Power in an electrical circuit, represents the energy consumed by a load from a source per unit time, indicating the rate of its consumption. Unit Watt
[W or W].
The current strength displays the amount of energy passed over a period of time, that is, it indicates the speed of passage. It is measured in amperes
[A or Am]. And the voltage of electric current flow (potential difference between two points) is measured in volts. Current strength is directly proportional to voltage.
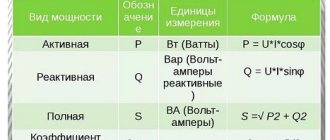
To independently calculate the Ampere / Watt or W / A ratio, you need to use the well-known Ohm's law. Power is numerically equal to the product of the current flowing through the load and the voltage applied to it. Determined by one of three equalities: P = I * U = R * I² = U²/R.
Therefore, to determine the power of the energy source when the current in the network is known, you need to use the formula: W (watts) = A (amps) x I (volts). And to make the reverse conversion, you need to convert the power in watts to the current consumption in amperes: Watt / Volt. When we are dealing with a 3-phase network, we will also have to take into account the coefficient of 1.73 for the current strength in each phase.
How many Watts are in 1 Ampere and amperes in a cotton wool?
To convert Watts to Amps at alternating or direct voltage you will need the formula:
I = P/U, where
I is the current strength in amperes; P – power in watts; U – voltage in volts, if the network is three-phase , then I = P/(√3xU), since it is necessary to take into account the voltage in each of the phases.
The root of three is approximately equal to 1.73.
That is,
in one watt there is 4.5 mAm (1A = 1000 mAm) at a voltage of 220 volts and 0.083 Am at 12 volts .
When it is necessary to convert current into power (find out how many watts are in 1 ampere), then use the formula:
P = I * U or P = √3 * I * U, if calculations are carried out in a 3-phase 380 V network.
This means that if we are dealing with a 12-volt automotive network, then 1 ampere is 12 Watts, and in a 220 V household electrical network, this current strength will be in an electrical appliance with a power of 220 W (0.22 kW). In industrial equipment powered by 380 Volts, as much as 657 Watts.
Ampere – Watt conversion table:
| 6 | 12 | 24 | 220 | 380 | Volt | |
| 5 Watt | 0,83 | 0,42 | 0,21 | 0,02 | 0,008 | Ampere |
| 6 Watt | 1,00 | 0,5 | 0,25 | 0,03 | 0,009 | Ampere |
| 7 Watt | 1,17 | 0,58 | 0,29 | 0,03 | 0,01 | Ampere |
| 8 Watt | 1,33 | 0,67 | 0,33 | 0,04 | 0,01 | Ampere |
| 9 Watt | 1,5 | 0,75 | 0,38 | 0,04 | 0,01 | Ampere |
| 10 Watt | 1,67 | 0,83 | 0,42 | 0,05 | 0,015 | Ampere |
| 20 Watt | 3,33 | 1,67 | 0,83 | 0,09 | 0,03 | Ampere |
| 30 Watt | 5,00 | 2,5 | 1,25 | 0,14 | 0,045 | Ampere |
| 40 Watt | 6,67 | 3,33 | 1,67 | 0,13 | 0,06 | Ampere |
| 50 Watt | 8,33 | 4,17 | 2,03 | 0,23 | 0,076 | Ampere |
| 60 Watt | 10,00 | 5,00 | 2,50 | 0,27 | 0,09 | Ampere |
| 70 Watt | 11,67 | 5,83 | 2,92 | 0,32 | 0,1 | Ampere |
| 80 Watt | 13,33 | 6,67 | 3,33 | 0,36 | 0,12 | Ampere |
| 90 Watt | 15,00 | 7,50 | 3,75 | 0,41 | 0,14 | Ampere |
| 100 Watt | 16,67 | 8,33 | 4,17 | 0,45 | 0,15 | Ampere |
| 200 Watt | 33,33 | 16,67 | 8,33 | 0,91 | 0,3 | Ampere |
| 300 Watt | 50,00 | 25,00 | 12,50 | 1,36 | 0,46 | Ampere |
| 400 Watt | 66,67 | 33,33 | 16,7 | 1,82 | 0,6 | Ampere |
| 500 Watt | 83,33 | 41,67 | 20,83 | 2,27 | 0,76 | Ampere |
| 600 Watt | 100,00 | 50,00 | 25,00 | 2,73 | 0,91 | Ampere |
| 700 Watt | 116,67 | 58,33 | 29,17 | 3,18 | 1,06 | Ampere |
| 800 Watt | 133,33 | 66,67 | 33,33 | 3,64 | 1,22 | Ampere |
| 900 Watt | 150,00 | 75,00 | 37,50 | 4,09 | 1,37 | Ampere |
| 1000 Watt | 166,67 | 83,33 | 41,67 | 4,55 | 1,52 | Ampere |
Why else do they choose Tesla kWh for power rather than Ah?
"kWh" is a standard unit of energy, which is indicated in the Tesla battery .
The kilowatt-hour rating of a Tesla battery is a measure of how much energy it can store. Indirectly, it is proportional to the range . That is, it can be used in comparative characteristics.
"Ampere-hours" are not a unit of energy. It is impossible to easily compare the energy consumption of different batteries with such a value.
You can have two batteries with the same amp-hour rating , but different energy capacity . It’s just that these units operate at different voltages, hence the differences in the capabilities of the vehicle.
Find out the difference between Ah and Wh using batteries for phones and laptops as an example.
Some industries use "amp hours" . For example, cell phone batteries are typically rated in "mAh" units . This is incorrect, but acceptable if the battery voltage .
In smartphones, “2000 mAh” will always be less than “2500 mAh” if both batteries have of 3.7 V.
And the Tesla battery is completely standards agnostic, patented, and its internal voltage is not something we (consumers) need to care about. Therefore, its Ah would be a meaningless metric.
We cannot compare the battery capacity of a Tesla with, for example, a BMW i3 . However, we can compare Tesla's batteries in kWh .
In any devices, 90 kWh is always more than 70 kWh , no matter what the voltage is.
Why do you need a calculator?
An online calculator will allow you to quickly convert current into power. It allows you to recalculate the current consumption of 1 Ampere into Watt of power of any consumer at a voltage of 12 or 220 and 380 Volts.
This power transfer is used both when selecting a generator for current consumers in a 12-volt vehicle electrical system with direct current, and in consumer electronics when laying wiring.
Therefore, a calculator for converting power into amperes or current into watts will be needed by absolutely all electricians or those who work in it and want to quickly convert these units. But still, the calculator is mainly intended for car owners. With it, you can count every electrical component in a car and use the resulting sum to understand how much electricity the generator should produce or what capacity the battery should be supplied with.
What is voltage, current and power
The three quantities discussed in this site article are network voltage, amperes and kilowatts. To avoid confusion, you should consider each of these quantities in order.
Mains voltage can be 220 or 380 volts. An electrical network is necessary to move unit charges that serve to transfer energy.
Current strength is measured in amperes and characterizes the amount of these same charges that can pass through the network in a certain amount of time.
Power - it is measured in watts and is expressed by the speed at which these same charges move.
1 kW is 1000 watts, this is necessary in order to quickly convert all the necessary calculations. Of course, everything described above is very superficial; in practice, everything is much more complicated. To obtain the power of electrical appliances, you should use the following formula: P=I*U*cosФ.
When applying this formula, it is worth understanding that for an active load cosF (power factor) is equal to 1. By active load we mean the operation of electrical appliances that have heating elements in their design. The remaining devices, which have an electric motor in their design, have a mixed type of load, including reactive load.
How to use
To use the quick conversion and convert Amperes to Watts, you will need to:
- Enter the voltage value that powers the source.
- In one cell, indicate the value of the current consumed (you can select Ampere or mAm from the list).
- The result of the “current to power” conversion will immediately appear in another field (by default it is displayed in Watt, but it is possible to set kW, then the value will be automatically converted to kilowatts of power).
The conversion can be done either from amperes to watts or vice versa from W to A; you just need to immediately enter the power of the consumer, and then another cell will display the current consumed in the network with a specifically indicated voltage.
What is ampere and ampere-hour?
Let's start with amperes: this is a unit of measurement for the rate of flow of electrons, or the flow of current, in a conductor over a second. Amplifiers are not often used in everyday EV terminology, but understanding them will help you understand the more common units of measurement.
Electrons are tiny negatively charged particles. Since they are negatively charged, they repel each other. Move one electron along a line and the rest will move. This is the basic concept of current or electricity. The measure of this current is known as an ampere.
One ampere (A) has a standard definition of 6.24 x 10 , which corresponds to the power of 18 electrons flowing per second. The more amps you have, the higher the current. For example, a typical laptop computer has a current of about 3A (three amps).
Ampere hour (Ah) is a unit other than amps and is used to estimate the amount of energy a battery can hold. In simple terms, it is used to determine the amount of current a battery can provide in an hour .
Therefore, amp hours are used to determine battery life. Amp hours divided by amps tells us the battery life in hours. So a 2Ah battery can draw two amps in one hour before it runs out, or four amps in half an hour.
FAQ
How many Watts are in Ampere?
If we are talking about a car network, then in one ampere there are 12 watts at a voltage of 12V
.
In a household electrical network of 220 Volts
, a current of 1 ampere will be equal to the consumer power of
220 Watts
, but if we are talking about an industrial network of
380 Volts
, then
657 Watts per ampere
.12 amps how many watts?
How many watts of power at 12 amperes of current consumption will depend on the network voltage with which the consumer himself operates. So 12A it could be: 144 Watts in a 12V car network; 2640 Watts in a 220V network; 7889 Watts on a 380 Volt power supply.
220 watts how many amps?
The current strength of a 220 Watt consumer will differ depending on the network in which it operates. This can be: 18A at a voltage of 12 Volts, 1A if the voltage is 220 Volts, or 6A when current consumption occurs in a 380 Volt network.
How to convert amps to kilowatts and back
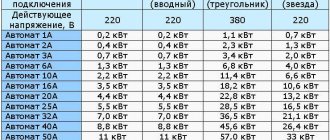
To convert amperes to kilowatts and find out the power, you need to multiply the network voltage, current strength and cosФ, which is equal to 1. For example, in a single-phase network the voltage is 220 Volts, and a 16 Ampere circuit breaker is installed on the meter.
To find out how much the circuit breaker can withstand, that is, what load in terms of the power of all electrical appliances can be connected to it, 220x16x1 = 3520 Watts is enough. Thus, it becomes clear that the circuit breaker is designed for a load of no more than 3.5 kW.
In the same way, kW is converted to amperes, only using division. Knowing the total power of electrical appliances and the network voltage, you can calculate the number of amperes. This will allow you to more accurately calculate which circuit breaker to install to protect the electrical wiring that connects electrical appliances in the house.
Let's say there is a kettle with a power of 2000 watts. For its operation you need a mains voltage of 220 volts. Divide the power by the voltage to get the current, that is, amperes. In this case, about 9 amperes of current come out.
It is always worth remembering that the wires themselves must withstand the load from the operation of electrical appliances. It is very important that the rating of the circuit breaker is not greater than the value for which the cable cross-section is not designed.
Share article on social networks
Watt, kilowatt and kilowatt-hour
The unit of measurement watt got its name in honor of the scientist James Watt, who studied electricity in the nineteenth century. It is he who is credited with the invention of the universal steam engine.
Today, any power is measured in watts, not just electrical power. For example, to measure the power of a car engine, watts are also used along with horsepower. However, most often it is not the “watt” itself that is used, but its derivative, the kilowatt (kW). By analogy with the meter and kilometer, as well as with the gram and kilogram, one kilowatt is equal to a thousand watts.
Energy is often also calculated in other units, multiples of the watt. For example, to measure high power it is convenient to use the megawatt, a unit that corresponds to a million watts. You can also use other prefixes of the international system of units, including those that correspond to tenths, hundredths, thousandths.
For example:
- deciwatt is a tenth of a watt;
- centiwatt - its hundredth part;
- A milliwatt is a thousandth of a watt.
The electric power that is consumed by ordinary household appliances such as lamps, refrigerators, and TVs is best measured in kW. If the watt and its derivative units are included in the SI system, then the kilowatt-hour is not there. KWh is a unit of measurement that is non-systemic. It was created only to keep track of the electrical energy produced or, conversely, used.
The use of kWh on the territory of the Russian Federation is regulated by GOST, which clearly indicates the name, designation and area in which it is used. A kilowatt-hour can be designated either by four Russian letters or three English ones. The Russian designation is “kWh”, and the English designation is “kW h”.
You might be interested in: Sequence in the discovery of electricity
Calculation features
Despite the fact that the power of electrical appliances is often indicated on their cases, you still often have to independently calculate how much electricity a particular household appliance consumes. In order not to make mistakes when calculating and to come to the correct result, you need not only to know about the differences between kW and kW-hours, but also to be able to convert these values from one to the other. For example, power often needs to be converted into energy and vice versa.
Before you start calculating the energy consumed by a particular household electrical appliance, you need to prepare a calculator, since the numbers may turn out to be such that it will be quite difficult to operate with them in your head.
Before converting power into energy, that is, kW per kWh, it is necessary to clarify what was previously measured. If the meter readings were measured, then everything will be extremely simple. It is enough just to correct “kilowatt” to “kilowatt-hour”.
You might be interested in: Electrician safety precautions when working with electricity
The meter reading is the energy consumed by electrical appliances per unit of time. It is also measured in kilowatt-hours. It’s just that in everyday life the name of this unit has lost the word “hour”. As a result, it became abbreviated to simply kW. Quite often, owners of any household electrical appliance convert kW to kW-hours in order to determine how much energy is consumed during its operation and, therefore, how often it needs to be turned on.
If the device consumes too much energy, you will have to use it rarely to save energy. In order to accurately determine how much energy this or that equipment, for example, an electric heater, will require, you need to know its operating time and power, which is usually indicated on the housing. For example, if the power of the device is 2 kW, and it works for 3 hours, then as a result of simple mathematical multiplication you can find out that the total electricity consumption during this time is 6 kilowatt-hours.
Minor problems may arise when calculating energy consumption if the power is indicated in units other than kW. The situation will get worse if time is also measured not in hours, but, for example, in minutes. Then, before starting calculations, it is necessary to convert power units into kW, and time units into hours. Only in this case the calculation results will be correct.
As an example, we can take an ordinary lamp, the manufacturers of which claim that its power is 100 W. Let's say you need to determine how much electricity is used if it burns all day. The power of the light bulb should be determined in kilowatts. Since Watt (watt) is a unit that is a thousandth of a kilowatt, you simply divide this light bulb wattage value by 1000.
That is, 100 W is divided by 1000 and the result is 0.1 kilowatt. This completes the conversion from one unit of power to another.
It is necessary to convert the time indicator to the desired unit. The condition requires determining how much energy the lighting device will consume per day. It’s simple here: there are 24 hours in a day, and therefore this figure can be considered the result of converting time units. All that remains is to multiply the numbers obtained as a result of the translation and find out how much energy will be consumed by the light bulb. 0.1 kilowatt is multiplied by 24 hours, and the resulting number is 2.4. This means that the energy consumption of the device is 2.4 kWh.
You might be interested in this: Checking a transistor with a multimeter
This way you can determine not only the amount of energy consumed by any one device, but also the total energy consumption of all electrical equipment in the house. The main thing is to know the duration of its operation and power.