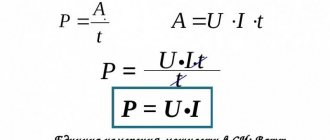What is power consumption?
Power consumption is a numerical measure of the amount of electrical energy required for the operation of an electrical appliance or converted by it during operation. For static devices (stove, iron, TV, lighting), current energy turns into heat during operation). During conversion (electric motors), the energy of electric current is converted into mechanical energy.
The basic unit of electrical power is Watt, its numerical value
P = U × I,
where U is voltage, Volts, I is current, amperes.
Sometimes this parameter is indicated in V×A (V×A for imported equipment), which is more correct for alternating current. The difference between Watts and VA for household networks is small and can be ignored.
Electrical power consumption is important when planning wiring (the cross-section of the wires depends on it, as well as the choice of ratings and the number of circuit breakers). During operation, it determines the costs of maintaining the home.
Formula for calculations
How to calculate electrical energy consumption
All data necessary to be substituted into the formula for calculations can either be measured or taken from the characteristics of the instruments used.
For your information. If the passport data indicates the value of cos ϕ, it means that the electricity received by the device will have a reactive component. This also needs to be taken into account when calculating.
The formula for calculation is:
P = I * U * cos ϕ,
Where:
- I – current in amperes;
- U – voltage in volts;
- cos ϕ – phase shift.
In the case of an active load, the phase shift is not substituted into the formula, and it has the form:
P = I * U.
The problem of proper operation of the household electrical network
From a constructive point of view, the household electrical network has been developed to a high degree of perfection: its normal operation does not require special knowledge.
The network is designed for certain operating conditions, the violation of which leads to complete or partial failure, and in severe cases, to a fire.
The condition for proper operation is the absence of overload.
At the same time, the load capacity of sockets and the consumption of equipment connected to them are measured in different units:
- for sockets this is the maximum permissible alternating current (6 A for traditional Soviet sockets of old housing stock, 10 or even 16 A for European-style sockets);
- connected equipment is characterized by power, which is measured in Watts (for powerful devices, larger units are indicated instead of Watts: kilowatts (1 kW = 1000 W), which allows you to avoid confusion with numerous zeros).
Hence the need arises:
- determining the relationship between power and current;
- finding the power of an individual electrical appliance.
The relationship between Watts and Amps is simple and follows directly from the definition of Watt above. The task is simplified by the fact that the voltage of a working household network is always the same (220 or 230 V). From here, power is always found along the current.
We use an electric meter
The third method is that almost all metering devices are equipped with a light indicator; the number of flashes means some kind of power consumption imp/kW.
We disconnect all consumers in the apartment, leaving only the device of interest connected. Within 15 minutes, we count the pulses and multiply by four (to get the number per hour). Having found out the figure, divide it by imp/kW and find out the power of the unit.
You can also record the meter reading and turn on the electrical appliance whose consumption we are trying to determine for some time, preferably for an hour. We record new readings, subtract the old ones from them, and as a result we find out the approximate power.
How to determine?
To solve the problem of finding power, you can use various methods. All of them are available for use even with knowledge of physics and electrical engineering at the school curriculum level.
More often, power is found by determining the current; sometimes you can do without intermediate procedures and determine it immediately.
We look at the technical passport
Typically, the power consumption is indicated in the passport or description of the device and is duplicated on the nameplate. The latter is located on the rear wall of the case or its base.
If there is no description, this parameter can be found on the Internet, for which you just need to search by the name of the device.
The power indicated by the equipment manufacturer refers to peak power and is consumed from the network only at full load, which is quite rare. The resulting difference is considered as a reserve. At the regulatory level, this reserve is determined through the power factor.
Ohm's law to help
The power of most household electrical devices can be fairly accurately estimated experimentally and by calculation using Ohm's law, known since high school. This empirical law relates voltage, current and load resistance R as:
P = U2/R. U = 230 V, and the resistance is measured by a tester. The following is a simple calculation using the formula P = 48,400/R W.
For example, with R = 200 Ohm we obtain power P = 240 W.
The method does not take into account the so-called reactance of the device, which is created primarily by input transformers and chokes, and therefore the resulting estimate is somewhat overestimated.
We use an electric meter
When determining power from a meter, you can proceed in two different ways. In both cases, only the device under test should be powered from the household network. Without exception, all other consumers must be disconnected.
In the first approach, an optical meter indicator is used to measure power, the intensity of its flashes is proportional to the power consumption. The proportionality coefficient is indicated on the front panel in units imp/kWh or imp/kWh, Figure 1, where imp is the number of pulses (indicator flashes) per kilowatt hour.
Figure 1. Front panel of a household electricity meter with optical indicator
After turning on the device under test, you must begin counting the indicator flashes for 15 or 20 minutes. The resulting value is then multiplied by 3 or 4 (for a 20- or 15-minute measurement interval, respectively) and divided by the coefficient from the front panel. The result of the calculation gives the power of the device in kW, which in some cases is conveniently converted into Watts by multiplying by 1000.
Example. For the counter we have k = 1600 pulses per kilowatt hour. With a 20-minute measurement interval, the indicator worked (flashed) 160 times. Then the power of the device will be 160*3/1600 = 0.3 kW or 300 W.
The second approach also uses a 15- or 20-minute time interval, but the energy consumption is determined on a digital scale. For example, with a difference in readings over 20 minutes of 0.2 kW×hour, the power of the unit is 0.2 × 3 = 0.6 kW or 600 W.
Wattmeter
A modern household power meter or wattmeter is convenient to use because:
- it is connected directly to the open circuit, for which it is equipped with a plug and socket, see Figure 2;
- equipped with an easy-to-read digital indicator and equipped with internal automatic adjustment circuits, which eliminates errors in readings;
- has good weight and size characteristics.
The device is ready for use immediately after switching on.
Rice. 2. Digital household wattmeter
Its only drawback is its narrow specialization, so this device is rarely found in the household.
Power measurement devices
To measure P, you can use special instruments. A multimeter is suitable for this, to which you can connect a current clamp. How to measure power with a multimeter? The tester is switched on to the alternating voltage measurement mode; the clamps should grasp only one conductor connected to the load.
Measuring with a multimeter
Separating conductors in a cable is not always convenient. In addition, after measurements you need to calculate the power using the formula.
Power meter
To measure, you can use a special device - a wattmeter. The device is plugged into a power outlet, and the load whose power needs to be measured is connected to its output socket. The results of the measurement are displayed on the display in kilowatts.
Power meter
Measuring power with an electric meter
Using a residential electricity meter, you can also check the power consumption of an individual device. To do this you need:
- turn off all energy consumers, leaving only the device under test in consumption mode;
- note the readings at the current moment and record their values in an hour;
- subtract the latest values from previous readings;
- the result will be a measured value.
The main disadvantage of this block of actions is the shutdown of other necessary household appliances.
Information. When using this method, taking a moment, you can see if there is a hidden current leak and the serviceability of the meter. When all devices are turned off, the electric meter should stop.
Direct current measurement
The methods of that group are characterized by higher accuracy due to the fact that they are based on direct measurement of current. There are two devices for performing this procedure at home.
Metering with current clamps
The most convenient to use are current clamps that do not require breaking the controlled circuit. Designed as a hand-held device with a measuring unit based on a toroidal core. To measure the current, the assembly is opened in the manner of pincer sponges, and then closed to cover the wire, Figure 3. The effective value of the current is determined by the change in the magnetic field, which is recorded by the Hall sensor.
Rice. 3. Measurement with current clamps
Measurement with a tester
The second method is based on the use of a tester, which is switched to ammeter mode and connected to an open circuit. The difficulties of implementing this procedure using simple means make it little popular in practice. We also cannot discount the fact that some tester models do not have current protection and fail (burn out) if the range is incorrectly selected (current overload).
Using Current Clamps
You can also determine the power consumed by a particular device using current clamps. To do this, the current value is measured in one of the wires supplying the device.
So, we have described to you the four most accessible ways to determine the power consumed by electrical appliances in your home. They will help you reliably identify those devices whose appetites are greatest.
Definition
Let's start with the definition of power : this is the work done per unit of time. And it doesn’t matter what kind of work we are talking about, electrical or mechanical. This physical quantity is an indicator of operating efficiency, as well as the amount of energy consumed by an electrical appliance.
Utility bills include the cost of electricity consumption. The following household appliances consume it:
The number of these devices is much larger. And each of them contributes to the amount for your utilities.
For example, the power consumption of your vacuum cleaner is 1 thousand watts per hour . Accordingly, if you vacuum for 30 minutes, it consumes 500 watts. One thousand watts per hour equals one kilowatt per hour. This is a common unit for calculating energy consumption in utilities.
For example, during this month you vacuumed your apartment 6 times for half an hour. Accordingly, the vacuum cleaner worked for 3 hours and consumed 3 kilowatts per hour from the electrical network. The cost of one kilowatt per hour is 3 rubles. This means that you need to pay 9 rubles for the energy that your vacuum cleaner consumed while cleaning the apartment. Using the same principle, your expenses with other electrical appliances are calculated.
Read also: Drawings for a manual jigsaw on wood
It is necessary to calculate power for the following purposes:
- Optimization of costs for consumed electricity.
- Ensuring your safety.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of your work.
Of course, all these calculations are made for different types of this physical quantity. There are two of them:
Let's talk in more detail about each of them.
We carry out calculations
As already mentioned, to begin with, the initial quantities must be brought to a single presented value. The best option is to use “pure” values, that is, volts, amperes, watts.
- Calculation for DC
There are no difficulties here. The formula was shown above.
When calculating power by current:
P = U × I
If the current is calculated based on known power,
I= P/ U
- Calculation for single-phase alternating current
Here there may be a peculiarity. The fact is that some types of loads in operation consume not only ordinary, active power, but also the so-called reactive power. Simply put, it is spent on ensuring the operating conditions of the device - the creation of electromagnetic fields, induction, charging powerful capacitors. It is interesting that this component does not particularly affect the overall electricity consumption itself, since, figuratively speaking, it is “dumped” back into the network. But to determine the ratings of protective automation and cable cross-section, it is advisable to take it into account.
For this, a special power factor is used, otherwise called cosine φ (cos φ). It is usually indicated in the technical characteristics of instruments and devices with a pronounced reactive component of power.
The power factor value (cos φ) on the nameplate of an asynchronous electric motor.
Formulas with this coefficient take the following form:
P = U × I × cos φ
And
I = P / (U × cos φ )
For devices in which reactive power is not used (incandescent lamps, heaters, electric stoves, television and office equipment, etc.), this coefficient is equal to one and does not affect the calculation results. But if for products, for example, with electric drives or inductors, this indicator is indicated in the passport data, it would be correct to take it into account. The difference in current readings can be quite significant.
- Calculation for three-phase alternating current
We will not delve into the theory and types of three-phase load connection diagrams. Let us simply present slightly modified formulas used for calculations under such conditions:
P = √3 × U × I × cos φ
And
I = P / (√3 × U × cos φ)
To make it easier for our readers to make the necessary calculations, two calculators are located below.
For both, the common reference value is voltage. And then, depending on the direction of the calculation, either the measured current value or the known power value of the device is indicated.
The default power factor is set to unity. That is, for direct current and for devices that use only active power, it is left as is, by default.
There probably shouldn’t be any other questions about the calculation.
Calculator for current calculations based on a known power consumption value
Go to calculations
Calculator for calculating power consumption based on the measured current value
Go to calculations
The obtained values can be used for further selection of the necessary protective or stabilizing equipment, for forecasting energy consumption, and for analyzing the correct organization of your home electrical network.
An example of how the parameters for a dedicated line are calculated with the subsequent selection of a circuit breaker is clearly shown in the video below:
Additional recommendations
Quite a lot of things in our lives depend on power. Therefore, we want to give you some tips to help protect and decorate it.
To reduce costs, it is necessary to optimize them. For example, when you leave a room, you can turn off the lights in it. This will reduce energy consumption, and at the end of the month you will receive bills with more pleasant numbers. Besides turning off the lights, there are many other ways to reduce the amount of energy you use.
You can use electrical appliances that consume less power. For example, the cleanliness in your apartment will not become worse if you use a medium-power vacuum cleaner. This also applies to other household appliances. The main thing is that your quality of life does not deteriorate. And this can be done using medium-power devices. After all, they do everything necessary and do not consume much energy.
If you still don’t understand all the details of calculating power, don’t torture yourself. It’s better to use an online calculator or install special applications on your smartphone to calculate it. Remember, in life it is important to save not only energy, but also time.
Electric power calculations are carried out by engineers who develop household appliances. They do this to avoid short circuits and fires. Remember, this is primarily for your safety.
Now you know how to calculate power, and what is the essence of this physical quantity. When choosing a household appliance, you will have an idea of how much power you need to achieve a particular goal. I wish you success!
We use an electric meter
The third method is that almost all metering devices are equipped with a light indicator; the number of flashes means some kind of power consumption imp/kW.
We disconnect all consumers in the apartment, leaving only the device of interest connected. Within 15 minutes, we count the pulses and multiply by four (to get the number per hour). Having found out the figure, divide it by imp/kW and find out the power of the unit.
You can also record the meter reading and turn on the electrical appliance whose consumption we are trying to determine for some time, preferably for an hour. We record new readings, subtract the old ones from them, and as a result we find out the approximate power.
An electronic meter allows you to view all parameters in real time: current, electricity consumption, network voltage, by going through the menu of the metering device. We talked about how to take readings from an electric meter in the corresponding article!
An analogue of an electric meter can be a household wattmeter, with which you can quickly and accurately determine the power consumption of electricity by the device. The video below clearly demonstrates the operation of this device: