USB Type-C is a specification for a USB connector system that is gaining popularity in the field of smartphones and mobile devices. USB Type-C is capable of both delivering power and transferring data. One of the features of USB C is that, unlike its predecessors, this connector does not have a clear top or bottom, meaning it can be flipped, so you don't have to try to connect it the first time.
This article will cover some of the most important features of the USB-C standard. Before we dive into the pinouts and explain what each pin is capable of, we'll quickly cover what USB-C is and what it does best at.
What is USB-C?
USB-C is a relatively new standard that aims to provide high-speed data transfer of up to 10 Gbps, as well as power transfer capacity of up to 100 W. These features could make USB-C a truly universal connection standard for modern devices.
Some people wonder how to write it correctly: USB-C or USB Type-C? These two terms are usually used interchangeably (we'll use both in this article). Although USB-C is more commonly used, USB Type-C is the official name of the standard, as listed on USB.org.
How to choose USB Type-C
The specification of the new connector is quite extensive and opens up great possibilities for use. It can be used in a variety of tasks for a variety of devices.
For charging
The new standard suggests that the charger can use up to 100W of charging power. But since there is a wide range for customization, the power used can be changed in different gradations. This is sometimes where the problem lies. Manufacturers may limit the charging currents for their devices, and thus, if you connect high-power charging using a cable with low permissible currents, the process of charging the device’s battery will be very long. That is, it is advisable to select a cable within the power limits within which the charging is located.
For video and audio transmission
USB Type-C is quite suitable in terms of characteristics for transmitting video and audio signals. To do this, it is capable of supporting alternative transmission modes: HDMI, VGA and Thunderbolt. Depending on the input present on the video device, for example, a TV, you can use one of the standards - HDMI, VGA or Thunderbolt 3. Although many TVs and monitors are slowly acquiring their own USB Type-C ports, which do not require any adapters.
To connect additional devices
Although the number of devices supporting USB Type-C is constantly growing, the transition will still be long. But since the new standard perfectly supports high speeds, there are already various hubs and adapters on sale that allow you to painlessly connect anything. The simplest hub with USB Type-C to Type-A can be found for 1000 rubles. Overall, just a straight-through cable costs the same.
For maximum data transfer speed
To ensure maximum speed, you need to choose a cable with a USB 3.1 interface. This will allow data transfer at speeds of up to 10 Gbit/s. For higher performance, you will have to use an alternative mode such as Thunderbolt 3 or MHL, which allow you to overclock to 20 and even 40 Gbps.
USB-C Features
The USB-C interface has three main functions and features:
- Has a reversible connector. The interface is designed in such a way that the connector can be reversed relative to the socket.
- It supports USB 2.0, USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 Gen 2 standards. Additionally, it can support third-party protocols such as DisplayPort and HDMI in an operating mode called Alternate Mode.
- It allows devices to negotiate and select the appropriate level of power flow through the interface.
In the following sections, we will see how these features are provided by the USB Type-C standard.
Historical information
And now on the fingers. A long time ago, in a galaxy far, far away, a data transfer specification called “USB” v1.0 was developed. Then USB 1.1 struck back. USB 2.0 has reached the masses. And USB 3.0, although not universal, has successfully settled in various devices. The USB 3.1 standard has made clarifications and amendments. And, most importantly, each standard had a bunch of corresponding connectors. By connector for different types of devices with different purposes and partial backward compatibility - USB type-A, USB micro-A, USB Micro-B SuperSpeed. It was the accumulated diversity and incomplete compatibility that brought confusion, inconvenience and gave rise to many jokes. So, the new USB type-C standard has become a “new hope”. It doesn't change the data transfer standard (but it does add one). This is a connector standard that combines the advantages of connectors from all previous USB standards and avoids their disadvantages.
USB Type-C connector power and ground lines
The VBUS and GND pins are the power and return paths for the signals. The default VBUS voltage is 5V, but the standard allows devices to negotiate and select a VBUS voltage other than the default value. The power supply allows the VBUS to have a voltage of up to 20 V. The maximum current can also be increased to 5 A. Therefore, USB Type-C can output a maximum power of 100 W.
A high power stream can be useful when charging a large device such as a laptop. The following figure shows an example from RICHTEK where a boost converter is used to produce the appropriate voltage requested by the laptop.
Note that power delivery technology makes USB Type-C more versatile than older standards because it makes the power level adaptable to the load's needs. You can charge your smartphone and laptop with one cable.
What devices use USB Type-C
Gradually, the list of devices supporting the standard is growing. Including adherents of non-standard types: Apple also began to introduce a new connector into its devices.
Computers
Naturally, this type of technology should be the first to master the new standard. Laptops from Apple can be called pioneers - MacBook 12'' and MacBook Pro since 2016. True, there is only one port there. Now almost every laptop from different manufacturers necessarily contains at least one Type-C port. And to support older versions, they also still have Type-A.
Smartphones
Mobile phones are also trying to keep up with trends, and manufacturers equip them with a Type-C connector. First, brands from the Middle Kingdom came, and then the rest, more well-known ones. Leagoo KIICAA Mix, Alcatel 5, Sony Xperia L1, Xiaomi Mi A1, Blackview P2 lite were among the first to receive this standard.
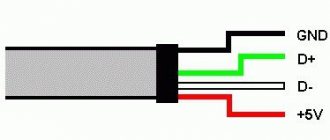
RX and TX lines of USB Type-C connector
The connector has two sets of RX differential pairs and two sets of TX differential pairs. One of these two RX pairs along with the TX pair can be used for USB 3.0/USB 3.1 protocol. Since the connector is switchable, a multiplexer is required to correctly route data across the differential pairs used through the cable.
Please note that the USB Type-C port can support USB 3.0/3.1 standards, but the minimum USB Type-C feature set does not include USB 3.0/3.1. In such cases, the RX/TX pairs are not used by the USB 3.0/3.1 connection and can be used by other USB Type-C features such as Alternate Mode and the USB Power Delivery protocol. Even all available RX/TX differential pairs can use this functionality.
Description USB 3.0 type C
| USB 3.0 type C plug | USB 3.0 type C socket |
Currently, USB connectors and cables dominate the market. Most modern devices support data transfer via USB interface. USB connectors are powered by a voltage of 5 V and a current of up to 0.5 A, and for USB version 3.0 - 0.9 A. It follows that the maximum power of the connected device does not exceed 2.5 W or 4.5 W for USB 3.0. This is quite enough for connecting low-power and portable devices (phones, players, flash drives, memory cards)
USB v2.0 and USB v3.0 connectors are also classified by type (Type A and Type B) and size (MiniUSB and MicroUSB).
USB Type-C or USB-C is a USB specification for a universal, compact, double-sided 24-pin connector for USB devices and USB cables.
The USB Type-C connector specification version 1.0 was published by the USB Developers Forum in August 2014. It was developed around the same time as the USB 3.1 specification.
USB Type-C connectors provide connections to both peripherals and computers, replacing the various Type A and Type B connectors and cables of previous USB standards, and providing future expansion options.
Using a USB Type-C connector does not necessarily mean that the device implements the high-speed USB 3.1 Gen1/Gen2 standard or the USB Power Delivery protocol.
Lines CC1 and CC2 of the USB Type-C connector
These lines are the channel configuration pins. They perform a number of functions such as cable insertion and removal detection, connector/plug orientation detection and current notifications. These pins can also be used for communications required for power supply and alternate mode.
The figure below shows how pins CC1 and CC2 determine the orientation of the connector/plug. In this figure, DFP stands for downstream output port, which is a port that acts either as a host for data transmission or as a power source. UFP stands for upstream output port, which is a device connected to a host or power sink. Flipped here means the connector is upside down, Unflipped means it's not upside down.
DFP pulls up pins CC1 and CC2 through resistors Rp, but UFP pulls them up through Rd. If the cable is not connected, the source sees a logic high on pins CC1 and CC2. Connecting a USB Type-C cable creates a current path from the 5V power supply to ground. Since there is only one CC wire in a USB-C cable, only one current path is formed. For example, in the top picture, the CC1 DFP pin is connected to the CC1 UFP pin. Therefore, the DFP CC1 pin will be below 5V, but the DFP CC2 pin will still be logic high. Therefore, by monitoring the voltage at the DFP CC1 and CC2 pins, we can determine the cable connection and its orientation in space.
In addition to cable orientation, the Rp-Rd path is used as a way to convey information about the current capabilities of the source. For this purpose, the power consumer (UFP) monitors the voltage on the CC line. When the CC line voltage is at its lowest value (about 0.41V), the source can provide the default USB power, which is 500mA and 900mA for USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 respectively. When the CC line voltage is about 0.92 V, the source can supply a current of 1.5 A. The maximum CC line voltage, which is about 1.68 V, corresponds to the source current capacity of 3 A.
Properties of USB type-C
Main innovations: - one connector for everything (for printers, smartphones, flash drives... monitors!) - mirror connector (no need to guess which way to insert it) - small dimensions (it is slightly larger than micro USB) - connector is very securely fixed in the socket ( hurray!) - must withstand up to 10,000 connections - the connector supports USB 1.0 – USB 3.1 standards - it allows devices to independently decide who to be master/slave and power source/consumer - the cable can be passive or active (with electronics inside)
The main old innovations: - the standard does not define the length of the wire, it has already been defined in data transmission standards - the connector can withstand up to 5A, but this is described in the BC1.2 and Power Delivery standards
Next, you can talk about DisplayPort integration, audio transmission, and more. And I will try to do this in the following reviews, but for now let’s look at the implementation of three USB Type-C cables with backward compatibility.
USB Type-C connector VCONN line
As mentioned above, USB Type-C aims to provide incredibly high data transfer speeds along with high levels of power flow. These functions may require the use of special cables when using the chip internally. Additionally, some active cables use a repeat driver chip to amplify the signal and compensate for losses incurred by the cable. In these cases, we can power the circuitry inside the cable by supplying 5V, 1W power to the VCONN pin. This is shown in the following figure.
As you can see, the active cable uses resistors Ra to pull the CC2 lines to ground. The value of Ra is different from Rd, so the DFP can still determine the spatial orientation of the cable by checking the voltage at the DFP CC1 and CC2 pins. Once the cable orientation is determined, the channel configuration pin corresponding to the "active cable IC" will be connected to a 5V, 1W power supply to power the circuitry inside the cable. For example, in Figure 5, the actual path Rp-Rd corresponds to pin CC1. Therefore, the CC2 pin is connected to the power supply labeled VCONN.
Recommendations for using USB Type-C
While the standard is still at the implementation stage, there will be compatibility problems. That is why device developers are still providing their gadgets with both a new connector and older USB type A. Naturally, at this stage the prices for adapters, adapters and cables are quite high.
By the way, you shouldn’t buy cheaper analogues of adapters from Type-C to any other standard. The fact is that the specification is very difficult to organize the correct transition from one standard to another. And many semi-basement factories in China do not implement the mechanism for determining currents for the cable configuration channel to the required extent. As a result, the port may receive incorrect information about the power of the device, which can threaten the failure of ports, power supplies or hubs.
Overall, the standard is attractive and effective. Perhaps it will be the one that will lead to the unification of connectors and ports so that you can connect anything through the same cable - from smartphones to monitors. The main task of the standard now is to “conquer” as many devices as possible.
USB-C power delivery
As mentioned above, devices using the USB Type-C standard can negotiate and select the appropriate level of power flow through the interface. These power negotiations are achieved using a protocol called USB Power Delivery, which is a single-wire communication over the CC line discussed above. The following figure shows an example of USB Power Delivery, where the receiver sends requests to the source and adjusts the VBUS voltage as needed. First, the 9-volt bus is requested. Once the source stabilizes the bus voltage at 9V, it sends a "ready to power" message to the sink. The receiver then requests the 5V rail and the source provides it and sends the power supply ready message again.
Importantly, these are not only negotiations related to energy delivery. In addition, other negotiations, such as those related to the alternative mode, are carried out using the Power Delivery protocol on the CC line of this standard.
Unboxing
And only now let’s look at the received parcel.
The review included ECU-10-BK (USB type-C to USB type-A) LCU-10-BK (USB type-C to micro USB 3.0) MCU-10-BK (USB type-C to micro USB 2.0) Each of which are packed in a little bag, in a cardboard box and in another little bag. Two of the three boxes were wrinkled during transportation. All cables are exactly 1 meter long and 3 mm thick (except LCU-10-BK, it is 4 mm). The wires are a little stiff and happily return to their old position.