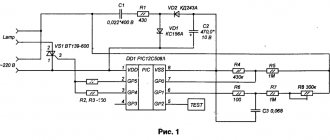
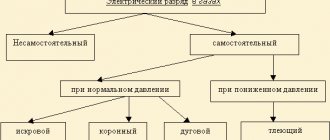
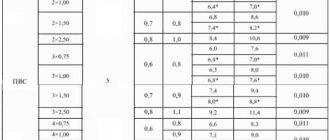
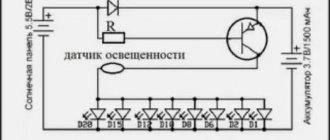
06/21/201606/26/2016 master
Lighting is always and everywhere the main attribute, without which it is difficult to imagine the modern world. At the same time, few people think about what light sources exist today, but each type of lamp creates its own luminous flux. Among the variety of light bulbs that can be screwed into a lighting fixture, gas-discharge light sources occupy a special place.
Today, gas-discharge lamps are found very often and in a wide variety of areas of human activity, from car lighting to home lighting. Therefore, it will not be superfluous to know what this product is and how it should be handled. Today's article will tell you everything you need to know about gas-discharge light bulbs.
Review
Gas discharge lamps are a modern light source that emits light energy in the range visible to the human eye. Basically, a gas-discharge light bulb has a glass bulb into which gas or metal vapor is pumped under pressure. In addition, the structure of the product contains electrodes that are located at the ends of the glass flask.
Lamp structure
The principle of operation of the light bulb is based precisely on this structure, since the entire system is activated when an electric discharge passes through the bulb. The main electrode is located in the central part of the flask. A current-limiting resistor is installed under it. Thanks to this design, a glow is formed in the flask when an electric discharge passes through it. In addition to the bulb and electrodes, the product also contains a base, thanks to which it can be screwed into various lamps to create home or street lighting. Note! Most often, gas-discharge light bulbs are found in street lighting systems. They are often screwed into lights, cars, etc. Gas discharge lamps are special devices that are capable of creating a glow using an electrical discharge.
Conclusion
Despite all their advantages and disadvantages, gas-discharge lamps will not go out of use for a long time. They are especially indispensable where a spectrum close to the sun is required. For powerful illuminators, this is still a universal option, since the ratio of all characteristics and price distinguishes them from other types of lighting.
- Related Posts
- Decorative neon lamp 220 V: principle of operation, characteristics, how to connect
- Aquarium lamps and fixtures: types, requirements and characteristics
- We'll tell you all about lamp sockets
How does a light bulb work?
We discussed the design features that gas-discharge lamps have in the previous section. We also briefly touched on the operating principle of this product. Now let’s look at the principle of operation in more detail to understand exactly how this type of light source generates lighting.
Operating principle of the lamp
Gas discharge lamps are special light sources that are capable of generating light due to the creation of an electrical discharge inside its bulb. The principle of operation of such a lamp is based on the ionization of gas, which is located inside a glass flask. The principle by which a gas-discharge light bulb works assumes that a certain gas is pumped inside the bulb under pressure. Most often, noble (inert) gases are used to illuminate houses, streets and cars:
- neon;
- krypton;
- argon;
- xenon;
- a mixture of gases in various proportions.
Mercury model
Very often, to illuminate houses, cars and streets, light sources that contain additional gases are used. For example, the gas mixture may contain sodium (sodium models) or mercury (mercury models). Note! Mercury lamps are more common today than sodium lamps. They are often inserted into lanterns when creating street lighting. They are also used to illuminate houses from the inside.
Mercury and sodium models are included in the group of metal halide light sources. When power is applied to the discharge lamp, an electric field begins to be generated in the tube. It leads to ionization of gas and free electrons. As a result of this, electrons that rotate at the upper levels of atoms begin to collide with other electrons of metal atoms (special additives in gas mixtures). As a result of the collision, electrons move to outer orbitals. Ultimately, energy and photons are released. This is how the light bulb glows.
Note! The lighting that results from the operation of such a light bulb can be different: from ultraviolet to infrared visible radiation.
Lamp glow option
To achieve a different color glow, a special luminescent coating is applied to the bulb of gas-discharge lamps. They cover the inside of the flask. This coating converts ultraviolet radiation into visible light.
Scheme for switching on a fluorescent lamp without heating the electrodes (instant start)
A distinctive external feature of such lamps and ballast is the presence of only one electrode on each side of the lamp, instead of two.
The advantage of this switching scheme is the lower power consumption of the ballast (1-2 per lamp) compared to other magnetic ballasts, the possibility of independent parallel switching of lamps (usually in a circuit with preheat, rapid start ballasts, the failure of one lamp leads to the fact that the others stop working burn), the possibility of installing the ballast more remotely from the lamp (for preheat, rapid start, usually the length of the wire from the ballast to the lamp should not exceed a meter, although there are special ballasts)
| to the top of the page back to the table of contents |
Types of gas discharge lamps
High pressure sodium lamps
A gas discharge lamp, which is used to create street lighting or car lighting, can have a varied structure that does not deviate from the principles of operation. This is the basis for the classification of such light sources. Today, gas-discharge light sources come in the following types:
- high pressure gas discharge lamps. They, in turn, can be divided into DRL (mercury models), DRI, DNat and DKsT. Their feature is that there is no need for a ballast. Such models can be found as street lighting (they are inserted into lamps of street lighting systems), cars, houses and outdoor advertising;
Note! High pressure gas discharge lamps are the most common (especially mercury models). Very often they are used (sodium and mercury models) to create street lighting. But at home such light sources are quite rare.
Low pressure lamps
- low pressure gas discharge lamps. They are divided into LL (various models) and CFL. Such light bulbs are now successfully replacing outdated incandescent lamps. They are used to create illumination for houses, streets (as part of a street lighting system) and even cars.
Note! The most common low-pressure lamps are fluorescent. Such models are often used for street lighting as part of a street lighting system. Especially often, such light bulbs are screwed into lanterns.
Gas-discharge light bulbs have become widespread due to their number of advantages.
Life time
According to the manufacturers, such a light source is capable of burning for at least 12,000 hours. Here everything depends on such a characteristic as power - the more powerful the lamp, the longer it lasts.
Popular models and how many hours of service they are designed for:
- DRL 125 - 12000 hours;
- 250 - 12000 hours;
- 400 - 15000 hours;
- 700 - 20000 hours.
Note! In practice, the numbers may be different. The fact is that electrodes, like the phosphor, can fail faster
As a rule, light bulbs cannot be repaired; they are easier to replace, since a worn-out product shines 50% worse.
There are several varieties of DRL (meaning mercury arc lamp), which are applicable both in everyday life and in industrial conditions. Products are classified by power, with the most popular models being 250 and 500 W. Using them, street lighting systems are still being created. Mercury devices are good due to their accessibility and powerful luminous flux. However, more innovative samples are appearing, safer and with better glow quality.
For general lighting of workshops, streets, industrial enterprises and other facilities that do not have high requirements for color rendering quality, high-pressure mercury lamps of the DRL type are used.
Device
The DRL lamp (see figure on the right) has the following structure: a glass cylinder 1, equipped with a threaded base 2. In the center of the cylinder there is a quartz burner (tube) 3 filled with argon with the addition of a drop of mercury. Four-electrode lamps have main cathodes 4 and additional electrodes 5, located next to the main cathodes and connected to the cathode of the opposite polarity through an additional carbon resistor 6. Additional electrodes make it easier to ignite the lamp and make its operation more stable.
Recently, DRL lamps have been manufactured as three-electrode lamps, with one starting electrode and a resistor.
Operating principle
In a burner made of durable, refractory, chemically resistant transparent material, in the presence of gases and metal vapors, a discharge glow—electroluminescence—appears.
When voltage is applied to the lamp between the closely spaced main cathode and an additional electrode of reverse polarity at both ends of the burner, gas ionization begins. When the degree of gas ionization reaches a certain value, the discharge moves to the gap between the main cathodes, since they are included in the current circuit without additional resistance, and therefore the voltage between them is higher. Stabilization of parameters occurs 10-15 minutes after switching on (depending on the ambient temperature - the colder it is, the longer the lamp will light up).
An electrical discharge in a gas creates visible white without the red and blue components of the spectrum and invisible ultraviolet radiation, causing a reddish glow of the phosphor. These glows are summed up, resulting in a bright light that is close to white.
When the mains voltage changes by 10-15% up or down, the working lamp responds with a corresponding increase or loss of luminous flux by 25-30%. If the voltage is less than 80% of the mains voltage, the lamp may not light up, but may go out when lit.
When burning, the lamp becomes very hot. Due to its peculiarity, the DRL lamp must cool down after turning off before turning it on again.
Traditional areas of application of DRL lamps
Lighting of open areas, industrial, agricultural and warehouse premises. Wherever this is due to the need for great energy savings, these lamps are gradually being replaced by low-pressure lamps (lighting of cities, large construction sites, high production workshops, etc.).
The abbreviation “DRI” stands for “arc mercury with radiating additives (metal iodides and bromides).” Along with mercury, sodium, thallium and indium iodides are introduced into these lamps, due to which the light output significantly increases (it is approximately 70 - 95 lumens / W and higher) with a fairly good color of the radiation. The lamps have ellipsoidal and cylindrical bulbs. A quartz or ceramic cylindrical burner is placed inside the flask, where a discharge occurs in vapors of metals and their iodides. Service life - up to 8-10 thousand hours.
Advantages and disadvantages
Street lighting
The main advantages of such light bulbs include the following qualities:
- high luminous efficiency (at 55 lm/W). It remains quite high, even if the lanterns in which the light bulb was installed have an opaque shade;
- long service period. The average performance of gas-discharge light bulbs is approximately 10 thousand hours. Therefore, such products are often used to illuminate streets and cars;
- high resistance (for example, mercury models) to poor climatic conditions. As a result, they are often used for street lighting. They can be screwed into lanterns and other types of lamps. But if the region is characterized by frosts, then it is impossible to use mercury models for street lighting, even if they are screwed into special lamps and car headlights;
- affordable price;
- cost-effectiveness, which allows you to avoid spending on expensive components for lighting equipment.
However, there are also disadvantages here:
- lamps have poor color rendering. This is due to the limited spectrum of rays. Thus, it will be somewhat difficult to see the color of the object in the light created by the light bulb. In this regard, gas-discharge light bulbs are often used to illuminate streets and are mounted in car headlights;
- can only work in the presence of alternating current;
- switching occurs using a ballast choke;
- there is a period required to warm up the light source;
- danger of use, since the gas mixture may contain mercury vapor;
- Such lamps have increased pulsation of the emitted light flux.
Separately, it should be noted that the installation of these products is carried out according to the standard scheme, like incandescent lamps.
Operating Parameters
- The service life ranges from two thousand to 20 thousand hours, reflecting the duration of active use.
- Luminous output in the range of 40 – 220 lm/W.
- Color temperature for each model ranges from 2.2 to 20 kK.
- The color rendering index shows the intensity of color perception of different surfaces.
- Power consumption determines the load from the electrical network.
- The readiness time indicates the time interval from the moment voltage is applied to operation in normal mode.
- The ignition voltage represents the smallest potential difference capable of starting a discharge.
Application area
The design features of gas-discharge light bulbs have provided them with a wide range of applications. Today, such products are used for:
- creating street lighting in urban and rural areas. These lamps look great if they are screwed into lanterns to create high-quality lighting for parks and squares;
- lighting of production facilities, shops, trading floors, offices, as well as public spaces;
- with the help of gas-discharge light sources that are screwed into lanterns, you can decorate street decorative lighting of buildings or pedestrian paths;
- illumination of outdoor advertising and billboards;
- highly artistic lighting of stages and cinemas. But here it is necessary to use special equipment.
Car lighting
Separately, it is worth noting that gas-discharge light sources today are very often used to illuminate vehicles. Here, high-intensity lights are often used (for example, neon). Many cars are equipped with headlights that are filled with a gaseous mixture of metal halide salts and xenon. Such headlights can be found in brands such as BMW, Toyota or Opel. Sometimes similar light bulbs can be found in home lighting. But here it is necessary to take into account the specifics of light sources so that their shortcomings can be minimized. But in general, the scope of application of these products is quite extensive and varied.