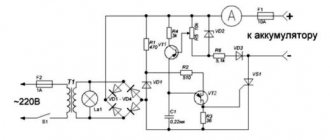
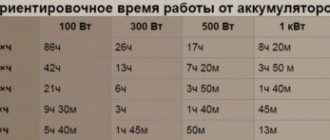
IN charging the battery Not only completely discharged (or just purchased) batteries need batteries, but also those that have become very weak during use. The difference between these two approaches is the different time required to fully charge a given battery model. With a new battery, it can last from 25 to 50 hours.
The charging time of used batteries is determined not only by how low they are, but also by their service life. In the case of very discharged and not new products, it may take 24-36 hours or even more.
Charging time calculator
If it is important to determine the time required to charge the batteries at your personal disposal, it is calculated very simply without delving into the details of the processes taking place. This does not require complex formulas, which in modern conditions are replaced by a calculator for calculating battery charging time . The whole procedure in this case comes down to filling out just two fields:
- In the “Battery capacity” field, the corresponding indicator of the device being serviced is indicated.
- Charging current field indicates the value of the parameter that is supposed to be used to charge the battery from an electrical device.
When you click on the “Calculate” button, the procedure for calculating the battery charging time from a given type of charger starts.
How to use the calculator
To find out how long it takes to charge your battery, you don’t need to go into the details of all the processes and calculation formulas, just use this calculator.
For online calculation you must fill in all three fields:
- In the “Nominal capacity” field, enter the capacity of the car battery being charged.
- In the “Degree of discharge” field, you can enter both the percentage calculated from the table and the voltage measured with a voltmeter.
- In the “Charging current” cell you need to indicate exactly what current you plan to charge the battery from the charger.
By clicking the “Calculate” button you will get the required time to fully charge the car battery.
How to charge the battery
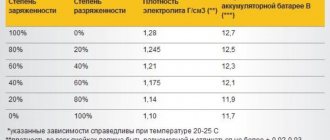
The discharge of a particular battery is usually judged by the density of the electrolyte poured into the jars, the value of which for a working battery is on average 1.26-1.28 g/cm³ (at 12.5 Volt voltage). It depends on what initial value this indicator had for the newly purchased device (it can be 12.7 or 12.9 Volts). The smaller it is for a given battery sample, the more significantly the device is discharged.
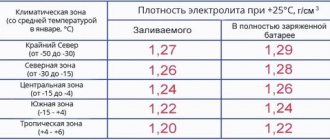
Table 1. Recommended electrolyte density depending on climate and time of year.
| CLIMATE AND SEASON WHEN MEASURING ELECTROLYTE DENSITY | DENSITY (g/cm3) | ||
| Battery charged | Battery discharged | ||
| By 25% | By 50% | ||
| Very cold (temperatures in January range from -50°C to -30°C) | 1,30 | 1,26 | 1,22 |
| Cold (temperature in January from -35оС to -15оС) | 1,28 | 1,24 | 1,20 |
| Moderate (temperature in January from -15°C to -8°C) | 1,28 | 1,24 | 1,20 |
| Warm humid (temperature in January from 0°C to +4°C) | 1,23 | 1,19 | 1,15 |
| Dry hot (temperature in January from -15оС to +4оС) | 1,23 | 1,19 | 1,15 |
Please note: A decrease in composition density of 0.01 g/cm3 relative to the nominal value means that this battery has been discharged by approximately 6-8 percent.
The degree of charge of the device is determined by the jar for which the meter shows the lowest density.
Cutaway car battery
Table 2. Battery charging time depending on the state of charge and electrolyte density
How to determine if it is a battery or an accumulator
Before purchasing, you should know a few nuances that will help you identify regular batteries from rechargeable ones:
Pay attention to the inscription on the case. If there is a capacity, then it is a battery, it is indicated in mah (milliamps) per hour
The higher this indicator, the longer it will last
If the case says rechargeable, then it is rechargeable. If the inscription sounds like do not recharge, then recharging is prohibited
Please pay attention to the cost of the product. Regular batteries are cheaper than rechargeable batteries
The price directly depends on power indicators and recharge cycles. Rechargeable batteries have a greater safety margin. They last a long time and charge gradually, but ordinary batteries stop functioning when connected to more powerful devices. The battery boasts a voltage of ~1.5 V, but the battery has a voltage of ~1.2v, ~3.7v. The crown will have 9 volts in both cases. If the markings on the case contain the letters: R, CR, LR and FR, then this is a battery. If the marking on the case contains: NiCd, Ni-MH, Ni-Zn, HR, ZR, KR, li-ion or li-pol, then this is a battery
The higher this indicator, the longer it will last. If the case says rechargeable, then it is rechargeable. If the inscription sounds like do not recharge, then recharging is prohibited
Please pay attention to the cost of the product. Regular batteries are cheaper than rechargeable batteries. The price directly depends on power indicators and recharge cycles
Rechargeable batteries have a greater safety margin. They last a long time and charge gradually, but ordinary batteries stop functioning when connected to more powerful devices. The battery boasts a voltage of ~1.5 V, but the battery has a voltage of ~1.2v, ~3.7v. The crown will have 9 volts in both cases. If the markings on the case contain the letters: R, CR, LR and FR, then this is a battery. If the marking on the case contains: NiCd, Ni-MH, Ni-Zn, HR, ZR, KR, li-ion or li-pol, then this is a battery
The price directly depends on power indicators and recharge cycles. Rechargeable batteries have a greater safety margin. They last a long time and charge gradually, but ordinary batteries stop functioning when connected to more powerful devices. The battery boasts a voltage of ~1.5 V, but the battery has a voltage of ~1.2v, ~3.7v. The crown will have 9 volts in both cases. If the markings on the case contain the letters: R, CR, LR and FR, then this is a battery. If the case is marked with: NiCd, Ni-MH, Ni-Zn, HR, ZR, KR, li-ion or li-pol, then this is a battery.
By following simple steps, everyone can determine the necessary batteries for themselves.
In the picture on the left there is a battery, as it is written on the case: 850 mAh, rechargeable and nickel metal hydride. On the right is the battery, as it only says Alkaline.
Table of battery charge level depending on electrolyte density
| Charge level (%) | Electrolyte density (g/cm³) | Degree of discharge (%) | Battery voltage (V) | Charge time at 10% capacity (hours) |
| 100 | 1,277 | 0 | 12,73 | Not necessary |
| 90 | 1,258 | 10 | 12,62 | 2 |
| 80 | 1,238 | 20 | 12,50 | 4 |
| 70 | 1,217 | 30 | 12,37 | 6 |
| 60 | 1,195 | 40 | 12,24 | 8 |
| 50 | 1,172 | 50 | 12,10 | 10 |
| 40 | 1,148 | 60 | 11,96 | 13 |
| 30 | 1,124 | 70 | 11,81 | 16 |
| 20 | 1,098 | 80 | 11,66 | 20 |
| 10 | 1,073 | 90 | 11,51 | 24 |
| 0 | 1,06 | 100 | 11,4 | Sulfation |
The degree of charge of a battery can be judged by the density of its electrolyte.
The lower the density, the more the battery is discharged. Typical batteries, discharged by more than half in the summer season, will have to be removed from the car and restored in the winter, even after 25 percent discharge. In addition, batteries whose density in different sections differs by more than 0.02 g/cm³ require additional recharging.
Charging time
Charger
Another very pressing question is how long to charge a 60 amp battery? The charging speed directly depends on the set current and voltage and the degree of battery discharge. Accordingly, the greater the supplied current and voltage, the faster the battery will be fully charged. If you follow all the above recommendations, a single charge cycle will last about 10 hours.
Some car enthusiasts, wanting to save their precious time and being in an eternal rush, use another unsafe method of charging the battery. They set a current strength exceeding 20 amperes, and the charging itself lasts no more than 5 hours. Of course, you cannot constantly charge in this way - the battery will quickly become unusable. However, in emergency cases this technique can be useful.
Selecting the charging current
The most suitable current for charging any battery is considered to be 0.05 of the full capacity (the so-called “equalizing” charge). When used, it is possible to completely restore the electrolyte condition in all sections of the battery.
As an example, consider the following cases:
- To charge a battery with a capacity of 55 A/hour, a current of 2.75 Amperes is required.
- For a 60 A/h product this figure will be 3 Amperes.
Additional information: The equalizing charging mode allows you to neutralize the effects of deep discharges.
It is also recommended to be used to eliminate the effect of plate sulfation, which is caused by prolonged use of the product at a charge level below 70 percent.
A “forced” method is often used, in which a different current ratio is selected charging In this case, its value is 10 percent of the battery capacity. A standard 55Ah battery is usually charged at 2.75-5.5 A, and for 60Ah batteries the charging current is set in the range from 3 to 6 Amps. In this case, it is always assumed that the lower the current entering the battery, the deeper the charge. This option is preferable, despite the fact that more time is spent on it.
Accumulator charging
Conversely, at high current the battery boils (the water contained in the solution decomposes into oxygen and hydrogen). This process has a destructive effect on the battery plates. A similar situation arises with the voltage applied to the battery (the higher it is, the faster the batteries can be charged). But its nominal value should always remain within 13.8-14.5 Volts. Increasing its value to 16.0-16.5 Volts is allowed only when charging maintenance-free models.
Tips for Newbies
There are fully automatic chargers that do not require any knowledge from the user at all. Just so as not to confuse the polarity of the connected wires. But if you need to do the job efficiently, it is still advisable to know and understand something.
Features of charging maintenance-free batteries
Maintenance-free batteries in sealed cases should not be subjected to long-term charging with high current, this can lead to deformation of the case.
They may sometimes require some excess charging voltage, up to 16 Volts, but the current should not go beyond the permissible limits. And if the current begins to drop and the voltage rises, exceeding the specified limit, then the battery has taken as much energy as it can.
You must understand that the declared capacity coincides with the actual one only for a new battery, and during operation it evenly drops, sometimes significantly if operating conditions have been violated.
What is fast charging
Accelerated charging is considered to be double the current, that is, about 20% of the declared capacity. This mode shortens the battery life, so you can use it only for a short time, no more than half an hour, and do not allow the electrolyte temperature to rise above 50 degrees.
There is not always a need for a full charge; sometimes it is enough to briefly “invigorate” the battery with a high current, after which the engine will start and the car can be operated. And it will be possible to bring the charge up to normal as soon as there is free time, using the rated current.
Selecting the optimal current strength
If you have time, the current can be reduced from the recommended 10 percent. But you should not try to revive the battery with low currents, about 3 Amps or less.
Let electricians do this, who know exactly in what rare cases this is prescribed. As a rule, such regimes do not justify themselves.
A typical battery charge with a manually operated device looks something like this:
- the initial period when the current can be set for ten minutes to a level of about 15% of the capacity;
- charging for a long time with a current of 10% of the capacity;
- a smooth decrease in current at the end of the charge with a voltage output of about 15 Volts and a drop in current to 1-2 Amperes.
It is unlikely that you will be able to charge the battery 100%, but this is not required. In real use, it is always charged even less. Attempts to force the mode will only lead to overheating, boiling and damage.
How long to charge a battery with a capacity of 60 Ah
If the discharge is deep enough, the entire process should take approximately 15 hours. As the charge level increases, the battery becomes very reluctant to convert the supplied power into chemically active substances, and a lot of energy is dissipated with heat. The efficiency of the process decreases and time drags on.
When there is no visible progress within an hour or two, charging stops and the battery is ready for use. If this happens much earlier than expected, it means the battery has already lost capacity and it’s time to think about replacing it.
Sometimes control and training cycles help, but this does not apply to batteries that have lasted more than three years.
Battery charging methods
There are several known methods, among which the following stand out:
- In constant current mode.
- Under conditions of constant voltage applied to the battery terminals.
- A combined method in which charging is carried out automatically.
- Fast procedure for a screwdriver battery , for example.
The penultimate and last options from the list are usually not considered, since they are used only in exceptional cases.
Constant voltage
Set the constant voltage to, say, 14.4 Volts. The current is automatically regulated (decreased), that is, at the beginning it can be 10 Amperes, and at the end of the charge 0.2 A.
Currently, almost all chargers work using this method, that is, the voltage is always constant, but the current varies.
Direct current
With this method, the current is constant throughout the charging process. Let's say we set it to 2 Amperes. At the beginning of the charge, the voltage will be 15 V, and at the end it may drop to 14.4 V.
How to check current leakage on a used car with a multimeter
The check includes:
- Turn off the engine, remove the key. Close the doors, but open the windows - the battery will not work continuously, and the car may be locked with a central lock.
- Make sure that the additional lighting and radio are turned off.
- Remove the negative terminal from the battery.
- Place one probe between the negative terminal and the negative terminal of the battery - the device will show the leakage current value.
The normal value is 15-70 mA. If the numbers are higher and you and the seller have time, try to find the reason. To do this, also connect a multimeter, then start removing the relays and fuses one by one.
The readings have returned to normal - you have found the cause of the current leak. Perhaps further repair or replacement of a part, or even the entire wiring, will be required. You can confidently ask the car seller for a discount or refuse the purchase altogether.
There may be several reasons for the leak. The following may be involved:
- battery;
- sensors;
- high voltage wires;
- generator.
Each element can be checked using a multimeter.
Calculating time using formulas
Before calculating the battery charging time , first of all, you need to familiarize yourself with the classic formula for determining the charging current. It looks like this:
I=Q*k.
where Q is the operating capacity of the battery,
k is a coefficient that takes into account the characteristics of the environment (its nominal value ranges from 0.04...0.06, and the optimal value is 0.1).
Based on this recommendation, to calculate the charging time for a completely dead battery, the formula takes the form: T = Q/ I. By substituting specific values into it, you can verify the significant amount of time required. But most often what is needed is not full charging , but only partial restoration of lost capacity. For this reason, the actual time will be significantly less.
To make an approximate estimate of how long it takes to charge batteries with direct current, you first need to determine the degree of their discharge.
We measure the voltage on the battery
Next, you will need to find out the lost capacity, after which, by selecting a specific value of the charging current, proceed to calculating the time required for complex charging. The formula for calculating this indicator when servicing a car with a charger looks like this:
Basic formulas for capacity
The basic calculation of a capacitor involves identifying the relationship between the capacitance and the charge held on the element, as well as the voltage on the plates.
C=QVC=QV
C – capacitance, or volume in Farads Q – charge held on the plates in coulombs V – potential difference between the plates in volts
This equation is used to calculate the work required to charge the capacitor and the energy stored in it.
Energy formula
W=∫Q0V dQW=∫0QV dQ
W=∫Q0qC dQW=∫0QqC dQ
W=12CV2
Important! It is necessary to know what effect a capacitor will have on any circuit in which it operates. It not only prevents the passage of the DC component of the signal current, but also affects any AC signal
Reactance
In a DC circuit, in addition to the battery, there may be a resistor that resists the current in the circuit. The same is true for an alternating current circuit with a charge-storing element. A capacitor with a small plate area allows only a small amount of charge to be stored, and this will prevent current from flowing. A capacitor has a certain reactance, and it depends on its value, as well as on the operating frequency. The higher the frequency, the lower the reactance.
You might be interested in: Features of differential current
The actual reactance can be calculated using the formula:
Xc = 1 / (2 pi f C)
Where
Xc – capacitive reactance in Ohms. f – frequency in Hertz. C is the capacitance in Farads.
Current calculation
The reactance of a capacitor, calculated using the above formula, is measured in Ohms. The current flowing in the circuit can then be calculated in the usual way using Ohm's law:
V = I Xc
Main capacitor indicator
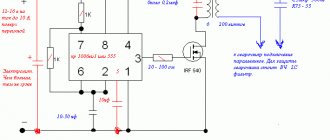
Fast charging
It is important for the modern user to know: can the battery be charged using an accelerated method if circumstances require it? Experts advise resorting to this method only in exceptional cases when no other options can be found.
Important! It is strictly not recommended to use the accelerated method for battery products with banks without filler necks.
When using this type of charging, so-called “maintenance-free” batteries can easily fail.
Typical maintenance free car battery
When considering this method, it is also important to take into account that batteries that have been in use for many years have a capacity that is very different from the nominal value. This feature forces experienced users to rely no longer on time calculation data, but to evaluate it by eye (to distinguish the accelerated mode from the normal one). Experts, as a rule, judge the possibility of using certain modes by the volume of gases released and the temperature of the electrolyte.
If it rises above 45°C, you should interrupt the process and allow the battery to cool slightly. If excessive gas emission is observed, then accelerated charging should be stopped and the charging current should be reduced to an acceptable value.
It is very difficult to continuously regulate the current entering the banks directly during the charging process (it is advisable to adjust its value at least every 5 minutes). To avoid confusion during such an adjustment, experts advise using a summary table called “charging”. It has only three columns, filled in as follows:
- The first contains the time (t) and data at that moment from the start of charging.
- The second column records the value of Q, which is used to judge how much time is left until its end.
- And finally, the third column records the value of the current (I) used when restoring the battery.
Table 3. Battery charging time using the accelerated method
| Charging time t, min | Capacity Q, missing to 100% of the rated charge, A*h | Charge current I, A |
| 0 | 60,0 | 54,0 |
| 5 | 55,5 | 49,9 |
| 10 | 51,3 | 46,2 |
| 15 | 47,4 | 42,7 |
| 20 | 43,8 | 39,4 |
| 25 | 40,5 | 36,4 |
| 30 | 37,5 | 33,7 |
| 35 | 34,7 | 31,2 |
| 40 | 32,1 | 28,9 |
| 45 | 29,7 | 26,7 |
| 50 | 27,5 | 24,7 |
| 55 | 25,4 | 22,9 |
| 60 | 23,5 | 21,1 |
| 65 | 21,7 | 19,5 |
| 70 | 20,1 | 18,1 |
| 75 | 18,6 | 16,7 |
| 80 | 17,2 | 15,5 |
| 85 | 15,9 | 14,3 |
| 90 | 14,7 | 13,2 |
| 95 | 13,6 | 12,2 |
| 100 | 12,6 | 11,3 |
| 105 | 11,7 | 10,5 |
| 110 | 10,8 | 9,7 |
| 115 | 10,0 | 9,0 |
| 120 | 9,2 | 8,3 |
| 125 | 8,5 | 7,6 |
| 130 | 7,9 | 7,1 |
| 135 | 7,3 | 6,6 |
| 140 | 6,7 | 6,0 |
Features of modern batteries
Contrary to popular myths on the Internet, modern Li-ion batteries do not need to be completely discharged all the time. They do not suffer from the "memory effect" that reduces the actual capacity, unlike older NiCd batteries.
The only problem that regular partial charging of Li-ion can cause is when the gadget incorrectly estimates the remaining operating time. The problem can be solved by discharging the device to 100% once while it is turned off. There is no need to leave the device dead for a long time; for a Li-ion battery, being in a completely discharged state for a long time leads to damage to the battery or to a partial loss of capacity.
Most manufacturers describe the battery life in cycles of complete discharge to 0%. This figure for modern batteries is approximately 500 – 1000 cycles. If the gadget is charged at a value of 10 – 20%, then this will not mean complete discharge, and the cycle time will approximately triple.
What happens if you charge with less current?
A small charge proportionally increases the recovery time of the battery capacity. In some cases, it is not possible to charge with the required current. Most non-professional chargers are designed with a maximum rating of 5 Amps. A battery with a capacity of 100 Amp-hours will take 20 hours to charge, that is, a day.
The good news is that small amounts of charge do not harm the battery. On the contrary, there is an ancient method of battery restoration. First, it is charged for a long, long time with a small value of 1 Ampere, then quickly discharged with extra current.
You need to monitor the temperature
The ideal temperature is important for the functioning of your phone's battery. When it is very hot or very cold outside, the battery discharges quite quickly. If it overheats or gets too cold, then from this form of abuse of the phone it may even break.
You should not leave your smartphone in the sun in the summer, especially in a car. In winter, you should not keep your smartphone in a pocket that is located on the outside of your clothing. In addition, use less of it if it is frosty outside.
How should you train your battery?
Every month it is advisable to completely discharge the phone, and then charge it to 100%. This maneuver makes it possible to calibrate its electronic part to correctly display the battery charge. After a certain time, if you do not do this, the indicator will begin to give incorrect data.
This procedure is also necessary on a new phone if you recently purchased it. A phone that has reached 0% should be connected to the PC for the first time for about 6 hours. In general, it is advisable to discharge the battery to 100% only when you have just started charging the battery.