Home / Electric boilers
Back
Published: 05/31/2019
Reading time: 3 min
1
10473
Using electricity for heating is a common way to heat a home. This method is environmentally friendly (no impact on the environment) and convenient.
The only factors limiting the spread of such heating are:
- Electricity tariffs and their growth in the future.
- Consumer expenses for supplying and connecting to housing the electrical power necessary to ensure comfort.
When the user decides on fuel for the boiler, he is limited in choice. There are no natural gas or district heating networks near his home, and there is no market for wood or agricultural waste.
Photo source: buildingwork.net
Then the electric boiler becomes the only alternative and the main source of heat. In bivalent heating systems it becomes a backup in combination with gas, solid/liquid fuel boilers or heat pumps.
- 1 Advantages and disadvantages of electric boilers
- 2 Electric boiler design
- 3 Operating principle 3.1 Boiler with heating element
- 3.2 Electrode boiler
- 3.3 Induction
Description and principle of operation of electric heating boilers
Gas boilers are popular due to the low cost of fuel, but it is not always possible to connect them due to the labor-intensive procedure and the need for coordination with government agencies. Energy sources for solid fuel units are even cheaper, but there are many more disadvantages - they pollute, require the removal of combustion products, fuel loading, and storage space.
The listed disadvantages are absent in electric boilers, which are sometimes the only option for heating if there is no possibility of supplying gas. Moreover, electrical devices are considered not only as additional or emergency sources, but also as the main devices for the preparation of coolant. With them you don’t have to worry about ignition and other inconvenient issues associated with fuel combustion.
The most economical electric boiler should be chosen from energy-saving induction and electrode models. But we must take into account that in any case, its operation will cost approximately 2.5 times more than gas units, at best 1.5 times. Economy is considered here for situations where there are no other alternatives to electricity or if this type of energy is cheap (there are alternative sources - solar collectors, etc.).
How electric boilers work, device
The general principle of operation of electric boilers for heating: the coolant (water) circulates using a pump along the circuit of the heating system, through the boiler (internal chamber, flask, coil) and is heated there by heating elements, heat exchangers with electrodes, and induction coils.
The main parts of the electric boiler: housing with heaters, circulation pump, power supply, expansion tank, control and safety system (pressure gauge, check valve and for releasing excess pressure).
Economical electric boilers are required in the following conditions:
- if it is not possible to use gas;
- a unit that is easier to maintain than fuel-powered devices is required;
- preference is given to a cleaner energy source;
- An additional heater is required in case the main device is turned off.
Basic elements of electric boilers
Regardless of the power of the electric boiler and its main purpose, it consists of the following main elements:
- The housing, which serves as a container for all components.
- A heat exchanger, which serves to transfer heat from the heating element to the coolant tank,
- Control, control and adjustment units.
A number of models of electric boilers may also have built-in circulation pumps to ensure the movement of coolant, and valves that redirect its flow.
A modern electric boiler is a high-tech device that heats flowing water with maximum efficiency, while operating in a completely autonomous mode. Even a child can operate such equipment - it is so safe and simple. Also, modern electric boilers have a fairly high efficiency, which will allow you to avoid unnecessary bills for wasted electricity.
water supply distribution
There is a great variety in the design of such electric heating devices. They come in a variety of shapes, with wall or floor placement.
Types of electric boilers for home heating
There are several types of electric boilers based on the principle of electricity use and operation. Traditional and familiar to everyone - heating elements. More innovative and energy-saving are induction (vortex) and ionic (electrode), they are more expensive, but the cost is paid off by extreme efficiency and efficiency, which weakly or does not decrease at all over time.
The efficiency of all electric boilers is the same - 94–99%, but some types are more efficient due to the design and method of operation. And also over time, due to scale, this characteristic decreases by 10–20% for heating element boilers, but this is not typical for induction and ionic products.
Types of electric boilers:
- with heating elements;
- ionic (heating by electrodes);
- induction (vortex).
Heating elements new electric boilers
Heating boilers with heating elements can only be classified as economical only conditionally: different models may have more efficient heating elements, programming capabilities, and power settings.
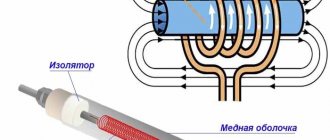
Inside the device there is a tubular electric heater - a copper or stainless steel tube (there may be sand or oil inside) with a filament (nichrome). The principle of operation is the same as that of a conventional boiler or air heater: the spiral inside the shell heats up and transfers heat through the tube in which it is enclosed to the water entering the chamber (flask) with the heating element.
When choosing electric heating for a home with a special emphasis on economy, units with heating elements should not be seriously considered. You can choose a high-quality device with more or less energy consumption, but it will still be more power-hungry than induction and ion boilers. On the other hand, the cost reduction can be compared to some extent, since a boiler with a heating element is cheap to maintain.
Advantages and disadvantages of heating elements electric boilers
Advantages of heating heaters with heating elements:
- cheap and convenient repair (the body is easily disassembled, parts are replaceable);
- advanced functionality: power adjustment, programmability, ability to connect a thermostat;
- usually produced in a monoblock compact case (there are convenient wall-mounted sizes) ready for operation, including a safety group, expansion tank, and pump. There is no need to separately purchase and install these elements; you only need to connect the device to the input and output of the heating system.
Minuses:
- the most uneconomical type of electric boilers, especially if two heating elements are used;
- Scale and plaque forms on the heating element, which requires periodic cleaning and replacement. A hard crust reduces efficiency by 10–20%. This statement is controversial, since the water of the heating system is not prone to intense scale formation, but it should not be ignored.
Induction boilers
Types of induction boilers for home heating (sometimes perceived as brand names):
- VIN - “vortex induction heaters”, more innovative with a ferromagnetic body. Smaller in size and 1.5–2 times more expensive than SAV, but more efficient;
- SAV - the principle is the same, but they are positioned as less advanced.
The second heating with vortex boilers is “inverter”. The product includes a current converter from direct to alternating current - an “inverter” (like welding machines).
Immediately after their appearance on the market, induction heaters for heating were positioned as the most advanced and efficient, but application experience showed more shortcomings than expected.
Operating principle of vortex SAV and VIN electric boilers
How does an induction SAV boiler work:
- A high-frequency alternating current (from 50 Hz) is supplied to a metal coil (inductor) - a rod (its role can be played by the coolant pipe itself) with turns of wire. A magnetic field is generated.
- The polarity and vector of the magnetic field change with high frequency.
- An object located close to the described phenomenon is penetrated by constantly changing fluxes of magnetic induction. Foucault eddy currents arise, turning electricity into heat, which heats the water.
The principle of heat transfer in induction boilers is non-contact - the object is heated by electromagnetic fields, and instantly. There is no need for physical contact with the inductor, which increases efficiency.
The electromagnetic principle is used in industry to melt metals. Even a small homemade induction device with a coil with a dozen turns and a few cm² in size is capable of heating metal to red in a few seconds, which illustrates the power and efficiency of a vortex boiler for heating.
Advantages of induction boilers for heating
Advantages of SAV boilers:
- heating is powerful, almost instantaneous;
- microvibrations repel dirt, so there is no scale or deposits on parts in contact with water, no cleaning required;
- economical, the highest efficiency among electric boilers.
Induction boilers are the best for preparing water as it flows through the apparatus, as they provide extremely fast heating. At the same time, heat loss is zero, which distinguishes VIN from heating elements units. Despite the disadvantages, if we consider purely the efficiency of using electricity, induction boilers are the most economical type of electric heaters.
Disadvantages of vortex boilers for heating, feasibility of use
Many sources list many advantages of VINs and SAVs, but in reality the picture is somewhat different; many shortcomings have been discovered:
- most standard sizes have significant dimensions;
- more expensive than heating elements and electrode units;
- heating is extremely powerful, so if the auto-shutdown system breaks down, there is an increased risk of explosion;
- the electromagnetic field is harmful, electrochemical processes provoke corrosion;
- complex repair. It would seem that the device is extremely simple - a coil and a housing - but usually the cylinder of SAV boilers is securely sealed, and it is extremely difficult to disassemble it. It contains electronic circuits of the control unit, which complicates repairs. The coil may burn out, and the cost of a new one is higher than, for example, a new heating element;
- if the SAV is not in a compact case, and the majority are, then a large control unit, a separate expansion tank, a pump, and a safety group will be required;
- in most cases, they are not equipped with a soft start - when turned on and even when simply switching modes, there is a sharp increase in the load on the network, which is fraught with voltage drops (flashing lights and similar effects).
Still, despite the listed disadvantages, a vortex energy-saving electric heating boiler should be considered as a heater for heating a house due to its high level of efficiency (30% more efficient than heating elements). Some of the listed disadvantages are relative, for example, there are small and compact sizes similar to those of products with heating elements. This is the only type of heater whose efficiency does not decrease over time.
Ion (electrode) boilers
Ionic (electrode) energy-saving heating boilers must be distinguished from induction units, despite the fact that they also use the properties of alternating current. The organization of energy use itself is different. The body of the device contains a sealed chamber with a coolant and electrodes located in it with a certain gap.
With a constant current, the cathode attracts water ions with a positive charge, and the anode attracts negative ones, but if you change the characteristic to a variable one (starting from 50 Hz), then a constant movement of these particles will occur. The medium has resistance, so the kinetic energy of moving ions (cations and anions) is transformed into thermal energy, and the electrolyte is heated.
In the ion boiler, a special electrolyte solution is heated, circulating in the pipes of the heating system; in certain cases it can be water. In fact, such a boiler is a simple heat exchanger.
Advantages of ion (electrode) boilers for heating systems
Advantages and features of ion boilers for heating:
- extremely compact: low-power models are only slightly larger than the diameter of the pipes. This is a small cylinder cut into the wiring. They do not require any space around them, so they can be installed literally anywhere;
- the cheapest - 4–9 thousand rubles. (A new heating element costs about 15-30 thousand), but if you have to buy an expansion tank, thermostat, safety valves, pump, then it’s another 10-12 thousand;
- scale does not form - this is prevented by electromagnetic processes;
- service life before the first breakdown is 12–15 years. According to this characteristic, electrode heaters are comparable to induction devices;
- maintainability. The design is simple and can be disassembled without much difficulty. Parts are replaceable and cheap;
- the safest: if induction or heating element boilers, if the automatic shutdown (protection against overheating and dry operation) fails, continue to heat up until an explosion or fire, then ionic boilers will simply stop working on their own without any intervention if the coolant leaks;
- no electromagnetic field.
Disadvantages of electrode heaters
Installation of the electrode device itself is simple, but it is somewhat complicated by the need to install a pump, safety group, and expander. There are also products with the last two elements on the body or in the form of a ready-to-use monoblock, but this arrangement is less common. In this aspect, heating element boilers have an advantage, since they are often produced in standard sizes with everything necessary in one housing.
Minuses:
- There are devices with a heat exchanger and an expansion tank on the body, but in most cases an additional purchase of these elements is required, as well as a pump and safety group;
- scale and plaque do not form, but electrical processes increase corrosion of the metal of the heating system circuit. In this aspect there is a similarity with SAV boilers;
- Pipe water can act as an electrolyte, but usually special solutions from the manufacturers of such boilers are always used. The mixture must be undistilled and unfiltered. Special substances are the most effective. Propylene glycol and ethylene glycol are used. You cannot use antifreeze, oil, or distilled water;
- requires replacement of the coolant every 3–4 years.
Electrode boilers consume 20–30% less electricity than heating element units, but they are slightly less energy efficient than induction models. That is, in the economy rating, if we take into account the convenience, low cost of the product and service, they are in the middle.
Operating principle of an electric boiler
Almost all electric boilers operate on the same principle: a heating element is placed in the heat exchanger, which, after applying electric current to it, begins to generate heat. The coolant entering the heat exchanger (usually simple tap water, and in closed heating circuits water with special additives or antifreeze) is heated after contact with the heating element.
By the way, water can be heated not only by a traditional heating element (that is, a heating coil enclosed in a protective casing), but also by induction or electrode methods. However, it is electric boilers with heating elements that are most widespread, both among imported and domestic models.
heating circuit
The power supply for heating boilers is also very diverse. They can be powered from standard household 220 volts, or they can have industrial power supply with three phases at 380 volts. There are even modifications that are powered by batteries.
Guidelines and what to consider when choosing an economical electric heating boiler
An economical electric boiler must have programmable operation, the ability to connect a rheostat for on/off. during periods of low tariffs or when a certain temperature is reached, as well as to regulate heating. At a minimum there should be at least a three-stage power switch.
The ideal option is if the device has smooth adjustment and factory economy modes. The product must be suitable for connection to room rheostats, which have many fine settings and respond to the air temperature in the room.
Single- and double-circuit electric boilers
If you need to provide hot water at the same time as heating, then choose double-circuit electric boilers. Moreover, the electricity consumption in such products is practically no different from single-circuit ones. DHW water is heated by washing the heat exchanger in the heating boiler circuit, without mixing with its coolant. Such heating does not require additional power, although for greater efficiency there are models with increased energy consumption.
Installation rules and requirements
All general requirements are described in the PUE (7th edition). Electric boilers with a power of up to 10 kW do not require approval from the Energonadzor services. However, if you want to install a meter that differentiates electricity consumption by zone of the day, which we recommend doing in order to save money, you will still have to coordinate the installation. For boilers with a power of more than 6 kW, three-phase power supply (380 V) is required; 8-12 kW models can operate from a single-phase (220 V) network, but it will not provide operation at full power.
The choice of installation location for an electric boiler is more extensive than for gas or solid fuel boilers. Electric boilers can be installed in a residential area, for example, a corridor, hallway or kitchen, but keep in mind that in any case you need to run pipelines, wiring, grounding and other communications to it. The installation of an electric boiler in the bathroom and toilet is prohibited.
The requirements for the installation surface are also minimal, it can also be a wooden wall, but in this case it is necessary to insulate the installation site with a layer of non-combustible material (basalt cardboard, xylolite sheet).
Fireproof protective plate when installing an electric boiler on a wooden surface.
Manufacturers also impose requirements on the space around the electric boiler necessary to ensure maintenance and repair. The values differ depending on the model, so before planning the installation location and wiring, you should find them in the operating instructions. Usually this:
- from 0.7 m from above the boiler;
- from 0.5 m on the sides (including to the pipeline) and below;
- from 0.7 m in front of the boiler unit;
- at least 3 cm between the wall and the boiler.
For example, the well-known Bosch Tronic Heat 3500 model requires only 0.6 m from the bottom and 0.2 m from the other sides. Any other additional installation requirements are always described in the operating instructions, which in almost all cases can be found in electronic form.
Calculation of power for the area of the house
We present a simplified calculation of power, since this issue is a topic for a separate article. Approximate calculation usually always gives results as close as possible to real needs.
If the electric boiler performs an auxiliary heating function in addition to the main gas or other unit, or fireplace, then for 120–150 m² a power of 3–6 kW will be sufficient.
Comparative table of average statistical electricity consumption by electric boilers
| Electrode | heating elements new | ||||
| Boiler power | Heating area, m² | Consumption, kW/hour | Boiler power | Heating area, m² | Consumption kW/hour |
| 3 kV 1 phase | 50 | 0.5–0.6 | 3 kV 1 phase | 30 | 1.5–1.8 |
| 5 kV 1 phase | 80 | 0.9–1.2 | 5 kV 1 phase | 50 | 2.0–2.5 |
| 9 kV 3-phase | 120 | 1.8–2.3 | 9 kV 3-phase | 90 | 3.6–4.2 |
| 25 kV 3-phase | 350 | 4.5–5.5 | 25 kV 3-phase | 240 | 9.5–11.0 |
If an energy-saving boiler is the main source of heat, then it is necessary to carry out calculations taking into account heat losses, which for an average private home with two-brick masonry and 2.7 m ceilings in the climate of the Moscow region is 1 kW/hour. It is recommended to select power with a margin of 10–20%, and for heating element heaters - by 20–30%, since their efficiency decreases due to scale. For 80 m² you will need an electric boiler of 9.6–10 kW (8 kW + 20%).
For SAV boilers, a power of 2.5 kW is 2100 kcal/hour, which is enough to heat 25–30 m². The calculation is affected by the required temperature. If you need to maintain 15–20 degrees in a room of 120 m², then a 6 kW unit will suffice.
An economical ion-type electric heating boiler with a power of 3 kW is suitable for heating 50 m². The same product with a heating element will heat 30 m².
Types of electrode boilers
When choosing equipment, the cost and possibility of installing automatic systems on boilers are taken into account.
The area of the house and the adequacy of the power of the equipment for heating the premises are taken into account.
Devices are classified according to the following criteria:
- power;
- connection and power supply method (three- or single-phase);
- number of connected circuits;
- method of distributing the coolant.
By number of circuits
The simplest system is a system with one circuit. Water from the boiler is supplied to the heating main, moves to the radiators, where it releases energy. The liquid passes through the registers and returns to the place of heating. The closed combination forms the heating main.
A single-circuit boiler supplies coolant to heat the house, and a double-circuit unit additionally supplies liquid for the hot water supply system. The electric electrode boiler operates from a three-phase or single-phase electricity line.
The circuits are connected to the distribution unit (collector). The center of the electrode heating system is installed for proper heat distribution along the main branches.
By number of phases
Three-phase units operate from a 380 V power supply and are produced with a power of over 9 kW. The electrodes are made up of plates, rings or cylinders and interact effectively with a coolant of low thermal conductivity. The amount of power is inversely proportional to the specific resistance of the fluid.
Three-phase devices consume the optimal amount of energy when heating water from +75°C. At low temperatures, thermal conductivity decreases and electricity consumption decreases; the opposite situation occurs when heating rates are set to high.
Single-phase electrode electric boilers for heating have lower power (2 - 6 kW) and are intended for small houses (40 - 120 m2). The type of power supply (single-phase or three-phase) is determined in the distribution panel. If there are 3 wires going to the house, the first option has been carried out; the presence of 4 - 5 wires indicates the second type of consumption.
By power
The power is constantly changing and depends on the water temperature. Connecting and starting the boiler in winter can lead to a lack of heating power. If cold water increases the thermal conductivity index to normal, after heating the main line the index will increase, network overload and an accident will occur.
According to the principle of coolant distribution
In closed systems it is necessary to install an expansion tank
Energy-saving units are installed in open and closed type mains, the latter type is used more often. In an open system, shut-off and control equipment is installed behind the expansion tank. The section of the circuit between the boiler and the compensating tank should not contain locking devices.
The closed system includes an expansion tank and a pump. The heating circuit is equipped with an air and safety valve, a pressure gauge, the safety group is located at the top point of the line. In the heating system, boilers are placed strictly vertically and additionally attached to the wall.
What to choose: comparison of consumption, cost, ease of use
If we focus on ease of installation, ease of operation, and average price, then the first place in the ranking is occupied by boilers with heating elements. As a standard, they are carried out in a monoblock case that is completely ready for operation after installation - it already has a safety group, an expansion tank, a circulation pump and other elements. You just need to connect it to the input and output of the heating system. But they are in last place in terms of economy and cannot be called energy-saving.
If we consider the question of which electric boiler is the most economical and with the best energy saving, then we should consider induction and ion units.
Vortex heaters are in first place in terms of economy, but they have a number of disadvantages that slightly offset this advantage: price, difficulty in repair, large dimensions. These are the most expensive and inconvenient electric boilers considered: the cost of such a 25 kW product is 86 thousand rubles. (A new heating element for 24 kW can be bought for 46 thousand).
Below is a table comparing different types of electric boilers. But the data in it should not be unconditionally trusted - manufacturers are trying to show their products in a favorable light. For example, in other sources, ion boilers are shown to be much more economical and efficient than heating element boilers.
| heating elementnew | Electrode | Induction | |
| Efficiency | 98 % | 94 % | 99 % |
| Loss of power after 12 months of use | 20 % | 15 % | 0 % |
| Maximum pressure | 3 atm | 3 atm | 6 atm |
| Heating temperature | Up to 90 degrees | Up to 85 degrees | Up to 115 degrees |
| Life time | 3–7 years | 10–12 years | 30–60 years |
| Probability of failure within 12 months | 15–20 % | 15–35 % | 0 % |
Another disadvantage of SAV and VIN is the large dimensions of the housing itself and the individual elements that include the control cabinet. A product with a tubular electric heater contains everything you need in a compact case, and an ion boiler generally resembles a thick water pipe. The weight of a 25 kW induction boiler is 80 kg, a heating element of the same power is 40 kg.
Vortex boilers are increasingly being chosen for private homes. Although such devices are the most energy-saving, they are more often used in places where induction heating is indispensable - in industrial, production environments, and chemical plants.
Economics of VIN use
| The name of a room | Heated area/volume | VIN model | power, kWt | Cost kW/h, rub. | Monthly payment, rub./month. | Payment for the heating period, rub. |
| 1 room apartment | 50 m² | VIN-3 | 3 | 2.0 | 1227.6 | 9147.6 |
| House | 100 m² | VIN-7 | 7 | 2.2 | 2864.4 | 21334.4 |
| Garage box | 450 m³ | VIN-10 | 10 | 3.2 | 5952 | 45888 |
| Hangar | 1000 m³ | VIN-20 | 20 | 3.2 | 11904 | 91776 |
Ion (electrode) boilers are the best choice in the economy class in all respects, especially in terms of cost, if you need an energy-saving heater for heating a private home. Their economy and efficiency may be somewhat lower than that of induction and heating elements products, but this is compensated by ease of maintenance and small size. An important fact in favor of ion boilers is the price - these are the cheapest energy-saving heaters for heating (4-5 thousand rubles).
Ion boilers are a good option as an additional heating source. If you use them as main devices, you can embed several of these cylinders for greater efficiency.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any electric unit for heating a private home, an electrode device has both its positive and negative sides.
The positive side is the high efficiency - 98% with small dimensions. At the same time, due to the ionization of the coolant, energy consumption is saved. If we compare, for example, with heating element heating boilers, electrode boilers consume 40% less electricity.
Voltage drops are a natural state of Russian electrical networks in countryside villages. So, energy-saving electrode-type heating boilers do not respond to these changes. In addition, there is no need to coordinate the installation and connection of the boiler with the boiler inspection.
The negative aspects of using an electrode heater include the impossibility of using it in a heating system where steel pipes and cast iron radiators are installed. In the first case, there is a high probability of scale formation on the walls.
In the second, there is a large volume of coolant, which the electrode boiler may not warm up. Here we add the filling of antifreeze and inhibitors, as well as the high cost of electricity.