What it is
One type of lighting is a sodium gas-discharge lamp (SL). This is an electric light bulb, the luminous elements of which are a gas discharge in sodium vapor. This allows you to get a bright yellow-orange light: it does not reproduce colors well, but copes well with street lighting in foggy conditions.
HPS lamp - high pressure sodium gas discharge lamp
Important! Sodium lamps are rarely used indoors, mainly where there are no requirements for good color rendering.
All sodium lamps are divided into:
- Low Pressure Sources (LPNS): Of all the LPs, they were the first to be created. They were common in Europe, where they are still used to illuminate country roads. The main differences between low-pressure lamps are the strong dependence of efficiency on ambient temperature and the production of the internal flask from borosilicate glass due to the high aggressiveness of sodium;
Light bulbs are divided depending on power and size
- High pressure luminaires (HPL): they are used for additional lighting of plants in industry. When creating it, it was necessary to solve two problems: how to neutralize the aggressive effect of sodium on glass and what to do with the high temperature of the electron arc. The tubes were made of aluminum oxide, the outer flask was made of heat-resistant glass. The burner is filled with gas mixtures and an alloy of sodium and mercury. There are also models without mercury.
High pressure lamps also come in several types:
- HPS: The acronym stands for Sodium Arc Tubular Lamp;
- DNaZ: Arc Sodium Mirror;
- DNaS: Arc Sodium in a Light Scattering Flask;
- DNaMT: Arc sodium Matt.
It is important to note the following: in Europe and America, DNaT lamps are called “High-Pressure Sodium Lamp” or “HPSL”, translated as “High Pressure Sodium Lamps”. When these lamps appeared in the USSR, various factories began producing them: they were divided according to power, glass transparency, shape and other parameters. The most popular models have become DNAT models of various capacities.
In other words, DNaT is a conventional cylindrical low-pressure lamp, and DNa3 is a mirror-coated lamp.
Features of sodium lamps
The main advantages of using HPS lighting:
- a large amount of light emitted;
- efficiency;
- lamps can serve as an additional source of heating;
- durability - about 20,000 hours of operation.
There is also a small drawback - the release of a large amount of heat during operation. But this disadvantage can be leveled out with the help of additional equipment - there are both ventilated and non-ventilated lamps for sodium lamps of the type DNaT(Z) on the market.
Advantages and disadvantages
HPS lamps have a large number of advantages, thanks to which they remain in demand today. Among its advantages:
- High level of light output compared to other light bulb models. High pressure lamps give up to 150-160 lm/W, low pressure lamps - up to 200 lm/W;
- Efficiency reaches 30%;
You might be interested in: Features of a fluorescent lamp
The lamp produces a strong yellow light
- A wide range of temperatures at which the light bulbs operate: from −60 to +40 degrees. In this case, the lamp lights up even at low temperatures;
- Long period of operation: minimum period - 10-12 thousand hours, maximum - up to 30-32 thousand;
- Cost-effective: HPS consumes 1.5-2 times less electricity. The production of lamps is also inexpensive: it has been established for a long time and works well, expensive materials are not required;
- Anti-fog effect: yellow and orange colors are poorly absorbed by water, and therefore lamps with such lighting are better visible in rain and fog.
However, the disadvantages of DNAT are no less significant:
- Weak color rendering: all lamps have a pronounced yellow or orange color. Lamps cannot be used in residential premises;
- Long burn-up: the first 5-10 minutes the lamp burns weakly while it warms up;
The light bulb contains mercury, which makes it dangerous.
- Certain electrical requirements. Lamps can only be used in networks with a fairly stable voltage;
Important! The second option is to use high-quality chokes.
- Presence of mercury: for disposal, lamps must be taken to a special collection point. A broken lamp can be dangerous if removed incorrectly or not thoroughly;
- Temperature: despite the fact that HPS lamps can operate at −60 degrees, the optimal temperature for them is from −20 to +30 degrees. At higher or lower temperatures, the light output will be lower and the service life will be reduced;
- The presence of quite strong ripples, they can reach 50 Hz. This results in constant flickering, which is tiring for the eyes.
Types of lamps
There are 2 types of HPS lamps - low and high pressure. They differ from each other in some characteristics.
The sodium light bulb takes several minutes to “warm up”
High pressure
These lamps are suitable for lighting industrial complexes, gyms and commercial facilities. They have better color reproduction, but some colors may appear duller than usual.
Low pressure
They are reliable in operation, consume little energy and have high light output for a long time. They are well suited for street lighting because they distort colors in enclosed spaces.
Technical specifications
Several types of HPS lamps of different powers are available: 70 W, 100, 150, 250 and 400. Below are the characteristics for 70 W and 400 W lamps:
- Lamp length: 16.5 cm and 27.8 cm;
- Diameter: 4.2 cm and 4.8 cm;
- Power: 70 W and 400 W;
- Luminous flux: 6 thousand lm and 45 thousand lm;
- Luminous efficacy: 66 lm/W and 88 lm/W;
- Power consumption: 90 W and 510 W;
- Lamp voltage: 90 V and 100 V;
- Service life: 14 thousand hours and 18 thousand hours.
You might be interested in this Features of a chandelier with remote control
Why do you need a capacitor?
In addition, it is recommended to use a capacitor in the connection kit. Although it is not present in all schemes.
Why is it needed? As is known, circuits using power chokes consume both active and reactive power. From the second, you will not get any beneficial effect.
This will not make the lamp shine brighter, but the losses will increase. It is in order to remove this reactive component that a phase-compensating capacitor is used.
For lamps of different power, you need to select the appropriate capacity. Here are the recommended capacitor capacitance parameters, depending on the power of the chokes:
A visual comparison of the current consumption of a HPS lamp with and without a capacitor:
As you can see, more than double the difference. In the first case, the compensated current (active) is shown, and in the second case, the full current (without a capacitor in the circuit).
Some people think that by doing so they also reduce energy consumption, but this is not entirely true.
Your meter is not designed to count reactive or apparent energy, and the actual cost savings can be a maximum of 3-4%.
But you will eliminate unnecessary losses due to heating of wires and iron.
Principle of operation
The inside of the flask is filled with a mixture of gases and contains an aluminum oxide burner. This is where all the work of the lamp takes place.
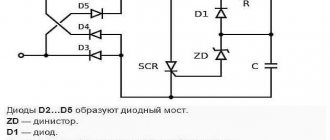
The connection principle is shown in the diagram
The sodium lamp has a simple design and simple principle.
- After switching on, the built-in ignition device begins to generate pulses;
- An arcing electronic charge is formed in sodium vapor, which causes the vapor to begin to glow. The light comes on;
- The burner gradually warms up and the light becomes brighter;
- In modern lamps, a choke is built into the design, which limits the arc current and ensures an uninterrupted supply of current.
Features of installation and operation
To connect the NL (DNaT and other types), it is necessary to install a special ballast (ballast), which are divided into electromagnetic (EMP) and electronic (EPG). In the case of DNAS, it is also necessary to connect a pulse ignition device, which is equipped with 2 or 3 leads. The device itself shows how to make the connection correctly.
The most common ballast devices are ballast inductive chokes, which limit and stabilize the current. The connection diagram for sodium lamps involves supplying supply voltage to the terminals of the lamp.
If you connect the NL yourself, it is recommended to use a wire connecting the ballast to the sodium lamp, no more than 1 m long. The use of cotton gloves is also recommended.
When used for artificial lighting of plants, NLs are located no closer than 50 cm from them. Power can be from 75 to 400 W. However, in the case of a power of 400 W, the distance to the plants should be increased to 1.8 - 2 m. Compliance with these conditions is important in order not to damage the plants.
A sodium lamp (usually an outdoor one) must be reinforced with a protective glass bulb to avoid damage due to differences in the internal temperature of the bulb and the external environment.
The quality of NL light also depends on their timely cleaning from dust and dirt. To do this, you can use a cloth moistened with alcohol.
Disposal of NL by special institutions is mandatory in order to avoid environmental pollution with mercury vapor (if contained), as well as to prevent an explosion of sodium gas that can occur when it comes into contact with oxygen.
What does it consist of?
The device is a flask made of special high-strength aluminum oxide, which can withstand both high temperatures and the action of sodium vapor. 2 electrodes are attached to the edges of the flask; the flask itself is filled with a mixture of inert gases, an alloy of mercury and sodium, and xenon.
DNAT has a simple device
The burner is housed in a smaller flask made of heat-resistant glass, usually borosilicate glass. A vacuum is created in the flask and supplied with a base through which the connection to electricity will be made.
In other words, it turns out to be a flask within a flask: in the center of the large outer one there is a small cylindrical flask with a burner inside. The outer flask acts as a thermos, protecting the burners from low temperatures, increasing efficiency and reducing heat loss.
Base
Through it, the lamp is connected to the electrical network. The most commonly used screw connection is type E (Edison) - E27 for DNAT 70 and 100, and E40 for DNAT 150, 250 and 400. The numbers on the marking indicate the diameter in millimeters: for example, E40 is a base with a diameter of 40 mm.
Burner
This is an important part of any HPS light bulb. It is a thin glass cylinder that is resistant to high temperatures and chemical reactions. It has tungsten electrodes inserted on both sides.
The light bulb consists of 2 bulbs - one placed inside the other
During its manufacture, deep vacuumization is carried out, that is, absolutely all the air and oxygen are pumped out. This is an important safety requirement: the base heats up to 1300 degrees, and if oxygen enters, the lamp can explode.
The difference between connecting 2 and 3-pin IZU
Please note that there are two-pin and three-pin IZUs. The first ones are connected in parallel with the lamp itself.
That is, strictly after the ballast, you must enter a phase into the IZU, and apply zero to its other terminal. It doesn’t matter where you get it from, even directly from the cartridge itself.
By the way, two-pin ones have not been recommended for use for a long time and here’s why.
The ignition process is associated with a high voltage pulse (from 2 to 5 kV). And this pulse is supplied in parallel not only to the lamp, but also to the inductor.
And this can easily break through the insulation of the ballast if it is not designed for this.
Therefore, such a parallel connection is more often found in low-voltage sodium lamps, or in those where an ignition pulse of no more than 2 kV is sufficient.
The capacitor is connected in parallel to the entire circuit. Just connect one wire to the machine phase, the other to zero.
All that remains is to stretch the cable and disconnect the cartridge.
From the starting device to the lamp itself, the recommended cable length is no more than 1.5 m.
Area of use
HPS light sources are not used in residential areas due to excessive power and distorted color rendering: for example, green often “turns” into black or dark blue. However, light bulbs have found application in other areas:
- Lighting of streets and roads. The lamps performed especially well when working in foggy areas;
- Underpasses, railway stations and airports, parking lots, tunnels;
The lamps work well even in fog and rain
- Industrial premises, warehouses, workshops, parking lots, sports complexes, for which the correct transmission of light is not important;
- Illumination of monuments and buildings;
- For greenhouses, flower beds and other complexes in which plants are grown. This allows you to grow plants all year round, regardless of the season.
You may be interested in: Features of connecting a chandelier
In greenhouses they use lamps with a power of 150-250 W; a 400 W lamp is also suitable, but it will need to be placed further away. For the street, lamps with a power of 70-150 W are required.
Important! For street lighting, it is important to choose lamps that are protected from moisture and dust.
How to connect a lamp correctly
It will not be possible to connect the light bulb to a regular household network, since the available voltage is not enough to operate it. In addition, it is necessary to limit the arc current so that work proceeds without interruption.
Important! All sodium lamps, both HPS and HPS, are connected according to the same circuit.
To connect the lamp you need the following elements:
- IZU is a Pulse Ignition Device that helps increase the voltage in the network until an arc forms. IZUs can be 2-pin and 3-pin: the former are cheaper and simpler, the latter perform better in operation. When connecting a two-terminal IZU, when turned on, the discharge is applied to the lamp and ballast, when connecting a three-terminal IZU - only to the lamp;
To connect you will need several additional elements
- A ballast is an electronic or electromagnetic ballast that limits the current after starting. Electronic ballast or electronic ballast is an electronic circuit, electromagnetic is a choke (a coil with an open magnetic circuit). When connecting, the inductor must be connected in series with the DNAT, and the IZU in parallel.
The connection diagram for a two-pin IZU occurs in several steps:
- The IZU is connected in parallel with the lamp;
- The “phase” wire after the inductor must be connected to the desired terminal of the IZU;
- The second tip is connected to the remaining clamps.
The connection diagram for a high-pressure sodium lamp and a three-terminal IZU is a little more complicated:
- One negative wire must be connected to the light bulb, the second to the same type of IZU terminal;
- Next, you need to open the phase and connect one cable from the panel to the inductor;
- The middle conductor is connected to the light bulb.
When connecting a HPS lamp, you must use the diagrams. If in doubt, it is better to contact a specialist rather than connect it yourself.
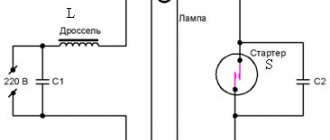
Connecting a HPS lamp
The connection is also primitive to the point of disgrace, as is the device of the lamp. So we won’t dwell on this for long and will only present one of the most typical diagrams for connecting a HPS lamp.
Typical connection diagram for a HPS lamp
Although here it is worth mentioning that in reality there are a huge number of options for connecting a HPS lamp. A compensating capacitor is also a mandatory connection component. As a rule, connection diagrams are indicated on the IZU blocks. But the picture above shows the simplest schematic connection option.
Life time
The service life of DNAT lamps is quite significant: the minimum life is 14 thousand hours (more than 1.5 years), the maximum is up to 32 thousand (more than 3.5 years). In this case, the duration of operation depends on external conditions (if the temperature is too low, wear will be greater), voltage in the electrical network and other nuances.
Light bulbs can be used as additional lighting for greenhouses
HPS lamps are high-pressure sodium lamps that have not lost their popularity. They are characterized by a long service life, low cost and high luminous efficiency. Despite a number of disadvantages (the main one being poor color reproduction), lamps of this type are still used for street lighting.
How to choose a lamp
The main criteria when selecting sodium lamps for your home greenhouse are power and base. The lamp power should be in the range of 75-400 watts - this is the optimal range in order not to burn the plants. The base depends on the power. For lamps with a power of up to 150 watts you can find an E27 base, for all higher power lamps only E40. We also recommend paying attention to the color rendering index and luminous flux markings: the higher it is, the better the light of the device will be.
By the way, for installation you will need a choke, a lighter and ballasts.