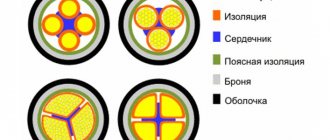
Application
Before the advent of corrugated electrical pipes as a material for hidden wiring, cables were buried in walls, covered with plaster, and the open edges were screwed to a support or passed through a metal pipe. This significantly complicated the dismantling and repair of the electrical network in the event of problems such as a short circuit - to remove the cable it was necessary to break the seam.
The corrugation for cables is also hidden in grooves (a gap in the wall for wiring) and covered with mortar, but the wire itself remains free, and if necessary, it can be easily removed by pulling the free edge. In addition, automotive corrugation is flexible, lightweight, environmentally friendly and affordable. Two characteristic advantages of this material deserve special attention:
- Fire safety. Corrugations made of self-extinguishing PVC (flammability degree B3 according to GOST 30402-96) not only do not burn themselves, but also prevent the spread of fire when the wiring catches fire, shrinking around the cable and limiting the flow of oxygen.
- The corrugation provides additional moisture insulation for electrical wiring, which is important for rooms with high humidity.
It appeared on the construction products market relatively recently, but, thanks to its beneficial properties, it almost immediately became very popular.
Corrugated pipes (corrugations) for electrical wiring.
Design
A corrugated pipe is a hose with specially shaped walls used to protect wires from external damage. The shape of the pipe is obtained by connecting rings of different diameters and thicknesses together. Thanks to the dense outer rings, the pipe has high rigidity, which ensures its resistance to lateral loads, and the inner, thinner rings retain flexibility, allowing an angle of 90˚ to be obtained during routing.
For the manufacture of electrical corrugation, self-extinguishing polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as well as composite low-pressure propylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are most often used. The characteristics of all these materials do not differ much. All of them are resistant to moisture, corrosive destruction, do not rot, some do not burn or melt. They retain their practical characteristics at temperatures from -25˚C to +95˚C. To distinguish them from each other, you can focus on the color of the tube: red or orange HDPE corrugation is more resistant to fire than black or blue, and PVC is almost always gray.
Color and type of corrugation
The first thing to note is the color of the corrugation. No one ever paints a corrugated sleeve on purpose, except in isolated cases of its decorative use.
Moreover, each color indicates the material from which the product was made.
- gray color is PVC - polyvinyl chloride
To ensure that it looks perfectly smooth and beautiful when mounted on the ceiling, experienced electricians advise buying it not in twisted coils, but in whips.
- black and orange color is HDPE - low-density polyethylene
- blue color PP – self-extinguishing polypropylene
Technical characteristics of PVC, HDPE, PP corrugated pipes:
PVCHPNDPP
PP
Many have probably come across beautiful photos and videos where black and orange corrugations spread across the ceiling.
Everything looks beautiful, no doubt about it. And HDPE corrugated material itself, although it costs a little more, is much stronger than PVC. Although it all depends on the brand.
This simplifies its installation and eliminates the possibility of accidental damage. However, such beauty is a ticking time bomb.
The danger is that both orange and black corrugations support combustion very well.
In this case, a fire in an apartment may not start due to a short circuit or overload in the electrical wiring. And now imagine that your entire ceiling is simply covered with such material.
It is enough for one tube to catch fire and the fire will be of such a scale and category that there will be nothing left of the apartment or house.
Your main task will not be to put out the fire, but at least to get out of there safe and sound. And the chances will be slim, given the fiery rain of burning molten polyethylene.
In addition, it is this corrugation that will cause the fire to move from one room to another. In those places where the wiring passes through a concrete wall into another room, the flame can easily penetrate there by spreading the combustion of the HDPE corrugated hose. There will be no problems with PVC.
Because as long as it is exposed to fire, it burns. As soon as the fire is removed, it immediately goes out, because... does not support combustion.
Therefore, gray PVC corrugation should be used in apartments and houses. Multi-colored can be used for embedding into walls and concrete, but not for open laying.
Black HDPE corrugation can and should be used outdoors. Not gray, but colored.
It was created to provide protection from ultraviolet radiation. PVC will crack over time and will not provide protection.
But don’t listen to all sorts of stories from installers that it’s ideal to use colored marks to wire low current and power circuits.
For the installer, this may be convenient during the work process, but you will have to live with this fire-hazardous material for the rest of your days.
Kinds
According to the conditions of installation and location, electrical corrugations are divided into the following types:
- Thin-walled sleeves. The lightest and therefore less resistant to mechanical stress pipes. They are used for both external and internal installations that do not involve pressure on the corrugations: frame structures made of plasterboard, suspended and tensioned ceilings, protection of wiring in cars, etc. As a rule, here the corrugated wires are simply laid out or tied to a support using bundles.
- Heavy pipes with increased strength. Capable of withstanding high mechanical, adhesive and climatic loads. Most often used for installing wiring in the ground, concrete and plaster.
- Extra heavy metal corrugations for wiring. Provide maximum protection against wiring damage. They are used in places that require the highest level of security: educational, medical institutions and other places with high traffic.
All pipes have approximately the same dimensions:
- outer diameter – from 16mm to 50mm;
- internal diameter - approximately 11.0 mm to 40.2 mm depending on material.
Corrugated cables are sold in coils from 25 to 100 meters long and in sealed packaging. As a rule, manufacturers put inside the wire of the appropriate length necessary for pulling cables, which is also called pulling.
Metal corrugation
Purpose
The main purpose of the cable corrugation is to protect the conductor located inside. However, depending on the operating conditions of the electrical wiring or the technological processes used, the purpose of each specific brand may differ.
For example, in case of contact with flammable substances or when laying electrical wiring indoors where smoke is not allowed, brands of corrugated pipes with fire retardants or made of metal are used. The first of them lead to self-extinguishing of the source of fire, while the second does not undergo combustion at all.
Hard shell grades are designed to provide additional resilience in the event of mechanical stress. For example, when laying wiring inside a plasterboard wall, where drilling can damage the integrity of the insulation.
Rice. 1. Impact of mechanical forces when pouring concrete
When poured into a concrete floor or other structures, the corrugation is designed to protect the cable from being compressed by the mass of the screed. It also simplifies subsequent replacement if necessary. In case of possible flooding, the corrugation is designed to seal and protect against moisture.
In the case of external installation, it serves as protection against direct exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation. Accepts the role of a damper of thermal expansion and contraction when environmental parameters change.
However, note that the presence of corrugation does not guarantee mechanical resistance to a hammer drill or shovel impact. There are a number of impacts under which the cable will still be damaged and become unusable. It is also necessary to take into account the type of product and the conditions of its use. Since an incorrectly selected corrugation will not be able to protect the cable or will not fully perform its functions.
Selection
To select an electrical corrugation of a suitable size, it is customary to rely on the diameter based on the following recommendations:
- for connecting thin wires to sockets or installing alarms, computer and telephone networks - 16mm;
- for connecting consumer devices and installing coaxial networks – from 20mm;
- for laying cables between distribution boxes – 25 mm;
- for connecting electrical panels - from 32mm;
- for laying cables between floors - 40-50 mm.
Examples of wire and corrugated pipe sizes
Depending on the conditions for which corrugations are used, they can be classified into two groups: for open and closed installation.
The first ones are intended for wiring installed inside walls, partitions, ceilings, and false structures of a similar profile. Based on fire safety, they are conventionally divided into three categories:
- Any pipes can be used for installation in non-combustible structures (concrete, brickwork, monolithic construction, etc.). In recent years, requirements have been developed for the use in the construction of infrastructure and social structures made of material that is resistant to fire and prevents its spread.
- For use in hollow frame structures made of non-combustible materials, it is allowed to use flame retardant PVC and LDPE corrugations.
- For installation inside flammable structures and ceilings (walls made of flammable materials, roofing, wood-clad concrete and brick walls, etc.), only pipes made of fire-resistant material are used. Plastic corrugation is prohibited for use in such places.
Electrical corrugations for open laying of cables for application and installation are divided into five main categories:
- For laying on non-combustible structures indoors (concrete, brick, slabs, etc.), any plastic corrugations are used.
- In rooms with flammable materials, it is permitted to use pipes made of flame retardant material subject to special rules. If the cable insulation is made of flammable material, laying is carried out at a distance of at least 10 cm from the surface of the flammable material, for example, from a wood-lined wall. If a cable with fire-resistant insulating material (VVGng, NYM, etc.) is used, the corrugation can be laid in close proximity to the combustible base.
- Street or outdoor installation. Fire safety requirements require the use of pipes made of fire-resistant material, and external environmental conditions require the use of rigid, dense pipes that are temperature-resistant. Corrugations made of polyamide (HDPE) and polyethylene (LDPE) meet both requirements.
- In rooms with a high fire hazard, only corrugated pipes made of flame retardant materials can be used, the exact requirements for which are specified in the design documentation.
- To lay wiring in explosive buildings, you can use metal and corrugated materials made of special materials that protect the premises from the magnetic field of the electrical network. Plastic pipes are prohibited for use in such areas.
Dimensions and cost
The choice of corrugation size depends primarily on the diameter of the cable and the number of its cores. Let's summarize this data in a single table:
| Wire cross-sectional area, mm | Number of wires, pcs | External diameter of corrugation, mm |
| 1.5 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 16,16, 20,20 |
| 2.5 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 16,16, 20,25 |
| 4 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 20,20,25,25 |
| 6 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 20,25,32,32 |
| 10 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 25,32,32,40 |
| 16 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 32,32,40,40 |
| 25 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 32,40,50,50 |
| 35 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 40,50,50,63 |
| 50 | 2, 3, 4, 5 | 50,50,63, 63 |
| 70 | 2, 3, 4 | 50,63,63 |
| 95 | 2,3 | 63,63 |
| 120 | 2 | 63 |
| 150 | 2 | 63 |
In addition, the choice of corrugation size depends on the area where the electrical wiring is laid:
- To sockets and switches - at least 20mm;
- For lighting devices and sensors - from 16mm;
- From the main distribution box or panel - at least 25mm;
- The connection between two panels is at least −32mm;
- The groove in the ceiling of the floors is a rigid corrugation with a diameter of at least 40 mm;
- Telephone, antenna, Internet and other low-current cables - from 25mm.
Prices
The price of corrugation depends on the material, size, color, purpose and technical characteristics. To summarize, the cheapest is flexible plastic corrugation for interior decoration, and the most expensive is metal.
It is sold in bays of 50 and 100 meters. You can find products in pieces, they are more expensive.
It is better to purchase material in specialized stores. There is no need to skimp on safety issues.
Let's summarize the approximate cost of products in a general table:
| Name | Type | External diameter | Inner diameter | Price per meter, average |
| PVC corrugation | light | 16 mm | 11.4 mm | 2.4 RUR |
| Black corrugated HDPE protective pipe | DKS | 15.7 mm | 11.3 mm | from 7.5 rub/m |
| Black corrugated HDPE pipe | DKS | 19.5 mm | 14.5 mm | from 8.9 rub/m |
| Red double HDPE pipe (two-layer) | tough | 50 mm | 41.5 mm | 78.5 rub/m |
| HDPE pipe is heavy | heavy | 31 mm | 23.4 mm | from 9.7 rub/m |
| PPL (polypropylene) corrugated tube | light | 19.7 mm | 14.8 mm | from 28 rub/m |
| Corrugated pipe polyamide | black | 21.2 mm | 16.8 mm | from 52 rub/m |
| Galvanized metal hose | metal | 20mm | 18mm | From 32rub/m |
Installation procedure
Laying electrical wiring using corrugated wires has some specific features that can cause difficulties for an inexperienced person. In order to avoid difficulties, it is recommended to adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
- The first step is to calculate the size of the wiring and cut the pipe to the required length. If metal corrugation is used, you will need metal scissors, and a polyvinyl chloride or polymer tube can be cut with a regular knife. Using side cutters or nippers, the broach is also shortened. It should be remembered that the wire is under tension and to prevent it from jumping inside, it should be held with your hand before cutting, and then bent. If a piece of the broach is missed, it will be necessary to make another cut to remove it.
- Now you need to pull the wiring through the corrugation. To do this, a rope or twist is created, fastened to a broach. Some craftsmen suggest lubricating the cable to make it easier to put on the corrugation, but for a beginner this can only complicate the process.
- The next step is installation of the corrugation on the surface of the construction site. Plastic clips or mounting tape are used for fastening. It should be noted that it is not recommended to lay the cable over a single piece of pipe longer than 25 m. The main thing is to secure the material from sagging. Wiring to switches or distribution boxes must be done so that the edge of the corrugation fits into the housing and does not leave the wiring visible.
Advantages and disadvantages of corrugated pipes
Such products have both pros and cons. The advantages are as follows:
- durability. The pipe can last more than 50 years, without loss of properties;
- moisture resistance;
- non-flammability;
- provides cable protection over a wide temperature range;
- light weight. This facilitates transportation and installation;
- chemical resistance;
- plastic is an excellent dielectric;
- allow you to quickly access a damaged cable;
- versatility (suitable for wires, sewers);
- flexibility. For connection, of course, corners, fittings and other elements may be useful, but in general, corrugated pipe can be laid even in places with differences in relief;
- protect the contents from mechanical damage, moisture, fire and other influences;
- rust resistance. Unlike its stainless steel counterpart, a plastic corrugated pipe actually lasts for decades.
You might be interested in: Features of heat shrink tube
As for the disadvantages, it all depends on the material of the pipe. Some products do not tolerate mechanical stress well, others do not tolerate elevated temperatures. To eliminate undesirable consequences, a specific corrugation is used in each area. The downside that all corrugated products have in common is difficulty in cleaning (a lot of dust collects between the ribs over time).
Important! PVC corrugation, despite a large list of advantages, cannot be used for laying cables on flammable substrates. Therefore, if electrical wiring is done in a wooden house, it is better to choose metal hoses.
Corrugated products have many advantages
How to stretch a cable inside a corrugation
To pull the wiring inside the corrugation, you need to connect it with a pulling wire. For this purpose, a so-called tourniquet is created. To prepare a group of wires, they should be tightly wrapped along their entire length. It is best to use PVC electrical tape for this - a smooth surface will not create additional obstacles. A single cable does not require such preparation.
The next step is to fasten the broach and the harness. This can be done in several ways:
- Wrap the wire tightly around the bundle and crimp it with pliers. It is better to make several such twists at a distance of several centimeters from each other.
- You can attach the wire to the bundle and wrap electrical tape over it. Sometimes this method is effectively combined with the previous one.
- When laying a single cable, you can carefully pierce its insulation at a distance of 4-5 cm from the edge and hook the wire into the hole.
Before you start pulling, the edge of the bundle is wrapped with electrical tape so that you get a smooth cylinder that will not cling to the walls of the corrugated pipe.
After this, the process of “putting” the corrugation on the cable begins. It is most effective to carry out this operation together - so that one person holds the broach, and the second one pushes the tourniquet. If there is no assistant, you will have to do this:
- The free end of the structure must be secured or tied to something to hold it.
- Holding the pipe taut with one hand, push the tourniquet inside with the other. At the same time, it is important not to overtighten the structure so that the broach does not jump off the harness. If this happens, you will have to cut off the worn part of the corrugation and tie it again. The result may be a pipe made up of several pieces; it is convenient to wrap the joints with insulating tape.
Be sure to watch the video. It's useful.
Corrugation. Use when laying on the floor/ceiling
macoi2, Wikipedia and Greenpeace are other sources of information. Wikipedia states that “The main problem associated with the use of PVC is the difficulty of recycling it. When PVC is completely burned, only the simplest compounds are formed: water, carbon dioxide, hydrogen chloride. However, normal incomplete combustion of PVC can produce carbon monoxide and toxic organochlorine compounds.[2][3][4]” supported by three references. Two of which are broken, and the third leads to an article where directly, with references to research and EU legislation, all the horror stories that Greenpeace collected in its propaganda and which you quoted here are refuted. Wikipedia does not say anything bad about PVC itself: we are talking about the process of burning waste on an industrial scale, where all kinds of shit are burned mixed with all sorts of shit and in the process, yes, carbon monoxide and toxic compounds can be formed. Or they may not be formed. That is, Wikipedia, as it were, did not lie, but presented the information in such a way as to suggest the danger of PVC.
Greenpeace is an interested party that feeds on the “fight for the environment.” In itself, this might not be bad if it were not outright business (racketeering of industrial companies and developing countries). For this, Greenpeace, as we see, does not hesitate to stoop to outright lies.
1. “PVC is one of the most problematic polymers invented by man” is an obvious lie. 2. “Not recyclable” is a lie. The PVC label contains a recycling symbol. PVC recycling itself is a whole industry. PVC waste is purchased as recyclable materials on an industrial scale. 3. “made from a carcinogenic gas, vinyl chloride” - and chlorethylene is also a strong poison, extremely explosive and flammable. Which says nothing about the properties of PVC itself. Just like table salt that you eat is not hydrochloric acid in its properties, being its derivative. The widespread use of PVC in everyday life (including children's toys and refrigerator parts), even in ecology-obsessed countries, confirms this. 4. “When burned, this polymer releases the most powerful poisons known to man - dioxins” - a double lie. a) Burning MAY release dioxins. To do this, generally speaking, you need to burn any chlorine-containing compounds along with various organics. When pure PVC is burned as such, the following are formed: water, carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid. Dioxins are released in nature during volcanic activity and forest fires. Special large-scale studies were carried out in the EU and the USA to prove the connection between the burning of PVC in garbage and the by-product appearance of dioxins. No connection found. When burning garbage, they do not appear because of PVC. acc. with a German study commissioned by the European Commission, only 30% of dioxin emissions come from waste processing (garbage in general, not PVC), 36% from industrial emissions (34% of which from pesticide production), 21% from fires. b) Dioxins are not “the most powerful poisons known to man.” This is what they are for guinea pigs. In humans, acute poisoning with large doses causes skin problems (acne, suppuration), signs of liver and kidney damage. Long-term: mild changes in metabolism and hormone levels. It is not at all the same as the effect of deadly poisons, which cause rapid death in terrible writhing. 5. “They accumulate both in the environment and in the human body, and are practically not excreted” - a lie. Dioxins in nature decompose within 10-20 years. Their traces have been found in fossil materials dating back to a period when no PVC existed. In the human body they accumulate in adipose tissue, slowly decompose (at approximately the same speed as in nature) and are excreted from the body. 6. “can cause disorders of reproductive functions and lead to cancer” - again a fraudulent distortion. a) The risk of developing cancer for people exposed to high doses of dioxins for 20 years, 100-1000 times higher than permissible, increases by 1.2-1.4 times. For comparison, the risk of developing cancer for a pack-a-day smoker is 4-5 times higher than for a non-smoker. Moreover, it has been discovered that dioxins do not have a direct carcinogenic effect; they act as a catalyst for the action of other carcinogens. And let me remind you that we are talking about dioxins, and not about PVC, between which no direct connection has been found. b) During the Vietnam War, the Americans massively used defoliants containing dioxins. Both the Vietnamese and the Americans then began to have offspring with disabilities. So the Americans then flooded entire areas with this poison from airplanes, and then polished them with napalm and God knows what else. But much more serious developmental disorders are provoked by the usual ingestion of alcohol. This has been known for a long time. And there is nothing, no panic or excitement about this. But a PVC pipe, which has absolutely no connection with the mentioned poisons (only by the common chemical elements in its composition) is, of course, horror and a reason for paranoia.
Recommendations
To create durable and safe wiring, when selecting and installing electrical corrugated pipes, you should be guided by the following recommendations:
- Avoid creating sharp corners. There should be no more than 2-3 of them (with an angle of 90˚) per 20-25 m of working material.
- When installing a long network, solid pieces of corrugation should be connected to each other by transit boxes, installing them at the corners or places close to the middle of the solid pipe.
- In monolithic construction, when heavy series metal corrugation is used, it is laid before pouring, fixing it to the metal structures. Wiring is carried out after the walls have been formed and hardened.
Why do you need corrugation?
Nowadays, most often the wiring is laid in a plastic corrugation.
This allows, firstly, to compensate for the deformations of the wires that are inevitable when the building shrinks and, secondly, to provide high-quality protection of the wiring from any external influences, including mechanical damage, steam and moisture. In addition, the corrugation will protect workers finishing the premises from possible electric shock, for example, if they spill primer on the wiring or catch it with a spatula. In newly built private houses, wiring must be laid with extreme caution, as the building shrinks. In this case, the corrugation acts as an additional strength factor.