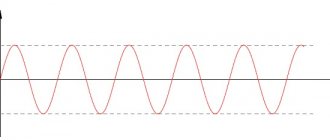
Pulse polarity
Impulses are mono- and bipolar. Monopolar impulses cause the dissociation of substances into ions , and are also capable of propelling electrically charged particles deep into tissues. Thus, monopolar pulsed current can also be used for iontophoresis. The substances used are the same as in iontophoresis with galvanic current.
Bipolar impulses cause oscillatory movements of charged particles on biological membranes. Symmetrical bipolar impulses compensate for electrolysis, and there is no skin irritation under the electrodes. Bipolar impulses overcome skin resistance better and feel more comfortable.
Indications for electropulse therapy
- Neurological diseases of an inflammatory, traumatic, degenerative, dystrophic nature (polyneuritis, neurological symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis, neuralgia, plexitis).
- Diseases of internal organs (chronic bronchitis, mild and moderate bronchial asthma, prolonged pneumonia, hypertension stages 1 and 2, biliary dyskinesia).
- Diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system (arthritis, arthrosis, spondylosis, muscle wasting after prolonged immobilization, myositis, rheumatoid arthritis with a minimal and moderate degree of process activity).
- Diseases of the vascular system (occlusive vascular diseases of the lower extremities, Raynaud's disease, chronic lymphostasis of the legs).
- Diseases of the female and male genital organs (adnexitis, infertility secondary to inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, chronic prostatitis, impotence).
- Urological diseases (cystitis, bladder atony)
- Obesity stages 1-3
- Muscle training in case of imbalance or insufficient muscle mass.
Pulse frequency
Most often, low pulse frequencies are used in physiotherapy: from single to 1000 Hz (pulses per second). Such a low frequency range used in physiotherapeutic cosmetology is determined by the electrophysiological lability of skeletal muscle fibers. To stimulate skeletal, smooth muscles and nerve conductors, different impulse frequencies are needed. When choosing the pulse current frequency, experimentally determined values can serve as a guide.
- To achieve the effect of activating blood circulation, the optimal frequency is about 10 Hz, corresponding to the rhythm of tremor, which affects the increase in capillary blood flow.
- The tonic effect is best manifested at frequencies of 50-100 Hz. (myostimulation).
- Pain relief and muscle relaxation are carried out at frequencies of 100-150 Hz. (neurostimulation).
- The effect on the projection of parenchymal organs is at high frequencies up to 1000 Hz.
The ability to change the pulse frequency significantly expands the scope of application of the device. And the “frequency drift” function offers frequencies for all excitable cells in one “packet” of pulses.
Pulse current
Pulse current is an electric current that is periodically repeated in short-term portions (pulses). In medicine, pulsed current
, consisting of rhythmically repeating current pulses of constant direction and various shapes - rectangular, trapezoidal, triangular, exponential (Lapik currents) or sinusoidal current pulses.
The main characteristics of a pulse current are: amplitude a, duration t and period T, or repetition frequency, as well as pulse shape. Acting on a normal motor nerve or muscle, a single impulse,
even with a short duration and intensity, causes a rapid and short-term
contraction
of the muscle.
With partially impaired innervation, impulses even tens of times longer in duration and several times more intense cause only sluggish contraction
.
In such cases, pulses with gradually increasing intensity (exponential) are used. Frequent impulses - more than 20 per 1 second - cause tetanic muscle contraction. These features of the reactions of the neuromuscular system to the action of pulsed current formed the basis of electrodiagnostics and electrical stimulation. Electrical stimulation is carried out to maintain muscle nutrition and function during the period of recovery of a damaged nerve or temporary forced inactivity of the muscle. For electrical stimulation, choose a type of pulsed current that would cause tetanic contraction with minimal current strength and the least painful stimulation. Previously, to induce tetanic contractions, so-called faradization was used, using the current of a Faraday induction coil. With the advent of electronic devices, the faradic current was replaced by a similar action and easily measured “tetanizing” current. When treating with this current, contractions must alternate with pauses. The UEI-1 device is intended for various types of electrodiagnostics and electrical stimulation. The devices “Amplipulse-3” (tube) and “Amplipulse-ZT” (transistor) generate alternating currents with a frequency of 5000 Hz, modulated according to a sinusoidal law in a series of oscillations of low (from 10 to 150 Hz) frequency. Sinusoidal modulated currents are used in the treatment of radiculitis, vegetative-trophic disorders, neuralgia, neuritis, plexitis, neuromyositis, obliterating endarteritis, consequences of traumatic injuries, sinusitis, subacute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs. Diadynamic currents (Bernard currents) are half-sinusoidal pulses of constant polarity with a frequency of 50 and 100 Hz. These frequencies are used separately or in continuous alternation in “short” or “long” periods. The indications for the use of diadynamic current are the same as for sinusoidal modulated current, however, the irritation of receptors and skin caused by diadynamic current, the painful burning sensation and tingling sensation under the electrodes limit its use (contraindicated in disorders of the autonomic nervous system). The sources of these currents are the SNIM-1 device, as well as the model 717 device intended for bedside assistance. Pulsed current
with rectangular pulses at a frequency of 100-200 Hz and a ratio of pulse duration to pause of 1: 10 (Leduc currents) have an analgesic effect and are capable of inducing electronarcosis.
Pulsed
current with rectangular pulses is also used in electrosleep therapy. See also Electrotherapy.
Current strength (amplitude)
Current strength is measured in Amperes (A). In cosmetology, fractions of an ampere are used.
- 1 mA (milliamp) – 1/1000 A,
- 1 µA (microampere) – 1/1000000 A.
The amplitude of the effect (current strength) is adjusted on each channel separately within a given range. The maximum current strength for the face and for the body should be different.
- From 0 to 100-120 mA – for myostimulation and lymphatic drainage of the body.
- From 0 to 10 mA – for facial myostimulation.
For comparison, the current strength for microcurrent therapy: from 0 to 600. The current strength during the facial or body myostimulation procedure is set manually, focusing on the patient’s sensations.
Electrosleep. Therapeutic effect, indications and contraindications
Electrosleep - a method of influencing the central nervous system with a pulsed current of low frequency and low strength - was proposed in 1948 by Liventsov, Gilyarovsky, Kirillova and Segal.
In the electrosleep procedure, the sleep itself is not important, but it is important to achieve normalization of the processes of excitation and inhibition, improving the influence of the brain on all processes in the body.
Devices: Elektroson-2, Elektroson-3, Elektroson-4 T, Elektroson ES-10-5, etc.
To obtain a weak rhythmic stimulus that causes inhibition in the cerebral cortex, turning into drowsiness and sleep, the authors of the method used pulsed direct current with rectangular pulses, low frequency, low strength, constant polarity. Pulse duration 0.2-2 milliseconds (ms). Pulse frequency 1-130 Hertz (Hz).
The first electrode (bifurcated) is applied to the skin of the eyelids of closed eyes, and the second, also bifurcated, is applied to the skin in the area of the mastoid processes behind the ears. The orbital electrode is connected to the cathode, and the occipital electrode to the anode.
Pulse frequency from 1 to 130 Hz (low frequencies), current strength is individual: until vibration appears in the eyelid area (but not more than 0.5 mA). Pulse duration 0.2-0.5 ms. Exposure: first procedure - 10 minutes, subsequent ones - up to 60 minutes. The course of treatment is 15-20 times, daily or every other day.
Mechanism of action of electrosleep
associated with the reflex action of alternating current through the skin receptors of the eyelids on the cerebral cortex.
Electrosleep promotes:
normalization of higher nervous activity, increasing the threshold of pain sensitivity, improving brain function, improves vascular reactivity, blood supply to the brain, and helps restore the functional state of the brain. With electrosleep, blood saturation with O2 improves to 98%, the functioning of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems with oxygen is normalized, breathing and blood pressure are normalized.
Indications:
neuroses, neurasthenia, schizophrenia, long-term consequences of brain injury, cerebral vascular sclerosis (initial period),
hypertension
stage I - II, hypotension, gastric and duodenal ulcers, bronchial asthma, eczema, dermatoses, neurodermatitis,
phantom pain
, obliterative vascular diseases of the extremities, toxicosis of pregnancy, rheumatic chorea, rheumatoid arthritis, periodontal disease.
Contraindications:
individual intolerance to current, inflammatory eye diseases, weeping dermatitis of the face, hysteria, severe circulatory disorders, arachnoiditis, myopia.
Types of rehabilitation: physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage: textbook. allowance / T.Yu. Bykovskaya [and others]; under general ed. B.V. Kabarukhina. - Rostov n/d: Phoenix, 2010. - 557, [1] p.: ill. - (Medicine). pp. 47-48.
Contraindications to electropulse therapy
General somatic contraindications
- systemic blood diseases;
- tendency to bleed;
- circulatory disorders above stage 2;
- renal and liver failure;
- neoplasms;
- pregnancy;
- active tuberculosis of the lungs and kidneys;
- thrombophlebitis (in the affected area);
- stones in the kidneys, urinary or gall bladder (when exposed to the abdomen and lower back);
- acute intra-articular injuries; acute injury to muscles, ligaments;
- acute purulent inflammatory processes;
- skin diseases in the acute phase in the affected area;
- implanted pacemaker;
- hypersensitivity to pulsed current.
Contraindications and effects
It is important to remember that there are certain contraindications for the use of physiotherapy methods using pulsed currents:
- Tumors of various etiologies;
- Individual intolerance to exposure;
- Pregnancy (second trimester);
- Hemarthrosis in the acute stage;
- Kidney and cholelithiasis;
- Spastic state of muscles;
- Dislocations, bone fractures;
- Bleeding.
Current pulses have an exciting, stimulating and irritating effect on the human body. Passing through the tissues of the body, the current causes increased functions of cell membranes and tissue tension. Cells are activated, their vital activity improves, the functioning of joints, blood vessels and nerve fibers is restored. This helps speed up the treatment of many diseases, as well as avoid all sorts of complications.
In general, as a result of exposure to pulsed currents, the following occurs:
- Reducing congestion in the pelvis;
- Metabolism improves, the body's defenses increase;
- The synthesis of organ secretion is activated;
- The permeability of cell membranes increases.
Physiotherapeutic procedures using pulsed current activate blood flow, so the drugs used penetrate the tissues faster, and the effectiveness of treatment increases.