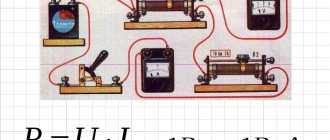
This table provides information on the monthly electricity consumption of electrical household appliances.
| Electricity consumer | Power, kWt | Qty | Average operating time | electricity consumption (kWh) |
| Fridge | 1 | 1 | 2 hours a day (including pauses) | 60 |
| Kettle | 2 | 1 | 0.3 hours a day | 18 |
| TV | 0,1 | 1 | 5 hours a day | 12 |
| Washing machine | 1,5 | 1 | 3 hours a week | 20 |
| Iron | 1,2 | 1 | 1 hour per week | 6 |
| Microwave | 1,2 | 1 | 15 min.day | 9 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 1,2 | 1 | 30 min. week | 3 |
| Lighting lamps | 0,06 | 10 | 3 hours a day | 54 |
| Convector (heater) | 1 | 1 | 4 hours a day (including pauses) | 120 |
| Water supply pump | 1,5 | 1 | with an average switching on of 40 days for 10 seconds. | 5 |
| Computer | 0,16 | 1 | 1 hour | 5 |
| TOTAL | 312 |
These data are based on the residence of an average family of 3 people. Also, please note that the number of appliances listed in the house is often used more. Sometimes, in a country house there are 2-3 refrigerators, dishwashers are used, there may be more than 1 heater, an electric stove, etc. not to mention houses that are heated entirely by electricity. We also have bathhouses, gazebos, watering pumps, site lighting and much more. So, once again, when you pay for the consumed electricity per month at 60 - 100 kWh, doesn’t this mean that you either use only a refrigerator, or use solar panels and wind energy generators.
How much electricity do household appliances consume?
Today, energy costs make up a significant part of the family budget. To intelligently approach the problem of energy consumption and associated costs, you need to know how much electricity different household appliances consume and how to calculate the cost of these costs.
How to calculate the electricity consumption of household appliances
Each device has a sticker on the back or side with its characteristics. The power of the device is indicated in watts (W or W). If you do not find a sticker with designations, the characteristics can be found in the instructions. To calculate electricity consumption, you need to multiply the power of the device by the duration of its operation in hours.
For example, a washing machine runs for an hour and a half at a time, and its power is 1,000 W. Then the amount of energy consumed per wash will be 1,000 × 1.5 = 1,500 Wh. Dividing this value by 1,000 will convert Watts to kW. The result is 1.5 kWh. Next you need to multiply this value by the number of washes per week or month. Let's take 3 washes per week, or 12 per month. This means that the washing machine uses 18 kWh over the course of a month. To calculate the approximate cost, multiply the amount of energy consumed by the tariff. The cost of 1 kWh is indicated on the receipt.
How much electricity do household appliances consume?
The total power consumed by the computer will be the sum of the powers of the power supply and monitor. The power supply requires from 350 to 550 W, depending on the work the device performs. If you chat on social networks, energy consumption will be minimal. While working in complex graphics editors like Adobe Illustrator will make the computer burn more energy. The power required by a monitor depends on its size: a 19-inch monitor consumes about 60 W, a 24-inch monitor consumes 80 W. In total, the average will be about 500 Wh, or 0.5 kWh.
Since the laptop only uses the power supply, no matter what functions it performs, its power consumption will be lower than that of a desktop computer. On average - from 0.05 to 0.1 kWh.
The energy consumption of a TV directly depends on the size of the screen and the design. Thus, devices with a cathode ray tube require from 60 to 100 W. Liquid crystal models require from 150 to 250 W, plasma models - 300-400 W. If you turn off the TV using the remote control, leaving it plugged in, the device will go into standby mode. A small red light will light up. Energy consumption in this case will be 2–3 W for models with a cathode ray tube and 4–6 W for LCD and plasma TVs.
The refrigerator is perhaps the only appliance that operates 24 hours a day, seven days a week. It must be remembered that depending on the time of year and workload, the same model will require different amounts of energy. In the cold season, the device uses approximately half as much energy as in the heat. A filled device requires less fuel than an empty one.
All refrigerators are divided into energy consumption classes. For models with low energy consumption, the required amount of energy is approximately equal to the volume of the device in liters. For example, a refrigerator with a volume of 240 liters uses 240 kWh per year. On average, this figure ranges from 230 to 460 kWh per year. The exact value for your model can be found in the instructions. To calculate the daily rate, you need to divide the annual consumption by 365. The result is from 0.6 to 1.2 kWh per day.
Calculation of electricity for a disabled person and his family
The situation is even more confusing with people with disabilities and socially vulnerable groups of the population, for whom discounts on electricity payments are established. First of all, before calculating electricity for a disabled person, you will need to register the right to benefits at the local social security department based on the following documents:
- A written application for benefits indicating the personal account number for payment of electricity;
- Photocopies of the passport and the original certificate of disability;
- Information about family composition.
For your information! There will be no benefits if at the time of application there is arrears on utility bills.
In 2022, the state provided benefits in the consumption of electrical energy for families of disabled people at a rate of 45 kWh and 70 kWh for a gas burner and electric stove, respectively. For single disabled people, the preferential rate is 50 kWh and 80 kWh. These volumes are paid at half the current tariff. Anything that exceeds the preferential volume must be calculated at the full tariff rate.
In the future, it is planned to provide subsidies, benefits and social norms for electricity only to households equipped with appliances of a consumption class of at least “B”. If you calculate the energy consumption after replacing conventional incandescent lamps with LED ones, you can be sure that the savings are at least 20% only on the internal and external lighting of the house.
Table of Approximate Energy Use of Electrical Appliances
Have your electricity bills shocked you? Don’t know where these amounts come from? It seems that you don’t do a lot of laundry, and don’t turn on the lights in vain, but the counter inexorably adds up to high numbers. It might be worth finding out how much energy all your appliances actually consume.
Without a doubt, the most kilowatts come from household appliances that you use constantly. How can you find out which devices are more economical and which are not?
To calculate the electricity consumption of a specific device per unit of time, you need to pay attention to the following characteristics:
Directly the power of the device itself: the engine or power supply.
The amount of time the device operates.
Ambient temperature.
Of course, not in all cases the above factors play a significant role. But for some household appliances (for example, a refrigerator), every point is important. The following table of electricity consumption for household appliances will give an idea of the approximate consumption per month.
Cost of electricity in the kitchen
If you don't have gas, you'll have to cook with electricity. Modern electric stoves are highly efficient, but they also consume 5 to 7 kilowatts of electricity per hour at full power.
The approximate cost of cooking with electricity will be from 300 to 500 rubles per month, regardless of the size of your home.
HOW MUCH ELECTRICITY DO HOUSEHOLD APPLIANCES CONSUME?
Surely, at some point in your life, some of you have heard from your family that increased electricity bills are entirely your fault. Either you watch a lot of TV, then you sit at the computer for a long time, then you iron a lot or do laundry often. Again, the question of the size of electricity charges may suddenly worry you yourself. Let's try to at least roughly figure out how much electricity household electrical appliances can consume.
By and large, if we count roughly and approximately, everything depends on the power of the power supply and the specific work that the computer is currently performing. With the declared power of the unit ranging from 350 to 550 Watts, it is unlikely to consume all of it even at full load. You can also add a monitor here - from 60 to 100 watts. Thus, the average 450 Watt power supply and 100 Watt monitor consume 550 Watts or 0.55 kW of electricity per hour. Again, these figures are greatly overestimated. For an approximate calculation, you can take almost the maximum value – 0.5 kW/h – we won’t be mistaken. When using a computer 4 hours a day, we get 60 kW/h per month. Accordingly, when used 8 hours a day - 120 kW/h, and so on.
The energy consumption of refrigerators is calculated over 365 days for a 220V/50Hz network. Designed for 100 liters of useful volume per day, it allows you to compare refrigerators of different sizes. Again, the amount of power consumed depends on the volume of the refrigerator and the amount of food stored in it. External conditions also leave their mark, changing depending on the time of year. The technical data sheet for the refrigerator indicates the energy consumption per year. In most cases, this figure ranges from 230 to 450 kW/h. By simple calculations, dividing this figure by 12 months, we get from 20 to 40 kW/h. Again, this number only applies under ideal conditions. In reality, it is unlikely that this value will be achieved.
Cost of lighting in a private house
If you install energy-saving lamps with an average power of 13-15 watts in all the lamps in your home, which is equivalent to a regular lamp of 75 watts, then your costs for lighting your home will be within very reasonable limits.
In winter, lighting operates for 10 hours a day, and in summer – for 3-5 hours, excluding external lighting. Of course, if external lighting is installed correctly and equipped with light and motion sensors, then external lighting will work no more than internal lighting.
So, you have a house of 100 sq.m., in which you have approximately 20 lamps with a power of 15 watts. That's only 300 watts per hour. With an average lighting time of 7 hours (both in winter and summer), this is only 2 kilowatts per day or 60 kilowatts per month.
That is, the cost of lighting in a private house of 100 square meters will amount to no more than 200 rubles per month.
Electricity consumers in the house
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 334 “On improving the procedure for technical connection of consumers to electrical networks” dated April 21, 2009 states that a private individual can connect up to 15 kW to his home. Based on this figure, we will make a calculation and see how many kilowatts will be enough for our home. To carry out the calculation, you need to know how much electricity each electrical appliance in the house consumes.
Power table of household electrical appliances
The power table for household electrical appliances shows approximate electricity consumption figures. Energy consumption depends on the power of the devices and the frequency of their use.
| Electrical appliance | Power consumption, W |
| Appliances | |
| Electric kettle | 900-2200 |
| Coffee machine | 1000-1200 |
| Toaster | 700-1500 |
| Dishwasher | 1800–2750 |
| Electric stove | 1900–4500 |
| Microwave | 800–1200 |
| Electric meat grinder | 700–1500 |
| Fridge | 300–800 |
| Radio | 20–50 |
| TV | 70–350 |
| Music Center | 200–500 |
| Computer | 300–600 |
| Oven | 1100–2500 |
| Electric lamp | 10–150 |
| Iron | 700–1700 |
| Air purifier | 50–300 |
| Heaters | 1000–2500 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 500–2100 |
| Boiler | 1100–2000 |
| Instantaneous water heater | 4000–6500 |
| Hairdryer | 500–2100 |
| Washing machine | 1800–2700 |
| Air conditioner | 1400–3100 |
| Fan | 20–200 |
| Power tools | |
| Drill | 500–1800 |
| Hammer | 700–2200 |
| Circular saw | 700–1900 |
| Electric planer | 500– 900 |
| Electric jigsaw | 350– 750 |
| Grinding machine | 900–2200 |
| A circular saw | 850–1600 |
Let's do a little calculation based on the data from the table of power consumption of household electrical appliances. For example, in our house there will be a minimum set of electrical appliances: lighting (150 W), refrigerator (500 W), microwave (1000 W), washing machine (2000 W), TV (200 W), computer (500 W), iron (1200 W), vacuum cleaner (1200 W), dishwasher (2000 W). In total, these devices will consume 8750 W, and given the fact that these devices will almost never be turned on at once, the resulting power can be divided in half.
Electricity costs in a private home - we count together
You go to the meter and look - and so on every month. What's in the apartment? Washing machine, TV, computer and a dozen light bulbs. A completely different story is a private house. It is sometimes impossible to understand where such a figure comes from in a month, even for those who live in the house. What if you are still a city dweller? If you still have plans to build a private house, and you are afraid that you will not be able to maintain it?
This is where our top-down calculations will help you - where the electricity goes in a private home.
How many kilowatts do you need to heat a house?
The main consumers of electric current in homes are lighting, cooking, heating and hot water.
During the cold season, it is important to pay attention to the heating of the house. Electric heating in a house can be of several types:
- water (batteries and boiler);
- purely electric (convector, heated floor);
- combined (warm floor, radiators and boiler).
Let's look at electric heating options and energy consumption.
- Heating using a boiler. If you plan to install an electric boiler, then the choice should fall on a three-phase boiler. The boiler system equally divides the electrical load into phases. Manufacturers produce boilers with different capacities. To choose the right one, you can make a simplified calculation by dividing the area of the house by 10. For example, if the house has an area of 120 m2, then for heating you will need a 12 kW boiler. To save on electricity, you need to install a two-tariff mode for using electricity. Then at night the boiler will operate at an economical rate. Also, in addition to the electric boiler, you need to install a buffer tank, which will accumulate warm water at night and distribute it to heating devices during the day.
- Convector heating. As a rule, convectors are installed under windows and connected directly to an outlet. Their number should correspond to the presence of windows in the room. Experts recommend calculating the total amount for the power consumption of all heating devices and equally distributing it across all three phases. For example, the heating of one floor can be connected to the first one. To another phase, the entire second floor. To the third phase, add a kitchen and a bathroom. Today, convectors have improved functions. This way you can set the desired temperature and choose the heating time. To save money, you can set the time and date of operation of the convector. The device has a “multi-tariff” option, which turns on the heater at the required power or at a reduced rate (after 23-00 and before 8-00). Energy calculations for convectors are similar to the boiler in the previous paragraph.
- Heating using underfloor heating. A very convenient heating option, as you can set the desired temperature for each room. It is not recommended to install heated floors in the place where furniture, refrigerators, and bathrooms are installed. Calculations show that a house of 90 m2 with an installed convector and heated floor on one floor consumes from 5.5 to 9 kW of electricity.
How many kilowatts are required to heat a house and how to save them
Heating a home is one of the largest energy consumption items; it consumes the largest number of kilowatts, especially in winter. Let us characterize several options for electric heating and evaluate their energy intensity. These options could be:
- Heating using a boiler. Three-phase boilers are considered the best. To select a boiler with optimal power, you need to divide the total area of the house by 10. To save electricity, you should use a two-tariff energy consumption mode. This will allow the boiler to consume cheaper electricity at night.
An additional means of saving kilowatts is a heat accumulator, which we discussed in a special article.
- Convector heating. Thanks to the presence of the “multi-tariff” function, this type of heating can be used most efficiently during the discounted tariff period.
- Warm floor. This heating option is attractive for its flexibility and the ability to select the temperature for each individual room. According to calculations, the electricity consumption required to heat a house with an area of 90 m2 in this way is about 7-8 kilowatts.
How to save energy?
Today there are many options for saving energy. These methods are not at all complicated, but for them to work you need to use them every day. Reducing energy consumption will not only save the family budget, but will also reduce emissions into the environment.
Simple and time-tested saving methods
- Use of energy-saving light bulbs. Such lamps practically do not heat up, so electricity is spent only on lighting. On average, the service life of such lamps is up to 3 years, and this will significantly save costs. Such lamps consume 5 times less electricity, their service life is 10 times longer and pay for themselves in 1 year.
- When using household appliances, it is important to follow the instructions. Let's take the refrigerator for example. It cannot be placed near a stove or radiator, as the device will need to work uninterruptedly to maintain the required temperature. The same applies to the moment when hot food is placed. It is important not to forget to defrost the refrigerator in a timely manner, since ice in the freezer contributes to high energy costs (up to 20%).
- When leaving the room, do not forget to turn off the lights. This advice is the most effective way to save energy.
- Clean light bulbs regularly. At first glance, such advice seems ridiculous. But few people know that dust can block up to 15% of the light. It is important not to forget about the cleanliness of the lampshades. You can use lower wattage lamps.
- Make some minor cosmetic repairs to the room. When choosing wallpaper, you should pay attention to light shades, as they can make the room 80% brighter and more comfortable. We should not forget about the ceiling; it should be made white. This way you will turn on the lights less often.
- Application of heat-reflecting screens. They are made from foil or foam foam. They should be installed behind the battery. Thanks to such screens, the temperature in the room can be raised by several degrees.
- Insulation of the room. It is necessary to insulate the windows or replace them with metal-plastic ones. Up to 30% of heat can be lost through windows. You should hang thick curtains on the windows. If possible, you need to insulate the entrance doors, as well as the walls, ceilings, floors and roofs of the house.
- Purchasing household appliances of class “A”, “A+” and “A++” can save up to 50% of electricity.
- It is not recommended to leave devices in “standby” mode. A person uses any technology for only a few hours during the day. The rest of the time it is in “standby” mode and gradually absorbs electricity. To save money, devices should be turned off from the network.
And so, we already know how many kilowatts are needed for a home. Let's summarize. From what was described above, it follows that if we use electricity sparingly, then we can easily invest in 15 kW, and for a small house this is even enough for heating. Then the whole family will feel comfortable in their cozy nest.
How to determine?
To solve the problem of finding power, you can use various methods. All of them are available for use even with knowledge of physics and electrical engineering at the school curriculum level.
More often, power is found by determining the current; sometimes you can do without intermediate procedures and determine it immediately.
We look at the technical passport
Typically, the power consumption is indicated in the passport or description of the device and is duplicated on the nameplate. The latter is located on the rear wall of the case or its base.
If there is no description, this parameter can be found on the Internet, for which you just need to search by the name of the device.
The power indicated by the equipment manufacturer refers to peak power and is consumed from the network only at full load, which is quite rare. The resulting difference is considered as a reserve. At the regulatory level, this reserve is determined through the power factor.
Ohm's law to help
The power of most household electrical devices can be fairly accurately estimated experimentally and by calculation using Ohm's law, known since high school. This empirical law relates voltage, current and load resistance R as:
P = U2/R. U = 230 V, and the resistance is measured by a tester. The following is a simple calculation using the formula P = 48,400/R W.
For example, with R = 200 Ohm we obtain power P = 240 W.
The method does not take into account the so-called reactance of the device, which is created primarily by input transformers and chokes, and therefore the resulting estimate is somewhat overestimated.
We use an electric meter
When determining power from a meter, you can proceed in two different ways. In both cases, only the device under test should be powered from the household network. Without exception, all other consumers must be disconnected.
In the first approach, an optical meter indicator is used to measure power, the intensity of its flashes is proportional to the power consumption. The proportionality coefficient is indicated on the front panel in units imp/kWh or imp/kWh, Figure 1, where imp is the number of pulses (indicator flashes) per kilowatt hour.
Figure 1. Front panel of a household electricity meter with optical indicator
After turning on the device under test, you must begin counting the indicator flashes for 15 or 20 minutes. The resulting value is then multiplied by 3 or 4 (for a 20- or 15-minute measurement interval, respectively) and divided by the coefficient from the front panel. The result of the calculation gives the power of the device in kW, which in some cases is conveniently converted into Watts by multiplying by 1000.
Example. For the counter we have k = 1600 pulses per kilowatt hour. With a 20-minute measurement interval, the indicator worked (flashed) 160 times. Then the power of the device will be 160*3/1600 = 0.3 kW or 300 W.
The second approach also uses a 15- or 20-minute time interval, but the energy consumption is determined on a digital scale. For example, with a difference in readings over 20 minutes of 0.2 kW×hour, the power of the unit is 0.2 × 3 = 0.6 kW or 600 W.
Wattmeter
A modern household power meter or wattmeter is convenient to use because:
- it is connected directly to the open circuit, for which it is equipped with a plug and socket, see Figure 2;
- equipped with an easy-to-read digital indicator and equipped with internal automatic adjustment circuits, which eliminates errors in readings;
- has good weight and size characteristics.
The device is ready for use immediately after switching on.
Rice. 2. Digital household wattmeter
Its only drawback is its narrow specialization, so this device is rarely found in the household.
Other electricity costs in a private home
The heating system circulation pump, boiler automation, VOC compressors, televisions, satellite receiver, computers, gate drives, washing machine, phone chargers - all these are consumers of electricity in a private home. And they all require kilowatts, although not much. It will cost you approximately 200 to 300 rubles per month to maintain these devices.
You need to pay for electricity, just like for any other resources and services. In order not to be deceived when paying, you need to learn how to calculate its expenses. There are special devices for this, for example, an individual meter, which is installed in each house or apartment. However, it shows the total consumption, and we will tell you how to calculate the electricity consumption of a separate device in this article.
How many kilowatts do our home assistants consume?
When building a house and thinking about its arrangement, you should remember that by government decision the consumption of a private home is limited to 15 kW. How to calculate the power consumed by the entire house? The answer is simple: all you need to do is know the energy consumption of each household electrical appliance.
The table below shows approximate energy consumption values for some of the most common household appliances. These figures can be used to estimate the amount of general house energy consumption:
Appliances
Power tools
As an example, let's estimate the power consumed by the house. Let's say your home is equipped with a minimum set of household appliances: lighting, refrigerator, microwave, washing machine, TV, computer, vacuum cleaner, iron and dishwasher. Adding their respective powers, we get the figure 8750 W. However, it practically never happens that the entire set of devices is put into operation at the same time, so the result obtained can be safely divided in half. This allows us to state that the energy consumption of our home is about 4400 watts.
The two best ways to reduce electric boiler consumption
How to choose an external thermostat for an electric boiler and save up to 30% on heating every month
If the automation does not provide the ability to program the operating mode, you can seriously reduce the energy consumption of the boiler by connecting a programmable room thermostat to it (if there are appropriate contacts, information about the possibility of connecting external control is always indicated in the technical specifications).
A programmable room thermostat controls the operation of the boiler based on measurements of the air temperature in the room in which it is installed, and not on the temperature of the coolant. However, the main and most important task for saving purposes is the programming mode of work settings for the next day and week. For example, during working hours when the owners are away from home, you can set the temperature to 15°C. And during sleep – 18 or 19°C. Such parameters will not affect comfort, but will significantly reduce the final energy consumption.
The second indispensable element when heating with an electric boiler is an electric meter, which differentiates electricity consumption by two, or better yet, by three time zones. For example, for the Moscow region the following tariffs are differentiated by time zones:
- peak zone (from 7:00 to 10:00 and from 17:00 to 21:00) – 5.06 rubles per 1 kWh;
- half-peak zone (from 10:00 to 17:00 and from 21:00 to 23:00) – 3.89 rubles per 1 kWh;
- night zone (from 23:00 to 7:00) – 1.68 rubles per 1 kWh.
In practice, the costs of purchasing, designing and installing a metering device that differentiates consumption pays off in a few months, since it reduces costs in monetary terms by 15-25%.
Instructions BoilersWays to save Electric boilers
Consumption based on house parameters
You can more accurately estimate the possible power consumption of an electric boiler by knowing the parameters of the house and its heat losses (also measured in kW). To maintain a comfortable temperature, heating equipment must replenish heat loss in the home. This means that the heating output of the boiler = the heat loss of the house, and since the efficiency of electric boilers is 99% or more, then, roughly, the heating output of the electric boiler is also equal to the electricity consumption. That is, the heat loss of the house approximately reflects the consumption of the electric boiler.
There are averaged data on the heat loss of houses made of various coating materials (houses with a ceiling height of 2.7 m, a standard glazing area, located in the climatic zone of the Moscow region are taken into account). The temperature difference is taken as 26°C (22°C in the house and -4°C outside), this is the average value for the heating season in the Moscow region.
| Heat loss of typical residential buildings with an area of 100 m2 | ||
| Coating type and thickness | Average heat loss, kW (per hour) | Peak heat loss at -25°С, kW (per hour) |
| Frame insulated with mineral wool (150 mm) | 3,4 | 6,3 |
| Foam block D500 (400 mm) | 3,7 | 6,9 |
| House according to SNiP Mos. region | 4 | 7,5 |
| Foam concrete D800 (400 mm) | 5,5 | 10,2 |
| Hollow brick (600 mm) | 6 | 11 |
| Log (220 mm) | 6,5 | 11,9 |
| Beam (150 mm) | 6,7 | 12,1 |
| Frame insulated with mineral wool (50 mm) | 9,1 | 17,3 |
| Reinforced concrete (600 mm) | 14 | 25,5 |
Reviews from owners of electric boilers about performance in practice
According to installation practice, reviews from owners and information from forums, we were able to obtain many examples of a wide variety of designs and consumption indicators, here are some of the most illustrative examples:
- The house is 160 m2, it costs 18-20 thousand rubles a month, but this is Siberia. Wall: expanded clay block + 5cm penoplex + brick lining.
- The house is approximately 165 m2, frame, insulated with PSBS-15 150 mm thick, roof - PSBS15 240 mm thick. We’ve been living in the house for the first year, so we haven’t gotten around to finishing the house yet, plus there are problem areas such as the iron entrance door, which freezes, and the uninsulated staircase in the 7 m2 basement. In total, 15,865 kilowatts were consumed over 141 days of the heating season.
- Area 120 m2, floor - 150 mm eps, ceiling - 300 mm glass wool, wall - 375 mm D300. Ventilation - 6 pieces of Blauberg A150 Pro ventilators + 150 mm supply pipe in the boiler room. For the calendar year from 03/09/2018 to 03/09/2019 - 16,812 kW. We consider 16812/120/365/24 = 15.99 Wh/m2.
- House 50 m2, standard 2-brick masonry and plaster without insulation, plastic windows with double glazing. The monthly cost is about 7-9 thousand rubles per month in winter and 5-6 thousand rubles in autumn/spring, at 0 degrees or above zero.
Efficiency and selection criteria for energy-saving electric heating boilers