DRL lamps, which are still actively used today, belong to gas-discharge lighting devices. Their distinctive feature is rich luminous flux and durability. Due to the mercury content, these products are used to organize artificial lighting of streets and industrial areas. But certain technical and operational nuances do not allow them to be used in domestic conditions. In the article we will look at what a DRL gas-discharge lamp is, how it works, the principle of its operation and where it is used.
What it is
The names of lamps usually indicate the type of light source. A specialist who understands labeling will quickly determine the parameters and operating principle of the device.
The decoding of the DRL is as follows:
- D - the electric arc formed when voltage is applied to the contacts leads to the ignition of the lamp. The design involves a choke, the task of which is to limit operating currents within specified limits;
- P - the device operates using mercury vapor;
- L - operating principle of the light source. The phosphor, which provides the luminescence process, converts ultraviolet light into the visible spectrum of radiation.
This is what the product looks like.
Additional information! When external energy is applied to a material, the light emitted begins a glowing process called luminescence.
The variety closest to DRL is DRV (mercury-tungsten). They are similar in design and principle of operation. Only in addition to the mercury discharge torch, a tungsten spiral is also installed, the task of which is to limit the strength of the current supplied to the burner. Accordingly, such lamps do not require additional ballasts.
Unlike DRL, DVR lamps:
- consume more electricity;
- work for approximately 3000 hours;
- light up for no longer than one minute.
Other “close” types are DRI and HPS bulbs.
Size depends on power characteristics
What is a throttle for?
The throttle is responsible for the correct operation of the light source. Often, powerful devices require impressive network voltage levels. This in turn leads to overheating and burnout of the device. The component allows you to avoid such consequences. In this case, it must be connected in series to the electrical circuit.
Thus, the inductor limits the voltage and current during operation.
Figure 1. DRL choke
To limit current drops, a connection is made through a resistance element. It is a ballast of several inductance coils with high resistance, which prevents the lamp from burning out. In the gas environment of the DRL, an electrical breakdown occurs, leading to the appearance of an arc discharge. The ionized gas loses resistance, which causes an increase in current and the release of a significant amount of heat. If the current is not limited by special chokes, the heated gas environment will damage the lamp.
If the DRL is directly connected to the network, then failure in most cases is a matter of time . More often than not, overheating appears instantly. The rate of breakdown is influenced by specific indicators of the electrical circuit, voltage, external factors (air temperature, humidity, etc.). This only applies to conventional mercury lamps, which make up the majority of the market.
When connecting the inductor, you can not observe the polarity. It will ensure stable operation of the lamp and prevent possible breakdowns.
The main parameter for the inductor is the rated current. It is on this basis that equipment is selected taking into account the power of the lighting device. You can use the following table.
| Power of used DRL | Rated inductor current |
| 125 W | 1.15 A |
| 250 W | 2.15 A |
| 400 W | 3.25 A |
| 700 W | 5.45 A |
Despite the usefulness of the throttle, it is increasingly becoming a thing of the past. They are being replaced by modern electronic arc stabilization units. With their help, you can fine-tune operating parameters and control workloads. The set values will be maintained even with significant voltage drops in the network.
Figure 2. Chokes of different parameters
The reactance of the inductor is related to the parameters of the inductor. 1 Henry of inductance passes 1 A of current at a voltage of 1 V. When considering coils, it is worth considering:
- cross-sectional area of the copper conductor;
- number of turns;
- core material;
- cross section of the magnetic circuit.
The coil also has active resistance, which must be taken into account when selecting parts for specific lighting devices. Chokes of certain sizes are suitable for each type of DRL.
Advantages and disadvantages
Arc mercury fluorescent light sources, including lamps, have the following advantages:
- high degree of luminous flux;
- serve for a long time;
- suitable for lighting at sub-zero temperatures;
- thanks to the built-in electrodes, they do not require an additional ignition device;
- available ballasts.
There are also a number of disadvantages, some of which impose restrictions on the scope of application:
- as GOST states, mercury and phosphor contained in these lamps must be disposed of using a special technology;
- low color rendering (about 45%);
- A stable voltage is required for full operation. If it drops to 15%, the lamp with such a light bulb will stop shining;
- at too low temperatures (more than −20 degrees Celsius), the light source may not light up. In addition, such operating conditions significantly reduce the service life of the lamp;
- to turn on the lamp again, you must wait 10 to 15 minutes;
- decrease in luminous flux after approximately 2000 hours of service.
You might be interested in: Features of a fluorescent lamp
As a rule, the manufacturer specifies a number of rules that should be followed when operating these light sources. This will allow them to last longer. Even if the lamp is installed in the wrong position, its service life will be affected.
Glow from a mercury lamp
Characteristics
The abbreviation does not reflect the parameters of DRL lamps. But, you need to know this information, which will allow you to choose the right product. The main parameter of the light source is power, expressed in numbers. Indicators that determine operating conditions:
- light flow. This determines how many lamps are needed to create the required illumination of the area;
- life time. Each model has its own guaranteed service period;
- standard size of the base and dimensions. They influence the choice of luminaire for which the lamp is suitable.
DRL power ranges from 50 to 2000 W. The most common type is DRL 250, with the following parameters:
- power - 250 W;
- voltage - 130 V;
- luminous flux - 13500 lm;
- light output - 54 lm/W;
- base - E40;
- diameter - 91 mm;
- height - 228 mm;
- service life - more than 12,000 hours.
During the first 10-15 minutes of operation, the lamp “warms up”, consuming power above the rated value.
Models and their parameters
Product details
DRL lamps (mercury arc lamp) are a light source that operates on the principle of optical radiation, which is generated by a gas discharge from mercury vapor. Today this is a fairly common lamp that has become widely used in a variety of fields. Today, such lamps are used to create lighting:
- at industrial facilities. These are excellent industrial lamps that create a good luminous flux and can work in various conditions;
- for outdoor lighting. Such lamps are placed on poles located along roads, pedestrian paths in parks and squares. Outdoor type lamps can withstand various climatic conditions and even sudden temperature changes;
- creating the required level of illumination in public premises;
- for home, etc.
Note! The most widespread are DRL type lamps (250 lamps are more often used than 400 lamps), as well as DNaT lamps, which are used for street lighting.
Street lamp
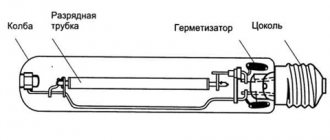
DRL lamps have an elongated shape, making them very similar to ordinary incandescent light bulbs. The product consists of the following components:
- metal base;
- glass flask;
- a tube containing mercury vapor. In the tube, mercury vapor is always under pressure. The tube is made of quartz glass.
Lamp structure
This structure determines the special operating principle of such devices.
Scope of application
DRL lamps are used as a source of artificial lighting. The following objects are illuminated with gas discharge devices:
- highways and streets;
- parks and squares;
- production workshops, warehouses, parking lots;
- greenhouses, conservatories and similar places where vegetables are grown.
with DRLs characterized by a powerful luminous flux. At the same time, their color rendering is poor, so they are not used for lighting residential premises.
Exploitation
Design
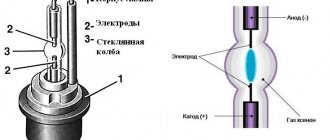
The design includes the following elements:
- glass container;
- threaded base;
- mercury-quartz burner filled with argon. Additionally, a drop of mercury is added;
- main cathodes;
- additional electrodes;
- additional carbon resistor.
Helpful information! The purpose of the additional electrodes is to facilitate lighting of the lamp. They are also responsible for stable operation.
The elements are discussed in more detail below:
- base It receives electricity from the network as a result of contact of the current-carrying parts of the lamp with the contacts of the lamp socket. As a result, electricity is transferred to the burner electrodes;
- quartz burner. It looks like a flask with two electrodes on each side (two are main, two are additional). The burner is filled with argon and a drop of mercury;
- glass flask. This is the outer part of the light bulb. Inside there is a burner with connected electrical conductors coming from the contact base. To pump nitrogen into the flask, all the air is first pumped out of it.
You might be interested in: Features of a sodium lamp
The first models of DRL lamps had only two electrodes. Such lamps were more difficult to light - an additional starting device was required. The modern, throttle version is equipped with four electrodes.
Device
Operating principle of the DRL lamp
The burner of the product is made of transparent, chemically resistant, refractory material - quartz glass or special ceramics. It is filled with a precisely measured dose of inert gas and a drop of metallic mercury. The luminous body in the structure is a column of arc electric discharge.
The principle of operation inherent in the DRL lamp looks like this. When electricity is supplied to the product, a glow discharge is formed between the main and ignition electrodes. The elements are located so close to each other that they provide a lower breakdown voltage. A glow discharge almost instantly becomes an arc discharge. The electrical and luminous qualities of the lamp become stable 10 - 15 minutes after energy is supplied. During this period, the current exceeds the rated values (the ballast is used for limitation). The starting mode largely depends on the ambient temperature - in cold weather the light bulb takes longer to “start”.
It is in the burner that all the action takes place
As a result of the electrical discharge in the burner, blue and violet radiation, including UV (ultraviolet) radiation, becomes visible. They provoke the glow of the phosphor located on the inner walls of the flask. The burner shines with white-green light, the phosphor - reddish. The shades are mixed and the result is a bright color close to white.
If the voltage fluctuates in the electrical network, this is reflected in the luminous flux. Permissible voltage deviations are from 10 to 15% (in this case, the luminous flux will fluctuate by 25 - 30%). If the supply voltage drops to 80% of normal, the product simply will not light up. If it was on fire before, it will go out.
DRLs get very hot during operation. Because of this feature, it is necessary to carefully consider the design: use heat-resistant wires and high-quality contacts on the sockets. As the lamp heats up, the pressure in its burner increases, and with it the breakdown voltage. That is, the network voltage may not be enough to turn it on again. To restart the product, it needs time to cool down. This is the main drawback of DRLs - power surges simply extinguish them, and turning them on again requires a pause.
Additional Information! If the surrounding air is warm, the product will quickly reach the maximum light emission mode.
You may be interested in How to arrange lighting in the garage
How to connect correctly
The DRL connects to the network in the same way as a traditional incandescent light bulb. The only thing is that for the gas-discharge product to operate, a ballast is required, namely a choke. It is he who regulates the operating current values. This element also prevents the lamp from burning out.
Additional Information! The choke not only “lights up” the lamp, but also corrects its operation. Its functional task is to stabilize the voltage supplied to the contacts of the gas discharge tube.
The chokes themselves are either independent or built-in. The choice of a suitable lamp depends on this.
Below is a connection diagram with the following symbols:
- EL1 - DRL;
- C is a non-electrolytic capacitor designed to operate with a voltage of at least 250 V. It reduces reactive power and, as a result, reduces electricity consumption;
- L1 - throttle. Selected depending on the power characteristics of the lamp;
- F1 - fuse.
If you try to start a light bulb without a choke, it will instantly burn out, as it will pass a large current through itself. DRL products should be handled carefully, since they contain, even if only a drop, mercury, which disperses throughout a room of 25 m2.
Connection diagram
Connection diagrams
Most DRL devices have a choke in the circuit. However, there are methods that allow you to use DRL without a choke.
Figure 3. Connecting to a light bulb socket
Throttle
The connection diagram for any DRL lamp is quite simple and includes connecting the loads in an electrical circuit in series. A 220 volt network is used, operating at a standard frequency. Due to this, even a high-power street lighting source can be connected to a regular home network.
Resistance stabilizes and corrects nutritional indicators. Due to it, a uniform glow is achieved without blinking and other undesirable factors. The luminous flux remains unchanged, which is important for any lighting source.
Figure 5. Connection diagram for DRL via inductor
During startup, the system consumes significant voltage, which often reaches two or three input ratings. The resistance stabilizes this voltage and prevents the device from burning out.
The DRL lamp does not light up instantly. In some cases, it can take up to fifteen minutes to fully warm up and reach maximum light output.
The power of lighting devices can range from 50 to 2000 W. Specific power indicators do not affect the connection diagram and always require a single-phase 220 V network with a frequency of 50 Hz.
No throttle
If you need to connect a DRL 250 lamp without a choke, a simple solution would be to purchase a DRL that functions without additional components. The devices have a spiral installed inside, which is responsible for stabilizing the voltage.
You can also use a traditional incandescent lamp. It must be equivalent in power to the DRL used and have the required resistance rating. The incandescent lamp acts as a resistor, effectively lowering the output voltage.
Figure 5. Connection diagram for DRL without choke
The resistance element can be replaced with a capacitor or a set of capacitors. In this case, it is important to calculate the current supplied by the circuit as accurately as possible so that it corresponds to the operating voltage.
Life time
According to the manufacturers, such a light source is capable of burning for at least 12,000 hours. Here everything depends on such a characteristic as power - the more powerful the lamp, the longer it lasts.
Popular models and how many hours of service they are designed for:
- DRL 125 - 12000 hours;
- 250 - 12000 hours;
- 400 - 15000 hours;
- 700 - 20000 hours.
Note! In practice, the numbers may be different. The fact is that electrodes, like the phosphor, can fail faster.
As a rule, light bulbs cannot be repaired; they are easier to replace, since a worn-out product shines 50% worse.
Products are designed for at least 12,000 operating hours
There are several varieties of DRL (meaning mercury arc lamp), which are applicable both in everyday life and in industrial conditions. Products are classified by power, with the most popular models being 250 and 500 W. Using them, street lighting systems are still being created. Mercury devices are good due to their accessibility and powerful luminous flux. However, more innovative samples are appearing, safer and with better glow quality.
High pressure mercury arc lamps type DRL
Lamps of the DRLF type have an increased proportion of radiation in the red region of the spectrum, a reflective reflective layer on the inner surface of the bulb and are intended for use in irradiation installations for growing plants in greenhouses, greenhouses, and phytotrons.
DRL, DRLF lamps are operated in alternating current networks with a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 220 V with the corresponding ballasts (ballasts).
High-pressure mercury arc lamps of the DRV type are operated without ballasts and are used for lighting park areas, open spaces, as well as for direct replacement of incandescent lamps used for outdoor lighting.
The DRV 750 lamp is intended for additional irradiation of plants in greenhouse farms. Type
| Voltage, V | Power, W | Light. flow, lm | Average cont. horizon, h | L, mm | D, mm | Base type | Rice. | |
| DRL 50(15) | 50 | 1900 | 10000 | 130 | 56 | E27 | 206 | |
| DRL 80(15) | 80 | 3600 | 12000 | 166 | 71 | E27 | 206 | |
| DRL 125HL1 | 125 | 5480 | 8000 | 178 | 76 | E27 | 206 | |
| DRL 125(10) | 125 | 6200 | 12000 | 178 | 76 | E27 | 206 | |
| DRL 125(15) | 125 | 6300 | 12000 | 178 | 76 | E27 | 206 | |
| DRL 125(6) | 125 | 5900 | 12000 | 178 | 76 | E27 | 206 | |
| DRL 125(8) | 125 | 6000 | 12000 | 178 | 76 | E27 | 206 | |
| DRLR 125 | 125 | 5700 | 12000 | 190 | 127 | E27 | 207 | |
| DRV 160 | 220 | 160 | 3000 | 3000 | 177 | 77 | E27 | 210 |
| DRL 250HL1 | 250 | 11500 | 8000 | 228 | 91 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 250(10)-4 | 250 | 13500 | 12000 | 228 | 91 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 250(14)-4 | 250 | 13500 | 12000 | 228 | 91 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 250(6)-4 | 250 | 13000 | 12000 | 228 | 91 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 250(8) | 250 | 13200 | 12000 | 228 | 91 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRVED 220-250 | 220 | 250 | 3250 | 1500 | 190 | 127 | E27 | 207 |
| DRV 250 | 220 | 250 | 4700 | 3000 | 225 | 91 | E40 | 210 |
| DRL 400HL1 | 400 | 20000 | 8000 | 292 | 122 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 400(10)-4 | 400 | 24000 | 15000 | 292 | 122 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 400(12)-4 | 400 | 24000 | 15000 | 292 | 122 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 400(6)-4 | 400 | 23500 | 15000 | 292 | 122 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 400(8) | 400 | 23700 | 15000 | 292 | 122 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRLF 400-1 | 400 | 20000 | 7000 | 350 | 152 | E40 | 208 | |
| DRLF 400-2 | 400 | 20000 | 7000 | 292 | 122 | E40 | 209 | |
| DRV 500 | 220 | 500 | 12500 | 3000 | 292 | 122 | E40 | 210 |
| DRL 700(10)-3 | 700 | 41000 | 20000 | 357 | 152 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 700(12)-3 | 700 | 41000 | 20000 | 357 | 152 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 700(6)-3 | 700 | 40600 | 20000 | 357 | 152 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 700(8) | 700 | 40800 | 20000 | 357 | 152 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRV 750 | 220 | 750 | 2500 | 368 | 152 | E40 | 210 | |
| DRV 750-1 | 220 | 750 | 22000 | 2500 | 368 | 152 | E40 | 210 |
| DRL 1000(10)-3 | 1000 | 59000 | 18000 | 411 | 167 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 1000(12)-3 | 1000 | 59000 | 18000 | 411 | 167 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 1000(6)-3 | 1000 | 58000 | 18000 | 411 | 167 | E40 | 206 | |
| DRL 1000(8) | 1000 | 58500 | 18000 | 411 | 167 | E40 | 206 |