Solving the problem of wireless transmission of electrical energy over long distances is a long-standing dream of mankind. You can imagine how much cheaper electricity would be without the cost of conductive products. The scientific and technological revolution does not stand still. There is hope that this dream will come true in the near future. This is evidenced by new developments in this area.
Humanity's dream is wireless transmission of electricity
History of wireless power transmission
The great French physicist Ampere in 1820, through numerous experiments, came to the conclusion that a magnetic field can excite an electric current in a metal body. This is how Ampere's fundamental law appeared.
Michael Faraday discovered the law of induction in 1831, which became the basis for the development of such a science as electromagnetism.
James Maxwell, after much experimentation, systematized his observations, the quintessence of which in 1864 became Maxwell's equation. The formula explained the behavior of the electromagnetic field.
Nikola Tesla improved the apparatus for generating an electromagnetic field, invented by Heinrich Hertz in 1888. At the 1893 World's Fair in Chicago, Tesla demonstrated the glow of phosphorus light bulbs without wires.
Nikola Tesla
Russian scientist Alexander Popov made his contribution to the development of wireless energy transmission. In 1895, at a meeting of the Russian Physicochemical Society, he showed the detector radio receiver he had invented.
Further, up to the present day, new inventions in the field of wireless transmission of electrical energy have been patented. A lot of experiments were carried out, an absolutely large number of discoveries were made. The latest achievement in this area is the transmission of electricity over long distances wirelessly using Wi-Fi technology. In 2022, a mobile phone without a battery will be invented.
Each device needs its own charger
The same problem with the positioning of electromagnetic coils ultimately leads to the next one - the lack of a uniform standard in the industry.
The companies agreed to use low-current Qi technology and unified the devices. But either Samsung or Xiaomi release models that do not work with other people’s chargers at full speed.
Xiaomi's high-power wireless charging, introduced a couple of months ago, only works when it hits the base exactly.
And it quickly charges the battery only up to 50%, subsequently reducing the power from 80 to 20 W. Moreover, even at maximum “speed” the efficiency is only 65 W.
This charger does not work “at low speed” with other smartphones - the coils are of a different size. For the same reason, standard Qi-chargers “swing” with the corresponding Mi 11 Ultra only up to 10 W.
A single process standard is needed, otherwise the infrastructure will only work for one manufacturer.
Even with smartphones, this is not beneficial to the user. And what about cars?
Especially when existing prototypes from Momentum Dynamic promise incredible, impossible 100% efficiency?
How it works
Transmission of electricity over a distance
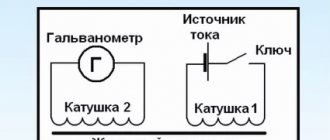
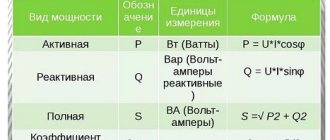
Wireless electricity is based on a phenomenon called electromagnetism. The work involves two coils of metal wires. One of them is connected to a current source, around which a magnetic field is created. The second coil, perceiving this field, induces a secondary electric current in its winding.
Scheme for transmitting electricity without wires
We will have to modernize the world's energy supply
Finally, there is one more reason that only opponents of electric vehicles like to mention. The existing world is already entangled with wires of a certain cross-section, developed electrical networks and equipped power plants.
Any sharp increase in electricity consumption requires serious modernization.
In Russian new buildings in industrial cities this is almost unnoticeable. But imagine: in London there are still houses with “plugs”, powered by thin lines that were centuries old. Entire streets have been preserved, powered with the personal participation of Westinghouse at the beginning of the last century.
And here it is proposed not only to use electricity everywhere, but to do it with low efficiency and huge heat losses.
Most cities are not ready for this. Because wireless charging still needs to be powered by something - and this line will have to be made VERY thick, increasing energy production.
That is, 50% more wind turbines, solar panels, or another thermal power plant will be required, since they do not scale well.
Transfer principles
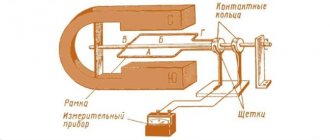
Power generation
The latest developments by scientists from the USA and South Korea used magnetic resonance systems CMRS and DCRS. Korean technology turned out to be more advanced. It was possible to transmit electricity over 5 meters. Thanks to compact DCRS dipole coils, it is possible to power all consumers in a medium-sized room without wires.
Important! The imperfection of modern equipment significantly limits the length of the path of electricity through the air.
Despite this, scientists around the world are busy developing new technologies whose task is to transfer energy over distances of tens and hundreds of kilometers. Already today, new scientific achievements in the field of electricity delivery without wired power lines are being developed and implemented.
Wireless way
Most modern homes and commercial buildings are powered by AC power. Power plants generate alternating current electricity, which is delivered to homes and businesses using high-voltage power lines and step-down transformers.
The electricity goes to the distribution panel, and then the wiring carries the electricity to the equipment and devices we use every day: lights, kitchen appliances, chargers, and so on.
All components are standardized. Any device rated for standard current and voltage will work from any outlet throughout the country. Although standards vary from country to country, in a given electrical system any device will operate as long as it meets the standards of that system.
A cable here, a cable there... Most of our electrical devices have an AC power cable.
Technologies
Non-contractual electricity consumption and its legality
The most promising directions in the development of new methods and methods for transporting electricity without material contact are:
- ultrasonic method;
- electromagnetic induction method;
- electrostatic induction;
- microwave radiation;
- laser method;
- electrical conductivity of the Earth.
Ultrasonic method
At a recent exhibition in 2011, students at the University of Pennsylvania (USA) demonstrated a method for transmitting electric current using ultrasound. The transmitter generated acoustic waves in the ultrasonic range, and the receiver converted them into electric current. Ultrasound was not chosen by chance as an energy carrier. Its effect on the human body is absolutely harmless.
The disadvantage of this method is that the transmission efficiency is very low, direct visibility between subscribers and a limited distance (7-10 meters) are required.
Electromagnetic induction method
The operation of an ordinary transformer gives an idea of how electricity is transmitted without wires by electromagnetic induction. The process involves two coils. The magnetic field excited by the current flowing through the turns of the primary winding induces an electric flow in the secondary winding of the transformer.
Examples of the use of the electromagnetic induction effect include smartphone chargers and electric toothbrushes. The disadvantage of this method of energy transfer is the inevitable proximity of the coils. Even with a slight increase in the gap between the windings, most of the energy begins to be dispersed in space.
One type of electromagnetic induction is the use of resonance. The essence of the method is that the receiver and transmitter operate in the same frequency range. The transmitting and receiving devices are a solenoid with a single layer of turns. The generating device is equipped with a capacitor circuit, with the help of which it is tuned to the receiver frequency.
Demonstration of the electromagnetic induction method
Electrostatic induction
The method is based on the principle of energy passing through a dielectric body. The method is called capacitive coupling. The generator creates an electric field in the container, which excites a potential difference between the two electrodes of the consumer.
Nikola Tesla used the electrostatic induction method to demonstrate a wireless lighting lamp. The lamp was powered by a high-frequency alternating electric field. It glowed evenly, regardless of its movement in the space of the room.
Microwave radiation
Space engineering specialists have developed a way to transmit electricity from orbital solar panels to spacecraft using a microwave radio signal. The problem with this method is that antennas with a very large aperture are required to receive and transmit the beam radiation.
NASA scientists in 1978 concluded that to transmit a microwave beam with a frequency of 2.45 GHz, the emitting antenna must have a reflective surface diameter of 1 km. The receiving rectenna should be 10 km in diameter. It is possible to reduce these dimensions by using ultrashort waves. However, signals in this range are quickly absorbed by the atmosphere or blocked by rainfall.
Note! The safe power density of the emitted energy is 1 mW/cm2. An antenna with a diameter of 10 km and a transmitting power of 750 MW meets this standard.
Laser method
Transmission of electricity over long distances wirelessly using lasers has only recently begun. The idea is that a laser beam, carrying an energy potential, hits the photocell of the receiving device, where high-frequency electromagnetic radiation is converted into electric current.
Laser energy transfer technology, previously used in the military field, is being successfully introduced into the civilian sphere of human activity. The developments of American scientists led to the invention of an unmanned aerial vehicle that receives energy power from a laser beam. In 2006, a drone was demonstrated that could fly non-stop, powered by a laser system.
In 2009, an experiment in space was successfully carried out to transmit energy over one kilometer with a power of 500 W.
Electrical conductivity of the Earth
There is a theory of using the Earth's interior and oceans for wireless energy transfer. The electrical conductivity of the hydrosphere and metal ore deposits can be used to transmit low-frequency alternating current. Electrostatic induction of dielectric bodies can occur in huge deposits of quartz sand and similar minerals.
The transmission of electric current is also possible through air space using the method of electrostatic induction. Nikola Tesla once suggested that in the future there will be technologies that will use the earth, ocean waters and the atmosphere of the planet to transmit electricity.
Worldwide Wireless System
For the first time, information about the Worldwide Wireless Electricity Transmission System became known from the great scientist Tesla. In 1904, he stated that creating a VBS using the high electrical conductivity of plasma and the Earth was quite feasible.
We get energy with and without coils
We try to remove etheric energy in two ways. At first, the transformer operates autonomously, without additional coils. On the left is the consumption voltage, on the right is the current. Voltage is about 11 volts, current is 1.8. Now we connect two identical coils. The removal tubes are inserted into their middle. The lights at their output light up. Those used in a refrigerator are 220 volts, 15 watts. The reels are wound in the same way as the pitcher. All ends of the bulbs will go into the ground. Let's see how the parameters change.
7. Information about frequency measurement on the board. How did this happen? Included in the secondary winding. He went from the coil, passed through the ferrite, then wound 3 turns of ordinary wire around the ring and the findings went to the oscilloscope. I started this. The limit is 1 microsecond. Voltage limit 1 volt. We are looking.
Real projects today
Of all that the electrical engineering market offers today, wireless power transmission includes chargers for smartphones and electric toothbrushes. They use the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Contactless smartphone charging
The aircraft industry has begun mass production of unmanned aerial vehicles powered by wireless transmission of electricity. A small microwave helicopter with a rectenna can rise to a height of up to 15 meters above the ground. Drones have appeared that can fly within the visibility range of a laser beam.
Chinese home appliance manufacturer Haier Group has been producing wireless LCD TVs since 2010.
What it is?
The coil is a transformer. The purpose of the device is to increase current parameters to enormous heights (up to millions of volts). Main Goal: Maximize AC frequency. Ideally, the same return coil should be placed at the energy receiving point, which will resonate with the device, allowing energy to be transferred over a distance.
Contactless energy transfer through a Tesla coil
Let's take a closer look at how a Tesla coil works. First, let’s swing - it’s not immediately clear what’s swinging in the coil. Direct current, which Edison used in his inventions, is expensive to produce. This energy has a pronounced vector of movement. Alternating current constantly changes the parameters of electricity: voltage and current. This is called electrical current fluctuations.
It is interesting that the basic laws of oscillation of an electric current and a mechanical pendulum coincide. Interestingly, there is also a resonance effect for electricity. When the frequencies of the two electric fields coincide, the amplitude of the oscillations increases. According to Tesla's idea, after the coils resonate, an electric current should appear in the receiver.
In fact, the receiver was never invented. The Tes coil is used as a reference, on it you can see the flow: in other words, the electric arc, the current discharge, artificial lightning and study the wireless transmission of electricity.
Prospects for wireless transmission of electricity
Research work is currently underway and projects are being developed to create electric vehicles that will move along the road surface with a current conductor that induces an electric current in the vehicle’s motor.
Electric vehicle power supply
A number of leading companies are developing wireless power supplies that can supply electricity to all consumers within the same room.
In the future, the emergence of routes consisting of a number of wireless sources of electricity that will be able to ensure the movement of aircraft over long distances.
With the advent of new materials, improved devices and inventions, wireless power transmission will in the near future cover all areas of human activity.
No one has canceled heat losses
The second problem is the thermal losses already mentioned above: the energy that is lost in the process of converting electric current from alternating to direct and when transmitting it over a distance is converted into heat.
Heating occurs. Mainly the charger itself, and due to this, the gadgets being charged.
For a conventional LiPo battery, losses even during normal charging are at least 15-20%. Add higher losses, typical for wireless transmission, and we get a lot of heat.
All this needs to be directed somewhere and dispersed in space: LiPo batteries are very afraid of any heat - often 100 degrees is enough for a small fire.
Another problem lies in the wireless charging device. What is this? A set of electromagnetic coils with a pair of chips that transmit the field to the same coils to the charging gadget.
Poor positioning and different coil sizes increase losses and heat, reducing charging speed.
Sometimes they try to solve this with magnets ( MagSafe ), sometimes with moving coils or increasing their number, sometimes by simply turning off the process when heating. The results are not bad, but only for low currents.
We increase the transmission power - we get a multiple increase in losses. In fact, even 65 W without precise positioning can be considered a small fire.
Is it worth the risk or leave the technology in prototype form until people get used to using wireless chargers?
Wireless electricity: Tesla's dream and our future reality
By harnessing the enormous potential of wireless electricity, our generation has much to gain and nothing to lose. In the years ahead, we can only hope that the current efforts to realize this monumental feat will yield positive results. Unfortunately, Nikola Tesla, the great inventor, is not with us so that he can see his dream come true. I am pleased to share one of Tesla's famous quotes, a great source of inspiration for aspiring scientists all over the world:
“If you want to unlock the secrets of the universe, think of it in terms of energy, frequency and vibration.”
- Data Science Profession Training
- Data Analyst training
Other professions and courses
PROFESSIONS
- Profession Web developer
- Profession Java developer
- Profession Frontend developer
- Profession Ethical hacker
- Profession C++ developer
- Profession Game developer on Unity
- Profession iOS developer from scratch
- Profession Android developer from scratch
COURSES
- Course "Python for Web Development"
- Advanced course “Machine Learning Pro + Deep Learning”
- Machine Learning Course
- Course "Mathematics and Machine Learning for Data Science"
- JavaScript Course
- Data Analytics Course
- DevOps course