Electrician in the house
Encyclopedia about electricity from A to Z
Masters catalog
Find the best master or company in your city
Types of wires PV 1
The PV1 wire is intended for installation in pipes, construction voids, cable trays and under plaster. It has found wide application both in production and at the household level.
After all, one of its main advantages is a very reasonable price with fairly good technical characteristics. And here you should dwell in more detail so as not to make a mistake in your choice.
- Explanation of the name and nomenclature of PV1 wires Explanation of the name of PV1 wires
- Nomenclature of wires PV1
- Mechanical characteristics of PV 1 wires
PV wire decoding and application
The PV cord is a copper conductor for transmitting electricity over distances from the source to the recipient. It is protected by a special layer - insulation made of polyvinyl chloride. It is used for connecting electrical devices and mechanisms, as well as for grounding lighting paths.
According to generally accepted standards, the abbreviation PV means the following:
The letter P stands for wire. The designation K is also possible - cable. The letter B indicates that the insulating layer consists of polyvinyl chloride or vinyl.
If there is no letter A in front of the PV, this indicates that copper conductors are used as a conductive element.
As a rule, after the abbreviation PV a number from 1 to 6 is indicated, each of which is responsible for the flexibility class of the wire. Remember - the first class is the least flexible, but the sixth is the most flexible of all the types presented. The level of flexibility directly depends on the design of the wire itself and its characteristic features.
PV wires are very resistant to mechanical damage, mold damage and are quite wear-resistant in their parameters. A special feature of this product is its self-extinguishing insulation, which protects the wire from overheating.
The PV wire is used in the following cases:
- for connecting electrical devices to a current source;
- for grounding stationary and power lighting networks;
- for connecting electrical devices and devices.
Let's consider each type of cable: their features and scope of application.
Explanation of the name and nomenclature of PV1 wires
But before we talk about the characteristics of the wire, let's look at the decoding of its name, as well as the types of PV1 wires produced in our country. In the future, this will help us make a technically competent purchase.
Decoding the name of the wires PV1
First of all, decoding the name. And you shouldn’t have any difficulties with this. Only the number 1 in the title may raise questions. But let's talk about everything in order.
Decoding of wires PV 1
So:
- The first letter is P. It means it's a wire. In addition to wires, there may also be Sh - cords or K - cables.
- The second letter is B. It indicates the type of wire insulation. In our case, this is polyvinyl chloride insulation. It has stable physicochemical properties and is therefore often used as a dielectric.
- The number "1" indicates the flexibility class. The lower this number, the larger the bend radius the wire can be subjected to.
This abbreviation gives us the answer to the question: is this wire installation or installation? An installation wire is a wire that is designed for long-term use in one position. That is, set it and forget it. And the installation unit can be restarted many times during operation.
That is, based on the flexibility class PV1, unlike PV 3 (see Wire PV 3 - characteristics and features) is an installation wire. And moving it repeatedly is not recommended.
Nomenclature of wires PV1
Now we can discuss the types of PV1 wires produced by our industry and their features. GOST 6323-79 will help us with this, to which all wires of this brand must comply.
Dependence of wire cross-section and its mass
First of all, it should be clearly defined that all PV1 wires are single-core, as you can see in the video.
This is not always convenient for domestic use, which is one of the main limiting factors:
- The wire cross-section can be from 0.5 mm2 to 120 mm2. At the same time, depending on the cross-section of the core, its structure and technical characteristics change.
PV wires 1 with a cross section of up to 10 mm2
- So, according to GOST 22483, wires with a cross-section from 0.5 mm2 to 10 mm2 can be made as a single core. These wires belong to the first class in terms of flexibility.
- But wires with a cross-section from 16 mm2 to 35 mm2 should already consist of at least seven cores. Due to this, their flexibility increases. Therefore, although such wires are called PV1, the instructions classify them as the second class of flexibility.
Wire PV1 16
- Wires with a cross-section from 50 mm2 to 95 mm2 must be made of at least 19 wires. But PV1×120 is already made from no less than 37 wires. Moreover, according to GOST, these wires already belong to the second class of flexibility.
Diameter of individual wires for wires of different sections
The next important factor is the thickness of the wire insulation. It also depends on the section. After all, it is quite logical that the larger the cross-section of the wire, the greater its insulation should be.
Wire insulation thickness depending on cross-section
Note! According to clause 2.4.2 of GOST 6323 - 79, the insulation of PV 1 wires can be two-layer. In this case, the thickness of the feather layer insulation should not exceed 70% of the thickness of the entire insulation.
The last criterion for differentiation is the color of the veins. According to GOST PV 1 wires, the color color can be selected based on customer requirements.
Coloring of wires PV 1
At the same time, there is a separate requirement for grounding wires. As you know, this core should have a yellow-green color (see Color of the ground wire). So, for her, on a 15 mm section of wire there should be at least 70% of one color and 30% of another.
Wire PV 3: technical characteristics
The PV-3 cable is deciphered as follows: P - indicates the wire, V - indicates that the cable design includes vinyl type insulation, and the number three indicates the flexibility class to which the electrically conductive core of the cable belongs. The higher the number, the more flexible the cable is.
Copper cable PV-3, which has a cross-section of 1x4, 1x6, 1x35, 1x25, 1x16, 1x10, 3x 2.5, 3x1.5 and 3x0.75, is produced by a Moscow company called MosKabelmet. This cable is often green or yellow-green. It also includes a copper core, which is very durable and flexible. This conductor is multi-wire, which means that it conducts electricity well, can be used for a long time and is very durable. Carrying out all the technical characteristics does not make sense, since only experts can understand some features of the cable.
There are 6 main characteristics, namely:
- This cable is used in power and lighting circuits;
- It is designed for operation with alternating voltage 400V and constant voltage 1000V;
- The temperature at which the cable can be used ranges from -50 to + 75 degrees, and installation is possible at a temperature not lower than – 15 degrees;
- Can be used at 100% humidity;
- The bending angle is possible up to 90 degrees;
- The warranty period is 2 years, but in practice it lasts up to 15 years.
Due to its wide cross-section, the cable can be used in any area. For example, installing wiring in an apartment, creating a separate electrical network, powering various electrical appliances, and the like.
Properties and scope
Wire PV-3 is one of the most popular and widespread. This is a single stranded copper wire with a vinyl sheath. The vinyl sheath perfectly protects against various types of influences, so this wire can also be used in rooms with high humidity. Can be installed in bathrooms, kitchens, etc.
The shell must be marked
The vinyl shell is weather resistant. In the basic version it has a wide temperature range for operation - from -40°C to +70°C. These properties make it possible to use PV-3 for laying both inside and outside buildings. Only installation is possible at temperatures from -15°C to +25°C. For some regions with low winter temperatures, this means that PV-3 wire cannot be installed outdoors in winter. Otherwise there are no restrictions.
Application area:
- power and distribution networks,
- lighting,
- connecting devices and equipment,
- installation of wiring indoors and outdoors.
A high degree of flexibility allows work to be carried out where other wires are deformed or cannot be bent at the required angle. So the PV-3 is very convenient and reliable.
PV-3 wire can have different colors
Since the wire is single - it has one core, the sheath is painted in different colors. It is better to choose colors according to the color markings of cables and wires:
- Yellow-green (less often light green) is used to connect protective grounding.
- Blue (white-blue) is used for neutral wiring (zero).
- Black, red, brown, white and others - for phases.
By adhering to these rules, you will not mix up the wires when connecting household appliances yourself or when wiring.
PV 1 parameters
Let's start with the design features. This is a single-core cable made of copper, in which the core itself can be either single-wire or multi-wire. By the way, tinned copper is used in production. As mentioned above, the wire insulation is PVC (polyvinyl chloride). As for the colors of the insulation, there is no specific color, so manufacturers offer their products in white PVC, black, blue, brown, red and yellow-green. That is, GOSTs allow this.
Now the cable specifications:
- It can be installed in a network with alternating current or direct current. In this case, the voltage withstood by the wire is 450-750 volts in the first case, and 1000 volts in the second.
- An alternating current network can have an oscillation frequency of up to 400 Hz.
- Currently, manufacturers produce wire with a cross-section from 0.5 mm² to 120 mm². That is, there is no wire marked PV3 4×240.
- The product can be operated at temperatures from minus 50C to plus 75C.
- Withstands transformer pressure 29.4x104 Pa and atmospheric pressure 5.3x104 Pa.
- Electrical resistance is not less than 1.0 MOhm/km.
- The length in coils is 100 m; upon request, a smaller value can be obtained, but not less than 20 m.
- The wire can be bent with a radius of 10 sections.
- The warranty period is 2 years, actual up to 15 years.
It is clear that the weight of the product will depend on its cross-section, so indicators on this issue can be found in the table below.
And one more point that concerns the question of how to correctly decipher the markings. For example, the installation wire is PV 3 10. The number “10” means that this is a cable with a cross-section of 1 mm². But in this case we are interested in another point. Everything below this section is single-wire products, everything above is multi-wire. That is, PV 1 6 is single-wire, PV 1 16 is multi-wire.
Among the variety of conductor products presented on the construction market in the category of electrical materials, a special place is occupied by the wire PV, due to its low cost and versatility of use when creating stationary electrical networks and connecting electrical installations. At its core, it is a single- or multi-wire copper conductor with one current-carrying core, enclosed in an insulating sheath made of polyvinyl chloride plastic compound. The copper design of the conductor provides this type of wire with elasticity, lower internal resistance, and the possibility of use in residential premises, in accordance with the current PUE standards. The insulating sheath provides the PV wires with high performance characteristics, such as moisture and heat resistance. Read how to create a good love relationship for yourself on our website.All wires with an insulating sheath made of polyvinyl chloride are marked as follows: “P” - wire, “B” vinyl chloride, sheath material, as well as a numerical indicator that characterizes the flexibility class of the conductor and determines its brand. It is the flexibility class that is the fundamental difference between this type of wire, which also determines the scope and cost of this type of conductor product.
PV-1 is the least elastic among wires of this type, and, accordingly, has the lowest flexibility class - 1 (in the range of cross-sectional diameters from 0.5 to 10 mm2), and class 2 (for cross-sectional diameters over 10 mm2), sometimes called PV-2. Also, this brand of wire can be produced with sections from 0.5 to 95 mm2. The maximum bending radius is up to 10 diameters. Due to the lack of elasticity, the stationary laying of this conductor provides for straight sections and additional mechanical protection, for example, the presence of a metal sleeve. It has the lowest cost among PV wires and is widely used in creating electrical wiring lines inside steel pipes and in various hollow channels, as well as for connecting a wide variety of devices and installations equipped with a mounting panel.
PV-3 is a conductor of increased elasticity, which allows it to be used when creating the most complex electrical networks in design, characterized by a large number of bends. Available in the same range of cross-sectional diameters as the previous wire. However, it also has a higher cost. The flexibility class of a wire of this brand varies depending on the cross-sectional diameter: class 2 - 0.5 to 1.5 mm2; class 4 – from 2.5 to 4 mm2; class 3 – sections exceeding 4mm2. Indispensable in lighting electrical networks and for connecting various electrical equipment.
PV-4 is the most elastic (4th or 5th class of flexibility depending on the cross-section) and the most expensive of all wires of this type. Like wire of the third class of flexibility, it is widely used in creating complex designs of power lines with frequent bends. True, it is produced with a limited range of section diameters - only from 0.5 to 16 mm2. Has a maximum bending radius.
Despite some differences in elasticity and cost, all brands of PV wires equally have high performance characteristics:
— wide range of operating temperatures from – 15 to + 70 degrees;
- long service life, according to manufacturers - 15 years;
— direct voltage up to 1000 V, alternating voltage up to 450 V at a standard frequency of electrical impulses of 40 Hz;
In addition, all PV wires are produced in a sheath of different colors, which have their own functional application (yellow-green - grounding, blue - zero phase, and so on), as well as with longitudinal stripes.
The copper design of the current-carrying core, low cost, quality, as well as versatility of use provide PV wires with high attractiveness for consumers, as well as a strong position in their category of electrical goods.
If suddenly the reader wants to purchase cash registers, then the best place for this is www.planetakkm.ru. A very large assortment of cash registers and other cash registers.
Features of installation and operation
The main purpose of the PPV is to connect fixed wiring at industrial or residential facilities
In addition to practicality and versatility, the product attracts attention with its low cost
During operation of the PPV, several important features must be taken into account:
The rigidity of the product is associated with the monolithic design of the cores. The bending radius during installation should not exceed ten outer diameters. Ten cycles - exactly this number of bends is permissible at right angles with a return to the original position. These values must be taken into account when designing the cable route. Try to eliminate unnecessary bends and kinks. Polyvinyl chloride is a chemically resistant material. It is laid along a brick or concrete base, and can subsequently be hidden under a layer of plaster or putty. There is no need to use additional protective equipment. Modern building mixtures contain various additives and additives, which, when exposed to a single insulating layer, destroy it over time. If you do not know the composition of the solution, then it is still better to use additional protection in the form of corrugated pipes and boxes. When laying PPV under plasterboard or plastic boards, MDF, the presence of corrugation or cable duct is mandatory. Installation in the open air is possible, but many experts recommend using canopies or other devices that protect the product from direct sunlight. Hygroscopicity allows the PPV to be used in damp and warm rooms (for example, in a bathhouse)
In this case, it is important to use plastic protection (metal is not suitable). The route should be located at the bottom or mid-height
Choose a three-wire wire with an RCD connection.
Wire storage and transportation conditions
During storage, the cable drum should stand and not lie down. It is allowed to store such wires outdoors, under a canopy, so that they are not exposed to precipitation.
During storage, the ends of the wire must be protected from external influences (ultraviolet rays, water, chemicals).
Important! Wires with fiber, enamel protection and sheathing made of other moisture-absorbing compounds should be stored only in warehouses.
Transporting cables in a reel
When opening the cable package, you need to place plywood or a board under the drum.
Important! If the packaging is damaged, it is not recommended to use this product.
The room temperature should be at least 15 degrees. Humidity is not allowed, because it causes fungi and mold to develop. It is also necessary to check whether there are any rodents in the warehouse.
From time to time it is recommended to check the product for mechanical damage. Since, if they are present, this can significantly reduce the service life of the product and lead to unpleasant consequences.
You might be interested in this Description of the KG cable
Important! Transportation is carried out only in a special truck, where the drum is placed using a loader. Next, the coils need to be secured with cables so that they are not damaged.
Proper storage
Do not try to drag or roll the coils on the ground yourself, as this may damage the outer rubber layer.
Manufacturers of PV-1 cable
At the end of 2022, there are more than fifty enterprises producing cable products in Russia. Experienced professionals recommend choosing factories that have been operating for a long time and have impeccable reviews. Below are a number of leading factories that supply worldwide.
"Belaruskabel"
The factory was founded in 1950 of the last century. Today it produces a huge number of cable products. There are more than 50,000 macro sizes of products in stock. The company actively cooperates with countries in Europe and Asia. They work in the agricultural industry, aircraft engineering, instrument making, etc.
Production process
"Rybinskkabel"
The plant was founded in 1949. During its existence, the company founded many branches throughout the country. The plant is famous for its high-quality products at fairly reasonable prices.
Important! The manufacturer offers an individual approach to even the smallest order. More than 25,000 thousand types of standard sizes available
"Kavkazkabel"
The company was opened in 1975. There are currently more than 35,000 thousand types of sizes in stock. The company has won regional competitions many times and has received many awards and commendations. Actively cooperates with European countries.
Section table
"Sevkabel"
One of the oldest factories, founded in 1879. The range includes more than 30,000 thousand macro-sizes of wires. By the end of 2020, the company plans to complete modernization. The latest equipment is installed in the workshops, and the plant also has its own testing center. Therefore, all products are of high quality. The plant has many awards and positive reviews.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the PV1 wire can be used not only for residential premises, but also in industry and aircraft construction. The product has proven itself to be excellent for permanently connecting devices.
How to choose the right PV-1 cable
Before purchasing, you must rely on the conditions of use and permitted loads during the energy transfer process. If conductors with a smaller cross-section than necessary are used, overheating may occur. Because of this, the outer sheath will melt and the wire will fail. When purchasing cable products, you must visually inspect them and check for damage to the insulation.
The same inspection must be carried out after transporting the cable or immediately before installation. This can be done by testing the wire.
Also, before purchasing you must request a certificate of conformity. It must indicate the plant itself, the length of the cable and the date of its production, and a seal about passing the tests. Correct cable products are manufactured in accordance with GOST standards.
The process of laying in a groove
When checking the certificate, you need to pay attention to the name of the manufacturer, which must be written in full, as well as the expiration date of the document.
Important! It is advisable to choose high-quality factories that have been on the market for more than 10 years. Therefore, before purchasing, you can read reviews about the best sellers of cable products.
How to choose the right PV 3 wire
When purchasing a wire from a little-known manufacturer, it is worth testing it. How to do this is indicated in the previous chapter. If the product is presented by a reputable manufacturer, then the consumer is unlikely to purchase a low-quality product. Naturally, such a wire will cost more. The cost of purchasing a high-quality wire will be more than recouped by trouble-free operation for many years.
Several domestic enterprises in the electrical industry produce high-quality wire products. These are plants such as Spetskabel, Moskabelmet and MTPC. Manufacturers provide a 2-year warranty on the PV 3 wire. Practice shows that cables of this brand last an average of 15 years.
PV cable 3
The design of the PV 3 cable is a single stranded copper core twisted into one bundle. Its feature is high strength and good flexibility, as well as high electrical conductivity.
PV 3 insulation is made of polyvinyl chloride. The color range is very diverse: the manufacturer offers white, yellow and black cords. If the wire is used for grounding, the color of its coating will be yellow-green.
Scope of application
The use of PV 3 cord is quite common in many areas of the manufacturing industry. For example:
- in communication systems;
- to create individual electrical conductive networks;
- for installation of conductive paths, both in the apartment and in open space.
A double layer of insulation will protect the user from adverse situations. The cord is excellent for working with high levels of electricity and is most protected from external factors, and therefore is often used in open, unprotected places.
Technical specifications
The PV 3 cable is resistant to moisture, steam and condensation, which makes it indispensable in such a working environment. It is perfect for use in damp environments: baths, saunas, and bathrooms.
The cable can easily withstand temperatures from +60 to – 70, therefore it is an indispensable PV in extreme conditions.
During the manufacture of the wire, a special component is added, due to which it emits an unpleasant odor that repels pests. It also copes well with mold, and thanks to its shell, if damaged, it does not allow sparks to pass beyond the affected area.
Laying conditions
Due to the strong insulation and the presence of one core, it is often laid directly without any bends in order to avoid damage that could lead to disruptions in the transmission of electricity, cause overheating or the appearance of microcracks in the core itself. For its installation, adapters are often used (in those places where cables such as PV 5 or PV 6 can be bent) in order to avoid unpleasant consequences. Quite often the cable is used as grounding.
Advantages and disadvantages of PV 3 wire
Like any conductor, PV 3 has its pros and cons. Positive sides:
- The conductor has an average level of flexibility, which is quite enough to solve many installation problems where PV 1 and PV 2 would perform poorly.
- Excellent resistance to external factors due to the insulating layer and polyvinyl chloride. A wire with undamaged insulation is not susceptible to water, moisture, mold or temperature changes.
- The presence of fire retardants in the insulation - special substances that extinguish themselves. If a wire catches fire due to a fire, its insulation will not begin to burn and will prevent the flame from spreading.
- Low cost. PV 3 wire is quite cheap compared to its analogues, which makes it even more attractive in the cable and wire products market.
- The guide is not afraid of rodents. This is possible due to the fact that the insulation is impregnated with a special substance that repels insects and mice.
Among the disadvantages of the wire, the following stand out:
- One layer of insulating coating.
- Mechanical memory of the core. If the cable has been lying twisted for a long time during use, it is not recommended to unbend it.
Storage of PV 3 in reels
Scope of application of wire PV-1
Taking into account the presented features, it is necessary to note good insulation parameters and low electrical resistance. Products in this category can be used to create power lines and connect a ground loop. Movement of the conductor during operation should be prevented. The lack of armor implies limited resistance to mechanical stress. There is no shielding, so the possibility of negative influence of electromagnetic interference must be taken into account.
For installation, you can use grooves in building structures, specialized cable ducts, corrugated and solid pipes. If the distance between supports is large, it is recommended to use trays and other supporting structures. It is necessary to correctly evaluate resistance to high temperature influences. This product does not belong to the series of non-flammable cables, which are designated by a special addition in the abbreviation - “ng”.
Wire PV 4
The PV 4 cord is designed as follows: copper wires twisted together into one wire, covered with a bright-colored insulating layer, used to turn on electrical mechanisms and lay lighting paths, as well as for assembling electrical circuits. PV 4 is much more flexible than its predecessor PV 3, so the cable is used in places where this flexibility is needed.
The insulation of PV 4 is single-layer. Electrically conductive cores are manufactured in accordance with GOST 22483.
The insulation tone is one-color. The buyer can choose the color of the cord from those presented by the manufacturer (red, yellow, green and others). Like all grounding cables, PV 4 has a green-yellow color.
PV 4 for grounding has a yellow-green color.
Scope of application
When working with PV 4, moderate temperatures should be observed. If work takes place in a cold room or during the winter season, then it is better to use PV-HL.
This species does not like moisture, so it should be placed indoors or with protection in the form of a canopy.
The cord differs from others in its high flexibility, therefore it is most often used in the distribution board. It is also indispensable for connecting electrical equipment to the network.
The wire is very popular in lighting installations. The cable is suitable for connection to a power supply, as well as for wiring inside a luminous object.
Technical specifications
The PV 4 cord differs from the others in the following characteristics:
- rated alternating voltage should not exceed 450 Volts;
- rated direct voltage should not exceed 1000 Volts;
- minimum temperature of use - -50 degrees Celsius;
- maximum temperature of use - + 70 degrees Celsius;
- bending radius - 5 outer diameters of the wire;
- The insulation resistance upon acceptance is 1 MOhm, and during operation it is at least 10 KOhm.
The length of the wire reaches 100 meters. PV 4 favorably tolerates vibrations and negative mechanical influences.
| Cross-sectional area, sq.mm | Number and diameter of wires | Weight kg/km | Nominal outside diameter | Max outer diameter |
| 0,5 | 16*0,20 | 8,65 | 2,14 | 2,6 |
| 0,75 | 24*0,20 | 11,63 | 2,4 | 2,8 |
| 1 | 32*0,20 | 14,3 | 2,54 | 3 |
| 1,5 | 21*0,30 | 20,61 | 3 | 3,5 |
| 2,5 | 46*0,26 | 32,44 | 3,9 | 4,2 |
| 4 | 56*0,30 | 48,56 | 4,2 | 4,8 |
| 6 | 84*0,30 | 72,6 | 5,1 | 6,3 |
| 10 | 77*0,41 | 116,76 | 6,6 | 7,6 |
The manufacturer provides a warranty on the wire for at least 2 years. The actual service life of PV 4 reaches 15 years.
Installation wires
Again about nuclear waste and fears
Where does Moskabelmet deliver?
Icebreakers encountered electrical installation errors
This group includes wires with copper and aluminum conductors intended for electrical installations in lighting and power networks, as well as for installation of electrical equipment.
Brands, design elements and applications
| Wire brand | Design features | Application area |
| Automatic reclosing | Wire with aluminum core with polyvinyl chloride insulation | For installation in steel pipes, hollow channels of building structures, on trays, etc., for installation of electrical circuits |
| PV1 | Wire with copper core and PVC insulation | Same |
| PV2 | Wire with copper core with PVC insulation, flexible | For installation of sections of electrical circuits where wire bends are possible |
| PVZ | Wire with copper core with polyvinyl chloride insulation of increased flexibility | Same |
| PV4 | PVC insulated copper wire, highly flexible | For installation of sections of electrical circuits where frequent bending of wires is possible |
| APPV | Wire with aluminum conductors with polyvinyl chloride insulation, flat with dividing base | For non-flexible installation |
| PPV | Wire with copper cores with PVC insulation, flat with separating base | Same |
| APBPP | Flat wire with two aluminum cores with plastic insulation and a sheath made of polyvinyl chloride plastic. | For fixed installation in lighting networks |
| PBPP | Flat wire with two copper cores with plastic insulation and a sheath made of polyvinyl chloride plastic. | Same |
| PBPPz | The same with the grounding conductor | Same |
| PUNP | Flat wire with copper cores, plastic insulation and PVC sheath | Same |
| PRKA | Wire with a copper core with an insulating and protective sheath made of silicone rubber | For fixed installation in devices and devices with increased operating temperatures |
Wires of the APV, PV1, PV2, PVZ, PV4, APPV, PPV brands are produced in accordance with GOST 6223-79, PRKA wires in accordance with TU 16.505.317-76. Wires of the ABPPP, PBPP, PBPPz and PUNP brands are produced in accordance with TU 16.K80-08-89, TU 16.K 13-020-93 and according to manufacturers’ documentation.
Wires of the APV, PV1, PV2, PVZ, PV4, APPV, PPV, PBPPz brands are intended for use in networks with rated alternating voltage up to 450 V with a frequency of up to 400 Hz or direct voltage up to 1000 V, the rest with plastic insulation in networks with rated alternating voltage 250 V with a frequency of 50 Hz, wires of the PRKA brand in networks with a rated alternating voltage of up to 660 V.
The long-term permissible temperature of the current-carrying conductors of wires with plastic insulation should not exceed 70 °C, for wires of the PRKA brand - 180 °C.
Wire design parameters
| Wire brand | Number of cores | Range of nominal sections, mm | Class lived |
| Automatic reclosing | 1 | 2,5-16/25-120 | 1/2 |
| PV1 | 1 | 0,5-10/16-95 | 1/2 |
| PV2 | 1 | 2,5-95 | 2 |
| PVZ | 1 | 0,5-1,5 2,5; 4,0 6,0-95 | 2 4 3 |
| PV4 | 1 | 0,5; 0,75/1,0; 1,5/2,5; 4,0/ 6,0; 10 | 5/4 or 5/5/4 or 5 |
| APPV | 2 or 3 | 2,5-6,0 | 1 |
| PPV | 2 or 3 | 0,75-4,0 | 1 |
| APBPP | 2 | 2,5; 4,0 | 1 |
| PBPP | 2 or 3 | 15-25 | 1 |
| PBPPz | 3 | 1,0-2,5 | 1 |
| PUNP | 2/2 or 3 | 1,0/1,5-6,0 | 1/1 |
| PRKA | 1 | 0,5-2,5 | 1 |
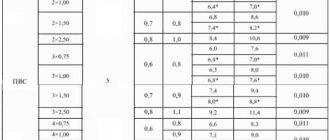
Nominal insulation thickness of wires of APV, PV, APPV, PPV brands, mm
| Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | Thickness values |
| 0,5-1,0 | 0,6 |
| 1,5 | 0,7 |
| 2,5-6,0 | 0,8 |
| 10; 16 | 1,0 |
| 25; 35 | 1,2 |
| 50; 70 | 1,4 |
| 95;120 | 1,6 |
The nominal thickness of the dividing base of wires of the APPV and PPV brands is 0.5 mm, the width is 1.0 mm.
The nominal insulation thickness of wires of the ABPPP and PBPP brands is 0.5 mm, the sheath thickness is 0.8 mm, for wires of the PUNP brand - 0.5 mm and 0.7 mm, respectively.
External dimensions of wires of APV, PV brands, mm
| Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | Wire brand | |||
| APV,PV1 | PV2 | PVZ | PV4 | |
| 0,5 | 2,4 | — | 2,6 | 2,6 |
| 0,75 | 2,6 | — | 2,8 | 2,8 |
| 1,0 | 2,8 | — | 3,0 | 3,0 |
| 1,5 | 3,3 | — | 3,4 | 3,5 |
| 2,5 | 3,9 | 4,2 | 4,2 | 4,2 |
| 4,0 | 4,4 | 4,8 | 4,8 | 4,8 |
| 6,0 | 4,9 | 5,4 | 6,3 | 6,3 |
| 10 | 6,4 | 6,8 | 7,6 | 7,6 |
| 16 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 8,8 | — |
| 25 | 9,8 | 9,8 | 11 | — |
| 35 | 11 | 11 | 12,5 | — |
| 50 | 13 | 13 | 14,5 | — |
| 70 | 15 | 15 | 17 | — |
| 95 | 17 | 17 | 19 | — |
| 120 | 19 | — | — | — |
External dimensions of wires of APPV and PPV grades, mm
| Number and nominal cross-section of cores, mm2 | Thickness | Width | Number and nominal cross-section of cores, mm2 | Thickness | Width |
| 2x0.75 | 2,6 | 6,4 | 3x0.75 | 2,6 | 10,2 |
| 2x1.0 | 2,8 | 6,8 | 3x1.0 | 2,8 | 10,8 |
| 2x1.5 | 3,3 | 7,8 | 3x1.5 | 3,3 | 12,3 |
| 2x2.5 | 3,9 | 9,0 | 3x2.5 | 3,9 | 14,1 |
| 2x4.0 | 4,4 | 10,0 | 3x4.0 | 4,4 | 15,6 |
| 2x6.0 | 4,9 | 11,0 | 3x6.0 | 4,9 | 17,1 |
External dimensions and weight of PUNP wires *
| Number and nominal cross-section of the core, mm2 | Thickness, mm | Width, mm | Weight, kg/km |
| 2x1.5 | 3,6 | 9,5 | 56 |
| 2x2.5 | 4,0 | 10,3 | 74 |
| 2x4.0 | 4,8 | 11,8 | 110 |
| 3x1.5 | 3,6 | 15,5 | 80 |
| 3x2.5 | 4,0 | 16,5 | 110 |
Weights of wires of APV, PV brands, kg/km
| Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | Wire brand | ||||
| Automatic reclosing | PV1 | PV2 | PVZ | PV4 | |
| 0,5 | — | 8,5 | — | 9 | 10 |
| 0,75 | — | 11 | — | 12 | 12 |
| 1,0 | — | 14 | — | 14 | 15 |
| 1,5 | — | 20 | — | 20 | 20 |
| 2,5 | 16 | 30 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| 4,0 | 21 | 45 | 48 | 48 | 48 |
| 6,0 | 29 | 65 | 69 | 70 | 70 |
| 10 | 47 | 110 | 115 | 115 | 120 |
| 16 | 66 | 170 | 180 | 180 | — |
| 25 | 110 | 270 | 280 | 290 | — |
| 35 | 150 | 370 | 380 | 380 | — |
| 50 | 200 | 490 | 520 | 520 | — |
| 70 | 270 | 700 | 710 | 730 | — |
| 95 | 370 | 970 | 980 | 990 | — |
| 120 | 440 | — | — | — | — |
Weights of wires of the APPV, PPV brands, kg/km
| Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | Wire brand | |
| APPV | PPV | |
| 2x0.75 | — | 22 |
| 2x1.0 | — | 30 |
| 2x1.5 | — | 40 |
| 2x2.5 | 32 | 62 |
| 2x4.0 | 43 | 92 |
| 2x6.0 | 58 | — |
| 3x0.75 | — | 33 |
| 3x1.0 | — | 45 |
| 3x1.5 | — | 60 |
| 3x2.5 | 48 | 94 |
| 3x4.0 | 64 | 140 |
| 3x6.0 | 87 | — |
Manufacturers
- CJSC "NO!" suppliers of hazardous products - On the prohibition of the use of wires of the brands PUNP, APUNP, PBNG, etc. according to TU 16.K13-020-03 (Material for TC No. 17/2007) - Notice of cancellation of TU 16.K13-020-93 - Electrical and fire hazardous wires - a universal and reliable option instead of dangerous PUNP If you have not found information on the products you are interested in, contact the forum and you will certainly receive an answer to your question. Or use the form to contact the portal administration.
For reference: The “Directory” section on the RusCable.Ru website is intended for informational purposes only. The directory was compiled by sampling data from open sources, as well as information coming from cable manufacturers. The section is constantly updated with new data and improved for ease of use.List of used literature:
Electrical cables, wires and cords. Directory. 5th edition, revised and expanded. Authors: N.I. Belorussov, A.E. Sahakyan, A.I. Yakovleva. Edited by N.I. Belorussov. (M.: Energoatomizdat, 1987, 1988)
“Optical cables. Manufacturing plants. General information. Structures, equipment, technical documentation, certificates" Authors: Larin Yuri Timofeevich, Ilyin Anatoly Aleksandrovich, Nesterko Victoria Aleksandrovna Year of publication 2007. Publishing house "Prestige" LLC.
Directory "Cables, wires and cords". Publishing house VNIIKP in seven volumes, 2002.
Cables, wires and materials for the cable industry: Technical reference book. Comp. and editing: Kuzenev V.Yu., Krekhova O.V. M.: Publishing House "Oil and Gas", 1999
Cable products. Directory Author: Aliev I.I., 2nd edition, 2004
Installation and repair of cable lines. Electrician's Handbook Edited by A.D. Smirnova, B.A. Sokolova, A.N. Trifonov 2nd edition, revised and expanded, Moscow, Energoatomizdat, 1990