When installing electricity meters in private homes, depending on the amount of current in the electrical circuit, a very specific connection diagram for a three-phase meter is used. It is connected directly to a break in the supply line or through a step-down current transformer. The second option for connecting a three-phase electric meter is used for consumption currents of more than 100 Amperes. Both of these methods of connecting a metering device have their own characteristics, which the owner of the house must understand.
Meter installation: basic rules and requirements
We install the electric meter in strict compliance with the approved rules. First of all, we study the safety requirements for the operation of electrical equipment of any type and purpose.
- We install the meter at a temperature not lower than +5 degrees. Accounting equipment, like any other electronics, does not withstand exposure to cold.
- When installing the meter outdoors, we build a sealed heated cabinet for it. All materials and equipment necessary for this are sold in specialized stores.
- We mount the electricity meter at a height of 1-1.7 m above the base. If the device is placed lower, it will simply be inconvenient for you to watch the readings.
A representative of the energy supervision service will familiarize you with all other recommendations and rules at the time of concluding the contract and receiving other necessary documents.
Existing electric meter designs
There are several options for this device:
- single-phase or three-phase;
- mechanical (induction) or electronic;
- single-tariff or multi-tariff;
- direct or secondary inclusion.
A two-tariff electricity meter and switching to a night tariff is one way to reduce energy costs.
The use of the expression “two-phase meter” is incorrect. In everyday life, this term refers to single-phase devices with the possibility of tariffication. They are produced by different manufacturers (“Energomera”, “Mercury”, “Neva”, etc.), differ in the number of pins, use cases, accounting capabilities, etc.
When choosing, you need to consider the following:
- Single-phase devices are used where the network voltage is 220 V. For example, when installing a meter in an apartment or office.
- If there are machines or powerful electrical equipment, a 380 V connection is assumed. Three-phase electricity meters are used.
- In both categories, multi-tariff devices are used when the price of electricity differs depending on the time of day or other circumstances.
- Mechanical (induction) devices, unlike electronic ones, cannot be used in unheated rooms. This must be taken into account when installing a meter in a garage and similar structures. However, they are reliable, durable and relatively inexpensive.
- Secondary switching is used where large currents pass - in transformer substations or in the entrance panel of the entrance.
Mechanical metering devices belong to the category of reliable electricity meters.
Electricity meters are “modular” devices because, like other switching equipment, they are installed on a special bus - a DIN rail. This is done for ease of installation of electrical equipment in the panel. In addition to the electric meter, there are automatic switches on it.
The machine is connected to the meter to protect the device from voltage surges or a person from electric shock.
Rules for connecting an electric meter
The electricity meter must be installed at a certain height and in a well-protected place from precipitation. As for the installation height of the electric meter, the recommended mounting height is 0.8-1.7 meters.
Sometimes it is not possible to install an electricity meter in a place well protected from precipitation. Then it is necessary to use a self-contained box for installation, which is sealed and easy to use.
When connecting an electric meter, it is allowed to use both copper and aluminum conductors. The minimum cross-section of a copper cable for connecting an electricity meter is a cross-section of 2.5 mm².
It is very important that the cable for connecting the electric meter has an insulating layer (it cannot be used without insulation). Also, there should not be any branches or twists before the meter, as a fine may be imposed for this.
The inspection period for electricity meters is for single-phase, every 2 years, for three-phase, every other year.
Varieties of semi-indirect method
There are several known meter connection schemes based on the semi-indirect method, but the most common are the following:
- ten-wire circuit;
- connection by disconnecting on a special block;
- star connection.
Ten-wire switching
Connecting a 3-phase meter using a 10-wire circuit is the simplest and most reliable way. To implement it, you will need to follow the order of connecting ten wires: three for each phase and one neutral. This option has one indisputable advantage, which is the ability to replace the meter while the power is on. The line may be left energized even when repairing a device disconnected from it. With this scheme, the current circuits are reliably grounded, so the possibility of dangerous potential appearing on them is eliminated.
Other connection diagrams
Connection through contact distributors refers to more complex methods, implemented by switching each of the wires coming from the current transformer. The star connection is also characterized by its complexity, but in this case fewer conductors are used. When installing the converter, first the unipolar outputs of all three secondary windings are collected at one common point. After this, the three mating ends of the CT windings are connected to the corresponding terminals of the meter.
Another known switching scheme using the semi-indirect method is called 7-wire. When organizing it, one of the ends of the windings are combined by jumpers directly in the current transformer itself. This option is used extremely rarely in private homes, which is explained by a number of disadvantages of the switching scheme.
Preliminary stage
Connecting an electric meter (ES) is the final stage of electrical installation work. Before installing a three-phase ES, you must first have a wiring diagram. The device must be checked for the presence of seals on the casing screws. These seals must indicate the year and quarter of the last inspection and the seal of the verifier.
When connecting wires to the clamps, it is better to make a reserve of 70-80 mm. In the future, such a measure will allow measuring power/current consumption and rewiring if the circuit was assembled incorrectly.
Each wire must be clamped in the terminal box with two screws (they are clearly visible in the photo below). The top screw is tightened first. Before tightening the lower one, you need to make sure that the upper wire is clamped by first tugging on it. If a stranded wire is used when connecting the meter, then its tips must be pre-crimped.
What documentation will be required?
To organize the supply of an electrical network to a building legally, it is necessary to collect a package of documents, which includes an agreement for technological connection to electrical networks, technical conditions (TU), an act of delineation by balance sheet and the actual project of power supply to the building.
The technical specifications describe the conditions on the basis of which electricity is connected to the house.
The project is the main document on the basis of which all electrical installation work is carried out. It includes a wiring diagram with three-phase input in a private house. To develop a wiring plan for a private home, you can use standard electrical wiring diagrams. The standard three-phase wiring diagram is divided into external and internal. The external one is sometimes performed separately and is called the launcher.
In the act of delineation by balance sheet ownership, the boundaries of responsibility between the energy sales company and the consumer are divided.
Advantages and disadvantages of a three-phase power supply system
It is no secret that three-phase power supply to a private home is becoming more and more relevant, and this is connected not only with the voltage level. Let's look at all the advantages of 380 Volts and here is a list of them:
- Connection of the most common asynchronous electric motors with a squirrel-cage rotor in everyday life and in production. When connected to a single-phase circuit, their power, torque, and efficiency are lost. After all, they were originally designed for three phases. The use of such electric machines in a private home may be necessary when installing a grinding, drilling or woodworking machine and other types of equipment. An owner who has the skills to operate such equipment will always find a use for it. A powerful pump is always useful at the dacha, so running 380 Volts won’t hurt here either.
- By connecting three phases, the owner of a private house receives, by and large, three independent single-phase networks at once, which he can dispose of at his own discretion. To do this, in order to obtain a single-phase voltage of 220 Volts, you need to connect one wire to the phase and the other to zero. It will be called phase. The voltage between two phases is 380 Volts and is called linear. You can read more about phase and line voltage in the article: https://samelectrik.ru/linejnoe-i-faznoe-napryazhenie.html.
- In the event of a breakdown or emergency at a distribution substation, one or even two phases may burn out. At the same time, the owner of a private house with three phases will at least have lighting and a refrigerator working. It must be remembered that for three-phase motors, operation on two phases will entail its inevitable failure.
Keep in mind that there are pitfalls here too. A three-phase network is needed if the power of a single-phase network is not enough. And even if single-phase is not enough, there is no need to rush to connect three phases, it is better to clarify the possibility of increasing the power limit for a single-phase network - this procedure is much simpler than coordinating and connecting three phases.
Three phases must be connected if it is necessary to power three-phase electric motors that cannot operate in single-phase mode, or if a large number of electrical appliances and equipment are used simultaneously, for example, if the house has a large household or some small-scale production has been established.
Several other disadvantages of the three-phase power supply system should also be noted. One of the disadvantages is the need to distribute loads evenly across each phase. The second drawback is the great difficulty in connecting, purchasing another shield, protective devices, etc. The third drawback is a great danger from the point of view of electric shock, since the house will have not only a single-phase voltage of 220 V, but also a linear voltage of 380 V
As you can see, the advantages of powering the consumer from a 380 Volt network are not always obvious. Now it’s worth figuring out what documents are needed to connect a three-phase network. This is what we will talk about now.
Features of the circuit design of single-phase meters
Single-phase meters are most often used in standard city apartments. Connection to the network is carried out directly, without transformers. The terminal block of such a device has four contacts.
- the first is for phase input;
- through the second, the phase is output to the load (to electrical equipment located in the apartment);
- the third is used to enter zero;
- the fourth – outputs zero to the load.
In addition, there is a special voltage screw used in the process of disconnecting the coil in induction-type meters when they are checked by regulatory authorities.
A distinctive feature of single-phase meters is the same arrangement of their terminals, regardless of the type, so the principle of connecting an induction-type device is similar to installing an electronic version.
The connection diagram for a single-phase meter is shown below.
To indicate phase “A”, a yellow line is used here, phase “B” is green, “C” is marked in red. In addition, there are schematic images of the neutral wire N, indicated in blue, and the ground conductor (PE), which is a yellow-green line. As an alternative to the standard package switch, this circuit allows the use of a two-pole circuit breaker.
In addition, you can use the wiring diagram for a single-phase direct connection induction electric meter. In this case, red is used to depict the phase wire and current coil, and the voltage coil and neutral wire are highlighted in blue.
Installation and connection of the metering device
Connecting the electric meter is preceded by installing the cabinet on the wall outside or inside the room. It is hung in a designated place at a height of 1.5 m from the floor and secured with dowels. Further work consists of installing and connecting all devices according to the diagram presented above. The procedure is as follows:
- Make sure the supply line is de-energized.
- Place the meter, machines and RCDs on DIN rails, securing them with latches. The correct position of the elements is with the input contact facing up, and not vice versa.
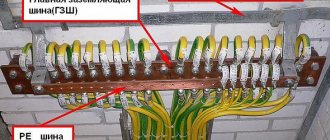
- Screw the neutral and ground bus to the housing. Pull the power and ground cable inside (use grommets outdoors), cut the ends and connect them to the main circuit breaker and buses according to the diagram.
- Remove the cover from the contact group of the meter and connect the wires to it as follows: to the first and third - respectively, phase and zero from the input circuit breaker, to the second and fourth - phase and neutral to the RCD.
- Distribute the phase wire from the RCD along the upper contacts of all circuit breakers, connect the neutral wire to the bus. Perform further wiring according to the diagram, as the master does in the video.
When laying wiring (both inside and outside the electrical panel), try to follow the generally accepted line designations in different colors. According to European standards, the neutral conductor must be blue, the grounding must be yellow-green, and the phase must be any other color. If you purchased identical single-core wires, use tags made from pieces of heat-shrinkable tubing of different colors for marking. How to correctly connect one of the common models of electricity meters from the Energomera brand is described in the next video:
Connection diagram for a single-phase electric meter
Meters for a 220 V network can be mechanical or electronic. They are also divided into single-tariff and two-tariff. Let us say right away that connecting any type of meter, including two-tariff ones, is carried out according to the same scheme. The whole difference is in the “filling”, which is not available to the consumer.
If you get to the terminal plate of any single-phase meter, you will see four contacts. The connection diagram is indicated on the back of the terminal block cover, and in a graphical representation everything looks like in the photo below.
How to connect a single-phase meter
If you decipher the diagram, you get the following connection order:
- Phase wires are connected to terminals 1 and 2. The phase of the input cable comes to the 1st terminal, the phase to the consumers goes from the second. During installation, the load phase is connected first, and after it is secured, the input phase is connected.
- The neutral wire is connected to terminals 3 and 4 using the same principle. To the 3rd contact there is a neutral from the input, to the fourth - from consumers (machines). The order of connecting the contacts is similar - first 4, then 3.
The meter is connected with wires stripped to 1.7-2 cm. The specific figure is indicated in the accompanying document. If the wire is stranded, lugs are installed at its ends, which are selected according to thickness and rated current. They are crimped with pliers (can be clamped with pliers).
When connecting, the bare conductor is inserted all the way into the socket, which is located under the contact pad. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that no insulation gets under the clamp, and also that the cleaned wire does not stick out from the housing. That is, the length of the stripped conductor must be maintained exactly.
The wire is fixed in old models with one screw, in new ones - with two. If there are two mounting screws, tighten the one on the far side first. Tug the wire slightly to make sure it is secure, then tighten the second screw. After 10-15 minutes the contact is tightened: copper is a soft metal and is pressed down a little.
This applies to connecting wires to a single-phase meter. Now about the connection diagram. As already mentioned, an input machine is placed in front of the electric meter. Its rating is equal to the maximum load current; it is triggered when it is exceeded, excluding equipment damage. Afterwards they install an RCD, which is triggered when the insulation breaks down or if someone touches live wires. The diagram is shown in the photo below.
Connection diagram for a single-phase electricity meter
The circuit is not difficult to understand: from the input, zero and phase go to the input of the circuit breaker. From its output they go to the meter, and from the corresponding output terminals (2 and 4) they go to the RCD, from the output of which the phase is supplied to the load breakers, and the zero (neutral) goes to the zero bus.
Please note that the input circuit breaker and the input RCD are two-contact (two wires enter) so that both circuits open - phase and zero (neutral). If you look at the diagram, you will see that the load breakers are single-pole (only one wire goes to them), and the neutral is supplied directly from the bus
Watch the meter connection in video format. The model is mechanical, but the process of connecting the wires is no different.
Basic rules for connection
Connecting single-phase and three-phase metering devices is not much different. First of all, you need to study the operating instructions for both electricity meters. And know the difference between three-phase voltage and single-phase voltage. To connect the latter, two wires are used - zero and phase.
When connecting a house to a three-phase voltage network, four wires are supplied: three phase and one neutral. The connection must be made by electricians who are authorized to service electrical networks. However, connecting to the line is not very difficult. Any person who can read diagrams and understands electrical engineering can handle it.
Types and sizes of electrical panels
We will talk about cabinets/drawers for installing automatic machines and other electrical equipment, and their varieties. Depending on the type of installation, electrical panels are available for outdoor and indoor installations. The box for outdoor installation is attached to the wall with dowels. If the walls are flammable, an insulating material that does not conduct current is placed underneath. When mounted, the external electrical panel protrudes above the wall surface by about 12-18 cm. This must be taken into account when choosing its installation location: for ease of maintenance, the panel is mounted so that all its parts are approximately at eye level. This is convenient when working, but can pose a risk of injury (sharp corners) if the location for the cabinet is poorly chosen. The best option is behind the door or closer to the corner: so that there is no possibility of hitting your head.
Electrical panel housing for outdoor installation
A panel for hidden installation requires the presence of a niche: it is installed and walled up. The door is flush with the wall surface; it may protrude a few millimeters, depending on the installation and design of the particular cabinet.
The cases are metal, powder-coated, and plastic. Doors are solid or with transparent plastic inserts. Various sizes - elongated, wide, square. In principle, you can find a suitable option for any niche or conditions.
One piece of advice: if possible, choose a larger cabinet: it’s easier to work in, this is especially important if you’re assembling an electrical panel with your own hands for the first time
Complete set and installation of a mounted distribution panel
When choosing a building, they often operate on such a concept as the number of seats. This refers to how many single-pole circuit breakers (12 mm thick) can be installed in a given housing. You have a diagram with all the devices listed on it. You count them taking into account the fact that bipolar ones have double width, add about 20% for the development of the network (suddenly you buy another device and there is nowhere to connect, or during installation you decide to make two from one group, etc.). And for such a number of “seating” places, look for a shield with a suitable geometry.
Connecting a three-phase semi-indirect meter
These devices are connected to the network through current transformers, making it possible to use them in networks with fairly high powers (up to 60 kW). Using this accounting method, to determine the flow rate, you need to multiply the difference in readings by the set transformation ratio.
There are several types of connection for semi-indirect connection meters.
1 Star connection of current transformers
The process of connecting wires looks like this:
- contacts 3, 6, 9, 10 – are closed and connected to the neutral wire;
- contacts I2 - closed, connected to terminal 11;
- 1 – to I1 phase A;
- 4 – to I1 phase B;
- 7 – to I1 phase C;
- 2 – to L1 phase A;
- 5 – to L1 phase B;
- 8 – to L1 phase C.
Figure - Star connection diagram
Connecting a three-phase indirect meter
These devices are designed to perform electricity metering at high-voltage connections (6-10 kV and more), the connection is realized using voltage and current transformers.
Below are the main diagrams for connecting three-phase meters via current and voltage transformers:
1) Scheme for connecting a three-element meter to a four-wire network with a grounded neutral: (figure below)
2) Scheme for connecting a three-element meter to a four-wire network. Three current transformers, direct connection to voltage:(picture below)
3) Scheme for connecting a three-element meter to a three-wire line - two current transformers, three voltage transformers: (figure below)
When connecting a three-element meter according to scheme No. 3:
- phase B current is calculated with the subtraction of the zero-sequence current;
- direct, negative and zero sequence currents of the fundamental frequency are not used (symmetrical components);
- active and reactive power in phase B are calculated by subtracting the zero-sequence current from the phase current;
- Electrical energy accounting is carried out taking into account the above comments.
4) Scheme for connecting a two-element meter to a three-wire line - two current transformers, two voltage transformers (figure below)
When connecting the meter according to schemes No. 4 and No. 5:
- The zero sequence voltage of the fundamental frequency is not measured (symmetrical components);
- direct, negative and zero sequence currents of the fundamental frequency (symmetrical components) are not measured;
- connection capacities are calculated using formulas;
- Electrical energy accounting is carried out taking into account the above comments.
5) Connection diagram of a two-element meter to a three-wire line - two current transformers, direct voltage connection (figure below)
Attention!: The possibility of connecting according to a specific scheme must be indicated in the passport or manual for a specific type of meter
In what cases is it allowed to connect a three-phase meter to a single-phase network?
The technical documentation for the three-phase meter states that it can only be used in a three-phase AC network. But these are the manufacturer's recommendations.
If you look at the structure of the device, it will become clear that it consists of three independent blocks, united by one unit for metering consumed electricity.
This means that there are no contradictions for using it on a 220 volt network. But the cost of a single-phase meter is less.
Therefore, it is necessary to figure out when it is possible to connect a three-phase meter to a single-phase network:
- The owner does not have a single-phase device, but has a three-phase meter and wants to use it. For example. if you need an electricity meter for the garage;
- The owner has been issued technical conditions for connecting three-phase voltage, but the power system currently does not have such technical capabilities. And the owner purchased the necessary components according to the project;
- It is required to connect a load of more than 10 kW to a single-phase network.
You can also install the meter in a garage or garden house. That is, where payment occurs according to a common meter, and individual ones are used for settlements between the owners and the board.
Division of responsibility for electrical appliances
The electrical distribution throughout the facility is protected by separate switches that regulate the maximum permissible current for sections of the circuit. Payment for their purchase and connection is made by the owner of the premises.
The electricity meter and the input machine can be physically located not only in the consumer’s area of responsibility. If these devices are located in a privatized apartment, in a garage, in a utility room or within the boundaries of a cottage or summer cottage, then their installation, maintenance and replacement are carried out by the owner of the property.
According to modern requirements, the panel with the electric meter must be installed outside the dacha or cottage. Therefore, they are now producing models that operate at low temperatures.
His responsibilities also include providing energy service employees and the management company with access to the meter for reading, sealing or checking. Also, specialists have the right to install magnetic seals. If the user of the premises refuses access to the premises without a valid reason, the electricity supplier may transfer him to a general tariff.
If the devices are located in municipal (non-privatized) property, common territory (entrances) or outside a private area, then all costs are borne either by the supplying organization or they are shared. In this case, the organization of work and payment is made by the management company, HOA, GSK or gardening partnership.
We talked in more detail about the legal intricacies of replacing and installing electricity meters in this material.
Rules for legal and safe installation
Before you begin installing an electric meter, and even before you run to the store to purchase it, you need to learn all the intricacies of its safe and legal installation.
Installing an electric meter is not our whim, but a requirement of the law and the electricity supplier.
Each electricity meter has a seal that is installed by the electricity supplier. It is impossible to replace the electric meter without damaging it. Therefore, you should notify your electricity supplier before replacing it.
Please note: before removing the electric meter, you need to rewrite its readings, which must be reported to the supplier.
After installing a new electric meter, you must invite a representative of the supplier to seal the new meter and check that it is installed correctly.
For your own safety, all work on replacing the electric meter should be carried out only with a complete blackout, which can be done by turning off the corresponding machine on the external panel. This is usually located in the staircase entrance, or not far from a private house.
Do-it-yourself installation of a meter in a panel on a landing or in a garage
On each landing of a multi-storey residential building, there is a metering panel with electricity meters that calculate electricity consumption on the entire floor. What is needed to install the meter in the distribution board:
- Prepare the necessary tools: wire cutters, pliers, wire strippers, screwdrivers, electrical tape, etc.
- Access to the input switch to disconnect the line of this floor from the network.
Connection diagram for the meter and circuit breakers.
Connecting the meter at the entrance
First you need to make branches from the supply line. To do this, the previously de-energized main wires are stripped of insulation using special pliers to a distance of 3 cm. A special terminal block for branching the wire is placed in this place. After installing the terminal block on the main wire, the outlet wire is connected to it, which will go to the input circuit breaker.
A branch is made from the neutral main wire in a similar way.
Then they install all the protection devices, and the meter itself, on the switchboard panel; this is more convenient to do using a Din-rail. After installing all components in place, the wires are connected.
The made branch from the phase main wire is connected to the input circuit breaker, then from the output of the input circuit breaker the wire is connected, according to the diagram, to the first terminal of the meter. The branched neutral wire is connected directly to the second terminal of the meter; a circuit breaker is not needed for it.
From the third terminal the wire goes to group consumer protection circuit breakers. The wire from the fourth terminal is connected to the common grounding bus, and all neutral wires from consumers will be connected to it.
The phase wires coming from the apartment are connected to the lower terminals of the circuit breakers, which are installed after the meter. For each phase wire (group of electrical appliances) it is necessary to install a separate circuit breaker. It is prohibited to connect several phase wires to one machine.
All neutral wires from groups of electricity consumers in the apartment are connected to a common neutral bus.
Remember that the panel on the staircase contains not only your meters and circuit breakers, but also those of your neighbors. To avoid confusion if any faults occur, be sure to mark your circuit breakers and meter with the apartment number.
Installing an electricity meter for a garage is similar. The only difference is that there is no need for a branch of the main wires, since ready-made separate power wires are brought into the garage.
How to assemble and install an electrical panel
Let's start with the fact that in any hardware store in the electrical goods department you can purchase a ready-made electrical panel in which circuit breakers and an electricity control device are installed. Of course, this is convenient, but there is one problem in this matter - the machines and the meter may not be suitable for the power consumption of your home’s electrical network. Therefore, the advice is to assemble the shield yourself. How to do it?
First of all, you need to check with the energy supply company in your area what brands of electric meters they use. Why? The latter are several models that differ from each other in accuracy class and power. It is these two indicators that need to be reconciled. By the way, if the store has a ready-made shield with such a counter, then you are in luck. If not, then you will have to select it to fit the size of the control device.
What else will you need for assembly?
- Copper wire one meter long and 2.5 mm² cross-section.
- Automatic switches (their number is determined by the number of input wires, and the power is calculated according to the power of consumers on each circuit).
- Fasteners (screws and plastic dowels). Some manufacturers supply mounting products complete with a shield.
First of all, it is necessary to pre-distribute all the elements of the electrical panel so that they do not interfere with each other and so that they do not cover the mounting holes. Now all this is secured, after which you can proceed to installing the wires.
We will not describe what connection diagram is used in the distribution panel. Here is one of the options in the picture below, where everything is clearly shown, so it is impossible to make a mistake.
The only point that you need to pay attention to is the numbering or designation of the electric meter terminals where the input and output wires will be connected
Here it is important not to confuse which terminal is phase and which is neutral. Therefore, it is worth opening the meter’s instructions and understanding this issue, because each model has its own positions. Therefore, it is worth opening the meter’s instructions and understanding this issue, because each model has its own positions
Therefore, it is worth opening the meter’s instructions and understanding this issue, because each model has its own positions.
So, the devices are installed and connected by wires to each other. All that remains is to carry out the installation. To do this, place the junction box on the surface on which it will be installed, and use a pencil or any other sharp tool (a screwdriver, for example) to make marks for the mounting fasteners. Now drill holes in them with a diameter of 6 mm and a depth of 6 mm, into which you drive the dowels. And through them you attach the shield.
Connection
If you can assemble and install the distribution panel without any problems, you do not have the right to connect it yourself. Therefore, you will have to call representatives of the energy supply organization, who will make the connection, that is, connect the control meter to the input cable. If representatives of the network company do not know how to do this, then you will have to look for an organization that has a license and access to carry out this type of work.
Please note that after connection, the controller must seal the electricity meter
And one moment. In order to be able to repair and dismantle the control device without problems, it is necessary to install another machine in the network (in front of it), which is called a general one. Most often it is large in size and is not intended for installation in a distribution panel. What to do in this case? The only solution is to purchase a box for the machine gun and install it next to the shield.
Types of three-phase meters
There are only three types of three-phase meters
- Direct connection meters, which, like single-phase ones, are connected directly to a 220 or 380 V network. They have a throughput capacity of up to 60 kW, a maximum current level of no more than 100 A and also provide for the connection of small-section wires of about 15 mm2 (up to 25 mm2)
Semi-indirect meters require connection via transformers, therefore suitable for networks of higher power. Before paying for consumed energy, you simply need to multiply the difference between the meter readings (current and previous) by the transformation ratio.
Indirect switching meters. Their connection occurs exclusively through voltage and current transformers. They are usually installed at large enterprises, as they are designed for energy metering through high-voltage connections.
When it comes to installing any of these meters, there may be a number of difficulties associated with their connection. After all, if for single-phase meters there is a universal circuit, then for three-phase meters there are several connection diagrams for each type. Now let's look at this clearly.
Types of three-phase devices
Meters can be divided into two types: single-tariff and multi-tariff. Some models have a division between daytime and evening rates.
A small microprocessor is responsible for locating tariffs and storing information in the device’s memory. Simply put, you can view the meter data for any convenient numbers.
Analog induction energy meters
The operating principle of such meters is similar to the single-phase device model.
Connection diagram for 3 phase meter
Electrical energy passing through the induction coil forms an electromagnetic field that acts on the iron disk. So he starts moving.
You may be interested in Features of the S1-67 oscilloscope
Three-phase socket device
Plug socket of open and closed types
The design of a three-phase electrical outlet may differ in design and design, but all of them are made with contacts, the number of which is at least four, where three are phase, and the fourth is a neutral contact or grounding. The figure below shows a three-phase socket paired with a plug, forming detachable electrical contacts.
Three-phase plug and socket
The number of connectors in the socket is selected as follows:
- If the load connection is made in a delta pattern, the number of connectors should be four: 3 phases A, B, C + protective zero PE.
- When the load is connected in a star configuration, the number of sockets will be five: 3 phases A, B, C + neutral N + ground PE.
- To provide very high protection against electric shock, seven connectors are used: 3 phases (each with its own working zero) + PE. Here, each phase circuit has its own RCD.
A four-pin socket can only be used in a delta load connection circuit, and a five-pin socket can be used in both circuits (triangle or star). The power connection is made only to the corresponding terminals. Then through this outlet it will be possible to turn on various electrical appliances.
The diameter of the wires connected to a three-phase socket must be at least 2.5 mm2. For powerful loads it reaches 6 mm2.
Sockets are classified as follows:
- Installation method. Open type models are installed for external wiring and attached in an overhead manner. They are used inside and outside the house, as well as in high humidity environments (depending on the level of protection). In residential premises with hidden wiring, closed-type sockets recessed into the wall are mainly used. For installation, you need to make a recess in it and install a socket box.
- Resistance to external influences is determined by marking with an IP code with two digits. The first characterizes the level of protection against foreign particles, where 0 means no protection, and 6 means maximum (complete dust tightness). The next number means water resistance, where 0 means no protection, and 8 means the device can be under water for a long time. In practice, you often find sockets and plugs marked IP44, which indicates a sufficient level of protection from the external environment in conditions of high humidity.
- By appointment. Sockets are without grounding and are connected to electrical appliances that do not have a grounding contact. Devices with grounding through plugs are made by adding special connectors (type CEE 7/5) or by having elastic contacts on the sides (type CEE 7/4). Sockets are available with plastic protective shutters that open when the pins of the plug are inserted into the sockets at the same time. Models may contain plug ejectors, timers and RCDs.
Preparatory work
Before starting the connection, be sure to prepare the installation site, all the necessary tools and materials. Since the convenience of work, the reliability of fastening and the final result directly depend on this. Tools and materials you may find useful:
- Multimeter or indicator screwdriver;
- Perforator, set of dowels;
- Wire cutters, pliers, screwdriver set;
- Insulation stripping pliers or utility knife;
- Ruler, tape measure, building level;
- Connecting wires of suitable cross-section and length;
- Soldering iron, sleeves or self-tightening terminals, heat shrink tubing;
- Modular protective equipment (circuit breakers, UDTs, SPDs, voltage control relays and others);
- Electrical panel or casing for the meter.
If the electric meter is installed and connected to an old switchboard, be sure to check that the old mount matches the new meter. If it turns out that the installation method is not suitable, prepare a new DIN rail or dowels. If a new facility is commissioned with the installation of a shield or casing, they must be installed at the preparation stage. For this:
- Remove the top cover, usually just unscrew the screws;
- Install the casing on the wall or in another place provided by the project;
- To mount the casing, you can use a dowel or other element, depending on the material of the mounting surface.
It should be noted that in the design documentation the installation location can be determined both indoors and outdoors - on the facade of the building or on a separately installed support. For each option, a separate list of preparatory work is carried out.
Installation of an electric meter indoors.
Before connecting the metering device, the power cable must be inserted into the room to free up space. The installation location is selected in such a way that access to the electric meter is not blocked by walls, interior elements, furniture, etc. You should not install it behind a door, directly in a passage or in places where people constantly move; avoid corners and surfaces that are exposed to dampness.
Installation of an electricity meter on the facade of the building.
The power cable is supplied to the electric meter through a continuous descent through pin insulators. When connecting on the facade of a building, it is advisable to avoid places of intense exposure to sunlight, precipitation, etc. If the wall has a soft finish, a special frame is built for the metering device. The line is inserted into the room near the ceiling to reduce the likelihood of electric shock if the insulation is damaged.
Installation of the electric meter on a separate support.
If the electric energy meter is connected to a separate support, you significantly reduce the risk of a building fire in an emergency. However, this method exposes the electric meter to the risk of destruction by vandals, so it is advisable to place it at a height of about 3 m. In connection with this, at the preparation stage it is much more profitable to assemble the shield before installing it on the support. Installation will be done using clamps rather than dowels, so a rigid base is first installed on the support.
Rice. 3. Fastening the electric meter to the support with clamps
Direct or immediate switching devices
The connection diagram for this meter is in many ways (especially in terms of ease of implementation) similar to the installation diagram for a single-phase meter. It is indicated in the technical data sheet, as well as on the back of the cover. The main condition for connection is strict adherence to the order of connecting the wires according to the color indicated in the diagram and the correspondence of odd wire numbers to the input, and even numbers to the load.
The order of connecting the wires (indicated from left to right):
- wire 1: yellow - input, phase A
- wire 2: yellow - output, phase A
- wire 3: green - input, phase B
- wire 4: green - input, phase B
- wire 5: red - input, phase C
- wire 6: red - output, phase C
- wire 7: blue - zero, input
- wire 8: blue - zero, output
Installation of three-phase
A three-phase meter already has as many as eight terminals.
There are five wires at the input of three-phase networks:
The terminals on the meter are located as follows:
- Connection diagram for a three-phase meter. (Press to enlarge) terminal 1 – for phase “A” input
- terminal 2 – for phase “A” output.
- terminal 3 – for phase “B” input.
- terminal 4 – for phase “B” output.
- terminal 5 – for phase “C” input.
- terminal 6 – for phase “C” output.
- terminal 7 – for zero input
- terminal 8 – for zero output.
The principle of connecting a three-phase meter is otherwise the same as a single-phase one. The “ground” input wire, if any, is connected directly to the corresponding terminal of the electrical panel.
Input wires in three-phase networks are usually multi-colored, like the terminals on the meter, which simplifies the connection process.
The connection of such wires is carried out according to the instructions for the electric meter.
It is important not to confuse these terminals with the main ones. With any design of a two-tariff electric meter, they will be displayed in a separate row.
Read a detailed article on how to connect a single-phase electricity meter here.
Varieties of semi-indirect method
There are several known meter connection schemes based on the semi-indirect method, but the most common are the following:
- ten-wire circuit;
- connection by disconnecting on a special block;
- star connection.
Ten-wire switching
Connecting a 3-phase meter using a 10-wire circuit is the simplest and most reliable way. To implement it, you will need to follow the order of connecting ten wires: three for each phase and one neutral. This option has one indisputable advantage, which is the ability to replace the meter while the power is on. The line may be left energized even when repairing a device disconnected from it. With this scheme, the current circuits are reliably grounded, so the possibility of dangerous potential appearing on them is eliminated.
Other connection diagrams
Connection through contact distributors refers to more complex methods, implemented by switching each of the wires coming from the current transformer. The star connection is also characterized by its complexity, but in this case fewer conductors are used. When installing the converter, first the unipolar outputs of all three secondary windings are collected at one common point. After this, the three mating ends of the CT windings are connected to the corresponding terminals of the meter.
Another known switching scheme using the semi-indirect method is called 7-wire. When organizing it, one of the ends of the windings are combined by jumpers directly in the current transformer itself. This option is used extremely rarely in private homes, which is explained by a number of disadvantages of the switching scheme.
Pros and cons of a three-phase meter
During the operation of single-phase meters, quite often a kind of phase imbalance occurs, which is why the voltage in the network will be constantly low. When using a three-phase device, such problems do not arise, because they can operate on the phase that does not relate to drawdown due to distortion.
What does the device look like?
When using a three-phase meter, the voltage will be quite high, so safety rules must be followed. But the device has a number of disadvantages:
- you need to obtain permission to install the device from the local energy company;
- high risk of injury from electric shock and short circuit. To avoid this, it is necessary to install a high-rated fuse before introducing phases into the living room;
- A lot of space is needed for a three-phase model.
Connecting a 380 volt meter
The main advantages of the device:
- it is possible to rationally distribute loads in the network;
- you can use powerful three-phase receivers;
- narrowing the cross-section of the introduced wire.
Basically, such meters are optimally used in private houses with a large area (from 90 sq. m.). Or in apartments in which many powerful household appliances are connected. The types of electricity metering devices are described below.
Connection to a single-phase circuit
To connect a meter designed for three-phase power to a single-phase network, you will first need to become familiar with the differences between these two types of power supplies. With each of them, the cable supplying voltage from the transformer substation contains a neutral working conductor N and phases (one or three).
In a single-phase network, the voltage difference between phase conductors A, B, C and zero is 220 Volts, and between the phases themselves is 380 Volts. The so-called “linear” voltage is formed due to the fact that the vectors of the acting potentials on each of the phases are shifted relative to each other by 120 degrees.
With the abundance of different models of single-phase current meters on the market, the inclusion of a three-phase meter in a single-phase network is used extremely rarely. In most cases, the circuit of such switching is similar to direct connection. The difference is that lines B and C are not connected to the meter; only one phase must be connected. A significant disadvantage of such inclusion is the possibility of problems with regulatory organizations, which really do not like all connection options that do not comply with current regulations and standards.
New connection rules
You can connect electricity meters in private homes in various ways. The choice of one or another circuit for switching on a three-phase meter is determined by the power of the loads being served, as well as the type of the meter itself. The new edition of the PUE number 7 specifically stipulates the procedure for installing and connecting three-phase and single-phase metering devices. The correct approach to solving this issue comes down to following the following recommendations:
- 3-phase electricity meters should be connected using the simplest and most reliable switching scheme;
- the current transformers used in this case must correspond to the conversion factor provided for the selected meter sample;
- When connecting an electronic device, it is imperative to ensure uniform loading of each phase of the supply line.
The last requirement assumes that the currents in each of the load circuits A, B and C must be approximately the same. Violation of this rule entails overloading the neutral conductor and its gradual destruction. Experts call this unpleasant phenomenon “zero burnout.” It is dangerous because if the zero is broken, the combined neutral conductor loses its protective function. In such a situation, the risk of accidental injury to an operator working on electrical equipment by high voltage increases sharply.
When considering methods for mounting a meter in a switchboard, the following approaches stand out:
- fixation using three fastening screws (this method is suitable for meter housings of type S or Ш);
- installation of the metering device on a DIN rail specially equipped in the switchboard (for R or P enclosures).
In the second case, the position of the mounting guide is adjusted so that the holes on the device body and its own slots completely coincide.
Nuances of choosing a meter for 3 phases
Meter with din rail mounting
A high-quality three-phase electricity meter will ensure accurate control of energy costs and financial savings. When purchasing a device you should consider:
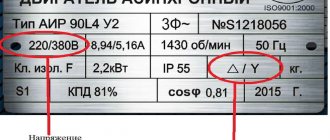
- The voltage parameters with which the device is compatible are indicated on the case or in the passport.
- If the installation is carried out outdoors, you need to familiarize yourself with the permissible temperature range.
- The accounting device must have black or red seals on the screw connections. On an electronic device there is one, on an inductive device there are two.
- The minimum period for checking the device is once every 8-16 years. A shorter time indicates a low quality meter.
- Availability of a certificate of compliance with domestic GOST and permission for installation on the territory of the Russian Federation.
- Installation type. A 3-phase meter for recording electricity costs is mounted on bolts or a DIN rail.
- The life of the seals must be on the meter for no more than 1 year.
- The accuracy class of a high-quality accounting device is at least 2.
- Power indicators. If all the apartment’s appliances in total use no more than 10 kW, a 60 A modification is suitable. An indicator from 10 kW requires the installation of a 100 A device.
- Automated flow control is needed to correctly show information to energy company representatives.
- Availability of tariff plans. Two-tariff models provide a schedule from 7 am to 11 pm and from 11 pm to 7 am. The night tariff provides for spending 50 less electricity.
Types of inclusions and their features
Depending on the method of switching the windings of current transformers, three-phase meters installed in electrical networks are connected according to the following schemes:
- direct connection;
- indirect inclusion;
- semi-indirect connection.
Direct inclusion is called direct inclusion, and to understand the differences between the second and third types, it is necessary to take into account the scope of their application. Purely indirect connection is the open installation of current transformers (CTs) on high-voltage power cables of a three-phase line (6-10 kV). This method is found only at power substations and at large industrial enterprises with their own power distribution networks. In domestic conditions, this type of connection of transformers is not used.
Connection diagrams for three-phase electric meters: options, methods
Let's consider existing methods for connecting three-phase metering devices. The intended connection diagram for the meter will be determined by its type. Today there are several types of three-phase meters:
- direct connection (meters 0.4 kV);
- indirect connection (via instrument transformers);
- semi-indirect inclusion.