Correct selection of RCD
December 16, 2019
Reading time:
In order to create safe living conditions for others when electrical equipment is running, special electrical devices are produced - residual current switching devices, which in practice are more often called abbreviated as “RCDs”. They protect against electric shock when coming into contact with equipment that is energized during emergency situations.
It is noteworthy that such protection is provided from both direct and indirect contact with the housing of equipment that is energized. In addition to this purpose, the RCD is used to monitor the technical condition of the insulating materials of the wiring. This guarantees auxiliary protection of the apartment from fire of electrical lines. Owners installing powerful household appliances will need to know how to choose an RCD to protect themselves and their loved ones.
Single- and three-phase devices
Leakage current
To ensure safety from electric shock, it is often necessary to increase the number of residual current devices and divide the network into several groups. At the same time, the use of very sensitive RCD devices leads to false alarms. The specialist’s task is to make the correct calculation and choice, taking into account all factors.
According to the rules of electrical installations, when Iut is unknown, it is taken equal to the product of 0.4 mA by the number corresponding to the calculated load current in amperes. The circuit leakage is assumed to be equal to the product of 0.01 mA by the length L of the phase conductor in meters.
According to the same rules, the total network losses must be less than one third of the rated residual current of the RCD. This also includes all leaks from constantly switched on and periodically connected electrical appliances. Let's do the calculation.
Total Iut= 0.4* IΣ +0.01*L
It follows that the maximum current of the RCD must be 3 times greater than the total Iout of the network.
Accordingly, the rated breaking current is equal to:
IΔn= 3*(0.4* IΣ +0.01*L), where
IΣ – total leakage current of all electrical installations in the network,
L is the length of the phase wire in meters.
Purpose and design of RCD
The device is an automatic device that turns off the voltage when a differential current (differential current, leakage current) occurs. It is precisely this, which occurs during one or another malfunction of electrical equipment, that in most cases is a consequence of accidents. The worst thing is that the fault causing the leak does not manifest itself in any way. The washing machine washes, the computer calculates the task, the boiler diligently heats the water. But as soon as a person touches the casing of such a device or gets under the shower, something irreparable will happen.
The task of the differential switch is precisely to detect leaks and emergency shutdown of faulty equipment when it appears. How does he do this?
Importance of the event
If you choose the wrong RCD model, that is, make a mistake with its characteristics, this is fraught with the following consequences:
- The automation will be triggered during a false alarm, because... minor electrical leaks are always present in the wiring, especially if it is old (in a wooden house in the country).
- The overly high power rating of the RCD you choose will not operate during a dangerous situation, resulting in an electric shock.
- The device will not be able to function when connecting the aluminum conductors of your home wiring, since most modern models are designed only for connecting copper conductors.
To prevent these errors, you first need to understand the characteristics of the differential switch, and then proceed to its selection.
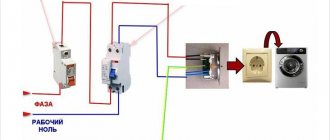
Let's look at typical schemes. Example 1. Which RCD should I install in my apartment?
In Fig. 2, after the meter, a differential protection is installed as fire protection. The lighting in each room is switched to a separate machine. Differential relays are installed for the most “demanding” rooms - children's rooms, living quarters and bathrooms (SNIP 31-110-2003 clause 14.40). The kitchen electric stove is separated only automatically. This was chosen with the expectation that there are no moving parts in the electric stove and the risk of damage to the insulation in it is minimal. Lighting is also not protected (recommendations of PUE 7.1.79), because Current leaks for lamps are insignificant and do not pose a danger, and, if necessary, can be easily localized.
Calculation of RCD for an apartment. 1st differential relay.
Let's make the calculation for the first
circuit serving consumers connected through sockets. We will assume that the following electrical appliances are working simultaneously:
Refrigerator, with a power of 3500 W with a wiring length of 15 m
Air conditioner, 3450 W, length 10m
Living room sockets 2400 W, 20m
Children's sockets 1500 W, 15m
Other sockets 2500 W, 25 m.
We select the values of the automata. From Table 1 it follows that for the refrigerator and air conditioner you need to choose 6 A machines, for children - 2 A, for others - 3 A. Class of automatic machines is C, as the most common in household electrical wiring. Let's calculate the natural leakage for consumers - (6+2+3x2) x 0.4 = 14 x 0.4 = 5.6 mA. We select the operating current from Table 1 based on a value greater than the total load - 16A.
How to choose an RCD. An example of choosing an RCD.
Purpose of RCD.
Electricity in the modern world is developing by leaps and bounds. In many apartments and residential buildings you can find elements of automation, which until recently were found only in industrial facilities. For example: voltage control relay, SPD, phase control relay. As you know, the RCD is still a widespread device for protecting the electrical network . Today we will analyze the algorithm of actions and complete a mission called “How to choose an RCD.”
Protective automation, SPD, RCD
RCD is a device that analyzes the supply circuit for current leakage. Having detected a malfunction (losses higher than the rated value of the device), the device turns off the electrical circuit, ensuring the safety of consumers.
To explain it more simply, this device compares the amount of current in two wires connected to the load . As a rule, in the “ideal version”, it will be the same, and its difference should tend to zero if the wiring is working properly.
RCD leakage current
However, in reality, losses occur under normal and abnormal conditions. In normal situations, losses are minimal.
How to choose an RCD. Criteria.
First of all, it is important to choose a protective device wisely. In particular, focus on the main criteria:
- Differential leakage current. Represents a key parameter of the device. Because it sets the permissible leakage limit.
- Rated operating current . In general, this characteristic reflects the amount of current that the protection device can withstand while performing its tasks in full;
- Device voltage. Most often 230 or 400 V;
- Type of RCD for monitoring the type of leakage.
- Conditional rated short circuit current.
In addition to these basic parameters, there are also additional ones, but we will talk about them in one of our next articles.
How to choose an RCD based on differential leakage current.
As you learned from the material above, there are regulated and non-standardized leaks. In particular, the calculation of standardized leaks is carried out according to clause 7.1.83 (PUE 7) with unknown data :
- For every 1 A of load, it is necessary to provide a standardized loss of 0.4 mA;
- For every 1 m of power cable it is necessary to provide a standardized loss of 0.01 mA.
Analyzing the above, a correctly selected device does not respond to standardized ones , but should turn off the network as quickly as possible in the event of emergency leaks.
To manufacturing plants in accordance with GOST R 50807 clause 5.4. , recommended: if the leakage level is less than half the device rating, the device should not disconnect the circuit. That is, a device with a leakage rating of 30 mA, with losses of less than 15 mA, should not operate. However, shutdown is permissible in the range of 15-30 mA - this point should also be taken into account.
According to the same paragraph 7.1.83 (PUE 7) , the differential current of the protection device must be 3 times higher than the calculated normalized losses in the network.
Selection of RCD based on operating current.
In addition, it is important to remember that the device is not protected from short circuits. Accordingly, a device of this type must be additionally protected with a standard automatic machine . First of all, it is worth considering the following:
The operating current of the RCD is selected at least one or two steps higher than the rating of the protective device (automatic machine) protecting this device.
In other words, this selection criterion is determined by certain time-current characteristics (TTC) of the machines, which allow overloads from 13 to 45% in the network in a time interval from a couple of minutes to an hour.
Selection of RCD by voltage.
If the network is single-phase (230 V), then we install a two-pole device, if it is three-phase (400 V), then we install a four-pole device. But it is worth remembering that there are two types of residual current devices:
- Electromechanical (works on a certain amount of leakage, operation does not depend on the presence of voltage in the circuit);
- electronic (they work for a certain amount of leakage if there is voltage in the circuit. If the circuit is without voltage, then the device will not work).
additional characteristics
In addition to these basic characteristics for which calculations are carried out, there are also quantities that require attention when choosing. This is the maximum short circuit current; for a home it is assumed to be 4500 A, for an apartment building 6000 A, for production 10000 A. On the body of the product it is depicted as a number surrounded by a frame. The type of disconnecting leakage current is indicated by letters:
- AC means it is variable;
- A – IΔn variable and pulsating constant;
- B – IΔn variable and constant;
- S – selective, turns off with a delay.
RCD type AC is used in apartments. Common consumers - lighting, refrigerators, heated floors. The maximum shutdown time for this type of RCD is 0.04-0.3 seconds, depending on the magnitude of the leakage current.
Type A is used where there are many devices with rectifiers and switching power supplies: computers, washing machines, televisions, dishwashers, microwave ovens. Sometimes manufacturers directly indicate that there should be an RCD A device, and then a current calculation is performed.
Type B is used mainly in industry, requiring detailed calculations before installation.
Type S (selective). The response time of such an RCD is 0.2-0.5 seconds, so it is not protective for humans. The device is installed at the beginning of the line after the main circuit breaker and is the second stage of differential protection of the entire facility from fire.
In addition, you need to determine which residual current device to choose: electromechanical or electronic. The first is more reliable, but also more expensive. The second type is cheaper than electromechanical, but its electronic components more often burn out under all kinds of overloads.
When organizing an electrical network protection system, it is necessary to take into account that more than 5 circuit breakers cannot be connected to one RCD. This may lead to false positives. In addition, with proper shutdown, it is impossible to understand where the leak occurred.
Protection in apartments and houses
When choosing a protection device, you need to understand why you need an RCD in an apartment or house. A correctly selected device will protect a person from electric shock and protect the apartment from fire.
The devices are installed in electrical panels, observing the following connection sequence: at the entrance to the house they install a general circuit breaker, an electricity meter, an input device, individual circuit breakers and protection devices.
In a private house, a fire protection or fire protection RCD is installed at 100 or 300 mA, depending on the size of the general leaks.
How many devices to install in a private home depends on the number of consumer groups.
Choice for an apartment
For an example of calculation, let's take an apartment in a multi-story building. There is a circuit breaker in the floor panel at the input. Let the machine be 40 Ampere. It protects against short circuits and overloads. A fire protection RCD is installed immediately behind it; we will calculate its nominal value later. It is needed for fire protection in case of cable insulation failure or breakdown. Further, to ensure greater safety and uninterrupted supply of electricity, RCDs with a certain Iout from 10 to 30 mA are installed for each or several groups. Depends on leakage currents. There are even sockets with their own RCD devices. Each consumer group is equipped with its own automatic overload switch.
The bathroom has a washing machine with a power of 1.8 kW. Since it is located in a damp room, for safety we will provide a 16 A circuit breaker and calculate the RCD based on power.
The operating current for a washing machine is:
The length of the phase wire to it is 20 m.
Hence IΔn= 3*(0.4* IΣ +0.01*L)=3(0.4x7.3+0.01x20)=9.36 mA.
The closest RCD in the row is 16 A, leakage current 10 mA.