In electrical installation work, one of the most important stages in the work is connecting the equipment. The successful operation of the entire complex of electrical installations at the enterprise depends on the correct execution of all operations at this stage. Before connection, power lines and cables, control circuit wires (secondary switching circuits) are laid. These circuits connect various elements of equipment with a control panel and a protection system. After installation is completed, individual wires and cables are tested before connection. In this article we will tell you why you need to test wires and cables and look at the main methods.
Basic dialing methods
Detection methods depend on the cable brand and location conditions; with colored insulation of the cores, there are no problems. The cable is connected to the equipment according to the color of the cores on both sides. The difficulty arises when the insulation of all or several cores in the cable is the same color, and the cables are not marked. It is in such cases that a test is carried out, the ends on both sides of the cable are determined to belong to the same core, their integrity is determined, and markings are made.
Basic methods and equipment:
- Continuity tester can be performed by one person within one distribution cabinet and at distances of up to 100m;
- A digital multimeter, used in similar conditions, the device is set to continuity or resistance measurement mode.
- A homemade device with a lamp and batteries;
- Telephone handsets with batteries in the circuit.
- A step-down transformer complete with indicator or measuring instruments.
conclusions
So, one more time.
If you are solving the problem of cable testing, then you need a test set. Some of the most popular sets in Russia are, for example, sets 701k-G, 701K-G/6A. If you choose a separate tone generator, then the choice must be made based on the functionality and characteristics of these devices. See also:
What is better for cable testing: a headset, a handset or a test kit?
How to quickly put the cross in order? Identification of subscriber ports on the cross with little effort!
The most complete guide to choosing a twisted pair cable tester!
Wiring continuity tester
Historically, at the initial stage of development of electrical engineering, a tester was called a pointer combined device, which includes:
- Voltmeter;
- Ammeter;
- Ohmmeter.
Then other options were added to modern devices, an electronic thermometer, light and sound indication elements, and controls and application methods were improved. As a result, instead of the old dial tester, it was replaced by its modern analogue, a digital multimeter with a liquid crystal display for displaying readings. One of the functions of the tester is wire continuity testing (checking the integrity of the wire).
Pointer combined device Ts 4342-M1. In order to ring a wire with a pointer tester, you need to carefully study the capabilities of the device, how to connect the measuring probes and in what position to put the switches on the control panel.
Familiarize yourself with the discrete division of the scale; the controls and scales are different on devices of different models. Let's consider the wire testing technique using the example of a pointer tester Ts 4342-M1:
- Set the batch switch of measurement modes to the 1 kOhm position, some models have Ohm.
- Turn on the fuse button, protecting the calibrated elements of the device circuit from incorrect connection. If in continuity mode the circuits are energized.
- Press the forward and reverse current measurement mode buttons, two black buttons at the bottom of the control panel;
- Connect the probe wires to the center and right terminals to measure resistance;
- To check the functionality of the device, connect the probes to each other, the arrow on the scale should move from left to right until it stops. Measurements are carried out on a scale marked kOhm, second from the top. If the arrow moves to the right towards zero, the device is working.
The advantages of this tester are reliable protection and measurement accuracy, but in case of continuity, it works as an indicator device. Accurate readings are not required here; the following can be considered disadvantages:
- the difficulty of setting the controls to the desired mode;
- large dimensions;
- Large measurement error when batteries are discharged; supply voltage should be within 3.5 - 4.5 V.
Checking the integrity of the wire in a coiled cable
To test wires in short cords or a coiled cable, just strip the insulation on the wires at both ends and start measuring:
- Connect the probe to a wire of a certain color, the second probe is connected to a similar wire at the other end. If the arrow deviates to the zero position of the scale, the wire is in good condition.
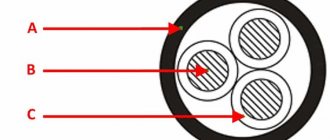
Testing a cable with colored wires, schematic connection of probes to single-color wires at different ends of the cable. A – cable insulation. B – Individual cable cores with colored insulation.
- With single-color wires or a laid out cable, where the distance does not allow the tester to work with different ends at the same time, all wires at one end are shorted together.
- On the other side of the cable, connect the probe to one wire and call all the other wires through it, in turn 1,2,3....
The disadvantage of this method is that it is not possible to isolate each core individually and label it. This must be done when the cable is rolled up in one place or using a transformer.
Insulation check
To test insulation with a megohmmeter or multimeter, the principle of continuity is the same as when searching for an electrical connection between the cable cores.
The testing algorithm is as follows:
- set the maximum range on the device - 2000 kOhm;
- connect the probes to the wires and see what the device display shows. Considering that the wires have a certain capacitance until it is charged, the readings may vary. After a few seconds, the device display can display the following values:
- one, this indicates that the insulation between the wires is normal;
- zero – there is a short circuit between the cores;
- some average readings, this can be caused either by a “leak” in the insulation or by electromagnetic interference. To determine the cause, switch the device to the maximum range of 200 kOhm. If the insulation is faulty, the display will display stable readings; if they change, then we can confidently talk about electromagnetic interference.
Attention! Before checking the insulation of the electrical wiring, it must be de-energized. The second important point is that when taking measurements, do not touch the probes with your hands, this can introduce errors.
Video: Wire continuity check - integrity check.
Testing wires with a multimeter
The probe with the black wire is inserted into the connector with the ground symbol (housing), red above, into the connector for measuring resistance with the Ohm symbol “ Ω”. The disadvantage of many digital multimeters in dial mode is the delay in the sound indicator signal when touching the contacts. It is necessary to fix the probes on the wire for 2-3 seconds to make sure there is contact. This inertia in operation creates some difficulties in checking the integrity of the wire.
Multimeters of the UNI-T type have good performance in dialing mode; the sound indicator operates almost instantly when the contacts are closed.
Comparison table of characteristics of Fluke-179 and UNI-T UN61 multimeters
Please note that for all instruments it is advisable to use probes with gold-plated rods. Unlike steel ones, they are not subject to oxidation and provide reliable electrical contact.
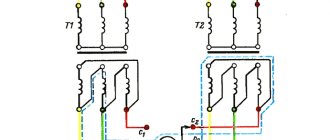
Continuity using a transformer
This method is effective for testing unrolled laid cables with wires of the same color. In this case, step-down transformers are used with different voltages at the taps of the secondary winding.
- The primary winding of the transformer is connected to a 220V AC source;
- The beginning of the secondary winding to the ground loop, to which the cable shield is closed;
- The remaining secondary winding taps with different voltages to the ends of the wires;
- On the other side of the cable, a multimeter is used to measure the corresponding voltage between the ground loop and the cable wires. Thus, the integrity of the core is checked and marked.
The multimeter is set to AC voltage measurement mode. It is recommended to use devices from Western manufacturers, since in this case the measurement mode is used, not the indication mode. Chinese S-99 type multimeters are very poorly calibrated; inaccurate voltage measurements can lead to errors when marking the cable. Therefore, for tapping a cable using a transformer, where voltage measurements are made, it is better to use a pointer device of the Ts-4342-M1 type.
Characteristics of the combined device Ts 4342 M1:
| Accuracy class | 2,5/4,0 |
| measurement ranges | |
| DC current in mA | 0,05 — 2500 |
| AC current in mA | 0,25 — 2500 |
| Voltage, DC | 0,1 — 1000 |
| Variable voltage in volts | 1,0 — 1000 |
| DC resistance in kOhm | 0,3 — 10000 |
| signal level when measuring voltage in dB(-) | -10 to+15 |
| frequency range in Hz | 45 — 2000 |
| Power supply | autonomous |
| Dimensions in mm | 215*115*90 |
| Weight in kg | 0,9 |
| operating temperature | from -10 to +40°С |
When taking measurements, you need to carefully look at the inscriptions with symbols. Summary table of main parameters for different models of multimeters:
| Model | LCD screen | U— | V~ | I— | I~ | R | The dial is connected. | Diode testing | Transistor testing |
| M830B | 7 segments 3.5 digits | 0.1mV - 1000V | 0.1V - 700V | 0.1mA- 10A | — | 0.1W-2mW | — | * | * |
| M830 | 7 segments 3.5 digits | 0.1mV - 1000V | 0.1V - 700V | 0.1mA- 10A | — | 0.1mW - 2mW | * | * | * |
| M832 | 7 segments 3.5 digits | 0.1mV - 1000V | 0.1V - 700V | 1mA- 10A | — | 0.1W-2mW | * | * | * |
| M838 | 7 segments 3.5 digits | 0.1mV - 1000V | 0.1V - 700V | 1mA- 10A | — | 0.1W-2mW | * | * | * |
To set the multimeter to the AC voltage measurement mode, you need to set the batch switch for changing modes in the sector with the “ V ~” icon to the maximum value within which measurements are taken. In our case, this will be any measurement limit greater than 20V; the wires from the probes are installed in the same connectors as when measuring resistance.
Making calls using handsets
The advantage of this method is that it is convenient to ring unrolled cables with wires of the same color. At the same time, electricians can communicate with each other. The disadvantage is that one person cannot do the work this way.
You will need two handsets and one battery, 4.5 volts is enough.
- Connect a 4.5 V battery into the microphone wire coming out of the handset. (Polarity does not matter). The main thing is that the current is constant and stable, without ripples, if not a battery is used, but a rectifier from an industrial network.
Connecting the power source to the handset, please note that polarity does not matter, the main thing is that the battery is connected to the circuit in front of the microphone.
- Connect the end of the wire connected to the capsule to the shielding sheath of the cable, the second to one of the cores;
- On the other side of the cable, the second tube is connected with one wire to the shielding sheath. The second wire is connected to different wires in turn until the installer at the other end of the cable responds.
Connecting tubes to a cable for wire testing; the positive wire can be connected to the shielding sheath on the cable or to the metal pipe in which it is laid. But it must be taken into account that the pipe must be solid or have electrical contact with a common ground loop for both sides of the cable.
Tip #1. To make the design easier, use a microphone headset from cell phones; in some cases this is very convenient.
Diagram for connecting micro headphones to a handset instead of a telephone capsule.
PART 4: Ethernet Speed Qualification Testers
Let's consider the capabilities of devices for speed qualification using the Softing NetXpert XG2-PLUS as an example.
The tester confirms the ability of a cable line (twisted pair, single-mode and multimode optics) to support the declared data transfer rate necessary for the smooth operation of Ethernet applications, enterprise automation systems, connected devices and machines. Operates at speeds: 100 MB, 1 Gbit, 2.5 - 5 Gbit, 10 Gbit.
The quality of cable installation and the environment in which it is located greatly influence the speed and accuracy of transmitted information. The device transmits real Ethernet data between the main and active remote units, which are installed on both sides of the communication line. This measures bit errors, signal propagation delay, and signal-to-noise ratio. A number of basic parameters are also checked: cable length (twisted pair and optical), pinout of the RJ45 connector, correct installation of the copper line, and even losses in the optical cable. The cleanliness of optical connectors can be checked using the optional video microscope.
The tester helps implement and maintain PoE devices powered over twisted pair cables: surveillance and security cameras, various sensors, access points, wired phones and other peripheral equipment. The device, simulating a powered device, measures the real voltage and power that reaches it and helps determine the problem segment: the PoE source, cable or device itself.
The device is capable of connecting to active networks via twisted pair, optical and Wi-Fi, while displaying the network configuration, connected devices and their names, it checks the functionality of DNS and DHCP servers, detects virtual VLANs, and tracks the data route. It also tests device availability using the Ping function and identifies problems associated with duplicate IP addresses. To increase service life, the device is equipped with a replaceable RJ45 port.
The device allows you to generate reports on the results of testing twisted pair, optical fiber and optical connectors in one software.
Market analysis showed the absence of domestic equipment manufacturers for such tasks. The set of functions of the Softing NetXpert XG2 PLUS tester is unique in its kind and has no analogues. Other testers do not combine in one device the capabilities of qualifying copper and optical lines, measuring the length of twisted pair and optics, measuring optical losses, troubleshooting twisted pair installation errors, testing PoE with load simulation, connecting to active networks over copper, optics and WiFi, perform the Ping function, track the data route. A good advantage is the replaceable RJ45 connector for connecting to the line, which significantly increases the service life of the device.
Comparison of Ethernet Speed Qualification Testers
| NetXpert XG2-1G NetXpert XG2-5G NetXpert XG2-10G | NetXpert XG2-PLUS | LinkIQ | |
| Manufacturer | Softing IT Networks | Softing IT Networks | Fluke Networks |
| Main unit of the tester | 1 PC | 2 pcs | 1 PC |
| Remote active block | 1 PC | 1 PC | |
| Remote passive block | 1 PC | ||
| RJ45 patch cords | 2 pcs | 2 pcs | 1 PC |
| Storage and transportation | case | case | bag |
| Speed qualification up to 1 Gbps | NX-XG2-1G (copper) | copper/optics | copper |
| Speed qualification up to 5 Gbps | NX-XG2-25-5G (copper) | copper | copper |
| Speed qualification up to 10 Gbps | NX-XG2-10G (copper) | copper/optics | copper |
| Cable qualification parameters and testing: | |||
| Ethernet Speed Qualification | 1G to 10G (copper) | 10G (copper/optics) | 10G (copper) |
| Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) Test | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Number of bit errors (BERT) | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Signal delay offset per pair | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Optical fiber length measurement | option | ♦ | |
| Fiber Loss Measurement and Trend | option | ♦ | |
| Video microscope for optics | option | option | |
| Active remote block support | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Cable length (maximum) | up to 457 m | up to 457 m | up to 305 m |
| Cable length (method) | TDR/capacity | TDR/capacity | TDR |
| Distances to cable break | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Distances to short circuit | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Confused and split couples | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Colored RJ45 pinout diagram | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Signal generator (analog) | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Signal generator (digital) | ♦ | ||
| Remote ID support | up to 24 pcs | up to 24 pcs | up to 7 pcs |
| Replaceable RJ45 port | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Active Ethernet Network Testing: | |||
| Network connection interfaces | RJ45/SFP/Wi-Fi | RJ45/SFP/Wi-Fi | RJ45 |
| Network connection status and speed | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| PoE testing up to 90W with load | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| LLDP/CDP protocol support | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| VLAN Discovery | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Finding the Switch Port Port ID | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Network structure, device display | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Ping to one IP or list of addresses | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Support for IPV4 and IPV6 protocols | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Checking the operation of DHCP and DNS | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Traceroute - data route | ♦ | ♦ | |
| PoE testing: | |||
| Polarity, type and class of PoE | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| PoE power and voltage | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| IEEE 802.3af PoE (Type 1, 15.4 W) | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| IEEE 802.3at PoE+ (Type 2, 30 W) | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| IEEE 802.3bt PoE++ (Type 3, 60 W) | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| IEEE 802.3bt PoE++ (Type 4, 90 W) | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Reports and PC communication: | |||
| PDF report format | ♦ | ♦ | ♦ |
| Open CSV format | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Editable: MS-Excel, XML | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Initial test data: ".tst" | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Loading a company logo into a report | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Saving to external USB drive | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Interface for saving reports | USB type A | USB type A | USB type C |
| Memory, number of tests | > 100 000 | > 100 000 | 1 000 |
| Firmware update | ♦ | ♦ | |
| General characteristics: | |||
| Interface (twisted pair) | RJ45 (Cat 6A) | RJ45 (Cat 6A) | RJ45 |
| Interface (optics) | SFP 10G - 2 pcs. | SFP 10G - 2 pcs. | |
| Wi-Fi (2.4 and 5 GHz) | ♦ | ♦ | |
| Port voltage protection | 60 VDC/50 VAC | 60 VDC/50 VAC | ♦ |
| Display | 1024 x 600 | 1024 x 600 | 800 x 480 |
| Operating temperature | -10°C to 60°C | -10°C to 60°C | 0°C to 45°C |
| Dimensions | 245 x 177 | 245 x 177 | 216 x 114 mm |
| Weight | 1.2 kg | 1.2 kg | 624 g |
| Code: | NX-XG2-1G | NX-XG2-PLUS | LIQ-100 |
Testing the cable with an indicator device with a light bulb
To do this you will need any power supply, a 1.5 battery; 4.5 or 9 Volts, wires with alligator clips and a lamp for the appropriate voltage.
Assembly of the circuit and procedure for use:
- Wires are soldered to the battery terminals;
- In the break of one of the wires, the polarity does not matter, connect an LED or a lamp;
- The dialing process is carried out using the same method as with a tester or multimeter. In this case, if the conductor is intact, instead of the arrow deflecting or the reading on the liquid crystal display, the light will light.
Such an indicator device allows you to test cables over distances of several hundred meters, depending on the state of charge of the battery.
Connection diagram for an indicator device with a light bulb for cable testing.
Tip No. 2 During installation work, when the lamps are constantly moving, it is recommended to use an LED. It is less susceptible to mechanical stress than a conventional incandescent lamp with a spiral and a glass bulb.
The most common mistakes made when testing cables
- Incorrect setting of measurement modes or connection of probes to the sockets of the multimeter or tester. On old pointer testers, the operating mode switch is set to the 1 kOhm position, on modern devices in the dialing mode, with a diode or buzzer sign;
- When testing wires using a step-down transformer, use a pointer tester to check the power source. The voltage should be from 3.5 to 4.5 volts, otherwise the voltage will be measured with a large error;
- Before testing, thoroughly clean the contacts on the cable wires and test leads. Gold-plated contacts do not need to be cleaned; you can wipe them with cotton wool and industrial alcohol.
- When using pointer instruments, do not confuse the scale when measuring; it should be for alternating voltage with the sign “V~”.
- When testing wires in the distribution cabinet harnesses, the contacts on both sides must be disconnected from all elements of the equipment.
- Technical characteristics of PRKA wire
Methods
Testing methods depend on the purpose for which it is performed. To check the integrity of the cable for a break or electrical connection between its wires (short circuit), the continuity test can be done with a tester based on a battery and a light bulb, or you can use a multimeter for this purpose. The latter is preferable.
Despite the fact that the price of a multimeter is higher than a primitive device, we recommend buying it; this device will always be useful in the household.
The simplest device for testing an electrical cable
To check the cable, the multimeter must be turned on in the appropriate mode (diode or buzzer image).
Multimeter set to dialing mode
The testing methodology is as follows:
When checking a wire for a break, the tester is connected to its ends as shown in the figure. If the cable is intact, the light will glow (when testing with a multimeter, a characteristic sound signal will be heard).
Checking for a break
Explanations for the picture:
- A – electrical cable;
- B – cable cores;
- C – power source (battery);
- D – light bulb.
If the cable has already been laid, then on one side it is necessary to connect the wires together and ring the wires at the other end;
Second option for checking the power cable
when checking the presence of an electrical connection between the cable cores, the tester probes are connected to different wires. Unlike the previous example, there is no need to twist the wires on the other side. If there is no short circuit between the wires, the light will not light (when testing with a multimeter, no beep will sound).