The industry of any country consists of a large number of diverse sectors, such as mechanical engineering or electrical power. These are the directions in which a particular country is developing, and different countries may have different emphases depending on many factors, such as natural resources, technological development and so on. In this article we will talk about one very important and actively developing industry today - the electric power industry. Electric power is an industry that has been constantly developing for many years, but it is in recent years that it has begun to actively move forward, pushing humanity to use more environmentally friendly energy sources.
What it is?
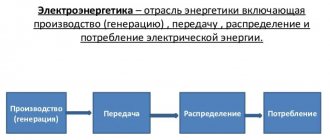
So, first of all, you need to understand what this industry actually is. Electric power industry is a division of the energy sector that is responsible for the production, distribution, transmission and sale of electrical energy. Among other industries in this field, the electric power industry is the most popular and widespread for a number of reasons. For example, due to the ease of its distribution, the possibility of transmitting it over vast distances in the shortest periods of time, and also because of its versatility, electrical energy can be easily transformed, if necessary, into other types of energy, such as thermal, light, chemical, etc. Further. Thus, the governments of world powers pay great attention to the development of this industry. Electrical power is the industry that holds the future. This is exactly what many people think, and that is why you need to familiarize yourself with it in more detail using this article.
How the electricity market works in Russia
Many will find the question about the structure of the electricity market quite strange, because everyone knows: you consume electricity, next month you receive a receipt and all you have to do is go to the online service/bank, pay the receipt and the electricity purchase and sale transaction is completed.
However, the entire complexity of the process is hidden from ordinary consumers. In reality, everything is somewhat more complicated. There is a wholesale market for electricity and capacity, and there are generating and network companies. The latter are federal and regional; after all, there are sales organizations known to everyone. Let's try to figure out how the electricity market works in Russia.
How electricity is produced
Electricity in our sockets and enterprises is “born”, as a rule, at a fairly large distance from places of consumption, at generating plants of electric power companies. There are several ways to obtain electrical energy, we list the main ones:
1. Non-renewable energy . Burning fossil fuels, mainly coal, petroleum products or gas.
2. Renewable energy . Hydrogeneration, wind and solar installations, etc.
3. Nuclear energy (NPP).
In Russia, gas-fueled power plants predominate (about 50%). A significant portion consists of nuclear power plants (about 16%) and hydroelectric generation (about 18%). Coal accounts for about 15%. The share of electricity produced from oil and renewable sources is very small.
Generators in Russia
There are many companies producing electricity in Russia. For example, even the oil company Lukoil has generating structures in the group, which in total provide a capacity of about 5.7 GW. Some of the generating companies are not listed on the stock exchange. For example, the only operator of nuclear power plants, Rosatom, is a non-public state company.
So, the main generating companies whose shares are listed on the Moscow Exchange:
1. RusHydro . Ticker HYDR. Installed capacity 39.1 GW. The assets include both hydro-generating capacities and hydrocarbon fuel stations. Thermal generation is represented by the RAO UES East subgroup. 2. Inter-RAO . Ticker IRAO. Installed capacity 32.7 GW. Mainly stations based on gas turbine and combined cycle gas plants. Electricity exporter. According to 2022 data, about 12% of the generated electricity was exported, which partially affects the dependence of quotes on the national currency exchange rate. It is also an energy import operator. (6.2 TWh in 2022) 3. Eurosibenergo . The largest private electric power company in the Russian Federation with a capacity of 19.5 GW. The structure includes both generating capacities and sales companies, as well as network divisions. The company is part of the En+ Group together with Rusal. Ticker ENPL. 4. OGK-2 . Ticker OGKB. Installed capacity is 18 GW. It includes thermal power plants operating primarily on gas. It is controlled by Gazprom Energoholding, a 100% subsidiary of Gazprom. 5. Irkutskenergo . Ticker IRGZ. Daughter of Eurosibenergo. Installed capacity is 12.98 GW. There are coal assets, hydroelectric power stations and thermal power plants. 6. Mosenergo . Ticker MSNG. Installed capacity is 12.8 GW. It consists of 15 power plants operating primarily on gas. It is controlled by Gazprom Energoholding, a 100% subsidiary of Gazprom. 7. Unipro . Ticker UPRO. Installed capacity is 11.2 GW. Gas is mainly used as fuel. 8. Enel Russia . Ticker ENRU. Installed capacity is 9.4 GW. The asset includes the largest coal-fired power plant in the Russian Federation - Reftinskaya State District Power Plant. Negotiations are currently underway for its sale. 9. TGC-1 . Ticker: TGKA. Installed capacity is 7 GW. The assets include both hydro-generating facilities and thermal stations. A small part of the generated energy is exported to Norway and Finland. It is controlled by Gazprom Energoholding, a 100% subsidiary of Gazprom. 10. TGC-2 . Ticker TGKB. Installed capacity 2.5 GW. Natural gas is mainly used as fuel. 11. TKG-14. Ticker TGKN. Installed capacity 0.7 GW. Generating assets are located in the Trans-Baikal Territory and the Republic of Buryatia. Coal is used as fuel. 12. Quadra. Ticker TGKD. Installed capacity 0.7 GW. Gas is mainly used as fuel.
Sales companies
Generating companies do not sell electricity directly to the public. This is what sales companies do. Legislative norms contradict the combination of sales, transport and electricity generation activities. This allows for the implementation of market mechanisms and promotes the development of competition, thereby optimizing price and quality for the end consumer.
But in the case of combining transport and electricity sales activities, the motivation to reduce costs disappears. Costs that could and should have been reduced are transferred to non-competitive activities. As a result, this may lead to higher tariffs, higher prices, inflationary pressure and other negative consequences for citizens and the economy as a whole.
However, for a number of reasons, there are now temporary conflicts when sales companies are in one way or another connected with network holding companies or generators. This allows us to somewhat reduce the negative effect of guaranteeing suppliers leaving the market due to low payment discipline in a number of regions.
It is worth noting that of all the components of the chain of production, supply and sale of electricity, the latter is the weakest link from the investor’s point of view. Problems with payment for electricity supplies and fixed tariffs for a number of consumers increase risks for the sales company in the event of an increase in generation costs and, accordingly, an increase in electricity prices on the wholesale market. More stringent requirements for suppliers of last resort have a negative impact on profitability.
A supplier of last resort is a participant in the wholesale and retail markets who is obliged to enter into an agreement for the supply of electricity to any consumer who contacts it. In general, the supplier of last resort bears great responsibility and must meet a number of requirements, in particular, provide bank guarantees for the supply of electricity. The requirements are described in more detail in the decree of the Russian government.
Generators use the wholesale electricity and capacity market (WEM) to sell the produced “goods”. A more detailed diagram of the functioning of the market is given in the material devoted to the CSA-2 program. Buyers in this market are sales companies , as well as directly large industrial consumers .
Schematic diagram of the functioning of the electricity market in the Russian Federation.
Several distribution companies are represented on the Moscow Exchange, but it happens that they are part of distribution network companies.
The most liquid shares of sales companies listed on the Moscow Exchange:
- Volgograd Energy Sales Company. Ticker: VGSB. 2. DEK - Far Eastern Energy Company. Daughter of RusHydro. Ticker DVEC. 3. Yakutskenergo . A subsidiary of RAO ES Vostok. Ticker YKEN. 4. Magadanenergo . A subsidiary of RAO ES Vostok. Ticker MAGE 5. Kamchatskenergo . A subsidiary of RAO ES Vostok. Ticker KCHE 6. Stavropolenergo . Ticker STSB. 7. Samaraenergo . Ticker SAGO. 8. Dagenergosbyt . Ticker DASB. 9. Lipetsk Energy Sales Company . Ticker LPSB. 10. Permenergosbyt . Ticker PMSB. 11. Krasnoyarskenergosbyt . Ticker KRSB. 12. RAO ES East . It is part of the RusHydro group (HYDR) and combines Far Eastern assets. 13. Sakhalinenergo . Part of the RAO ES East group. Ticker SLEN. 14. Chelyabenergosbyt . Ticker CLSB. 15. Kaluga sales company . Ticker KLSB. 16. Kostroma sales company . Ticker KTSB. 17. Saratovenergo . Ticker SARE. 18. Mordovian energy sales company . Ticker MRSB. 19. Ryazan Energy Sales Company . Ticker RZSB. 20 . TNS Energo group of companies . One of the largest independent energy sales companies. It is represented by branches in the central and southern parts of the Russian Federation, which are also public companies and are listed on the Moscow Exchange. Ticker TNSE. 21. Vladimirenergosbyt . Ticker VDSB.
- 22. Tambovenergosbyt. Ticker TASB.
Most sales companies and some network companies are represented on the stock exchange not only by ordinary companies, but also by privileged companies. Sometimes, due to the peculiarities of the charter and dividend policy, an ordinary retail investor may be interested in precisely “prefs”. The ticker for preferred shares is distinguished by the presence of the letter P at the end. For example, the ticker LSNGP is assigned to Lenenergo preferred shares.
Network companies
network companies as subjects on the Wholesale Electric Power Market Firstly, in this way they compensate (through sales companies) for the losses of electricity that are inevitable during its transmission, especially over long distances. Secondly, many sales outlets, despite legal restrictions, are still part of network holding companies (temporarily).
After electricity has been received at the power station, it must be distributed to end consumers. They can be private individuals or legal entities, factories and enterprises, as well as government facilities. For these purposes, there are network companies, which in the current situation are mainly represented by the Rosseti holding and FGC UES.
Federal Grid Company
FSK is engaged in the transmission of electricity through the Unified National Electric Network (UNEG). Simply put, FSK transmits electricity through high-voltage main lines and is a subject of a natural monopoly. Tariffs are regulated by the state. It is necessary to note the permanently high investment program. The key shareholder of FGC is Rossetti (80.13%). For this reason, FSK maintains relatively high dividend payments. This helps distribute funds within Rosseti for investment programs of other subsidiaries.
Russian networks
PJSC Rosseti, excluding its share in FSK, is an operator of energy networks and related equipment (substations, transformers). In essence, this is a holding that controls 15 interregional distribution grid companies (IDGCs). That is, these are the power lines and other infrastructure that we are used to seeing in urban infrastructure.
The controlling shareholder of PJSC Rosseti is the state with a share of 88.04%.
Below are the most liquid issuers of network companies on the Moscow Exchange.
1. FGC UES . The stock ticker on the Moscow Exchange is FEES. 2. Rosseti . The stock ticker is RSTI. 3. MOESK . Ticker MSRS 4. IDGC of Center and Volga Region . Ticker MRKP. 5. IDGC of Center . Ticker MRKC. 6. IDGC of the North-West . Ticker MRKZ. 7. Lenenergo . Ticker LSNG. 8. IDGC of the Urals. Ticker MRKU. 9. IDGC of Volga. Ticker MRKV. 10. IDGC of the South. Ticker MRKY. 11. IDGC of the North Caucasus . Ticker MRKK. 12. Kubanenergo . Ticker KUBE. 13. TRC - Tomsk distribution company. Ticker TORS. 14. IDGC of Siberia . Ticker MRKS.
Features of investing in shares of the electricity sector
Finally, let's cover a few important points when investing in electric utility stocks.
Let's start with the positive
1) The electricity market is more or less stable. Consumption is steady and growing as the economy develops. Even in crisis years, electricity consumption usually falls by 2-3% and is restored literally within 1-2 years. This determines the “protective” properties of the sector during crises in the economy and financial markets. That is, the market is not elastic.
2) In established, relatively developed economies, the sector is a dividend sector. The lack of market growth and a stable, well-functioning investment program contributes to an increase in payments to shareholders. In developing economies, the emphasis is more towards growth in consumption, therefore energy rather than “cash cows”.
3) At least in the Russian electricity market, the investment activity of generators is stimulated by programs of guaranteed return on investment, like CSA. Increased payments for capacity and rising tariffs have a positive impact on the return on investment in such a conservative sector.
4) Relative protection against inflation. Tariffs for the purchase of electricity for individuals and for the transmission of electricity are usually indexed within the inflation range or above its values. Some companies may be considered defensive. However, to make an investment decision, it is necessary to consider all aspects of the issuer, including debt burden and investment program.
Now about the negative aspects
1) Due to the high level of regulation in the industry, including regarding tariffs for the sale and transmission of electricity, companies do not immediately respond to rising fuel costs and rising capex due to the weakening of the ruble. Profitability is declining.
2) In addition, due to permanently high capital costs, companies with high debt loads are sensitive to tightening monetary conditions in the economy. Rapidly rising rates tend to hurt energy stocks.
3) Let's move on to the features of Russian energy. Companies in the sector mainly operate in the domestic market. Profits are received in rubles. This is not very interesting for an investor at a time of national currency devaluation. In addition, part of the costs and capital expenditures of companies are in foreign currency. During the weakening of the ruble, shares of most electric power companies are not in demand. An exception may be electricity exporters.
4) It was already noted above that the least attractive are the shares of supply companies. Some of them are in a difficult financial situation due to legislative issues regarding payment discipline and payment for energy and capacity in the wholesale electricity market.
Subjectively speaking, the established system of relationships in the Russian electric power industry favors electricity and heat producers more. They are key consumers of coal and gas in the country. The stability of the entire energy system also largely depends on generators.
5) If we focus on the sustainability of electricity supplies, then it is definitely worth mentioning the electric grid complex (FSK, Rosseti), namely the permanently high investment program. Taking into account the Russian reality, in terms of the age of equipment, distances, climate and consumption culture, most likely, high capital costs will accompany network companies for quite a long time. This means that company dividends will depend on the decision on the investment program of FGC UES and Rosseti. As for Rosseti's subsidiaries, from time to time companies begin to pay high dividends, thus redistributing investment resources between various IDGCs.
6) A large number of generating and network companies are state or quasi-state. This may influence the desire of the board of directors and management to ensure growth in business value and capitalization. The priority before profit growth and dividends is rightly the stability of supplies, social responsibility and support of the local labor market.
Open an account
BCS Broker
Progress in Electricity Generation
To fully understand how important this industry is to the world, it is necessary to take a look at how the electric power industry has developed throughout its history. It is immediately worth noting that electricity production is indicated in billions of kilowatts per hour. In 1890, when the electric power industry was just beginning to develop, only nine billion kWh were produced. A big leap occurred by 1950, when more than a hundred times more electricity was produced. From that moment on, development took giant strides - several thousand billion kW/h were added every decade. As a result, by 2013, world powers produced a total of 23,127 billion kWh - an incredible figure that continues to grow every year. Today, China and the United States of America provide the most electricity - these are the two countries that have the most developed electricity sectors. China accounts for 23 percent of the world's electricity, while the United States accounts for 18 percent. They are followed by Japan, Russia and India - each of these countries has at least four times less share in global electricity production. Well, now you also know the general geography of the electric power industry - it’s time to move on to specific types of this industry.
The importance of the electric power industry in the economy of the Russian Federation
Stable economic development is impossible without a constantly developing electric power industry. Electric power is the basis for the functioning of the economy and life support. Reliable and efficient operation of the electric power industry and uninterrupted supply to consumers are the basis for the progressive development of the national economy and an integral factor in ensuring civilized living conditions for all citizens. Electric power is an element of the fuel and energy complex. The Russian fuel and energy complex is a powerful economic and production system. It has a decisive influence on the state and prospects for the development of the national economy, providing 1/5 of the gross domestic product, 1/3 of the volume of industrial production and revenues of the consolidated budget of Russia, about half of the federal budget revenues, exports and foreign exchange earnings.
In the development of the electric power industry, great importance is attached to the issue of the correct location of the electrical industry. The most important condition for the rational placement of power plants is to ensure a comprehensive balance of demand for electricity in all sectors of the national economy and the needs of the population, as well as the needs of individual economic regions in the long term.
One of the principles for locating the electric power industry at the present stage of development of a market economy is the construction of thermal power plants of predominantly low power, the introduction of new types of fuel, and the development of a high-voltage network for transmitting electricity over long distances.
An important feature of the development and location of the electric power industry is the extensive construction of combined heat and power plants (CHPs) for heating various industries and public facilities. HRSG units are located at points of steam or hot water consumption, since heat transfer through pipelines is economical only over short distances.
An important direction in the development of the electric power industry is the construction of hydroelectric power stations. A distinctive feature of the modern development of the electric power industry is the construction of electric power systems, their interconnection and the creation of a unified energy system (UES) of the country.
Thermal power engineering
You already know that the electric power industry is a branch of the energy sector, and the energy industry itself, in turn, is a branch of industry as a whole. However, the ramifications do not end there - there are several types of electric power, some of them are very common and are used everywhere, others are not so popular. There are also alternative areas of the electric power industry, where non-traditional methods are used to achieve large-scale electricity production without harming the environment, as well as neutralizing all the negative features of traditional methods. But first things first.
First of all, it is necessary to talk about thermal power engineering, since it is the most widespread and well-known all over the world. How is electricity generated in this way? You can easily guess that in this case, thermal energy is converted into electrical energy, and thermal energy is obtained by burning various types of fuel. Combined heat and power plants can be found in almost every country - this is the simplest and most convenient process for obtaining large volumes of energy at low costs. However, this process is one of the most harmful to the environment. Firstly, natural fuel is used to generate electricity, which is guaranteed to run out someday. Secondly, combustion products are released into the atmosphere, poisoning it. That is why there are alternative methods of generating electricity. However, these are not all traditional types of electric power - there are others, and we will further concentrate on them.
A little theory
Energy is one of the sectors of the economy of the Russian Federation, which includes both the process of generating thermal and electrical energy, as well as its transmission and operational dispatch control. In recent years, production indicators have been steadily growing, and in 2018-2019, consumption of primary fuel resources amounted to about 700 million tons of oil equivalent.
Today, Russia primarily uses natural gas, which accounts for 53% of all electricity generated. But at nuclear stations they receive only 12 percent of the total energy supplied to the general network. Total electricity production in Russia is about 1.093 trillion kilowatt-hours. At the same time, there is a trend towards a decrease in generation volumes at thermal stations with an increase in production at gas stations and alternative energy.
Nuclear power
As in the previous case, when considering nuclear power, a lot can be gleaned from the name alone. Electricity generation in this case is carried out in nuclear reactors, where atoms are split and their nuclei are fissioned - as a result of these actions, a large release of energy occurs, which is then transformed into electricity. It’s unlikely that anyone else knows that this is the most unsafe electric power industry. Not every country's industry has its share in the global production of nuclear electricity. Any leak from such a reactor can lead to catastrophic consequences - just remember Chernobyl, as well as the incidents in Japan. However, recently more and more attention has been paid to safety, which is why nuclear power plants are being built further.
Hydropower
Another popular way to produce electricity is to obtain it from water. This process takes place at hydroelectric power stations; it does not require either dangerous nuclear fission processes or environmentally harmful combustion of fuel, but it also has its disadvantages. Firstly, this is a violation of the natural flow of rivers - dams are built on them, due to which the necessary flow of water is created into the turbines, which is how energy is obtained. Often, due to the construction of dams, rivers, lakes and other natural reservoirs are drained and destroyed, so it cannot be said that this is an ideal option for this energy sector. Accordingly, many electric power enterprises are turning not to traditional, but to alternative types of electricity generation.
Heat supply
The life of a modern person is associated with the widespread use of not only electrical, but also thermal energy. In order for a person to feel comfortable at home, at work, or in any public place, all premises must be heated and supplied with hot water for domestic purposes. Since this is directly related to human health, in developed countries suitable temperature conditions in various types of premises are regulated by sanitary rules and standards. Such conditions can be realized in most countries of the world only with a constant supply of a certain amount of heat to the heating object (heat sink), which depends on the outside air temperature, for which hot water is most often used with a final temperature for consumers of about 80-90°C. Also, various technological processes of industrial enterprises may require so-called production steam with a pressure of 1-3 MPa.
In general, the supply of heat to any object is provided by a system consisting of:
- heat source, such as a boiler room;
- heating network, for example from hot water or steam pipelines;
- heat sink, for example a water heating battery.
District heating
A characteristic feature of centralized heat supply is the presence of an extensive heating network, from which numerous consumers (factories, buildings, residential premises, etc.) are powered.
For district heating, two types of sources are used:
- Combined heat and power plants (CHP), which can also generate electricity;
- Boiler houses, which are divided into: Water heating;
- Steam.
Decentralized heat supply
A heat supply system is called decentralized if the heat source and heat sink are practically combined, that is, the heat network is either very small or absent. Such heat supply can be individual, when separate heating devices are used in each room, for example, electric, or local, for example, heating the building using its own small boiler house. Typically, the heating capacity of such boiler houses does not exceed 1 Gcal/h (1.163 MW). The power of individual heating sources is usually quite small and is determined by the needs of their owners.
Types of decentralized heating:
- Small boiler houses;
- Electrical, which is divided into: Direct;
- Accumulative;
Heating network
A heating network is a complex engineering and construction structure used to transport heat using a coolant, water or steam, from a source, a thermal power plant or boiler house, to heat consumers.
From direct network water collectors, hot water is supplied to populated areas using main heating pipelines. The main heat pipelines have branches to which are connected the wiring to the heating points, which contain heat exchange equipment with regulators that supply consumers with heat and hot water. To increase the reliability of heat supply, the heat mains of neighboring thermal power plants and boiler houses are connected by jumpers with shut-off valves, which make it possible to ensure uninterrupted heat supply even in the event of accidents and repairs of individual sections of heating networks and heat supply sources. Thus, the heating network of any city is a complex complex of heat pipelines, heat sources and heat consumers.
Alternative power engineering
Alternative electrical energy is a collection of types of electrical energy that differ from traditional ones mainly in that they do not require one or another type of harm to the environment, and also do not expose anyone to danger. We are talking about hydrogen, tidal, wave and many other varieties. The most common of them are wind and solar energy. They are the ones the emphasis is placed on – many believe that they are the future of this industry. What is the essence of these types?
Wind energy is the production of electricity from wind. Windmills are built in the fields, which work very efficiently and provide energy not much worse than the previously described methods, but at the same time, windmills only need wind to operate. Naturally, the disadvantage of this method is that the wind is a natural element that cannot be controlled, but scientists are working to improve the functionality of modern windmills. As for solar energy, here electricity is obtained from the sun's rays. As in the case of the previous type, it is also necessary to work on increasing the storage capacity, since the sun does not always shine - and even if the weather is cloudless, in any case, at a certain moment night comes when the solar panels are not able to produce electricity.
Electricity transmission
Well, now you know all the main types of electricity generation, however, as you can already understand from the definition of the term electric power industry, everything is not limited to receiving it. Energy needs to be transmitted and distributed. Thus, electrical energy is transmitted through power lines. These are metal conductors that create one large electrical network throughout the world. Previously, overhead lines were most often used - these are the ones you can see along the roads, thrown from one pole to another. However, recently cable lines that are laid underground have become very popular.
History of the development of the Russian electric power industry
Russia's electric power industry began to develop at the same time as the world's - in 1891, when the transmission of electrical power over almost two hundred kilometers was successfully carried out for the first time. In the realities of pre-revolutionary Russia, the electric power industry was incredibly underdeveloped - the annual electricity generation for such a huge country was only 1.9 billion kW/h. When the revolution took place, Vladimir Ilyich Lenin proposed a plan for the electrification of Russia, the implementation of which began immediately. Already by 1931, the planned plan was fulfilled, but the speed of development turned out to be so impressive that by 1935 the plan was exceeded three times. Thanks to this reform, by 1940 the annual electricity generation in Russia amounted to 50 billion kWh, which is twenty-five times more than before the revolution. Unfortunately, dramatic progress was interrupted by World War II, but after its conclusion, work recovered, and by 1950, the Soviet Union was generating 90 billion kWh, which accounted for about ten percent of total electricity generation worldwide. By the mid-sixties, the Soviet Union had reached second place in the world in electricity production and was second only to the United States. The situation remained at the same high level until the collapse of the USSR, when the electric power industry was far from the only industry that suffered greatly due to this event. In 2003, a new Federal Law on the electric power industry was signed, within the framework of which the rapid development of this industry in Russia should take place in the coming decades. And the country is definitely moving in that direction. However, it is one thing to sign a federal law on the electric power industry, and completely different to implement it. This is exactly what will be discussed further. You will learn about what problems exist in the Russian electric power industry today, as well as what ways will be chosen to solve them.
Green renewable energy
In recent years, wind farms and numerous solar power parks have increasingly contributed to the generation of electricity. Initially, such green modern electricity appeared in Western countries, but today, with the development of technology, it has become relevant, including for Russia. With the help of powerful windmills, large volumes of electricity can be generated, and such installations are completely safe; their installation is possible in various areas, including mountainous areas.
Benefits of green energy:
- autonomy of stations;
- complete environmental friendliness;
- high efficiency.
One of the most promising green energy technologies is solar panels, the efficiency of which has increased significantly in recent years, while at the same time the cost of production and installation of such equipment has decreased. It is not surprising that today in Russia parks that are large in size and capacity are being developed; this is especially true for the southern regions, where the sun shines 300 days a year. Also, such solar energy opportunities can be used by ordinary homeowners who receive a complete autonomous supply of electricity to suburban buildings that are remote from large central networks.
In Western countries, various tidal power plants are most widespread, but in Russian conditions it is extremely difficult to use them. They would be effective on the coast of the Arctic Ocean. However, in this region there are practically no settlements or large consumers of industrial enterprises that would need such energy supply.
Therefore, after the not very successful launches of several such energy projects to implement tidal stations, today these technologies are practically not used in Russia.
Excess electricity generating capacity
Russia's electric power industry is already in much better shape than it was ten years ago, so we can safely say that progress is being made. However, at a recent energy forum, the main problems of this industry in the country were identified. And the first of them is an excess of electricity generating capacity, which was caused by the massive construction of low-power power plants in the USSR instead of the construction of a small number of high-power power plants. All these stations still need to be serviced, so there are two ways out of the situation. The first is the decommissioning of facilities. This option would be ideal if it were not for the enormous costs of such a project. Therefore, Russia will most likely move towards the second option, namely increasing consumption.
Import substitution
After the introduction of Western stations, the Russian industry very acutely felt its dependence on foreign supplies - this also greatly affected the electric power industry, where in almost none of the modern fields of activity the complete production process of certain generators took place exclusively on the territory of the Russian Federation. Accordingly, the government plans to increase production capacity in the necessary areas, control their localization, and also try to get rid of dependence on imports as much as possible.
Billions of debt
Today, the total debt of electricity users throughout Russia is about 460 billion Russian rubles. Naturally, if the country had at its disposal all the money that was owed to it, it could develop the electric power industry much faster. Therefore, the government plans to tighten penalties for late payment of electricity bills, and will also encourage those who do not want to pay bills in the future to install their own solar panels and supply their own energy.
Regulated market
The most important problem of the domestic electric power industry is the full regulation of the market. In European countries, regulation of the energy market is almost completely absent; there is real competition there, so the industry is developing at a tremendous pace. All these rules and regulations greatly hinder development, and as a result, the Russian Federation has already begun purchasing electricity from Finland, where the market is practically unregulated. The only solution to this problem is a transition to a free market model and a complete abandonment of regulation.
Condition for economic growth - electric power industry
Electric power is one of the main conditions for economic growth and social development and has the importance of electricity for all types of life-supporting activities.
Although energy security has always been a key issue in all countries, countries are increasingly aware of the challenge of ensuring the growth of the sector in an environmentally friendly manner. Electricity and sustainable development are closely linked, and the sector has gained an important position. Agenda 21 urges countries to increase the contribution of environmentally friendly and cost-effective energy systems, especially new and renewable ones, by reducing pollution and increasing efficiency in energy production, transmission, distribution and use.
In particular, key issues on the 21st century agenda have shaped the role of electricity:
- improving access to electricity;
- addressing environmental and social issues in the energy sector;
- improving energy efficiency and using environmentally friendly energy systems (including advanced fossil fuel technologies);
- mobilization of financial resources, including private sector participation;
- promoting the development of renewable energy sources;
- resolving issues related to the use of electricity in transport;
- strengthening international and regional cooperation in the field of electricity supply.