For a number of reasons, the electric current transported through the wires of high-voltage power lines cannot be used directly. The main reason is high voltage, reaching tens or even hundreds of kilovolts. Therefore, before supplying electricity to consumers, a step-down transformer is used, which converts the voltage of 380 volts into the usual 220 volts.
In many cases, even this voltage is too high to power modern electrical equipment. This problem is solved by repeatedly lowering the voltage, often by rectifying the current. Until recently, each household appliance was equipped with its own step-down transformer. Today, transformerless power supplies already exist, but they cannot fully replace transformers due to their low output power. In electrical engineering, a step-down transformer will be in demand for a long time.
Transformer characteristics
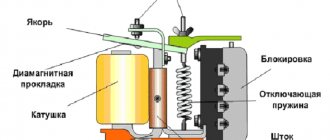
The design of the box with the transformer can be very diverse. The main element of the mechanism is a ferromagnetic core, the windings of which are framed by a special copper conductor. The primary part of the winding controls the voltage in the network, while the secondary is responsible for removing the reduced voltage.
The core emits alternating current, which creates a coupling between the two existing windings. The windings are not connected to each other by electric current. By the way, the ability to reduce tension arises due to the difference in the number of curls between these components.
Most often, these elements are protected by a special case, however, the structural features and varieties allow for various variations.
Types
In operating condition, the transformer core is constantly exposed to an alternating magnetic field, which causes the formation of eddy currents around it. This leads to heating of the magnetic circuit, which means useful energy is wasted. The percentage of losses depends on:
- core material;
- frequency response of magnetization reversal;
- maximum magnetic induction.
The easier it is to magnetize a metal, the easier it is to remagnetize with a mutual reduction in losses. Therefore, the cores are made from steel with pronounced magnetic properties. The phenomenon of eddy currents in monolithic conductors is gaining maximum momentum, since the material is endowed with low resistance. To reduce losses associated with this, this resistance is increased by assembling a magnetic circuit from steel sheets not exceeding 0.5 mm in thickness, with insulation in the form of varnish and scale. The insulating layer does not allow eddy currents to affect the magnetic flux in the core, which has a positive effect on losses. Assembly is carried out using one of two technologies:
- end-to-end - the core itself is assembled, then windings are placed on it, at the final stage everything is fastened together with a yoke (a simpler method, but losses are higher);
- interlacing (lamping) - the plates of each next row overlap the joints of the previous one (greater demand due to lower losses).
The geometry and type of magnetic circuit determine the typical differences between transformers. The type of magnetic circuit can be tape or plate. In turn, its shape gives the name and designation: armored magnetic cores are made W-shaped and are designated by the letter Ш, rod ones are U-shaped and P, ring ones are O-shaped and O, three-phase magnetic cores are made E-shaped, and orthogonal ones are designated three letters OPL. For tape magnetic cores, the letter L is added to the designation, for example, ШЛ, PL, OL, EL.
Thus, the armored transformer can be type Sh or ShL.
Sh
The most common type of BT. The middle rod with the general flow passing through it is closed by two outer rods. The cross-section of the outer rods is equal to half the cross-section of the middle one.
SHL
Tape (twisted) armor magnetic cores ШЛ also have the following subtypes:
- ShLM – with a reduced I1/I ratio;
- SHLO – with an extended window;
- ShLP – with an increased B/l ratio;
Types of step-down transformers
- Single-phase models are the most popular; they are connected to the network of the same name.
- Three-phase transformers include 380 V step-down transformers, which reduce the voltage level to the desired level.
- The multi-winding type contains more than two windings.
- The armor type is not very powerful. Framed with a magnetic drive.
- The toroidal type is a favorite for radio electronics masters. It is quite miniature, but powerful.
- Rod transformers do not have ornate designs and cope well with medium and high voltage.
Operating modes
T, like any secondary power source, has certain operating modes. The modes differ in the consumption of I. There are 2 modes: idle and load. When idling, T consumes a minimum amount of I, which is used only for magnetization and losses in the windings for heating. In addition, the magnetic field is dissipated. Ф is created by I magnetomotive force, which is generated by the primary winding. In this case, I idle is 3−10% of the nominal value (In).
When there is a load, winding I appears in winding II, and therefore magnetomotive force (MF) appears. According to Lenz's law: the MMF of the second winding acts against the MMF of the primary winding. In this case, the EMF in the primary winding during load T is equal to U and is directly proportional to F. In this case, obtaining k can be written as: I1 / I2 = w2/w1 = 1/k.
Based on the formulas for calculating k, you can get another relation T: e1 * I1 = e2 * I2 = 1.
This ratio shows that the power consumed by the primary winding is equal to the power consumed by the second winding under load. Power T is measured in volt-amperes (VA).
Transformer functions
So, why do we need step-down transformers? Let's start with the fact that very often this mechanism regulates the voltage in the network in industrial buildings.
Thus, the 220 V step-down transformer has found wide application in industry and households. In addition to their everyday use, these designs reduce the voltage in power lines and regulate the operation of the current.
Operating principle
The action of electromagnetic sweat of a transformer
The principle of operation of a single-phase transformer is based on the law according to which the alternating electromagnetic field acting in a turn induces an emf in a nearby conductor. The phenomenon is called Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, who was the first to discover this interesting effect. To substantiate it, the scientist developed an entire theory, which formed the basis for the operation of most modern electrical devices and units.
Its main provisions:
- when current passes through a coil of wire, a magnetic flux is formed around it, capturing all the same coils located nearby;
- under the influence of this flow, an EMF is induced in them, the shape of the changes coinciding with the original field;
- If there is a ferromagnet in it, this effect is enhanced.
All these principles form the basis of the operation of a modern transformer product. When connected to the secondary winding of the load, the operating circuit is closed, and the energy is transferred to the consumer with virtually no losses.
How to choose a step-down transformer?
There are many varieties and types of transformers, but when choosing them, you should pay attention to the following characteristics:
- Incoming voltage parameter, the parameter of which is usually marked on the product body. For domestic purposes, a 220 V transformer is used.
- Markings on the device body should also indicate the amount of output energy. In order to become more familiar with the features of the case and markings, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with photos of step-down transformers on the Internet.
- Make the following calculations to correctly select the power characteristics. Add up the energy value of all devices that will be connected to the device and add another 20%.
Power supply for 12 volt halogen lamps
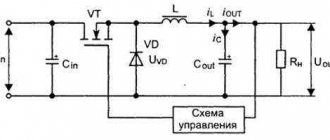
In order to use an electronic transformer as a power source, a number of electronic parts must be connected to it. In general terms, the circuit of such a power supply will work as follows.
The 220 V mains voltage passes through filters to a special part of the circuit called the driver. The current, passing through the key transistor and the primary winding, saturates the core, forming an EMF on the signal turns.
The resulting current charges the capacitor of the self-oscillating circuit, the voltage on the capacitor plates increases until the transistor closes. The potential difference on the signal winding disappears, and the capacitor is discharged through it, and the transistor switch opens again. The whole process occurs anew, its frequency is on the order of tens of thousands of Hertz. To obtain a constant voltage of 12 V, a diode bridge with a smoothing electrolytic capacitor is connected to the output of the device.
Pros and cons of transformers
This technique has its advantages and disadvantages. When choosing certain models, you need to take into account all the nuances. Let's start with the pros:
- Human safety at home and in industrial environments is guaranteed by this mechanism, which reduces the level of electric current intensity to 12 V, thereby guaranteeing the preservation of life and health.
- The input voltage does not matter too much since the output current is stable.
- Compact and miniature box.
- Easy to move and install.
- Low heating of the case.
- Accurate voltage regulation.
- Not too long a service time.
- High price.
- Insufficient power.
Application area
Today, many appliances used in everyday life require reduced voltage. These are modern televisions, personal computers and laptops, and various gadgets.
However, these devices either come complete with a transformer, called a power supply, or it is built into the device. But lighting is a separate issue.
Halogen or LED lamps (especially those installed in rooms with high humidity) require a separate voltage reduction device. This is due to safety requirements, although efficiency also plays an important role.
When purchasing a transformer for 12 volt LED lamps for the bathroom, you need to pay attention to the IP protection class. The device must be protected from splashes to avoid short circuits and failure. For a living room or bedroom, this requirement is not significant.