Current relays are special devices that are installed on electrical transformers, electric motors, devices for industrial needs, etc. Their main purpose is to protect the circuit from overloads and short circuits.
Current relays are special devices that are installed on electrical transformers, electric motors, devices for industrial needs, etc. Their main purpose is to protect the circuit from overloads and short circuits. If such a relay is missing, then damage to the wires, insulation failure and other malfunctions are possible, which can ultimately lead to an emergency or lead to a complete or partial breakdown of the circuit.
About the features of operation
A current relay closes and opens an electrical circuit at specific current levels. It is a plastic case with a round or rectangular rod on which a copper wire with a dielectric varnish coating applied to it is wound, as well as additional components responsible for the full operation of the relay.
Used in electrical circuit diagrams and electronics. The product is a logical element of a circuit that closes and opens it under certain conditions.
Relay components and operating principle
Reel _ Works according to the laws of electromagnetic induction. When voltage is applied, the coil attracts the relay contact, completing the circuit. If the value of the current in the circuit drops below the nominal value for which the coil is designed, then the magnetic force becomes insufficient to close the relay and the contacts open, thereby de-energizing the operating circuit or switching the flow of electricity from one circuit to another.
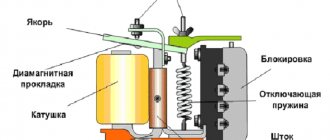
Core . A component that becomes a magnet when voltage is applied, attracting or releasing contacts.
Rod . An oblong, rectangular or rounded component on which the coil is wound, and the core is also fixed.
Movable anchor . A mechanism that makes and opens contacts.
Contact group. They act as an input/output of electricity from the network into the relay circuit. Minimum quantity is one pair. In more complex relay designs there may be several pairs of them. When the relay contacts open, the voltage on them disappears, which leads to the opening of the entire electrical circuit.
Spring. Component of a movable anchor. Necessary to return the contact to its original position when the relay opens.
Coil power supply . A control contact that is powered from a secondary network that is not related to the consumer network.
Phase voltage is supplied to the incoming relay contact. In the normal state, the coil is energized and, due to the magnetic field, closes its contact, which is part of the moving armature. When the current decreases, the magnetic field of the coil weakens and the armature contact due to the spring returns to the open state, thereby opening the circuit passing through the group of input and output contacts. The consumer power supply circuit or its section is de-energized.
Operating principle
Operating principle of an electromagnetic current relay
An electromagnetic device is activated by an electromagnetic connection created when alternating current flows through a coil and causes attraction of both halves of the core. This seemingly simple action hides some nuances:
- the spring on the moving part prevents the two halves from approaching each other;
- it is possible to overcome its resistance only with a certain current strength in the coil;
- this value is the main indicator characterizing the operation of the current relay.
When a current appears in the coil, an EMF is induced in the core, due to which the halves are attracted, but not completely - a spring prevents them from doing this. When it reaches a certain value, the EMF becomes so large that it overcomes its resistance.
To return the system to its original position, the current in the relay will need to be reduced to a certain value, depending on the return coefficient. This indicator is related to the design features of current and voltage relays and is adjusted for each of them individually. To do this, it is enough to adjust the spring tension, which you can do yourself.
Main types and technical characteristics
Due to the fact that relays are used for different purposes, since the control and power supply circuits for consumers are also different, magnetic relays are divided into several categories.
General characteristics for each relay type:
- Sensitivity: the current strength at which the relay is activated, breaking the circuit.
- Coil winding resistance.
- Closing current: the minimum current to operate the electromagnet that closes the relay;
- Opening current: the minimum opening current of the relay contacts;
- Operating frequency at operating load: how many times the relay can operate at rated load per unit time.
Contact and non-contact relays
Based on the principle of influencing the network, relays are divided into the following categories.
Contact. The relay opens and closes using internal contacts mounted on a special armature. Such devices are used mainly in switchboard circuits that power electric drives and various installations.
Contactless. A relay designed not to de-energize a circuit, but to abruptly change its operating parameters: a decrease or increase in current, voltage or resistance. At the same time, the contactless relay device does not have internal contacts, but operates using electronic elements. Such relays can often be found in electronic circuits that control its logical part.
By control signal power
This refers to the sensitivity of the relay. The higher the actuation power, the lower the sensitivity of the relay operation. There are:
- High power relay: more than 10 watts.
- Medium power relays: from 1 to 9 Watts.
- Low power relay: up to 1 watt.
By speed
This refers to the speed at which the relay operates when closing and opening:
- Free-running relay: less than 1 thousandth of a second;
- Fast action: from 1 hundredth to 5 hundredths of a second;
- Adjustable: the ability to independently set the relay response speed.
By type of control voltage
As you know, the network can be of alternating and direct voltage. Accordingly, relays are produced for the appropriate type of electrical circuit: there are relays for direct and alternating voltage.
According to the degree of protection from external factors
External factors affecting the operation of the relay may be moisture, dust, ambient temperature values and the possibility of physical contact of the device with various external objects.
So, according to the degree of protection, relays are divided into:
- Sealed. They do not allow air and moisture inside. The internal device is sensitive to the external environment, upon contact with which the performance of the relay components may be lost.
- Covered. Also protected from external factors, this may be a fire hazardous room or a place where devices dangerous to the relay are operating.
- Open. They are used in a safe environment where there is no access to moisture and there is no possibility of physical contact with heavy objects.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any element, relays have their advantages and disadvantages, however, despite the disadvantages, in some cases it is simply impossible to do without the use of these devices.
pros
- Simple design
- Easy to repair, you can always disassemble it to clean contacts or replace individual elements
- Low contact resistance
Minuses
- Limited resource due to mechanical elements used
- Contacts sometimes burn out
- Low speed when triggered, unlike semiconductor elements, a mechanical device is a hundred times slower than an electronic device, but the trigger speed is still quite high
- Possible contact rattling if there is insufficient voltage on the coil
- Clicking noise when switching
Types of contact groups
According to the type of contact groups, relays can be either closing or breaking circuits. Closing relays are usually used to open the main circuit. The contacts that open at this time activate the secondary circuit. The contact groups of various relays have their own resistance in the closed state. This resistance is called stable.
A relay can have one pair of contacts or many. However, they all operate according to the same principle: magnetic induction attracts them and the circuit closes; when voltage is lost, the relay contacts open. Contacts are also divided into normally open, closed and changeover.
About electromagnetic relays
Neutral relays perceive, according to the same principle, direct current directed along opposite sides of the winding.
Advantages:
- low prices (much cheaper than semiconductor models);
- does not require cooling, since little heat is released and the voltage across the contacts has a slight drop;
- high quality electrical insulation;
- resistant to impulse loads and interference caused, for example, by a lightning strike when switching circuits of high-voltage lines;
- the ability to connect a load of up to 4 kW if the relay volume is below 10 cm3.
Flaws:
- malfunctions and problems in the case of connecting inductive devices and DC loads;
- the appearance of radio interference in the case of power contacts;
- the resource reserve is small;
- low speed mode.
About differential relays
Such relays are used for domestic and industrial needs. Their role is to prevent current leaks in wiring and equipment. Devices that require protection are office equipment, boilers, household appliances, and lamps. These relays will be able to protect the user from electric shock if they come into contact with the body of the device itself.
About integrated electric relays on microcircuits
The basis of such relays is made up of semiconductor elements. They are stable in operation even with strong vibration, therefore very practical.
Purpose and connection methods
TR is the main component of all protective devices installed in power circuits. Based on this, the features of using the device should be considered.
Its main purpose is to serve as an executive element as part of circuit breakers, residual current devices and many similar devices. In accordance with this, the scope of their application in conjunction with the devices indicated above is determined.
- Power circuits of high-voltage lines and the protective equipment included in them.
- Switching distribution boards, in which TRs are included separately or as part of other devices.
- Household single-phase inputs and distribution (linear) devices installed within household panels.
In accordance with the purpose of the switching devices, their connection circuits are selected.
To connect a relay machine to existing electrical networks or other circuits, several methods can be used. They differ according to the type of equipment protected:
- three-phase asynchronous motors;
- consumers included in 380 Volt power networks;
- loads connected at the output of circuits with a supply voltage of 220 Volts.
In accordance with the first of these points, TRs are used as electromagnetic releases that disconnect the circuit when operating currents exceed the permissible level. When installed in three-phase circuits, they perform the same function, but with a wider range of functionality. As releases, they are part of powerful contactor devices and electric starters.
Relays installed in input (linear) circuit breakers and RCDs have a slightly different purpose. Here they perform the function of sensitive elements that provide operation at a current cutoff (set point). When turned on, they are configured for such extreme operating conditions as overcurrent, short circuit and leakage.
Application
Voltage current relays are used in situations where there is an overload in the supply environment. As a rule, devices in such networks are divided into two classes: devices with priority, and the category of non-priority devices.
The first type includes devices that are computers, equipment for shooting or storing certain data. As for non-priority devices, this includes additional appliances and household technology products. This circumstance is the main reason for installing a relay, it prevents network overload, and also eliminates its subsequent shutdown.
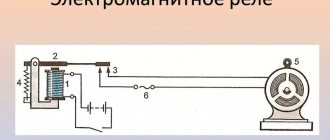
Current relay device
It is most convenient to get acquainted with the design features and operating principle of a current relay (CR) using its most common type - an electromagnetic device.
Unlike induction and electronic analogues, the design of an electronic protective device allows you to visualize how it works.
Any solid-state current relay contains the following mandatory elements:
- Magnetic core (core), consisting of 2 parts and having a constant or adjustable air gap.
- A frame with a coil located on the stationary part of the core.
- A spring placed on its movable half and creating a counter moment when the relay is activated.
Connection Guide
There are many connection methods to suit different devices. To install relays for EPP model devices used in relay protection systems, you need to perform the following steps:
- turn off the power;
- install a relay on the bus located in the control panel;
- connect the power supply, taking into account the technical documentation;
- pass the cable using the measured line through the through channel for connecting the relay;
- connect the alarm supply to the required contacts of the current monitoring device, taking into account a certain order;
- setting the necessary parameters on the device current scale.
Rules for choosing a voltage relay for an apartment or house
It is necessary to approach the choice of RKN wisely, because the device is responsible for the safety of the network and electrical appliances. Correct operation of the relay is only possible if the technical specifications are selected correctly. When choosing a voltage relay, you must consider:
- maximum load current and phase connection type;
- maximum consumer power;
- operating voltage range;
- protection response time;
- type of control (digital and electromechanical);
- degree of device protection;
- reliability (reviews about the manufacturer and model).
The main parameter when choosing a device is the maximum permissible current. You should choose a model one level of protection higher than the circuit breaker installed in the distribution board. If the maximum breaker current is 32A, then the relay should be 40A.
Tip: you should pay attention to additional functions, such as digital display of voltage, device temperature, ability to control time, etc.
Scheme
A current relay, designed to disconnect a non-priority circuit when the permissible limit is exceeded, is used in cases where at least two consumers are connected to the network and perform work autonomously.
To connect a relay of this type, you need:
- connect voltage to the zero terminal and phase;
- connect the low priority circuit to a specific terminal and zero;
- connect the high priority line to the contact and neutral wiring.
Systems with a similar design also have time relays, which are an additional device in such situations.
Checking and adjusting the intermediate relay
These devices require periodic checking and adjustment. In this case, you need to know the basic provisions. To reduce the operating voltage and slow it down, you need to reduce the initial distance between the armature and the core. Reducing the final distance reduces the return voltage and also delays the return.
If the number of closing contacts increases and the springs are tightened, the voltage increases and the return is delayed. In this case, an increase in the number of break contacts leads to a delay in the response time, as well as an increase in voltage.
Using these basic rules, you can select the appropriate method for changing the relay values. At the same time, it is worth considering that these methods affect the operation of contacts.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=d6BA3PFlwCU
Operating principle of RMT
Using the example of the operation of the REO-401 relay, you can clearly understand the principle of operation.
Main design elements of the REO-401 current relay
The coil is connected at its ends to an open circuit; when current flows through the winding, an electromagnetic field is induced, which, when the set current threshold is reached, pushes the rod out of the tube in the center of the coil. The core presses on the rod, which moves the closing plate, compressing the spring, after which the circuit opens. As the current drops, the spring pressure on the plate weakens, and the plate again closes the gap in the circuit. Read also the article ⇒ Voltage relay.
The magnitude of the response threshold in this embodiment is regulated by the depth of immersion of the tube with the core into the cylindrical hole of the coil. The tube is screwed in or out of the coil, thus adjusting the response threshold. In some designs, the tube moves freely inside the coil and is secured with a clamping screw.
This example shows the classic version, where the principle of operation of the relay is clearly visible; there are many models with other designs and additional functions. The basic principle in all options is the same: when the set maximum current threshold is exceeded, the relay disconnects the circuit from the power source.
Tip No. 1 It is recommended to install the current relay in a distribution cabinet; this is convenient and simplifies the process during repair or replacement.
How does the device work?
When the controlled current value set by the users is exceeded, a special microcontroller opens the circuit. In case of severe overvoltage (25%), the system will automatically turn off the power until the voltage in the network normalizes.
If there are no sudden surges in electricity for 5-20 minutes, the device will automatically connect to the network. If the electricity is unstable for 10 minutes and turns off three times, the device will be blocked. It can only be started in manual mode.
News: most read
- Vulcan Million and its capabilities
- Kuzbass residents will be able to get preferential mortgages under the new program
- Online betting on eSports at GGBET
- How to bet on Dota 2?
- Over six months, corporate clients of VTB Bank deposited more than 40 billion rubles into their accounts
- Tomsk Pisanitsa will celebrate Maslenitsa on a grand scale
- Ksbet – eSports online
- "Pitfalls" of a credit card
- Houses to be demolished
- Extreme entertainment in Moscow
(Visited 64 times, 1 visits today)
Safety precautions
A current relay can not only protect the device from breakdowns, but also cause harm to health. This happens in cases where people neglect safety rules and do not take into account the recommendations of experienced specialists.
Required Security Measures:
- Any work on adjusting or checking the current relay should be carried out in compliance with safety precautions.
- Only highly qualified employees with extensive experience in such work have the right to carry out repair or preventive measures.
- Only people who are familiar with the device instructions and safety regulations can install the relay.
- It is prohibited to carry out repairs while the device is connected to the network. Otherwise, there is a high risk of electric shock, which can cause serious health problems.
- You cannot use a device that has visible damage to one or more elements.
- Before turning on the equipment, it is necessary to check all current relay contacts for damage and any defects. If they are detected, the problem should be carefully eliminated using special tools or their equivalents.
- Any worn-out structural part must be immediately replaced with a new one.
- Do not use the protective device when there is strong vibration or excessive dust.
- The device should not be used to protect equipment operating in areas with high humidity or a high probability of ingress of any liquid.
- Some active chemical vapors and gases can destroy the insulating layer. Because of this, it is not recommended to connect the relay in potentially hazardous areas.
- It is prohibited to use the protective relay in rooms where flammable and explosive materials are stored.
- The protective device can only operate at temperatures from -20 to +40 degrees Celsius and humidity not exceeding 80%.
- All components of the structure must comply with standards and be correctly labeled. If any inappropriate element is used, an emergency may occur, which will entail many additional problems.
A minimum current relay is an effective protective device that helps avoid operating equipment with low network performance. When used correctly and following all the recommendations of specialists, you can significantly increase the operating life of the device and avoid any problems.