What is SIP wire
To understand the purpose and design of the cable, you first need to decipher the markings:
- C – self-supporting;
- I – isolated;
- P – wire.
This cable is used for laying electrical transmission lines over the air. This is an ideal option when installation is carried out according to the “pole to house” system. On the other hand, the conductor cannot be led directly into the house or living quarters, since the insulation is not intended for such use. As a result, the SIP is extended to the distribution panel, which is the input node and is located on the street. An electric meter and an automatic input device are placed inside it. Other cables are laid from the panel into the house, usually with copper conductors and good insulation. Their diameter is much smaller and their flexibility is higher.
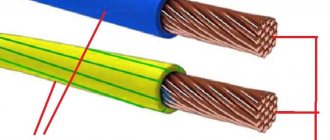
Structurally, a wire differs from a cable in the absence of insulation, which is why our product is called “self-supporting insulated wire.” There is no additional protection in the form of an outer shell or armor, and only the conductors are insulated. Thus, technically calling it a SIP cable is incorrect.
The adjective “self-supporting” indicates that for overhead lines there is no need to use a dielectric cable to which the remaining wires are attached. SIP of any brand is characterized by a high load-bearing capacity, which is sufficient for the cable to withstand its own weight and additional loads due to wind or precipitation (for example, snow settling on power lines).
Instructions: how to lay wires yourself
Installation of SIP cables has some features. It is important to carry out the installation in suitable conditions, select the correct components, and also follow the necessary algorithm for installation.
Conditions
The wire is installed at a temperature of -60…+40 °C. It is advisable to carry out work in calm weather. The distance from the pole to the house should not exceed 25 m. If this figure is greater, additional support will be required. It is necessary to do the ending when entering it into the machine.
Required components
When connecting to copper wires, adapter sleeves should be used. Anchor brackets and clamps may be required during operation.
They are selected taking into account the cross-section and other characteristics of the cable. Caps are needed to insulate the ends. If connection to a power line is required, piercing clamps are required.
Algorithm of actions
Installation of SIP includes the following steps:
- installation of supports;
- fixing special hooks or brackets;
- unwinding and hanging the leader cable;
- lifting the SIP and tensioning it;
- fastening the wire to the supports;
- formation of linear branches.
Design and composition
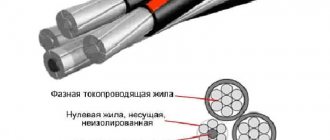
Structurally, SIP consists of aluminum cores twisted together and protected by a durable layer of polyethylene. The conductors are light-stabilizing, therefore, when exposed to ultraviolet rays, their technical and operational characteristics do not change.
The shell of individual conductors in SIP is black. The cable includes a load-bearing element connected to the zero. The rest of the wires are wound around it.
In general, SIP consists of the following components:
- current-carrying conductors;
- steel wire core;
- high-strength polyethylene shell.
The SIP-3 power cable is made of aluminum conductors and a steel core with a round cross-section. The number of cores is formed in accordance with the standards of specifications individually for the selected brand. The design of SIP may imply the use of a self-supporting aluminum core; in SIP-3, SIP-4 and SIP-5 it is absent.
Important! The quality of the SIP can be judged by how the phase wire is twisted. It always moves clockwise relative to zero.
In the electric cable SIP-2, SIP-3 or SIP-5, the sheath is made of cross-linked XLPE, which increases light stabilization. In SIP-1 and SIP-4 it is made from thermoplastic polyethylene (LDPE).
The technical parameters of the product depend on its design features. One or two capital letters placed in brackets can be added to the abbreviation SIP:
- SIP (N) – the shell of the conductors is made from materials that are resistant to combustion.
- SIP (G) - insulation protects the wire structure from exposure to water or moisture.
- SIP (NG) - cross-linked polyethylene is used for the shell, resistant to both combustion and moisture penetration.
Reproduction and lifespan
The bird loves constancy; it nests in high places, on mountain slopes, between cracks in rocks. The bird settles in colonies (up to 20 pairs). Mating of a male and female occurs between January and March.
The female lays one white egg, but both the male and the female, alternating with each other, incubate the egg for 50 days and feed the chick for 130 days after hatching.
Griffon vulture chicks have their first downy plumage as a white color, after molting, the change in plumage becomes longer down and either a creamy shade or grey. By the fourth year of life, young males and females are sexually mature, but they begin nesting later.
Males in search of females to create their families begin to prepare from the beginning of January. Their preparation consists of repairing old nests or building new ones. Moreover, each nest is woven from twigs and stems of grass and strong sticks.
Birds build their nests in places inaccessible to humans and other animals, for example, in a rock crevice, but cattle must graze nearby. The nests have a height from 200 to 750 mm, a diameter from 100 to 3000 cm.
Most often, only one calf is born to a griffon vulture.
During the mating season, the male begins to attract the female while flying, he performs unusual tricks. On the ground, in order to attract the female to mating, the male demonstrates his stately profile and full face, spreading his wings and fluffing his tail, showing the beauty of his plumage, while creating crooning songs. This whole process takes place in the male in a bent state.
Egg sizes can range from 8 - 10 cm x 6.5 - 7.8 cm. The male and female replace themselves while laying the eggs to search for food. Parents feed their baby food that they regurgitate from their mouths. What food is complete for a baby due to its softness?
Small SIP, learns to fly from 3 or 4 months. He begins to master the technique of flight only at the age of one; his parents protect him. When the baby begins to fly, the whole family can fly from one place to another, but during the mating season it can return to its original place.
Types and purpose of SIP wires
SIP wire is the best option for running power lines to a private home. This is an inexpensive product with good technical and operational characteristics, which is available in three varieties:
- exposed carrier neutral;
- isolated carrier neutral;
- self-supporting cable.
The main material for the manufacture of current-carrying cores and supporting conductors is aluminum. In the latter case, an alloy with high load-bearing capacity is used. Let's look at the main types of SIP.
Wire SIP-1
In this case, the wire is manufactured with a bare carrier neutral in accordance with the European standard. Structurally, SIP-1 is one load-bearing bare wire made of pure aluminum or a reinforced alloy, around which one to four current-carrying conductors with LDPE insulation are twisted. The latter material protects the product from ultraviolet rays.
This wire is used during the installation of main electrical transmission lines and various branches, provided there is dry or normal air with a minimum amount of dust. Suitable for electrical networks with a total voltage of 600 or 1000 V at a frequency of 50 Hz.
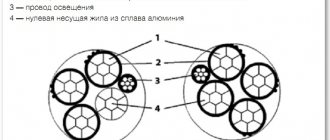
All conductors, protected by insulation, are twisted around the supporting wire with a certain pitch. An individual core may consist of one or more wires. The neutral core is made from a high-quality core. Steel or aluminum can be used. Round aluminum conductors are placed around the core. The diameter of the supporting core is much larger.
After laying the SIP, the weight of the entire structure is restrained by the load-bearing core installed on guy wires, attached to poles, etc. This is associated with an increase in thickness relative to other current-carrying conductors. In most cases, the thickened core is zero. The remaining cores are necessarily insulated with thermoplastic polyethylene, capable of withstanding air temperatures up to 70 degrees. Celsius with continuous heating or up to 125 degrees. Celsius at short-term. Also, the power line at SIP-1 will withstand heavy snow loads.
The main disadvantage of using SIP-1 is that when a phase imbalance occurs, a high and life-threatening voltage may appear on the exposed supporting wire. To prevent this, the neutral at each pole is grounded. But even if there is such a possibility, it is not recommended to lay street cable along the facade of the building.
Wires SIP-2 and SIP-3
Wires of brands SIP-2 and SIP-3 have an insulated neutral. The supporting neutral wire, unlike SIP-1, is protected by a high-quality sheath, while the remaining structural elements remain unchanged: one to four current-carrying conductors are twisted around the thickened neutral, insulated with cross-linked polyethylene with high light-stabilizing properties.
Operation of SIP-2 is permissible in electrical networks with a voltage of 600 or 1000 V. Unlike SIP-1, the second category can be used in conditions of high humidity and high salt content in the air (for example, on the coast of seas and oceans, near salt marshes, etc. .). The wire can also be fixed directly to the walls of residential buildings. This is an ideal solution when laying lines from a pole to a house.
SIP-3 is identical in structure to the cable of the second category, but is characterized by a thicker sheath. Thanks to this, the prefix “protected” is added to the description of the wire. Operation is permissible in networks with a much higher rated voltage - up to 20 or 35 kV, depending on the specific product model. As for technical characteristics, the cable is identical to SIP-1, although differences can be found when comparing permissible current loads.
SIPs of the second and third categories are suspended on a supporting conductor of increased diameter. Since it is insulated, possible current induction is eliminated. However, there is a risk of shell rupture due to excessively high mechanical stress. Thus, when designing a power transmission line on SIP-2, installers try to reduce the span (the distance between the nearest poles) to a minimum.
Wire SIP-4, SIP-5 and SIP-7
In design, all three categories of wires differ significantly from those listed above:
- the product does not have a supporting conductor, so the load is immediately placed on all current-carrying conductors;
- the strength of the cable is much lower than SIP-1, SIP-2 and SIP-3, which is precisely due to the lack of a support wire;
- they cannot be used in regions with large amounts of precipitation in the form of snow or frequent icing.
It is also worth noting that the wire can consist of two, three or four conductors (there are no single-core SIPs of the fourth, fifth or seventh categories). One or two wires for lighting can be added to the product. The veins twist together to form a common center. The twist pitch depends on the specific model. One core is made zero, all the rest are made phase.
SIP-4 is used in electrical networks with a voltage of 600 or 1000 V. Since the design does not imply the use of a thickened load-bearing core, the cable is characterized by increased flexibility, and the minimum bending radius is 7.5 radii of the total diameter.
This is the most popular SIP wire, due to its reduced cost and good technical parameters. There are several additional types of SIP of the fourth category:
- SIPn-4 is manufactured with high-quality insulation that does not support combustion.
- SIPsn-4 has non-flammable insulation and one or two lighting conductors. It can also be upgraded with one to three copper conductors for control circuits. In this case, numbers are added to the abbreviation through a “plus” indicating the number of these auxiliary conductors.
- The SIPgsn-4 cable differs from the previous version in that it can additionally prevent moisture from entering.
The last two types of wire have a European analogue called AsXSn. The purpose and most technical and operational characteristics of these products are identical.
The next category - SIP-5 - differs from the previous one in that it is not possible to turn on auxiliary conductors for signaling or lighting. The product contains current-carrying conductors of identical diameters. The total number of conductors is from two to four: as always, one of them is neutral, the rest are phase.
Single-core wire SIP-7 is produced with reinforced insulation, consisting of several layers:
- screen made of electrically conductive polyethylene;
- cross-linked polyethylene;
- weather-resistant polyethylene.
This cable can be used in electrical networks whose voltage reaches 110 kV. An excellent option in cases where it is not possible to carry out underground electrical installations, and the use of bare conductors is unacceptable. The most striking example is park areas and other high-traffic areas. SIP-7 is suitable for use in temperate, cold or tropical climates. Less common is copper insulated cable SIP-7.
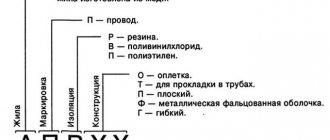
Explanation of SIP markings
In comparison with other brands, SIP wire is a current-carrying element for transmitting electricity, which is deciphered by the three letters of the name:
- C – means that the wire is self-supporting;
- And - indicates the presence of insulation around current-carrying conductors;
- P - indicates that this is a wire, despite the presence of an insulating coating and branching along the cores, which is why it can be equated to a cable.
Consider an example of such a designation - SIP-1-3×20+1×25-0.4, here SIP-1 indicates the brand, 3×20 indicates that three insulated conductors have a cross-section of 20 mm2 each, 1×25 means that the neutral core has a cross-section of 25 mm2, 0.4 is the rated voltage for this model.
Depending on the specific brand, there are five main types of SIP wire, designated by the corresponding numbers after the letter designation. There may be one letter at the end, indicating design differences and operational features. These differences in SIP brands are determined by design parameters, so it would be more appropriate to consider them using specific examples.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let us list the main advantages of SIP wires:
- Easy to install and lay. The process takes less effort and time compared to installing other bare wires. There is no need to attach the conductors to insulators.
- Reducing the likelihood of unauthorized connection to the line. Switching requires certain skills and work experience, so not everyone can perform such actions.
- SIP insulating shells are made from high-quality material that repels wet snow and condensation, which eliminates serious icing of the line. If ice appears, it is in small quantities.
- Reducing the likelihood of electric shock. The presence of conductor insulation reduces the risk of electric shock during repair work and maintenance of power lines. Many operations can be performed without turning off the voltage.
- Economical. Due to the SIP design, the wire is less susceptible to breakage. Minimal funds are spent on maintenance; the wire can be installed on the facades of residential buildings (with the exception of some categories), thereby reducing the number of installed supports.
- Reduced inductance. Due to the low reactance in the wire, the amount of power and voltage losses is significantly less. This eliminates the formation of current pickups and allows you to mount self-supporting insulated insulated wires on supports for low-voltage lines.
The disadvantages include:
- High cost compared to simple bare wires. For quite objective reasons, the price of SIP is significantly higher than the cost of conventional non-insulated cables.
- When using SIP, you must contact qualified specialists. Only they can perform high-quality installation and maintenance of power lines using these wires. This is due to the fact that such products appeared relatively recently, so they have not yet become so widespread. Add to all this the fact that domestic electrical supply systems are not suitable for the transition to self-supporting insulated conductors.
Laying conditions
Cable laying does not require special qualifications. In the process of performing such work, special supports or structural elements of buildings can be used.
It is easier to consider the laying conditions using the example of its placement on reinforced concrete supports:
- the safety of the insulating coating is ensured by special plastic rollers or thimbles that allow unimpeded movement of the cable;
- the wire must not be dragged along the ground or tree branches, so as not to damage the insulation;
- before mounting on the support, the cable is pulled through the movable device and fixed;
- You cannot wind two or more wires together when laying them together.
Fastening the SIP on the support and supplying it to the meter on the support List of materials required for installation of the unit:
- Mounting tape – F 207.
- Clamp - A 20.
- Intermediate suspension kit – ES 1500.
- Sealed piercing clamp FIDOS 4-35/6-150 – RS 35-150.
- 2x Adapter for clamp PC 35-150 – F 2.
- Anchor brackets – CA 1500/2000.
- Anchor clamp for wires of subscriber branches - RA 25.
- Measuring and distribution cabinet made of polyester 320x665x235 - MRO 1-S.
The absence of errors when performing work will eliminate the need for subsequent revisions and repairs.
Also read: What are low-voltage complete devices (LVDs)
Cable termination
Selecting a section and checking the product
When going to the store to purchase a self-supporting insulated wire, pay attention to the rated current. To calculate the required value, a diagram is formed that takes into account the length of the power network sections and the load on each of them.
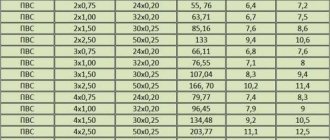
After you calculate the approximate current value, compare it with the one indicated in the table below to select the SIP brand and cross-sectional size. Table of SIP cross-sections depending on permissible currents:
| Core cross-section, sq. mm | Permissible current for LPDE insulation | Permissible current for XLPE insulation |
| 16 | 70 | 100 |
| 25 | 95 | 130 |
| 35 | 115 | 160 |
| 50 | 140 | 195 |
| 70 | 180 | 240 |
| 95 | 220 | 290 |
| 120 | 250 | 340 |
For example, if the calculated current is 110 A, then you need to purchase SIP-1 with a cross-section of 35 square meters. mm or SIP-2 with a cross section of 25 sq. mm. The latter option is preferable, since such a wire will be lighter, stronger and more protected from wind and precipitation.
Advice! When choosing SIP, try to buy a wire with current-carrying conductors of a larger diameter than required according to the calculation. This will cover any load increases that occur in the future.
Before installing the wire, make sure that all wires are intact. To do this, use a multimeter:
- Switch the toggle switch to the “Test” position of the resistance sector, then connect the red and black probes to each other. If the device is working properly, you will hear a signal indicating that the dialing mode is activated.
- Using two probes, touch both ends of the SIP wire. If there is no damage to the conductor, you will hear a beep indicating that the charge has passed from one end to the other.
- These steps will need to be repeated for each core.
Similar checks should be carried out for a toggle switch installed in the resistance measurement sector from 200 Ohm to 200 kOhm. If the display shows “0”, then the conductor is intact, “1” - there is a break in the line.
Cable designation
According to GOST, the marking of conductors should look like:
- The first symbols are “SIP”, indicating the type of conductor;
- The numbers from 1 to 4 are indicated with a hyphen;
- At intervals, numbers are added that indicate the number of each type of core, then through the multiplication sign - their cross-section. Numbers related to each type are separated from each other by a “+” sign;
- A dash indicates the rated voltage of the cable;
- Technical specifications may also be indicated at intervals.
For example, if the marking SIP-2 3×70 + 1×95 + 2×25 – 0.6/1 TU is indicated, then the parameters of the self-supporting insulated wire are as follows:
- designed for organizing overhead power lines;
- has veins:
- 3 main sections 70mm2;
- 1 insulated carrier with a cross-section of 95mm2;
- 2 auxiliary sections 25mm2.
- The cable is designed for voltage 0.6/1 kV.
Manufacturers and cost of SIP cables
There are a huge number of factories and small manufacturers producing various brands of SIP cable. The companies listed below mostly produce high-quality products in accordance with the stated requirements:
- Kamsky Kabel LLC;
- LLC "GK Sevkabel";
- JSC "Moskabel Plant"
The cost of the product depends on the specific manufacturer and category of wire. For example, SIP-1 can be purchased on average for 20, SIP-2 – 25, SIP-3 – 60, SIP-4 – 100 rubles/p. m. The indicated prices may vary depending on the selected region of our country.
Areas of use
The materials from which it is made, the design features, and therefore the scope of application depend on the brand of the product. In particular:
- SIP 1 wire is most often used in the construction of power lines and inputs into buildings;
- SIP 2 cables are also used for laying power lines and power supply to buildings. Their key feature is the type of atmospheric design, which allows them to be installed in places with high humidity, for example, on the shores of seas, lakes, in areas with poor environmental conditions and harsh climatic conditions, since their insulation is resistant to aggressive environmental influences;
- Products with the SIP 3 brand are used for laying sections of power lines with voltages from 10 to 35 kV. In addition, such a wire is used to connect equipment operating under high voltage. This is due to the cable design, which is able to withstand high-level loads;
- SIP 4 wires are used primarily for arranging various branches, since they have a higher level of flexibility. They are also distinguished by their frost resistance, which allows them to be used when laying power lines in the Far North;
- SIP 5 cable is used almost exclusively for installing branches.
So, a SIP cable, which means that it is self-supporting (it has both phase and neutral wires) and insulated, is intended for laying power supply lines and branches from it. The operating voltage under which this product can be operated ranges from 0.4 to 1 kV, but for some brands it can reach 35 kV. The main advantages of the described products are ease of maintenance and low weight, which can significantly reduce costs when laying power lines. At the same time, it meets all requirements regarding the safety and stability of energy supply.
Packaging, storage and transportation of SIP products
In accordance with GOST, self-supporting insulated wire is supplied in drums. The product can only be transported in them. Sometimes transportation with subsequent storage in bays is possible. In this case, two conditions must be met: the cross-section of the core must be 16-25 square meters. mm, the total weight of the coil is up to 25 kg. When storing, use sheds or closed areas. Short-term outdoor accommodation is possible.
According to standards, the outer surface of the drums must be protected with special mats. An accompanying document in the form of a label or technical passport must be added to the product. It is attached to the drum cheek or bay. To prevent the label or passport from getting lost, it should be placed inside a moisture-proof package.
Thus, the SIP wire discussed in the article has practically no disadvantages. If you find a qualified installer, regardless of the slightly inflated cost, then there will be no disadvantages at all. Keep in mind that the costs will soon pay for themselves due to the absence of voltage and power losses, protection against unauthorized switching leading to the theft of electrical energy, and savings in the maintenance of power lines.
Description and features
The griffon vulture lives in Asia, Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, on the island of Sardinia and Sicily, also in the Russian Federation, Belarus and in wild places untouched by man. Such terrain includes elevated areas, plains, deserts, semi-deserts, and rocky areas.
The griffon vulture is a large scavenger bird, which has a body length of 90 to 115 cm, the weight of the bird reaches from 6 to 12 kg, with a wingspan their length is 0.24-0.28 meters. Females are always smaller than males and do not differ in color from each other.
The appearance of the bird is gray-red in color from the back. The abdomen is dark in color; along with the crop there is a spot, usually dark brown. On the bird's neck the collar has thick white fluff. The beak has a yellow and blue-gray tint. The paws are also gray in color and short in length.
Young individuals differ from old ones in shade. A young bird has a back with darker colors, a light bottom of the coverts, which change over the years and acquire the adult color of the bird within 5 years.
Specifications
When choosing a specific brand of SIP wire, it is important to pay attention to the compliance of the characteristics and parameters with the individual requirements of the consumer and the installation method.
To do this, the following technical characteristics are taken into account:
- Number of cores - as a rule, models with the number of current-carrying elements from 1 to 4 are used;
- Cross-section – for different SIP models, this parameter varies from 16 to 240 mm²;
- Voltage class - there are two categories in total - up to 1 kV (SIP-1, 2, 4, 5) and up to 35 kV (SIP-3);
- Temperature regime - implies a normal operating temperature at which the wire will transmit electricity for a long time without losing its parameters;
- Permissible short-term heating - can occur in emergency modes, but should not exceed more than 8 hours of the annual load;
- Bending radius - determines the ability to bend the wire without compromising the mechanical strength of the insulation and its dielectric properties.
All technical characteristics compared for all brands are shown in the table below:
Table comparing characteristics of SIP brands
| Wire brand | SIP-1 | SIP-2 | SIP-3 | SIP-4 | SIP-5 |
| Number of current-carrying cores, pcs. | 1 ÷ 4 | 1 ÷ 4 | 1 | 2 — 4 | 2 — 4 |
| Core cross-section, mm2 | 16 ÷ 120 | 16 ÷ 120 | 35 ÷ 240 | 16 ÷ 120 | 16 ÷ 120 |
| Zero core, bearing | aluminum alloy (with steel cores) | aluminum alloy (with steel cores) | absent | absent | absent |
| Current-carrying core | aluminum | aluminum | aluminum alloy (with steel cores) | aluminum | aluminum |
| Voltage class, kV | 0.4 ÷ 1 | 0.4 ÷ 1 | 10 ÷ 35 | 0.4 ÷ 1 | 0.4 ÷ 1 |
| Core insulation type | thermoplastic polyethylene | light stabilized polyethylene | light stabilized polyethylene | thermoplastic polyethylene | light stabilized polyethylene |
| Operating temperature | -60оС ÷ +50оС | -60оС ÷ +50оС | -60оС ÷ +50оС | -60оС ÷ +50оС | -60оС ÷ +50оС |
| Permissible heating of cores during operation | +70оС | +90оС | +70оС | +90оС | +90оС |
| min wire bending radius | not less than 10 Ø | not less than 10 Ø | not less than 10 Ø | not less than 10 Ø | not less than 10 Ø |
| Life time | at least 40 years | at least 40 years | at least 40 years | at least 40 years | at least 40 years |
| Application | branches from overhead lines; — power supply to living quarters; - household construction laying along the walls of buildings and structures. | branches from overhead lines; — power supply to living quarters; - household construction laying along the walls of buildings and structures. | for installation of overhead lines with voltage 6-35 kV | branches from overhead lines; — power supply to living quarters; - household the buildings; — laying along the walls of buildings and structures. | branches from overhead lines; — power supply to living quarters; - household the buildings; — laying along the walls of buildings and structures. |