Rheostat as a simple dimmer
In simple words, a dimmer is an AC rheostat, but with a more complex design. The variable resistor was first invented by J. Poggendorff in the 19th century to change voltage (U, V) and current (I, A) by increasing / decreasing resistance (R, Ohm).
Depending on the type of rheostat, the value of R changes smoothly or stepwise.
To reduce the brightness of a light source, you need to reduce the voltage using a rheostat, and for this, resistance is added.
Due to the increase in R and I, the device becomes very hot and releases heat to the surrounding air. As a result, such a regulator has low efficiency and, as a result, is not used.
Purpose
The word “dimmer” comes from the English “dim”, which literally means “to darken” in Russian. But Russians themselves often call a dimmer a dimmer, because it is an electronic device with which you can change electrical power (that is, adjust it up or down).
Most often, such a device is used to control the lighting load. The dimmer is designed to change the brightness of the light emitted by LED lamps, as well as incandescent and halogen lamps.
The simplest example of a dimmer is a variable resistor (or rheostat). Back in the 19th century, German physicist Johann Poggendorff invented this device so that it could be used to regulate the voltage and current in an electrical circuit by increasing or decreasing resistance. A rheostat is a resistance-adjustable device and a conductive element. Resistance can change stepwise and smoothly. To obtain low brightness of light, it is necessary to reduce the voltage. But the resistance and current will be high, which will lead to strong heating of the device. So such a regulator is completely unprofitable; it will operate with low efficiency.
Autotransformers can also be used as a dimmer. Their use is due to their high efficiency; throughout the entire adjustable range, an almost undistorted voltage will be produced with the required frequency of 50 Hz. But autotransformers are quite large, weigh a lot, and require considerable mechanical effort to control them. In addition, such a device will be expensive.
Electronic dimmer - this option is the most profitable from an economic point of view. It is compact and has a slightly different operating principle. Let's talk about it in more detail.
Application
Due to their simplicity of design and functionality, modern dimmers are widely used.
Main directions:
- Creation of different lighting modes in one and/or several rooms.
- Reducing electricity costs by switching lighting to standby mode.
- In a power tool to reduce and increase the speed of a commutator electric motor.
- Zoning a room into several conventional areas.
- Illumination of art objects, for example, sculptures or paintings. Different degrees of lighting allow you to draw more attention to the exhibit.
- Creating the illusion of a person being in an apartment/house by changing the lighting level.
- In electric heaters to regulate their power.
- Change brightness for birds/animals that have special requirements for this parameter.
- Warming chicks immediately after birth. Depending on the degree of brightness, the degree of heating also changes.
- Carrying out home parties when brighter lighting is required at the table, and dim lighting in the dance area.
- Creating an intimate atmosphere in the bedroom.
The scope of application of dimmers is huge, and everyone can come up with a new option, taking into account the capabilities of the electronic device.
The dimmer is equipped with a microcontroller and has a wide range of options:
- changing the brightness level;
- automatic shutdown;
- creating the effect of the presence of people thanks to automatic on/off;
- flashing/dimming modes;
- smooth switching on/off of lighting;
- remote control via IR channel, radio channel, acoustic noise (for example, cotton), etc.
The best manufacturers and models of LED dimmers
It is a pity that a concern such as Schneider Electric does not produce dimmers for LED lamps - they limited themselves to devices for LED strips. However, there are many other manufacturers on the Russian market whose product quality is high. Let's try to choose the best of them. We will consider, which is not very widely known, but produces very high-quality and relatively inexpensive dimmers.
Quite a miniature device controlled by a key fob
A large manufacturer with an excellent reputation - “Arlight” with model LN014
This manufacturer specializes mainly in the manufacture of dimmers and controllers for LED equipment. The quality of the products is always at its best, and therefore we could not ignore it.
| brand, model | Max. Power, W | Dimensions, mm | Remote/control connection | Availability of remote control | Load current |
| LN014 | 220 | 104×68×30 | RF radio | Included | 1A |
Arlight LN014
Dimmers are among those products that are practically not counterfeited. Thanks to this, you can be sure that if the manufacturer has a good reputation, you don’t have to worry about quality. This does not apply to Chinese products.
Current dimmer SRP-1009-50W (220V, 200-1500mA)
Quite an interesting device. Although the dimmer supports remote control function, a remote control is not included. However, the device itself is made with high quality. Of course, the price is a little high, but the durability in operation justifies it. Let's look at the characteristics of the product.
This is what the Arlight SRP-1009-50W dimming device looks like
| brand, model | Max. Power, W | Dimensions, mm | Remote/control connection | Availability of remote control | Load current |
| SRP-1009-50W | 50 | 210×50×32 | RF radio | No | 0.2-1.5 |
Current dimmer SRP-1009-50W
This model is suitable for those who use 2-3 LED lamps for lighting. Considering that the average power of one is 11-15 W, this power is quite enough.
Another dimmer - CT20-DIM
This is the cheapest and weakest of the dimmers considered today. It makes sense to install this only in very small rooms with one light bulb. However, the quality of the products is at the highest level. That is why the device is included in our top three.
| brand, model | Max. Power, W | Dimensions, mm | Remote/control connection | Availability of remote control | Load current |
| CT20-DIM | 20 | 102×60×30 | RF radio | No | 0.35-0.7 |
dimmer CT20-DIM
Considering various manufacturers and the cost of their products, we came to the conclusion that if there is a desire to install a dimmer at home, then with the assortment that is offered to the buyer, choosing the appropriate model is not difficult. Moreover, this applies to all segments of the population, regardless of income level.
Remote control control is very convenient, but some people refuse it in favor of Wi-Fi
Electronic dimmers
For those who want to go deeper into the topic.
These are small in size and economical devices, the operation of which is based on a control switch: transistor or triac.
Most of these dimmers have a non-sinusoidal output signal, and the sinusoid sections are “cut off” by the existing switch.
Such dimmers are not intended for connecting devices powered by currents with low harmonic distortion.
The category of such devices includes electric motors, induction type transformers for halogen lamps, etc. This is due to the risk of device failure due to overheating.
In addition, budget electronic dimmers without special filters are sources of strong interference.
What is a dimmer
The simplest light controller is a variable resistor, including a rheostat, but such a variator produces significant power indicators, which causes a very low efficiency when the device heats up too much.
The variator increases the efficiency of devices
A car transformer can also serve as a standard luminous flux regulator.
History of invention and improvement of the device
The first mechanical dimmers were invented by Granville Woods more than a century ago, and were widely used to achieve smooth and slow dimming in theatrical lighting. A little later rheostats appeared. Such electrical devices, invented by Johann Poggendorff, were used to regulate the strength of current indicators and voltage within an electrical circuit. The device was represented by a conductive element and a special device that smoothly or stepwise regulated the electrical resistance.
The very first variators were distinguished by a mechanical control method and were capable of only changing the brightness of the lighting fixture. The most modern and multifunctional light controllers are equipped with a microcontroller and also have a whole set of advanced functions, including:
- lighting brightness control;
- automatic shutdown;
- simulating the presence of people;
- smooth switching on and off of light;
- various dimming or flashing modes;
- remote control.
Electronic devices deservedly belong to the category of the most compact and very economical devices. All the most modern electronic variators have a power element in the form of a semiconductor triac or transistor switch, but a significant part of such devices produce cut-off sections of a sinusoid at the output.
A lighting fixture with a regulator can become multifunctional
For this reason, it is strictly forbidden to connect to such regulators any devices that require power from current indicators with low harmonic distortion values. It is important to remember that cheap and low-quality electronic regulators do not have a special filter, and therefore are capable of generating too much electromagnetic interference.
Application area
Modern light controllers are widely used in domestic and industrial settings. The main purpose of such a device is to save electrical energy, change the brightness of lighting in the conditions of modern design solutions, and use lighting during celebrations.
The dimmer can be combined with security systems
Using a dimmer switch in incandescent lamps at low brightness levels in the evening or at night is ineffective. In addition, the operation of controllers when using LED strips makes it possible to easily adjust the color of the emitted light flux, the level of brightness, and also helps to create dynamic lighting effects not only in residential premises, but also when arranging billboards and modern store displays.
Design and principle of operation
Externally, dimmers resemble ordinary switches, but they allow you to adjust the brightness level. Let's look at different execution schemes and their features.
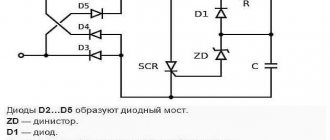
On a thyristor
In most cases, a thyristor is used as the main element.
The general operating algorithm is as follows:
- While the SCR thyristor is closed, the capacitor (C) gains charge through the resistance.
- The voltage of the input half-wave increases.
- At a certain moment (when the voltage increases above 32 Volts), the ZD dinistor opens, and after it the SCR thyristor opens.
- A current passes between the terminals and flows until the value drops to the level required to close the ZD.
- The capacitor is discharged through D1 (diode) and SCR.
- The thyristor closes and the process repeats again.
By opening the thyristor at certain intervals when passing through “0,” it is possible to “cut off” the sinusoid and thereby change the voltage parameter and load current.
With throttle
Many dimmers use switches that, when added to the circuit, produce electromagnetic (EM) oscillations in a wide frequency range.
Such waves cause current to appear in the wires connecting the dimmer, power supply and load, thereby creating interference.
To combat the problem, inductance chokes or LC filters are used. They are installed near the load or power source.
The higher the frequency, the more compact the inductor. By choosing the right filter, you can reduce the level of interference to a minimum.
On a resistor
Dimmers with resistance R are used to change the brightness of incandescent lamps.
Structurally, the device consists of a rheostat / variable resistance, and operates on the basis of Ohm's law.
As the resistance increases, the current in the bulb decreases, which reduces the activity of the filament.
The design is very simple, but it has a big disadvantage - constant power consumption, regardless of the adjustment position.
So, as the resistance increases, the current decreases, but the total load remains unchanged. Excess energy is converted into heat and goes into the air.
Therefore, it will not be possible to save electricity using such devices.
Resistor dimmers are rare, but are used to change the brightness of semiconductor lamps.
We are talking about an analog control method, which is almost never used due to low efficiency and high sensitivity.
On a triac
This circuit is a little more complicated than the resistor version. A triac is used here, playing the role of a key and changing the current parameters.
During operation, the voltage represents pieces of negative / positive half-waves, and when the brightness decreases, the light bulb is powered by “stumps”.
A 200 Hz signal arrives at the PWM generator. In this case, the brightness changes taking into account the time interval and pulse length. The current/frequency parameters remain unchanged.
Despite the great complexity of execution, the triac circuit has a number of advantages.
Thus, increasing the brightness does not increase the current load. In addition, such devices can be controlled/switched on remotely or near the light source itself.
How it works - DIMMER
What is the difference between regular and dimmable LED lamps
LED lamps can be divided into 2 categories - dimmable and non-dimmable (regular). The latter, of course, are cheaper, but their use does not involve connecting via a dimmer - you still won’t be able to dim the light. Dimmable light bulbs can be distinguished by the inscription “dimmable” and markings on the body and packaging. In the picture below you can see what it looks like.
A light bulb with the ability to reduce the luminous flux using a dimmer and corresponding markings
A dimmable lamp differs from a regular lamp in the presence of a special PWM (pulse width modulation) block in the circuit. It is this that allows you to adjust the light intensity in the range from 10% to 100%.
Doctors say that watching TV in complete darkness has a very strong effect on the eyes and spoils vision. With all the lights on, viewing cannot be called comfortable either. For such cases, the ideal solution would be dimming - dimmed, unobtrusive light will protect the eyesight of household members.
Pros and cons of dimming: what you should know about dimmers
Dimming 220V LED lamps has quite a few advantages:
- a lamp with a dimmer consumes less electricity;
- the service life of lighting devices increases;
- it becomes possible to zone the room using the difference in luminous flux;
- absence of radio interference during operation;
- you can purchase devices with additional functions (switch off/on timer, control via Wi-Fi or remote control);
- The dimmer is easy to connect - this work does not require special knowledge or skills.
But there is only one negative side - the rather high cost, especially for complex electronic models with many additional functions.
Quite an expensive device - Wi-Fi dimmer
Before purchasing a dimmer, you should weigh the pros and cons. If you plan to use it frequently, then over time it will pay for itself in the energy saved. If the dimmer is rarely used, then such a purchase can hardly be called rational - although you should not save on your health.
Types of devices
Depending on the scope of application and tasks assigned to the dimmer, it may differ in appearance, cost and functionality.
Below we will consider the main types of dimmers, which differ in installation, control and type of lamps.
By installation method
Based on installation features, all dimmers can be divided into several types:
- Wall. It is screwed to the wall in an overhead way or mounted in a mounting box with a diameter of 6.8 cm. With this installation, you do not need to disassemble anything, and the main requirement is the presence of wiring laid along the walls.
- Portable. Structurally similar to a tee or relay, it has connectors for connection and a plug. The device connects like a regular device with the ability to change the brightness of the lighting. You can connect a lamp, floor lamp or lamp to such dimmers. Can be used as a heating source in the presence of an IR lamp.
- Hidden (modular). This type of installation is relevant for modular structures that are mounted on a DIN rail in a panel with automatic machines. The power first goes to the dimmer, from which the wires branch out to the light sources. The advantage of this design is that you can replace several individual devices with one device with multi-channel control. To adjust the light, you need to open the flap and make settings.
- Built-in. Combines the advantages of hidden and wall dimmers discussed above. Such equipment is mounted in partitions, and a control panel is mounted at the top. Externally, the device has much in common with a switch. The difference is that there are elements of smooth control here.
- Suspension. It is small in size and is mounted in the section of the light bulb's power wire. The use of such a dimmer allows you to adjust the light even in the absence of an option.
By management
All dimmers differ in the way they are controlled:
- Rotary. Structurally, they consist of a casing and a wheel, the movement of which changes the brightness. Changing the position of the regulator allows you to turn the lighting to maximum or turn off the light altogether. This version of the dimmer has no memory, so after turning off all settings are reset and you have to set them from scratch.
- Push-button. They have much in common with conventional switches. They consist of a pair of buttons responsible for turning on and brightening the lighting. To select a parameter, you must press, hold it pressed, or release the control element.
- Turn-push. Structurally, they have much in common with a switch, in the center of which a round control element is installed. To adjust the brightness you need to press on it, and to turn it off you need to press the button. After switching off, the device retains its settings, making it easier to use.
Schneider Electric Blanca - Sensory. The principle has much in common with the push-button version. The difference is that to change the brightness, you just need to touch a specific button (up/down arrow), hold it, or release it. To enable/disable a separate button or a combination of them is used. There is a mode saving function.
By type of signal transmission
Most modern dimmers have remote control capabilities.
The following options are possible here:
- Infrared. Such devices have an IR sensor directed towards the receiving device. Dimmers with such control are inexpensive and only work in direct line of sight of the signal. Even with a thin barrier, control becomes impossible.
- Radio signal. Unlike the option discussed above, the waves easily bypass obstacles, which allows you to adjust the light even from another room.
- Wi-Fi. The remote control is a phone or tablet PC with software installed on it from the dimmer manufacturer. To issue a command, you can remotely adjust the lighting parameters. The main thing is that both devices are connected to the Wi-Fi network. Regulation is available simultaneously to several people who have a smartphone with the desired program. For example, all family members.
- Acoustic. These dimmers are controlled by voice command. The memory of the dimmer contains control elements (clap, words), to which the dimmer reacts and executes the command. At this stage, such devices are still being improved to increase efficiency.
By type of lamps used
Each lamp type uses a compatible dimmer model. If the manufacturer claims to support several types of light sources, a “smart” controller is mounted inside the equipment, and this affects the cost.
There are two types of devices here:
- For voltages up to 230 V. They are suitable for simple / halogen lamps. There is a special regulator inside that allows you to work both with a 220 V strip and with diode lamps.
- For 12/24 V. For such devices, a step-down transformer is used.
In terms of supported bulbs, incandescent dimmers generally work for halogen bulbs and some LED bulbs.
What are the differences between dimmers?
If you are going to use a switch with brightness control, you first need to find out what they are. And in general, can all LED lamps be dimmed?
Dimmers differ according to the following criteria:
- By type of installation;
- on execution and method of management;
- according to the method of regulation.
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
By installation type
For outdoor installation – surface-mounted switch with dimmer for LED lamps. To install such a device, you do not need to drill a niche in the wall; it is simply mounted on top of the wall. It is very convenient to use in cases where the interior is not a priority or external wiring is installed.
For indoor installation - they will fit perfectly into any interior, such as this one.
For DIN rail mounting they are very specific and at first it may seem that they are not practical. However, this dimmer for LED lamps works with a remote control, and is hidden from prying eyes in the electrical panel.
By execution
According to the design, the light controller for LED and incandescent lamps can be:
- Rotary;
- rotary-push type;
- push-button;
- sensory;
Rotary is one of the simplest options for dimming an LED lamp; it looks unpretentious and has the simplest functionality.
The turn-and-push one looks almost the same as the rotary one. Thanks to its design, when you press it, the light turns on with the same brightness as it was set the last time you turned it on.
A push-button controller for LED lighting looks more technologically advanced and will fit seamlessly into a modern apartment. Like this switch with a dimmer for LED lamps.
Touch models can be completely different - from luminous circles to smooth single-color panels for adjusting the voltage of LED lamps.
According to the adjustment method
Dimmers vary not only in their design, but also in their operating principle. This applies specifically to AC dimmers.
type of dimmer is more common and cheaper, due to the simplicity of its circuit - a leading edge cutoff dimmer . A little further on, its operating principle and circuit will be discussed in detail; for comparison, take a look at the type of voltage at the output of such a regulator.
The graph shows that the remainder of the half-wave is supplied to the load, and its beginning is cut off. Due to the nature of the load switching on, interference is generated in the electrical networks, which interferes with the operation of televisions and other devices. A voltage of the set amplitude is applied to the lamp, and then it fades out when the sine wave passes through zero.
Can a leading edge dimmer be used for LED lamps? Can. LED lamps with a dimmer of this type will only be well adjustable if they were originally designed for this. This is evidenced by the symbols on its packaging. They are also called “dimmable”.
The second type works differently, creates less interference and works better with different light bulbs - this is a falling edge dimmer .
LED lamps with this type of dimmer adjust better, and its design better supports non-dimmable light sources. The only drawback is that these lamps can adjust their brightness not from “zero”, but within a certain range. At the same time, dimmable LED lamps are simply superbly adjustable.
The best solution is to use a Falling Edge LED dimmer.
A special word can be said about ready-made LED lamps with adjustable brightness. This is a separate class of lighting devices that do not require the installation of additional regulators, but have them in their design. Their adjustments are made using buttons on the case or from the remote control.
Advantages and disadvantages
When considering dimmers, it is important to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
Pros:
- Automatic on/off.
- Possibility of remote control by voice, clap, via radio or IR channel, as well as via Wi-Fi network.
- Simulating the presence of a person, which allows you to scare away intruders from a house/apartment when the owner is in another place. To do this, a specific program is set, which at a certain moment turns on / turns on the lights in different rooms.
- Smooth switching on/off of the lamp, which eliminates current surges and reduces the risk of burnout.
- The opportunity to radically change the design of the room and create the necessary atmosphere.
- Increased service life of light sources
- Save electricity by 10-15%.
- Saving on the purchase of complex lamps and chandeliers. Brightness adjustment occurs using a dimmer without using a large number of lamps.
- Possibility of connecting to the “smart home” system and setting modes by time/command.
Minuses:
- Narrow scope of application and the ability to use the dimmer for those sources that it supports.
- High risk when working with moving tools/machinery. The appearance of a stroboscopic effect can lead to distortion of the real picture.
- Risk of electromagnetic interference, including at radio frequencies.
- Low efficiency when used with incandescent lamps. It is often easier to use less powerful incandescent bulbs, dimmer circuits, or dimmers for LED bulbs.
- The relationship between output voltage regulation and load resistance is nonlinear.
- The power of the dimmer should be equal to, or preferably 20-50% greater than, the total load of the light sources.
- It is impossible to use dimmers with fluorescent lamps and light sources with additional devices: driver, transformer, electronic ballasts, etc. The exception is models that are specifically designed for use with dimmers. Some companies are already developing such devices.
- Non-sinusoidal output voltage, which makes it impossible to connect step-down transformers.
- For normal operation, it may be necessary to update the wiring and carry out cosmetic repairs.
- Sensitivity to temperature changes. Dimmer is afraid of both heat and cold.
Dimmer circuits
Dimmer for 220V voltage, with leading edge cut-off, works on the principle of phase-pulse voltage control. During operation, the elements of such a dimmer supply voltage to the load at certain moments, cutting off part of the sinusoid. This is depicted in detail and more clearly in the graphs.
The area of the sinusoid shaded in gray is the area of the voltage or its effective value that is supplied to the load (a lamp or any other device described above).
The red dotted line shows the voltage waveform at the dimmer input for LED lamps. In this form, it is supplied through a regular switch without adjustments .
How to connect LEDs via a dimmer?
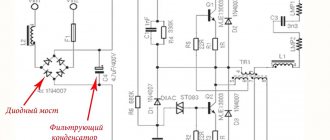
Component ratings and all information are indicated on the dimmer diagram.
The device is installed in a break in the wire going to the light source, motor, heating element or any other device.
The logic of the circuit is as follows: capacitor C1 is charged through chain R1 and potentiometer R2. Depending on the position of the potentiometer, the capacitor is charged to the opening voltage of the dinistor VD1.
The circuit used a DB3 dinistor, which is approximately 30V. Through an open dinistor, a control pulse for opening a triac (bidirectional thyristor) is supplied to its control electrode.
The greater the resistance set by the potentiometer knob, the longer it takes for the capacitor to charge, respectively, the later the dinistor-triac circuit will open, and the voltage will be lower, since most of the sine wave will be cut off. And vice versa - less resistance means more voltage at the output of the regulator.
There are many options for circuits on the Internet with all sorts of modifications, all of them are good. Here is a simple diagram; the figure shows the installation of this version of the scheme.
Installation Features
Installing a dimmer in a house or apartment does not cause problems. Thanks to its simple design, the dimmer can be easily installed instead of conventional switches and connected in a similar way.
When purchasing semiconductor devices, pay attention to compatibility. If available, the box should have the inscription “dimmable”.
It is also necessary to look at the installation method, because some models have an overhead design or are built into a break in the supply wires. We talked about this in more detail above.
Types of dimmers and their connection diagram
Dimmers with mechanical manual control are made according to the classical design and are switched on like light switches in a phase wire break (usually dimmers have a built-in switch). They even come in the form factor of household lighting switches for ease of installation and installation.
The simplest dimmers turn off the lighting when the handle is turned from the minimum lighting position to the extreme position (until it clicks). The disadvantage of such a system is that after turning it on, each time you need to re-set the desired lighting level. More advanced devices adjust the lighting level by turning the handle, and turn the light off and on by pressing it. However, the brightness level does not change.
Features of operation
When purchasing and using dimmers, it is important to consider a number of features of their use.
Let's highlight the basic nuances:
- The use of dimmers near radios and other highly sensitive devices is not recommended. This is due to the appearance of interference during the operation of such devices. For example, when you turn on a soldering iron with a regulator, the oscilloscope will show extraneous signals, and you won’t be able to listen to the receiver on long/medium waves.
- Connecting a dimmer to an incandescent lamp allows you to avoid a current surge and, accordingly, protect it from burning out ahead of schedule. In reality, such protection does not always work, and when turned on, the lamps still light up (although the likelihood of such a situation occurring is lower). By the way, the starting voltage at the minimum regulator level depends on the type of dimmer.
- The efficiency of an incandescent light bulb decreases noticeably along with a decrease in the potential difference at the input. Therefore, instead of reducing the brightness, it is better to connect a lamp of lower power and without a dimmer.
- The dimmer may cause interference when recording audio using a pickup or microphone. This feature must be taken into account in special rooms where sound is recorded or in radio stations. In such places, incandescent lamps should be connected directly or special circuits should be used.
- When adjusting the lamp power using a dimmer, not only the brightness changes, but also the color temperature. In particular, as brightness decreases, the light becomes redder.
- A powerful incandescent lamp, when dimmed using a dimmer, can produce high-frequency noise that can be heard in complete silence. This occurs due to mechanical vibrations of the filament, which burns with the participation of currents with HF harmonics (appear at the moment the triac switches). If you power the light bulb directly, there will be no such effect.
What types of dimmers are there?
Power regulators can be divided into two large groups:
- For work in alternating voltage circuits (220V);
- for operation in constant voltage circuits (for 12V LED strip).
Drills also need a regulator to adjust the speed; it is located in the button.
It can be used for a variety of purposes, listed in order of popularity:
- Light brightness adjustment, dimming of LED and incandescent lamps;
- adjusting the heating element temperature in various heaters;
- adjusting the speed of the commutator motor.
Example of popular models and their characteristics
The modern market delights buyers with a huge number of dimmers, differing in design features, mounting method, manufacturer and other parameters.
Below we highlight some of the most popular options.
Touch dimmer RF6-18, 12/24 V, 3*6A/18A, 216/432 W, IP20
Dimmer with touch control, designed for illumination of LED lamps for 12 and 24 Volts. Control is carried out using the remote control.
Dimmer capabilities allow you to turn the strip on/off and change the brightness.
Characteristics:
- voltage - DC;
- power - 432 W;
- degree of protection—IP20;
- output voltage - up to 18 V;
- dimensions - 17.8x6.5x5 cm;
- case material - plastic;
- number of colors - 3;
- Possibility of use with a “smart home” - yes.
Dimmer EKF Minsk ERD06-101-10
Dimmer in a frame, designed for vertical/horizontal concealed installation.
Works with incandescent and halogen lamps for voltages up to 230 V. Mounted with a spacer or with screws. Supplied complete with frame.
Switching on is carried out by turning or by turning with pressure.
Characteristics:
- voltage - AC;
- voltage - 230 V;
- degree of protection—IP20;
- power - from 40 to 600 W;
- rated current - 3 A;
- dimensions - 8.4x8.4x4.7 cm;
- White color;
- Case material: plastic.
Mini dimmer WI-FI 12-24 V, 8A, 96/192 W, IP20
A small dimmer designed to control a 12 or 24-volt LED strip from Android or iOS phones. Works via radio channel.
With it you can turn on/off the device, change the brightness. The dimmer is programmable.
Characteristics:
- voltage - DC;
- power - 192 W;
- degree of protection—IP20;
- output voltage - up to 8 V;
- dimensions - 17.8x6.5x5 cm;
- case material - plastic;
- number of color channels - 3;
- Possibility of use with a “smart home” - yes.
How to choose a dimmer
In order not to regret the purchase, you need to choose the right model and type of device. There are several parameters that you need to pay attention to.
- The power of the device should be one and a half to two times the total electricity consumption of all light sources connected to it. That is, if the total power of the chandelier is 300 W (five lamps of 60 W), then you will need a dimmer rated for 450-600 W.
The same principle can be seen when connecting several lighting devices to one device, for example, a pair of sconces, a track system or several spotlights. The power of all devices is added up and then multiplied by 1.5, or better yet, 2.
It is very important to strictly observe this rule when purchasing devices with a significant power reserve. A dimmer that is constantly operating at the limit will overheat. It may cause a short circuit or fire.
- It is also important to consider the installation method. Monoblock products require connection to electrical wiring and pulling cables to the installation site. Externally, they are similar to standard or innovative switches. They work with various types of lamps, as indicated on the housing and in the instructions for the device. They are divided into two types.
Surface-mounted dimmers have a number of advantages: quick and convenient installation, which does not require drilling niches in the walls; products can be installed at any time, regardless of repairs, especially if external wiring is installed. However, such models are more difficult to fit harmoniously into the interior.
Built-in models fit perfectly into the environment and look like part of the interior decor. But to install them, you need to groove the walls for the cable and drill niches. These two types of dimmers are most in demand in private houses and apartments.
The dimmer on the cord is intended for lamps that are connected to the network with a plug through a socket. These are floor lamps, sconces, table lamps, night lights and other products. Such devices only work with incandescent lamps.
Very interesting models are designed for installation on a DIN rail. They hide from indiscreet glances in the electrical panel and are equipped with a remote control, so the owners do not have to run to the device every time. In addition, they do not require major or cosmetic repairs during installation. The devices work with halogen and incandescent lamps using step-down transformers. With their help, they regulate the intensity of lighting in the courtyard, in the vestibule and hallway, on terraces and verandas, at the entrance and garages.
A thoughtful approach to choosing a device allows you to buy exactly the dimmer that will be most convenient for homeowners. It will become an invisible assistant, providing everyday comfort in the home.
Recommendations for selection
When purchasing dimmers for LED lamps, including those used in a radio/luminaire, you need to choose wisely. When looking for a suitable option, pay attention to the following points.
Lamp type
Dimmers are capable of working with certain types of light bulbs, because there are no universal devices.
Dimmers can support incandescent lamps, halogen lamps, LED devices, LED modules and other light sources.
Let's consider the subtleties of choice for different types of lamps:
- Incandescent. Finding a dimmer for such lamps is the least problematic. Dimmers for incandescent lamps have a simpler design and are easy to connect.
- Luminescent. There are almost no dimmers for such light bulbs due to the complexity of the circuit implementation. Here you have to use a controller and a ballast, and this requires additional costs.
- Energy saving. If there are ballasts (ballasts), the brightness changes using a special regulator. If it is not there, difficulties arise with dimming.
- Halogen. For such lamps, separate dimmers or devices are sold that can simultaneously be used for incandescent lamps.
- LED LED lamps. For 220 V light bulbs there is no difficulty in finding. In this case, pay attention to the label and the presence of an inscription indicating the possibility of using such a device.
- 12 volt LED lamps. Dimmers for LED lamps of this type require the use of a step-down transformer and a special controller. A special control panel may be required.
Power
When choosing a dimmer based on power, you need to calculate the total load. If the calculations are made incorrectly, the device may not work or may fail prematurely.
To calculate the total power of the light bulbs, add up the parameters indicated on the packaging.
When choosing a dimmer, be sure to add 20-50% to the design power. For example, if the resulting parameter is 200 W, it is better to take a 300 W dimmer.
Features of execution
When choosing, pay attention to the type of dimmer, because the possibility of its installation and combination with the design of the room depends on this.
As noted, you can find keyboard, rotary-push, touch and other models on the market.
Dimmer device
It is easiest to consider a standard diagram of a regulator device using the example of a rotary variator, the design of which is characterized by simplicity of execution, but may differ in build quality and number of components.
The power of the triac should be 20–50% higher than the load
The triac regulator circuit is usually the same, but the main difference is the presence of some additional elements that provide more stable operation under conditions of low output voltage.
The triac must remain operational at a voltage of 400 V
The actual dimmer circuit is indicated taking into account the differences in some parameters in devices produced by different manufacturers. In this case, triacs can be anything, but they directly depend on the load power indicators. The values of resistors and capacitors are influenced by the starting and ending ignition points.
Dimmer Review
I came across a simple Chinese dimmer of an unknown brand, let's look at it in more detail.
On the front panel we see a control element - a rotary knob. When turning to the zero position, a click is heard - this triggers the switch, which de-energizes the entire circuit. To install or dismantle such a dimmer, you need to remove the handle and unscrew the nut. Appearance of the dimmer and its disassembly
Mounting frame and terminal blocks for connecting wires
If we remove the bottom plastic cover, we will see a printed circuit board with electronic components.
By the way, pay attention to the excellent quality of soldering of the terminal blocks to the board. This is a special circular soldering technology that will ensure an exceptionally long product life (no). Dimmer board
Here we see a minimum set of components similar to the circuit discussed above.
The potentiometer is not used as an ordinary one, but with a switch (the click that I wrote about above was made by it), as evidenced by its different appearance and dimensions from conventional potentiometers, as well as the number of pins (the two largest pins in the central part of the printed circuit board). The triac is screwed with a small bolt to the radiator in the form of a metal plate. It is not magnetic, most likely made of aluminum. The declared power of this dimmer is 600 W, which is indirectly confirmed by the characteristics of the triac (600 volts and 8 amperes), its marking BTB08-600B. Triac
How to connect a dimmer instead of a switch
Recently, people are increasingly replacing conventional switches with dimmers. Changing a switch to a dimmer is very simple. The switch has two outputs (two terminals), and the dimmer also has two terminals. We simply connect the dimmer instead of the switch, using the same wires that were connected to the switch.
Polarity doesn't matter. However, if you have determined where the phase is using a phase indicator (indicator screwdriver), then it is better to connect the phase conductor to the L terminal of the dimmer. Just for order.
The only condition that the manufacturer imposes is to comply with the connection of the terminals to the phase and to the load. Although, as practice shows, you don’t have to worry about this - everything works well with any connection.
If previously the chandelier was turned on through a two-key switch, then through the dimer all the bulbs will light up (glow) simultaneously. We connect a phase to one terminal of the dimmer, and the other two wires to the second.
Sources
- https://php64.ru/poleznoe/dimmer-dlya-led-lent.php
- https://stanok.guru/bez-rubriki/dimmer-chto-takoe-gde-i-kak-primenyaetsya.html
- https://www.elektro.ru/articles/detail/chto-takoe-dimmer-i-kak-on-rabotaet/
- https://moskvacenter.com/dimmer-chto-eto/
- https://SvetodiodInfo.ru/texnicheskie-momenty/dimmer-dlya-svetodiodnyx-lamp.html
- https://sampochinil.ru/elektrika/kak-rabotaet-dimmer/
- https://zen.yandex.com/media/samelectric/vse-chto-vajno-znat-pro-dimmer-5c966894ce69b900b456bee8
- https://zen.yandex.com/media/lampexpert/o-dimmerah-dlia-osvesceniia–obzor-shema-i-princip-raboty-5d98556cd4f07a00acb79a35
How to determine compatibility of LED lamps and dimmers
First, you should understand that an LED lamp and an LED strip are completely different lighting devices. This means that the dimmers for them will be different. If additional electronics are required for the operation of the strip, then the light bulb is screwed into a regular E14 or E27 type socket. Also, the lamp base can have a different shape - G or MR. It is designed to operate on a 220V/50Hz network and does not require additional components.
When purchasing a dimmer, you should take into account the total load from all light sources that will be connected to the dimmer. If the light bulbs have already been purchased (don’t forget about the dimming markings), the ideal option would be for the buyer to come to the store with the lamp. In this case, you can check the compatibility of the lighting fixture and the dimming device on site.
When purchasing a dimming device in a store, it is better to immediately check it for compatibility with your lamp
However, the main thing in the matter of compatibility is the dimming protocol of both devices.
What are dimmable lamps and luminaires?
Lamps, regardless of their operating principle, have a certain power, on which the intensity of the luminous flux depends. To increase or decrease the illumination, users have to replace the light bulbs or turn on a certain number of them, if this is provided for by the electrical wiring.
Dimmable lamps allow you to change the luminous flux at any time at your discretion using a dimmer - a direct or alternating current device, which is also called a dimmer or dimmer.
Manufacturers also offer LED lamps - this is a separate group of lighting devices that do not need additional regulators, since the dimmer “filling” is built inside them. The lighting intensity is changed using the remote control or buttons located on the body.
Why can't regular lamps be used with a dimmer?
Ordinary lamps cannot be connected in the same circuit with a dimmer. It's all about the design. A simple LED lamp has a micro-rectifier that converts the input AC voltage to DC. A regular LED light bulb can only be in two positions - on or off.
A dimmer assumes a completely different approach to lamp operation. With its help, a smooth and gradual change in the level of illumination is carried out. If you screw an ordinary, non-dimmable lamp into a circuit with a dimmer, it first blinks and then turns on 100%.
If the lamp burns at full power in the same circuit with the dimmer, both devices become unusable after a short time. Inside dimmable light bulbs there is a special unit through which the brightness is adjusted.