Every year the number and variety of equipment in apartments and houses increases. In such conditions, the likelihood of electric shock or various injuries increases significantly. To avoid such situations, various devices are used - “automatic machines” and others. In order to understand what an RCD is, it is worth carefully studying its characteristics and purpose. If the question arises as to why an RCD is needed, then first of all this device provides protection to users from electric shock.
RCD complete with cord for a conventional water heater Source remont-vodonagrevateley.ru
Operating principle of the device
Unlike a standard “machine”, when installing an RCD, two conductors are connected to it - the working zero and the phase. If an electrical device operates without leaks, then the current strength in the conductors should be the same. In emergency situations, when a current leak occurs, the device turns off. As a result, the electrical device is de-energized and stops working. Thus, the RCD helps preserve the health and life of ordinary users.
The RCD protects the house from fire and controls electrical wiring and equipment from current leakage Source electro-king.com.ua
All equipment has a slight current leakage. But usually its level is not sufficient to cause harm to human health. All RCDs are set to the level of electrical energy that poses a danger to people or will lead to disruption of electrical appliances.
The speed of automatic shutdown is such that a child who stuck a nail into the socket will not even experience any discomfort - the device will automatically turn off the power in the entire house.
After automatic shutdown of the device, it is necessary to detect a current leak Source zen.yandex.uz
RCDs are developed in accordance with GOST 31603-2012
Portable residual current devices for household and similar purposes, controlled by differential current, without built-in overcurrent protection (RCD-DP). General requirements and test methods
Unlike a machine, the protective shutdown opens the circuit as soon as voltage reaches the housing - this was the decisive factor for its installation.
Nikolai
Protection is still needed
The use of low voltage or the use of galvanic isolation is not a very convenient way to protect people, therefore they are used only in narrow areas, where there is no other way. But how can we protect people from electric shock without significantly changing the existing electrical networks? The idea is simple and ingenious - you need to analyze the differential current.
Differential current is the difference in current between two conductors, for example between the phase one going into the load and the zero one returning from the load. The appearance of a noticeable differential current in a circuit is most often abnormal, and it is better to turn off the circuit; what if the current flows into the ground through a person? It's like comparing the coolant flow into and out of a heating battery. If 100 l/min goes into the battery and 100 l/min returns, then the system is sealed. If 100 l/min is supplied to the battery, but for some reason only 98 l/min is returned, then 2 liters leak out somewhere!
In an ideal world, it is enough for us to install a device that controls the very fact of the appearance of differential current. If everything is in order, then there is no differential current. If the current appears, we turn off the load. But in the real world, unfortunately, differential current (leakage current) appears in devices even if everything is working properly, so you have to make a compromise and choose a certain threshold value of the differential current, the excess of which will cause a shutdown.
Let's put ourselves in the shoes of engineers at the beginning of the 20th century and try to invent a device for detecting differential current. We need to detect the occurrence of a leak of 30 mA, since with smaller leaks, even if it passes through a person, there is no particular danger to life.
The first design - two identical electromagnets, opposite each other, are engaged in pulling the armature. The current flowing into and out of the load, flowing through the windings, creates a magnetic field, the stronger the greater the current. If there are no leaks in the circuit, then the currents through the electromagnets are equal, they develop the same magnetic field and the armature stands still. If we have a leak in the circuit, then the current through one of the electromagnets will be less (load current - leakage current) than through the second (load current), the armature will be pulled and open the contacts.
Theoretically, the scheme is working, but it is too capricious - it required very precise manufacturing of electromagnets and fine-tuning of the mechanics. Therefore, engineers began to think about how to get rid of unnecessary mechanics. This is how we came to a modern circuit with a transformer:
On a closed magnetic circuit, two windings are made, connected in antiphase, and a third winding to drive the solenoid. If the currents through the first and second windings are equal, then the magnetic fields are equal, and since they are directed towards each other, then the total magnetic flux through the third winding will be zero. If there is a leak, the currents become unequal, and a magnetic field proportional to this difference will begin to circulate through the third winding. And where there is an alternating magnetic field, there is induction and a current is excited. If it is enough to trigger the solenoid, the armature will release the latch and turn off the circuit.
A device ingenious in its simplicity and reliability. True, it didn’t turn out to be cheap - the mechanics still turned out to be delicate and capricious, is it a joke - to detect a 30 mA difference at a rated current of 16A is like hearing the squeak of a mouse against the background of the roar of a train. This is what an electromechanical RCD looks like:
Then they made a modernization - they threw out the delicate, expensive and oversized mechanics and installed an electronic amplifier, the current from the winding of the differential transformer is amplified by a special microcircuit, and this already supplies voltage to the opening solenoid. Such RCDs turned out to be more compact and much cheaper.
And now attention, an important point, what will happen if there is a short circuit in the load? Nothing! Since there is no condition for triggering, there is no difference in currents at the input to the RCD and at the output from the RCD. The wires will become red-hot, the insulation will drain onto the floor, and the RCD will not turn off because it does not have overcurrent protection. Therefore, an RCD without built-in overcurrent protection ALWAYS used in conjunction with a circuit breaker or a fuse. By crossing RCDs and circuit breakers, manufacturers have developed a hybrid - RCBO (residual current circuit breaker), which is more often called a diffavtomat in jargon; such a device is self-sufficient and does not require an additional circuit breaker.
The invented RCD worked perfectly, if not for the proliferation of semiconductor devices. Many devices began to transform the voltage and type of current within themselves - making direct current from alternating current, then alternating current again, sometimes of a different frequency or magnitude. Because of this, all sorts of unpleasant features became possible, for example, if one of the lines with direct current in the device is shorted to the housing, then the leakage current will be pulsating - only positive half-waves of current will go to the ground. A conventional RCD may not work in such cases. For such cases, special RCDs have been developed that are designed to operate not only with a sinusoidal leakage current, but also with a constant pulsating leakage current and called them type A. And the old RCDs, which operate only on alternating current, were called the AC type . And for very unpleasant cases (for example, breakdown of circuits after power switches in converters with high conversion frequencies) they came up with type B. The difference between types of RCDs is most clearly demonstrated by this picture from German Wikipedia:
To ensure selectivity, when connecting RCDs in series, special selective options have been created, often with the designation S or G in the name. They have a built-in delay of several tens to hundreds of milliseconds. So, if there is a selective RCD at the entrance to the house, and a non-selective RCD on the floor panel, then when the voltage is shorted to the body of the washing machine, the non-selective RCD on the floor will first trip, while the selective one gives a delay. If at the end of the delay the differential current does not disappear, the selective RCD will trip. I wrote about selectivity in a post about fuses (LINK). The selectivity does not depend on the rated threshold differential current, that is, in the event of a breakdown on the housing, both a 30 mA RCD and a 100 mA RCD will operate immediately, which is why I had to tinker with the delay.
And now that it has become clear HOW the RCD works, it’s time to talk about grounding, will the RCD work if there is no grounding contact in the sockets? Will! The only difference is that if the washing machine has a breakdown on the housing in a grounded network, the RCD will turn off immediately, since the differential current will be huge (it will go from the housing to the grounding conductor). But if there is no grounding in the network, the washing machine will stand like a guerrilla in the bushes with a voltage of 230V on the body, and the RCD will turn off only when the current flows through a person. That is, the presence of grounding increases safety, but is not a prerequisite for the operation of the RCD.
Reasons for automatic shutdown of RCDs
Before starting repairs, it is worth finding out why the RCD is triggered. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon, and the method and cost of repairs depend on them.
- Current leakage in the network . This problem often occurs in buildings with old wiring. Over time, the insulating coating loses its elasticity, cracks, and the wiring is exposed in some areas. If the wiring has been installed recently, it is worth checking the quality of the wire connections. Sometimes an accidentally driven nail can damage the insulation layer. A conventional machine does not respond to current leaks, so the RCD is designed to provide adequate protection.
- Malfunction of the device to which the RCD is connected . Among the damages, the most common failure is the failure of the cord, motor winding or heating element of the water heater.
- Installation error . If the device is installed incorrectly, the automation may periodically operate for no reason. Before installing the device, you should carefully study the instructions or use the services of a specialist.
When installing, it is important not to make mistakes, otherwise the device will turn off for no apparent reason Source www.ets96.ru
- Incorrect device selection . When purchasing a unit, it is important to take into account all its characteristics and purpose. Failure to comply with these parameters may result in a false shutdown.
- Human touching a wire without insulation . In fact, this device is designed specifically to protect a person in such situations.
- Damage to the mechanism itself . Sometimes the trigger mechanism is damaged, and the slightest vibration triggers an automatic shutdown.
- Incorrect placement of the device in the electrical wiring . To avoid this problem, it is worth installing the device after the meter and in front of the machine. If there are many electrical appliances with high power in the house, then you should use several devices for each group. This will allow you not to turn off the power in the entire house in case of problems, but only in certain areas.
- According to the rules of the PUE, grounding and working zero cannot be combined . But sometimes electricians do not take this prohibition into account. A short circuit of these two lines may occur, which will cause the RCD to automatically turn off.
Installing conventional machines is much easier. To install the protective shutdown, we had to contact specialists.
Basil
During installation, you must adhere to all safety requirements Source repair-need.ru
- Weather conditions . A machine installed outdoors is susceptible to moisture. As a result, moisture accumulates in the internal mechanism, a leak occurs, and the machine is triggered. If there are minor current leaks in the house, then lightning during a thunderstorm can intensify them. This is also the reason for automatic shutdown. At very low temperatures, the device's microcircuits may fail, and the RCD simply will not work in cases of current leakage.
- High level of humidity in the room . If you tried to hide the installed wiring using putty, then connect the electricity after drying, otherwise the automatic protection may work.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in electrical work.
HOW TO CORRECTLY CONNECT THE RCD IN A PRIVATE HOUSE
RCD connection diagrams in a private house are no different from diagrams for an apartment, cottage, etc.
They are listed on the corresponding pages of this site, but for convenience I will duplicate them in this material.
Connecting an RCD without grounding, if done correctly, in a private house is no less effective than if there is a grounding bus (Fig. 1).
In this case, you need to use a socket with a grounding contact, which is connected with a separate wire to point A, always before the residual current circuit breaker and to the neutral wire.
In this case, when a device with a leak to the body is connected to a socket (naturally, it must have an appropriate plug), part of the current will bypass the neutral conductor past the RCD, which will cause it to trip.
Please note - the protection will work even if there is no contact in the body of the faulty device
– this is an undoubted advantage of such a scheme.
Connection without grounding can be simplified (diagram in Fig. 2).
In this case, the protection will work when a person touches the housing on which the phase falls. The leak will go through the body, which is unpleasant. But if the leak is small, then you may not even notice anything.
How to find the area where there is a leak
In order to find out the reason why the RCD knocks out, you should take the following steps:
- Carefully check that the connection is correct . Installation errors are the main reasons for automatic operation.
- To check each area or electrical appliance, you should turn off the circuit breakers and protection on each line : kitchen, bathroom, lighting, appliances.
- When the machines are running, it is necessary to enable leakage protection . If the RCD trips while the product is running, it means there is a malfunction in the mechanism. If automatic protection does not work, then the following mechanisms should be checked.
- To check the integrity of the electrical wiring, it is necessary to disconnect all electrical appliances in the house from the power supply and turn on the input circuit breaker and connect the electricity . If the RCD trips, then the problem is in the wiring. If everything works as usual, then the reason is technical.
If there is a leak in the electrical wiring, then it is necessary to check the entire system Source m.yukle.mobi
Where is fire protection device used?
Fire protection RCDs are used to protect against fire in apartment buildings. Residents install a protective device in their switchboards at the entrance to the apartment. In this case, the RCD, according to the requirements of the energy supply organization, is installed after the metering device. With rare exceptions, standard fire protection devices with leakage currents of up to 100 mA are used. For an average apartment with modern wiring, this rating is optimal.
Another area of application for a fire protection RCD is protection for a private wooden house. The material of the walls is important here. Wood is more susceptible to burning. It has lower resistivity than concrete. Therefore, in a wooden house, the risk of a fire due to problems with wiring is an order of magnitude higher than in a concrete building. Accordingly, RCD is much more relevant for buildings made of natural materials than for brick or concrete ones.
RCD can also be used as part of more complex fire extinguishing systems. For example, in combination with fire protection equipment from companies such as AAB Technology.
Troubleshooting
By checking each individual device, you can find out which of them has a malfunction. When connecting faulty equipment to the RCD, the protection will automatically operate. The most common problems occur in the operation of washing machines, electric ovens and water heaters. To solve this problem, you should not open the equipment yourself. To fix the problem, you should contact a service center or call a specialist to your home.
If the problem is in the old electrical wiring, then it often has to be changed completely. If the lines were laid recently, then it is worth looking for errors in connections, connecting wires or weak machines. It is necessary to inspect distribution boxes and sockets. If the automation is triggered when the lighting is turned on, the reason may be in the lighting device itself. Also, do not neglect checking the cable along the entire line. If there is open wiring in the room, this makes the task easier. To diagnose closed wiring, you should use a special device. It helps to find the location of the cable break.
For a number of reasons, we had to do open wiring in the office. I was really happy about it when the time came to expand - it turned out that machines and additional lines could be added without any problems.
Alexei
Finding out the reasons for the operation of the RCD is a long and troublesome process that requires a lot of time and patience.
Purpose and operating principle of RCD in pictures
The residual current device is a current protection device and ranks second after the circuit breaker in terms of safety. It has already saved the health of many people and prevented electrical injuries.
The need to use RCDs has been confirmed by the requirements of the time and is dictated by electrical safety rules.
How does protective shutdown work when a leakage current occurs?
The phase comparison body controls the magnitude of the vectors of incoming and outgoing currents along the phase and zero potential conductors, constantly comparing their magnetic fluxes.
If the value of the second vector has decreased more than the permissible set value, then a conclusion is drawn that a malfunction has occurred. The power contacts are automatically disconnected from the resulting leakage current.
Additional purpose of the device: preventing a building fire due to a violation of the dielectric properties of the insulation, creating random paths of emergency currents.
The differential element operates in all building grounding systems. However, the most correct and safe situation is created in the TN-S and TN-CS , TT with an additional PE grounding line.
Buildings with the old TN-C roughen the sensitivity of the reference organ.
RCD electrical circuits: 2 options for apartments and houses
The protection is produced in ready-made modules for installation on a Din rail with the possibility of installation in single-phase or three-phase wiring.
Connection diagram for single-phase RCD
The 220 volt network includes a module with two current lines with phase and zero potentials.
A diagram of the internal design of the protection is printed directly on the case and is given in the documentation. The incoming phase wire is connected from above to terminal No. 1, and from terminal No. 2 it goes to consumers.
The zero potential is applied to the upper terminal N and removed from the lower one. These connection rules cannot be changed: otherwise the phase comparison organ will not be able to work correctly and false alarms will occur.
Connection diagram for three-phase RCD
Three input phase conductors are mounted alternately to the upper terminals No. 1, 2 and 3. From the bottom of the module from terminals No. 2, 4 and 6 they are removed and sent to the consumer. The zero potential is connected from above to the “N” terminal and removed from the bottom.
Various manufacturers constructively place the working zero line to the right or left of the phase lines. All these variations are shown in a picture diagram on the protection housing.
It is permissible to swap phase lines with each other, but they should not be confused with the zero current line. The winding of the “Test” check button is connected to it. When pressed, the protection will not work correctly.
Features of choosing an RCD
Before you start choosing an RCD, you should determine the type of electrical wiring, analyze the operational features of the room and select a connection diagram for the device for protection.
There are RCDs on sale with different limiting values of differential currents. Each device has its own purpose. For household use, devices with levels of 10 mA, 30 mA, or 100 mA are used. This is usually sufficient to protect residential buildings or offices.
Types of RCDs must be selected in accordance with specific conditions Source samodomik.ru
The standard version of the device is not able to disconnect power contacts if the network is overloaded, or protect the wiring from short circuits. To avoid unpleasant situations, it is worth supplementing the protection with automatic switches or other protective mechanisms.
Also, every buyer should know how to check the RCD. For this purpose, each device has a test button. When it is pressed, current leaks and the power contacts should automatically turn off.
When you press the test button, the device should turn off Source electrikmaster.ru
How does an RCD protect?
In everyday life, current cannot “flow” through air. Current can only "flow" through parts of devices that can potentially conduct current. As a rule, metal housings of devices become such conductive parts. The occurrence of this current is detected by the RCD, and when a certain value is reached, the RCD is triggered and breaks the electrical circuit, which is potentially dangerous to humans. This type of RCD protection is called protection against indirect contact. To protect against indirect contact, you need a residual current device (RCD) with low and medium sensitivity.
Related articles: Electrical insulating materials: fabrics and sheets
In addition to protection from indirect contact, the RCD additionally protects a person from direct contact with live parts that are live. That is, if you touch a wire or wiring element that is energized, the RCD installed in this circuit will trip. True, for this there must be a highly sensitive RCD, and we do not practice such a purpose for RCDs.
In addition to protecting people and animals from indirect and/or direct contact, the RCD limits the risk of fire in the premises. By disconnecting the circuit from the power supply when an insulation fault current occurs, the RCD interrupts the very possibility of the device igniting at the site of the fault.
conclusions
Similar
Types of RCD
A large selection of appliances often confuses the buyer. Each device has different technical parameters that should be taken into account when purchasing. They cannot be changed or configured during operation, so it is better to immediately purchase a device with the required technical characteristics.
- Automatic shutdown speed . An ordinary household appliance works instantly. But there are multi-level systems where sequential shutdown is important. For such cases, selective RCDs are purchased that disconnect power contacts with some delay.
Circuit with selective RCDs Source yaelectrik.ru
- Type of current . There are two types of devices - AC and A. The first type is switched off if an AC leak is detected, and the second type is switched off if there are problems with direct and alternating current. In industry, RCDs with the designation B are used. They are suitable for direct and rectified current. The letters S or G may also be added to the marking. They indicate a shutdown delay.
- Type of relay . There are electronic and electromechanical options. Electromechanical relays break the contacts mechanically, and in electrical versions the power is interrupted using semiconductor systems.
Protective device with electromechanical relay Source www.etm.ru
RCD characteristics
- Manufacturer.
- Model name. In this case, the letters “VD” in the model name mean “Differential Switch”.
- Operating current. The maximum current value that this RCD can switch. In other words, if there is a load of 30A on the line that protects the RCD with an operating current of 25A, the device will fail.
- Electrical network parameters. Here two main parameters are indicated for which this device is designed: voltage – 230V and frequency – 50Hz. These are standard characteristics for a household electrical network in Russia.
- Leakage current. The magnitude of the leakage current at which the RCD will trip.
- RCD type. In this case, this is an “AC” device, for alternating current. We will look at all types in more detail below.
- Operating temperature range. From -25 to +40 degrees Celsius.
- Rated conditional short circuit current. This is the amount of possible current during a short circuit that the RCD can withstand without loss of functionality if it is protected by a circuit breaker of the appropriate rating.
- RCD device diagram. Depending on the manufacturer, the markings on the devices may differ slightly, and some characteristics may be added or removed. But the basis is the same everywhere and such important indicators as operating current and leakage current are always indicated by everyone.
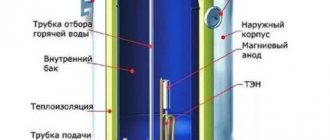
Features of choosing an RCD connected to a water heater
In domestic conditions, storage and instantaneous electric water heaters are used. Using the device, along with a machine, protects equipment from current leakage or fire. An RCD for a water heater is installed directly in front of the device itself, and the electrical energy that powers the equipment passes through it. In cases of current leakage, the device senses the changes and automatically turns off the power system. For this purpose, the device is equipped with special sensors and switches.
According to safety requirements, the RCD installed on the water heater must be supplemented with grounding. Also, to protect equipment from overloads or short circuits, boilers are additionally equipped with automatic switches.
RCD and difavtomat for additional protection of equipment Source strbuild.ru
Connection diagrams for a single-phase RCD: 3 options for use in an apartment
The protection module in the apartment panel can be mounted on:
Introductory RCD: protection of all wiring in the apartment panel
The protective shutdown device at the entrance to the apartment is installed directly behind the meter and the input circuit breaker.
An example of the location of the protection modules shown in the photograph of the electrical panel is supplemented by an explanatory diagram. To enter it, a conventional single-phase circuit breaker is used.
It only breaks the potential of the fault current phase. This is quite acceptable for most tasks that arise in matters of household wiring safety.
A circuit with a two-pole input circuit breaker is created according to the same principle, except that the zero potential passes through its second line to the input of the input RCD.
After leaving the residual current device, the zero potential is connected to a separate insulated busbar N. From it, cables are routed through the conductors to consumers.
The PE conductor protective lines are mounted using their own PE busbar. The corresponding core from the input cable is connected to it and the outgoing lines to all consumers are assembled without any breaks.
Technical characteristics of the RCD: rated current and leakage value - how to choose the right one for the input module
The 2 listed parameters are factory built into the design of any module. We will not be able to change them after purchasing it. Therefore, it is important to choose them correctly before purchasing.
The rated current and leakage response setting are marked directly on the protection housing.
How to choose an RCD based on rated current
This value characterizes the current strength that the internal circuits of the unit can normally withstand without damage, for example, with a value of 40 amperes, as shown in the picture.
If more current flows through the internal protection circuit, it will simply burn the windings, wires, and insulation. This cannot be allowed.
Each residual current device is connected through an individual circuit breaker with a lower rated current by one step of the standard series.
Based on this principle, a machine with a current of 32 A for an input RCD of 40 amperes was selected for the upper circuit. Its setting for short circuit load and overload saves our module from burning out in any accident.
The cost of the difavtomat is slightly higher than the components of the RCD and the machine together, but its use saves space in the apartment panel, which is often quite justified.
How to choose an RCD based on leakage current
Currents flow through almost any layer of insulation. It’s just that materials with high dielectric properties have very small ones due to high electrical resistance.
Damaged insulation has low confining capacity. High currents flow through it.
PUE regulates the total leakage current (differential) through the insulation. It should never exceed a value that is safe for humans.
There are special laboratory instruments that allow you to measure leakage current through the insulation of electrical wiring. When they are absent, an approximate calculation is performed using the proposed method.
For ordinary premises, a residual current device with a safe differential current of 30 mA is selected. In a humid environment, such as a bathroom or kitchen during cooking, its value drops to 10 or 6 mA.
At the entrance to the building, it is permissible to install a residual current device with a rating of 100 mA.
An input RCD of 100, 300 or 500 mA is not capable of saving a person from electrical injury. Its task: to prevent fire due to ignition of electrical wiring.
RCD for a bathroom: example of choosing a protection module for one consumer
An option for placing a protective shutdown inside an apartment panel is shown in the photo below.
The connection diagram of the protection module for one separate line (bathroom) with the location of the phase and neutral lines is shown in more detail in the general picture for apartment wiring.
The circuit breaker of this line, like the others, is powered from the assembly behind the input circuit breaker.
I would like to draw your attention to how the working zero bus is connected here and its differences from the method chosen for the circuit with an input module.
The working zero is supplied from the input cable directly to the meter, and from it is discharged to bus N. From it, wiring is carried out to all consumers with cables of outgoing lines.
The working zero is supplied to the bathroom sockets through a separate power contact of our protection.
Installation of the PE busbar is carried out according to the previous option without changes.
In this scheme, the internal structure of the module is protected from exceeding the rated current (16 amperes) by its own circuit breaker (rated 10 A).
Group RCD: economical protection of several outgoing lines
Installing an individual module for each individual consumer is the most justified solution in matters of ensuring safety and locating the location of a malfunction.
However, this installation scheme is the most costly and expensive. It requires the use of a fairly capacious apartment panel and a large number of RCD modules or differential circuit breakers. It takes a lot of money to buy them.
Group RCD allows you to save them. It is simply connected to several outgoing lines, placing a separate unit in front of individual circuit breakers.
It is convenient to install them inside the apartment panel in separate groups. This technique provides clarity during operation and repair.
The connection diagram for a group RCD to several outgoing lines is shown below.
Here, the protection of the group module at a rated current of 50 amperes is performed by a 40A input machine.
With such a circuit, novice electricians make an erroneous calculation, selecting the rated current of a group RCD as the sum of the ratings of the connected loads.
For example, in the diagram, all consumers are powered through 32, 25 and 16 ampere circuit breakers. Their total sum is 32+25+16=73. It is pointless to look for protection with such a denomination or more.
This issue is solved more simply: the input circuit breaker in this apartment wiring has already been selected for 40 amperes. He is obliged to turn off large currents, while simultaneously protecting the group RCD.
Therefore, its rating is quite enough to choose one step more from the standard current series: 50 amperes.
Differences in the configuration of the working zero circuits for the group RCD circuit
The considered circuit combines both of the above-discussed options for forming chains for connecting to the N bus:
The installation of the PE bus and the wires to it does not change.
Additional RCD functions
To protect human life and health, devices are used that detect leakage currents of 30 mA and 10 mA. All RCDs that have the highest indicators do not provide protection for human life. Very often, in multi-stage schemes, fire protection RCDs are used as the first stage of protection. These are fire protection RCDs that are set to leak current from 100 mA to 300 mA.
They are installed in distribution boards on each floor, or in metering boards. They perform the function of protecting the input cable and consumer lines that do not have separate protection. Also, these devices provide additional protection in case of malfunction of a downstream device or machine.
RCD in the distribution board Source www.drive2.com
In order for fire protection devices to successfully perform their function, devices with different sensitivity to current and different response times of automatic protection should be installed.
Even if you are not going to install anything other than automatic machines right now, I advise you to take a larger shield - if in the future you have to strengthen the circuit, or add more circuits, it will come in handy.
Kirill.
Rating of fire protection RCD
The choice of a fire protection RCD to protect a home is associated with the need to turn off the power when a leakage current appears in several lines at once. In this case, the leakage in each individual cable may be small, but the total current is significant. For example, a similar situation occurs when there is high humidity in the bathroom or the apartment is flooded by neighbors from the top floor.
In addition, the parameters of the fire protection RCD must ensure that there are no trips when one of the protective devices located closer to the accident site is turned off. These requirements are met by a two- or three-stage protection system, in which the setting current of each next stage is higher than the previous one.
| Information! The rated current of the RCD is determined by the input circuit breaker and must be equal to or greater than the rated current of the circuit breaker. |
Checking the RCD for serviceability
In order to be sure that the device is in good working order, it should be checked not only before installation, but also during operation, approximately once a month. To find out how to test the RCD for functionality, you should read the instructions.
Each device has a large test button. Pressing it simulates an emergency current leak. If the RCD is working properly and all wires are connected correctly, then it should work regardless of the connection of household appliances to it. For such testing you do not need to have special knowledge or qualifications.
Each device must be tested once a month Source zoon.ru
Design
The design of the RCD will help us understand how it reacts to current leakage. The main working units of the RCD are:
- Differential current transformer.
- The mechanism by which an electrical circuit breaks.
- Electromagnetic relay.
- Test node.
The transformer is connected to opposite windings - phase and zero. When the network is operating in normal mode, these conductors in the transformer core help induce magnetic fluxes that are in the opposite direction relative to each other. Due to the opposite direction, the magnetic flux in total is zero.
The device and principle of operation of the RCD is clearly shown in the following video:
An electromagnetic relay is connected to the secondary winding of the transformer; under normal operating conditions it is at rest. A current leak occurs, and the picture immediately changes. Now various current quantities begin to pass through the phase and neutral conductors. Accordingly, there will no longer be equal magnetic fluxes on the transformer core (they will be different both in magnitude and direction).
A current will appear in the secondary winding and, when its value reaches the set value, the electromagnetic relay will operate. Its connection is made in conjunction with a release mechanism; it will instantly react and break the circuit.
An ordinary resistance (some kind of load, the connection of which is made without passing through the transformer) serves as a test unit. Using this mechanism, current leakage is simulated and the operating condition of the device is checked. How does this check work?
There is a special “TEST” button on the RCD. Its main purpose is to supply current from the phase wire to the test resistance and then to the neutral conductor, bypassing the transformer. Due to the resistance, the current at the input and output will be different, and the created imbalance will trigger the shutdown mechanism. If the RCD does not turn off during the test, then you will have to abandon its installation.
Note! The RCD must be checked regularly, ideally once a month. This is a fire safety requirement and should not be neglected.
The internal design of different RCD manufacturers may differ, but the general operating principle remains unchanged.
All devices differ in the operating principle. They come in electronic and electromechanical types. Electronic RCDs have a complex circuitry and require additional power to operate. Electromechanical devices do not require external voltage.
How to calculate the device
The RCD is calculated based on operating conditions. If the network is single-phase, then a two-pole device is needed. In a three-phase network, four-pole devices are used.
The choice of device taking into account current leakage depends on the quality of wire insulation, length of wiring, number and power of devices.
When installing an RCD, you need to know that the total current of all network leaks and electrical devices should not be more than a third of the rated current of the device. If there is no information about the equipment, then with a load of 1 A, 0.4 mA of leakage is taken into account. Also, a network cable loses 10 µA per 1 m of length, because electrical energy can leak through ordinary insulation. This phenomenon complies with safety regulations.
An example of connecting an RCD to a group of machines in a three-phase network Source samodomik.ru
Differences from the machine
So, what is the difference between an RCD and a machine in electrical engineering? Without going into details of the design, the machine is triggered at currents exceeding the maximum load on the network (for example, there are machines for 10, 16, 25 amperes), and the most popular models of protective shutdown are triggered by a leakage current of 30 milliamps (mA). That is, the current turns out to be almost 1,000 times weaker. The protection response time is approximately 100 milliseconds (0.1 s). For such a short moment of impact, a person will not even feel the blow.
Main parameters of product selection
It is necessary to select an RCD in strict accordance with the main operating indicators of the electrical system located in the house.
Too strong protection, far exceeding the power of all household appliances available to the owners, will not cope with the task in the future and will not be able to protect the user and home from fire hazards because it will not detect a dangerous leak.
It is better to purchase an RCD with a small margin. Otherwise, the appearance of any new household appliance module in the house will cause an overload and lead to the constant operation of the protective device
A device designed to operate at relatively small excesses simply cannot withstand a basic load. In addition, it will start to operate too often, thus causing a lot of inconvenience to the owners of the premises.
Selection by type of network voltage
Voltage 220 V is a classic indicator relevant for single-phase networks used to supply power to standard consumers. The normally permissible deviation from the indicator is within +/-5%.
According to these data, the voltage range of 209-231 V is considered optimal and does not put unnecessary stress on the system and the devices connected to it.
If several electrical branches come out of the distribution panel, you need to equip each of them with a separate RCD. This will entail additional costs, but if there are problems and the device is triggered on one line, everyone else will be able to continue working as usual
To protect such a network, usually laid in a small house, a simple RCD is used, designed for connection to a single-phase network and for minor voltage surges and to work correctly with the circuit breakers already in the house.
The power indicator of the protection device must be an order of magnitude higher than the total total power of all household appliances available in residential premises.
In large houses with a large number of household appliances and the presence of specific electrical appliances that ensure the vital functions of the room, a more powerful and operationally stable three-phase 380 V network is often used.
A special protective device is used for it, slightly different in configuration from the standard single-phase one. The response threshold level of such a product is very high. It is placed in a special shield. In the panel, RCDs and circuit breakers are located in a certain order according to their purpose and selectivity rules.
The distributor, regardless of the number of floors of the building, is always located below in the area of the entrance to the house. As a rule, “S” protection is mounted on it with a certain delay time and a leakage current of 100 mA.
To avoid false alarms of the device, in some rooms where the wiring is outdated and has served its useful life, an RCD built into the socket is installed. Such a device monitors the level of current flow when activating household or lighting equipment and reduces the load on the system
Electrical lines across floors, living rooms, technical rooms, kitchens and bathrooms are laid from an input machine. In separate rooms where, according to fire safety requirements, the leakage current cannot exceed 30 mA, an individual single-phase protective unit is installed.
Number of poles for devices
The presence of a certain number of poles for safety devices is also an important selection criterion. Bipolar products are used only in single-phase networks where it is necessary to connect one working phase and zero.
If a single-phase network is equipped with a grounding system, then the installation of the RCD is carried out according to the diagrams given in the article we recommend. It describes in detail the options and rules for connecting the protective equipment to phase, grounding and zero.
Located in ordinary electrical panels, RCDs with two poles occupy two seats according to the generally accepted DIN standard. For correct operation, a four-pole device requires 4 places
In three-phase systems with a base voltage of 380 W, units with four active poles are used, designed to activate zero and three phases.
Forward current level
The throughput or rated current of the RCD directly depends on the number and total power of devices and equipment connected to the electrical network.
In order for the input protective device to work correctly and not lose phase when the user simultaneously activates several units of household appliances, this indicator must be calculated for all energy-consuming modules available in the house.
The most common products used in everyday life are designated 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80 and 100 amperes. For linear-type protective units, the operating power is calculated based on the number of electrical products connected to each individual branch
For ease of selection, manufacturers mark safety elements with numbers indicating the maximum throughput current in amperes.
Difference in leakage current
Leakage current is a certain value, upon reaching which the RCD opens the electrical circuit and stops powering the devices. This extreme threshold is called the rating and is usually 10, 30, 100, 300 and 500 Ma for different protective devices. You will learn how to install a selective RCD from the following article, the contents of which we recommend that you familiarize yourself with.
A 30 mA unit is considered optimal for small private houses. It copes well with the assigned task and turns off the line when a leak is detected that does not pose a danger to human life.
Products of a lower rating are overly sensitive and will deactivate the energy supply to devices with the slightest network fluctuation. There are other reasons for knocking out the RCD, which a prudent owner should be aware of.