almost infinity (air specific resistance 1016), heating increases.
Added to the heating of the contacts is the sparking of the contacts, which is accompanied by a colossal release of heat. As a result, burnout of contacts, burning of installation products, or, as the most dangerous option, a fire in the house.
The main reasons for heating the wiring cable and power cord of electrical appliances
Heating of the supply wire is an extremely dangerous phenomenon that requires immediate elimination. But before you begin repairs, you need to understand where and why heating occurs. In this article we will look at the main causes of heating and how to eliminate them. So, let's begin.
yandex.ru
Why might the cable or power cord get hot?
So, let's start by defining the main causes of heating. There are several main reasons, namely:
1. The cable or power cord cannot cope with the current load.
2. The wiring was installed incorrectly and this causes heating.
3. Wire connections are not made properly.
4. Unsatisfactory quality of the power cable or cord.
These are the main reasons for cable heating, now let's talk about them in detail, immediately looking at solutions.
How to solve a problem
First, let's look at the case when the power cord of an electrical appliance gets hot.
So, first of all, determine the heating location:
– the area near the power plug gets hot.
– the area near the electrical appliance itself gets warm.
– or the entire power cable heats up.
So, in the first option, there may be two reasons: this is poor contact of the wires inside the plug itself. And the solution is this: disassemble the fork and, if necessary, tighten the bolted connection.
The second reason may be the socket itself: due to intensive use, the sponges of the socket do not securely fix the plug and because of this, heating occurs in this place. The solution is as follows: ideally, change the socket to a high-quality one with special pressure springs. But if this is not possible, then simply use pliers to squeeze the contact jaws
Attention. Work on the socket can only be done after the circuit breaker supplying this line has been turned off and the absence of voltage has been checked using a multimeter (indicator).
Another option for heating an outlet is that its rating does not match the current flowing. Perhaps your outlet is rated for 10 A
, and you connect a powerful electrical appliance to it.
is
only to replace the outlet with a more powerful one, rated for 16 A.
yandex.ruIf your cord is heating up near an electrical appliance, then poor contact is also to blame. To eliminate this, open the housing of the electrical device and tighten the bolted connection on the device itself.
But if your entire power cord is heating up, it means that a careless manufacturer saved money and instead of, for example, installed a wire with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2 with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2. In this case, only a complete replacement of the power cord will help.
Now let's look at the reasons for heating the wiring itself
Let's start with the most banal and common reason. In many houses there is old aluminum wiring and when it was laid it was designed for single loads, but now the electrical loads on the network have become disproportionately greater. And because of this, the wiring begins to overheat. In this case, there is only one way out: a complete replacement of the wiring in the house (apartment).
yandex.ru
It is also a very common scenario when the wire in the distribution panel overheats. The reason for this lies in poor contact or incorrect connection.
For example, if a flexible wire is used, then connecting it to a machine or to a grounding bus without prior crimping is strictly prohibited.
yandex.ru
Heating can also occur in distribution boxes. The reason is the same - poor contact. In order to eliminate this problem, it is necessary to replace the twists with a high-quality connection, for example, crimping with sleeves.
yandex.ruImportant. If copper and aluminum are connected in a distribution box, then such a connection can only be made through special connecting terminal blocks
Also, all work in distribution boxes and panels must be carried out with the voltage removed.
Separately about extension cords
I also want to talk separately about extenders (surge protectors). Many people are mistaken that if there are 4 sockets in an extension cord, then you can plug a load of 16 Amps into each of them,
So, to each socket of such an extension cord you can connect a load designed for
16/4 = 4 A.
And if you are using a drum-type extension cord, then when connecting, for example, welding, be sure to completely unwind the wire from the drum. Since in the wound state, inductance appears in the wire, which additionally heats it up, and this can lead to melting of the insulation.
Solutions to the problem
If you notice a heating cable, then you need to know how to solve this problem. There are several popular ways to determine the problem and fix it.
Appliances
Household appliances are the main cause of overheating of the electrical network. Excessive heating of conductors occurs due to the high power of the consumer and the cable not designed for such power. But if this is not the reason, then a simple sequence will help you quickly find and fix the problem.
- Check whether the cable is equally heated along its entire length, or whether a high temperature is observed in one place. A common problem is poor electrical contact between the plug and the cable leading to the household appliance.
How to fix:
- It is necessary to unscrew the bolts securing the fork body and remove the top cover.
- Loosen the wire fastening contacts and remove the wires.
- Clean the wires and contact points - remove all obstacles to the passage of electric current. Then put the wires in their place and carefully tighten the bolts.
- The final stage is assembling the cover.
- Poor cable contact at the input of the household appliance. If the plug is intact, the quality of the contacts is at the proper level, and the wire is heating up on the other side, then you should check the distribution box (or, as it is called, the terminal box) of the household appliance.
How to fix:
- Unscrew the 4 bolts securing the upper cover of the terminal box and remove the cover itself. Below it there is a terminal block in which direct contact is made between the input wire and the wire of the household appliance.
- The block should be unscrewed, the wires should be taken out and stripped, as well as the places where the block is attached. For cleaning, it is convenient to use a small needle file or fine-grained sandpaper.
- After stripping, install the cables into the terminal block, tighten with bolts and replace the cover.
- If the cable heats up along its entire length, and the socket is designed for the permissible current of the household appliance, then there is only one reason - the poor quality of the cable. This conductor should be replaced.
Wiring
Excessive heating of wires in home electrical wiring is accompanied by the smell of burnt insulation and leads to improper operation of household appliances. In some cases, electrical appliances may even fail.
Fault detection sequence:
- The main problem may be the connection location of the power cables in the apartment panel. Usually the input cable is attached to a copper bus, from which the wires will go further into the apartment. A loose contact on the bus leads to gradual heating of the cable, and sparking is also possible. It is enough to strip the wire and tighten the contacts a little.
Important! Stranded copper wires must first be crimped with a sleeve, after which the tip is secured to the busbar using a bolted connection
- Another reason for an increase in conductor temperature is a weak contact on the circuit breaker or its malfunction. The high rating of the machine leads to gradual heating of the cables, melting of the insulation and its fire. It is enough to turn on several powerful household appliances, for example, a washing machine and a boiler, while the machine is not working, and the result will not take long to arrive. Poor contact between conductor and circuit breaker
- The junction box is one of the most unsafe places in electrical installations. One under-tightened twist leads to burnt insulation and a possible short circuit. Therefore, it is better to make all connections in distribution boxes using copper terminal blocks.
The wiring in the apartment is heating up
There are several possible reasons for overheating of current-carrying conductors, namely:
- the cross-section of the cable or wire is not able to withstand the load from the connected household appliances;
- The electrical wiring was installed incorrectly, resulting in overheating of the cable line;
- poor quality wire connection;
- poor quality of the cable itself.
Now we will look at instructions for determining the malfunction, and will also tell you what to do if the cable gets hot in one case or another.
Causes and solutions to heating cables
Heating of power wires is a common cause of fires not only in production, but also in apartments. The high temperature of the conductor leads to melted insulation, and as a result, to an open source of fire. If you notice that the cable is heating up, then the cause of its heating should be eliminated immediately. This article will help in determining such a reason and bringing a household appliance to the appropriate level of electrical safety.
Temperature limit for typical cables
What is this maximum temperature? How hot can the cable get? And how does heating the cable harm? Pure copper has a melting point of approximately 1085 C. But it should be remembered that a typical electrical cable is additionally equipped with insulation of much lower strength. Standard braids can withstand temperatures up to approximately 90 C, special braids can withstand temperatures up to several hundred. In order not to exceed the specified temperature, the cable should be selected in accordance with the current that we plan to pass through it. Here is a table of values to follow:
Operating current for insulation resistance up to 60 C, 75 C and 90 C
Conductor cross-section [mm 2 ] Current [A] for 60°C Current [A] for 75°C Current [A] for 90°C
2,5 15 20 25 4 20 25 30 6 30 35 40 10 40 50 55 16 55 65 75 25 70 85 90 35 95 115 130 50 110 130 145
The larger the cross-section of a conductor, the lower its resistance and the larger the surface area capable of dissipating heat - hence the conductor can withstand a higher current. The table above applies only to a theoretical situation - a single copper wire suspended in air at a temperature of 25 C. The actual load capacity of the cable depends on many other factors, such as the installation method, the number of conductors in it, the ambient temperature or external conditions. True, manufacturers of electrical cables meet halfway and provide special tables that take into account all factors.
Resistance slows down the passage of electrical current. As a result, the kinetic energy of the electrons is converted into thermal energy stored in the conductor.
Faulty plug
There is no point in delaying repairs - the socket may spark and an unpleasant burning smell will appear. In addition to equipment failure, it is simply dangerous, for example due to the risk of fire or electric shock. It is necessary to limit the use of sockets and plugs, or better yet, stop.
If smoke or other serious signs appear, turn off the electricity. Usually the switch is located in the meter on the distribution panel. You need to hire a specialist or fix it yourself. Work is carried out after a power outage.
If the plug breaks, you can replace it or try to repair it.
Overheating of the neutral conductor - why is it dangerous?
You don’t need to be a specialist to understand the fact that excessive overheating of the neutral conductor can subsequently lead to its burnout, and as a result, cause emergency situations.
So, for example, if in apartment buildings a three-phase power supply network is used (zero is common, and the phases are distributed alternately between apartments), then burning out the neutral conductor will inevitably cause phase imbalance, with the possibility of increasing phase voltages to linear values (380V). Naturally, without additional protection in the form of a voltage relay, household appliances with such power supply parameters will certainly fail.
When using a single-phase supply voltage, if the neutral conductor breaks, a potential will remain on its conductors (through switched-on consumers), which is dangerous to humans.
Electricity in the house. Zero burns out, or why 380V appears in the apartment
Unfortunately, almost each of us has had to face a situation where the tension in the apartment increases sharply
and massive combustion of equipment occurs.
It is relatively rare, but there are situations when, during the next repair, an amateur electrician simply confused zero with phase and connected 380 V to your apartment.
Most often, such situations arise if the house periodically loses voltage on one of the phases and home-grown electricians run to the site to the switchboard to transfer the power to their apartment to another phase that is currently working.
As you understand, the result of such a “mistake” can be expensive and it is much cheaper to call an electrician to your home than to repair a washing machine, TV, microwave, etc.
But, nevertheless, much more often a sharp increase in voltage in an apartment occurs for another reason: a break in the neutral wire
(the so-called neutral), or, as they say, zero burnout.
To understand why when a wire breaks, the voltage does not disappear, but also rises to almost 380 V, you need to remember a little about the basics of electrical engineering. To begin with, let us remember that the generator at the power plant produces three-phase current.
In the same form, it is transmitted by all power lines, transformers and enters our house - for example, to the distribution panel on our landing. Thus, 4 wires are inserted into the landing panel: neutral N and three phase wires - A, B and C.
In apartments, the current is distributed through two wires: neutral (N) and one of the phases - A, B or C. It is known that the voltage between any phases, line voltage, is equal to 380 V, and the voltage between any of the phases and the neutral wire, phase voltage , equal to 220 V.
Thus, a phase voltage of 220 V is supplied to our apartments
.
note
What will happen to the voltage if in apartment 3, or on the supply to it - point 1, the neutral wire is disconnected? Nothing scary! It’s just that the residents of apartment 3 will be left without electricity, and the residents of apartments 1 and 2 won’t even notice it - nothing has changed for them. A completely different situation arises in the event of a break in the common neutral wire - point 2.
For example, consider the situation that arose in this case for two neighboring apartments 1 and 2. The actual power supply diagram for these two apartments, which arose when the common neutral wire was broken, is shown in the following figure. As we can see, in reality these two apartments began to be powered with a voltage of 380 V
.
Will both apartments have 380 V? No! After all, the current consumers in apartment 1 and the current consumers in apartment 2, by chance, turned out to be connected in series. In this case, the voltage across the apartments will be distributed inversely proportional to the switched on load. Let's give a couple of examples.
If at the time of the neutral wire break in apartment 1 and apartment 2 only one 75 W light bulb was on, and all other equipment was de-energized, then each light bulb will receive half the supply voltage - 190 V.
If in apartment 1 only the TV was turned on, and even that was in standby mode, and in apartment 2 the electric oven was turned on, the air conditioner and iron were working, then the TV in apartment 1 would take the brunt of the blow - the voltage supplied to it could increase up to 380 IN!
Based on the analysis, the following conclusions can be drawn:
– if the neutral wire breaks, those who have their energy consumers turned on at high power have a better chance of saving their equipment; - if your refrigerator is shaking and the light bulbs are white-hot, then you urgently need to turn off all electrical appliances - preferably with a common automatic switch on the panel. If it is not possible to turn it off on the dashboard, then turn off expensive equipment first. Remember, whoever turns off electrical appliances first (you or a neighbor) will save more equipment.
– if at the moment the voltage rises you are in the kitchen, then first turn ON
electric oven, stove, and then run to turn off the TV, computer, stereo system, etc.
– don’t be lazy to unplug (!)
equipment not currently in use. This will also save you energy.
Top tip: Install a surge protector
– see the article “Electricity in the house. How to protect electrical appliances from power surges.”
Source: https://dizainremont.com/poleznoe/otgoraet-nol.html
Why are there short circuits in wires and contacts?
The main factor of a short circuit is a breakdown of the insulation of current conductors. Violation of the integrity of the insulating sheath of wires, breakdown of contact resistance in an electrical or electronic circuit - all this causes a short circuit.
The main causes of short circuits include:
- high voltage surge;
- insulation wear;
- mechanical damage;
- penetration of foreign objects;
- lightning strike.
High voltage surge
Voltage fluctuations in the centralized power grid are often observed in remote areas of rural areas; such cases also occur in urban environments.
During a voltage surge that far exceeds the permissible standard, the risk of breakdown of the insulation of wires or electrical circuits increases sharply. A situation is created in which the wiring shorts and a short-term arcing may occur.
Insulation wear
The old dielectric sheath of wires dries out over time and can self-destruct. Failure to replace old wires over decades often leads to short circuits.
Mechanical damage
External mechanical impact on the electrical network leads to damage to the insulating layer of conductors. An example of this would be drilling into walls with hidden wiring. A drill caught between the wires causes a short circuit.
Penetration of foreign objects
Dust and small debris that get inside the housing through the cracks of the ventilation grille of an electrical or electronic device most often provoke the occurrence of a short circuit between the elements of the device. Short circuits are sometimes caused by insects and small rodents.
Lightning strike
Natural electrical discharge “attracts” the electromagnetic field of various electrical equipment. A powerful magnetic circuit can become the target of lightning.
Why do cables and wires heat up during operation?
Electrical installation work involves high risks. That is why it is necessary to know and take into account all the important factors affecting safety. These include strong heating of the wires during operation. This feature is inherent in all wires and cables. In addition, it determines the rules for installing electrical wiring and further connecting energy consumers to the network. Heating of the cable also affects the choice of a specific brand of cable and wire products and the maximum value of the connected load. In order to find out the degree of heating of the wires, it is necessary to understand the cause of this phenomenon.
The main reason for the heating of cable and wire products is the nature of the electric current. After all, the movement of charged electrons along a conductor is carried out under the influence of an electric field. In addition, when moving, electrons need to overcome the crystal lattice of metals, which is distinguished by very strong molecular compounds. That is why quite a large amount of heat is released, because electrical energy is converted into thermal energy.
The conversion of electricity into heat is a two-way phenomenon, that is, on the one hand, this effect is undesirable, but on the other, it is very useful.
Positive side
lies in the possibility of using electrical energy for heating in absolutely any equipment (from a simple household kettle to industrial ovens). The same principle applies to any lighting technology.
Main disadvantage
This phenomenon lies in an increased level of danger, since strong heating often leads to serious consequences. In addition, a strong increase in the temperature of the windings of transformers, electric motors and other equipment leads to a decrease in efficiency. If the maximum heating rate is exceeded, the equipment malfunctions and subsequently fails.
The most dangerous situations
occur when the temperature of those cables and wires that are used to connect various consumers to the electrical network (wiring in residential premises, cable and wire products for connecting industrial equipment to the network) is greatly exceeded. Significantly exceeding the heating temperature of the insulated cable is fraught with fire of the insulating material or its melting, which will subsequently cause short circuits. In such situations, the likelihood of ignition directly depends on the protective devices used.
Consequently, the phenomenon of heating cable and wire products is one of the main factors in the occurrence of fires. That is, short circuits are the main cause of the lion's share of all fires that occur in residential and administrative buildings.
It is worth noting that heating over a long period of time changes the mechanical properties of the metal. This is why such situations occur, for example, as power line wires break, which leads to both large financial losses and a serious danger to human life.
When using one or another cable and wire product, it is worth remembering the maximum permissible heating temperature corresponding to a specific brand. This temperature indicator is directly related to the properties of the material from which the insulation is made. For example, a rubber-insulated wire should not heat above 50-65 0 C
, with paper insulation - a maximum of
80 0 C
, and with insulation made of the latest high-tech polymers, the heating temperature
reaches 100 0 C. The exact properties of each cable or wire are indicated directly by the manufacturer.
Only the correct choice of cable for a specific situation, taking into account all its features and nuances, will help to avoid overheating and further ignition. To make the right choice, it is important to take into account all the factors that affect the degree of heating of a particular cable. Simple formulas, known to everyone from school physics lessons, will help with this:
Q= I 2 Rt
– the main formula that describes the process of converting electricity into heat (Joule-Lenz law), where
Q
is the amount of heat that is released during the passage of current through a conductor,
I
is the current strength,
R
is the resistance of the conductor,
t
is the time during which the electric current goes along the conductor.
Based on the formula, it is clear that the heating of the wire increases simultaneously with the increase in load and resistance index. It is worth noting that the amount of heat released is directly proportional to the time of passage of the electric current. And the heating rate is directly dependent on the current electrical power. The latter, in turn, is determined by the product of voltage and current, i.e. P=UI
. Thus, the power of consumers connected to the cable directly affects the strength and intensity of its heating.
These formulas, namely Q= I 2 Rt
and
P=U I
, help to find out the exact parameters that can be changed by controlling the amount and speed of heating of the wires.
You need to know that the amount of current depends on the rated power of the connected conductors in the aggregate. This value serves as the basis for important calculations. The main changing parameter is resistance, the value of which is determined by the properties of the metal of the conductor and the cross-section of the cable. Therefore, the cross section should be determined on the basis of power. This is what can reduce the electrical resistance of the cables and, therefore, reduce the heating temperature to an acceptable level.
When choosing the cross-section of cable and wire products, you need to remember not only about the safety of the electrical network, but also about savings. Thus, cables and wires with the largest cross-sections require large unjustified costs. But in the situation of possible connection of additional devices to the network in the future, it is desirable that the cable has the largest cross-section.
To correctly determine the required cross-section, you need to calculate the maximum current consumption in the following way: you need to divide the total rated power of all consumers by the voltage indicator.
The Planet Electric retail chain has a very wide range of cable and wire products, which you can familiarize yourself with in more detail on our website.
Eliminate Heat
Before you begin to troubleshoot any problems associated with electrical appliances, you must first stop the current supply to them. To achieve this, you need to turn off the machine, or unscrew the plugs on the electrical panel, after which the cover is removed from the socket, which is secured with a screw in the central part of its body.
If it is noticeable that the contact wires have been exposed to high temperatures, then this is the reason for the heating of the socket. To bring them back to normal, you need to completely remove the socket from its socket, after loosening the screws that secured it. After this, clean the contacts and place them back into the contact clamps, properly tightening the mounting screws. Then the socket is assembled and installed in its place.
Tags: machine, sconce, view, choice, switch, house, , clamp, replacement, sign, cable, like, , magnet, installation, multimeter, voltage, nominal, skew, potential, principle, wire, manufacturer, , work, relay , repair, socket, switch, row, light, LED, network, connection, wire connection, resistance, ten, type, current, , phase, filter, shield, electricity, electrical panel