Features of operation, selection and connection of RCDs
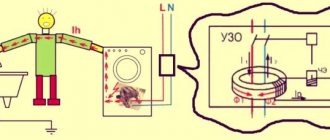
The residual current device is triggered due to problems in the network.
The protection device is necessary to de-energize the power line in the presence of short circuits and current leaks. The device operates on the principle of comparing the parameters of incoming and outgoing current. With a difference of 30 mA, the circuit is automatically opened. A person touching the equipment body cannot receive electrical injury.
Requirements for a protective device
The water heater safety device must meet the following criteria:
- Power. The indicator depends on the power rating of the home network and the number of phases.
- Voltage on the power line. Single-phase models are suitable for heaters connected to a 220 V network, three-phase - for a 380 V network.
- Degree of protection. The optimal models for an apartment are those with a shutdown for a leak of 30 mA.
- Installation location. For an apartment boiler or heater in a private house, modifications marked C16 and C25 are suitable
- Class. Class A RCDs are suitable for equipment with high energy consumption. AC class models often burn out.
The device is installed in a socket or switchboard. In the latter case, a three-core copper cable is used. Since the heater is a high-power device, you will need to ground the outlet.
Why does the RCD trip?
In some cases, the protection device is triggered, and in others, the electricity in the apartment is turned off. For these reasons, the RCD may periodically turn on:
- Short circuit in the water heater. It also appears in the wiring if there are a lot of electrical appliances on the site. This happens when the integrity of the wiring is violated.
- The RCD is incorrectly selected. It is selected based on the leakage current and rated current.
- Errors in connecting the RCD to the electrical protection. If the ground is connected to zero, the device often trips.
Classification of residual current devices
A high-quality device ensures disconnection of energized consumers, controls the throughput of the rated current, and de-energizes the circuit when there is a difference between the input and output currents. Manufacturers produce a wide range of devices with various characteristics, based on which they are divided into several types.
Household and power traction voltage
Depending on the conditions in which the RCD will operate, you can select the following types:
- AC - responds to sudden or slowly increasing changes in alternating differential sinusoidal current.
- A - triggered by a sudden increase or slow increase in the parameters of alternating sinusoidal and pulsating direct differential currents.
- B – turns off when alternating, rectified, or direct current changes.
- S and G are selective devices equipped with a switch-off time delay mode.
Models with electromechanical control are not tied to the supply voltage. The signal for them is differential current. Electronic options are powered from an electrical line or other source.
By number of poles
Depending on the characteristics of the electrical network, you can select an RCD:
- 2P, or two-pole. Suitable for single-phase lines. They are equipped with 4 pair terminals on each side for connecting to neutral and phase.
- 4P, or four-pole. Suitable for three-phase and single-phase networks. On each side of the device there are 3 terminals for phases and one for connecting the neutral.
The RCD compares currents, so the number of poles must match the number of conductors.
By rated current
The value must be equal to or greater than the total rating of the switches for the groups. For domestic use, modifications of 6000 A are suitable, but if there is a new house and a transformer station nearby, a 10 kA RCD is installed at the input.
By differential current
Optimal for the protection of humans and animals will be devices that operate at a differential current of 30 mA. Switches that operate at currents of 100 mA or more are used for fire protection purposes - they will completely de-energize the line.
The devices are mounted on the wall, on a DIN rail. There are devices that have the design of carriers, adapters, and sockets.
Troubleshooting methods
Let's start by checking the automatic device or RCD. At least once a month you need to press the “test” button to create conditions for current leakage and check its operation. If the circuit breaker does not operate during the test, it must be replaced.
Unfortunately, low-quality products end up on the consumer market and the RCD is no exception to the rule. There are times when blackening appears on it, when you shake it, you can noticeably hear the disconnection of the internals, the indicator does not light up (usually “green” lights up when it’s off, and “red” when it’s on). You need to visually inspect the device, you can disassemble it. If there are burnt elements inside, then you should not try to do it, most likely the operation took place under increased load.
Burnt elements on the RCD
If there is no external damage to the machine and it operates during testing, you need to check the quality of the connection in the terminals of the electrical panel, the absence of moisture on and inside the device, and check the degree of its heating in the operating position.
Replacing the residual current device
When selecting a new product, the buyer needs to focus on the main characteristics:
- Voltage: 220 V (if you have a single-phase network), 380 V (with a three-phase network). They differ in appearance, having 2 and 4 connectors in the upper and lower parts, respectively.
- The rated load current must be calculated either for all electrical appliances located in the apartment (if there is only one RCD on the input wiring), or for the maximum load of the water heater (device for the boiler). Usually you buy a product with a slightly higher load current - from 16 to 100 A. When installing in an apartment, focus on a current of up to 30A.
Individual RCD for water heater
- An important point is the leakage current at which the machine is triggered. A range from 6 to 500 mA is available. In high-quality boilers, the manufacturer may indicate leakage currents (for example, 2 mA), then a separate RCD for the heater is selected at 10 mA. For a general device in an apartment, 30mA will be enough. Old wiring can be an indicator of large leaks, so this factor must be taken into account.
- The last characteristic that must be taken into account is what type of electricity this device protects from. For an apartment or small house, buy products of type AC (protection against alternating current leaks) or A (protection against alternating and pulsating direct current leaks).
Advice! It is necessary to remember the rules for installing RCDs - the total current of all leaks in the home electrical network, taking into account all electrical appliances, should not exceed 1/3 of the rated current of the machine. In the absence of information for electrical appliances, 0.4 mA leakage is assumed per 1 A load current. For a network cable, leakage per 1 m is about 10 µA.
We made sure that the machine was working or replaced it with a new one, but when the water heater is turned on, it still works. Then we move on to the next stage.
Main and additional reasons for triggering
If bare wires come into contact with the body, the RCD will trip constantly.
If the boiler knocks out the machine, the reasons most often are as follows:
- Damage to the insulation of electrical models with heating elements-tubes. The protective layer is destroyed when water comes into contact with conductive components. To check the part, you will need to remove it from the tank and inspect it. Cracks indicate that the heater needs to be replaced.
- Current leaks. They occur when connecting the water heater to old wiring, a cable with exposed wires, mechanical damage to the insulation and installation errors.
- Short circuit of the exposed cable to the housing. When a bare wire comes into contact with the body, the machine will turn off permanently. The phenomenon leads to electric shock.
- The RCD does not comply with the voltage and power parameters. The knockout is periodic - the device simply cannot cope with the load.
- Malfunction of the device itself. The main reasons are wear of the trigger mechanism or a stuck test key.
Often shutdown occurs after heating the water. The malfunction occurs in boilers with deformed bodies in contact with the phase.
Why does the RCD of Termex boilers trip?
Termex instantaneous and storage type water heaters are popular due to their ease of connection, tank capacity, good power and low cost. When an RCD is triggered during operation, it is possible that the Termex water heater is damaged or the electrical network is faulty:
- Hull breakdown. If there is grounding, the device will work immediately.
- Broken wiring in the room. Most often the neutral is damaged.
- Mechanical damage to the heating element. The heater coil comes into contact with water in the presence of permanent scale.
- Contact between housing and phase. The shutdown occurs after heating the water.
- The riser ground line is connected to the network zero. If the boiler turns on, there is a risk of injury.
- Malfunction of the RCD itself. Chinese complete devices often fail. They need to be changed.
- Exceeding the load rating. When the boiler, stove and iron are turned on at the same time, protection against network overloads is activated.
Boilers are installed only with a grounding line.
Causes of problems in the washing machine
If the electrical wiring has been inspected and the detected faults have been eliminated, but the RCD still triggers, then a problem has arisen in the machine.
To begin inspecting the device, drain all the water from it and disconnect it from the network. This is to prevent injury from electricity and rotating parts of the washing machine.
Reasons leading to the tripping of the RCD:
- malfunction of the plug connector on the supply wire;
- short circuit of the water heating element (TEN);
- the network filter is short-circuited;
- engine breakdown;
- the noise filter is burnt out;
- control button is broken;
- damage to the wiring inside the washing machine.
Do you turn off the water tap after washing?
Oh yes! No.
Damage to the power cord or plug
The inspection should begin with the wire and plug connecting the washing machine to the apartment’s electrical network. The electrical cord is very often subject to overlap, tension, and pinching. Damage to the wire is checked using a multimeter.
To replace the electrical cord, follow these steps:
- the washing machine is disconnected from the power supply, the water supply valve is closed;
- the remaining water is drained from the device;
- the panel is unscrewed and removed;
- remove the network filter;
- the latches are pressed, the plastic stopper is removed;
- Disconnect the cord from the terminals and remove it from the device.
Multimeter
Installing a new cord is carried out by performing the steps in reverse order.
Heating element - short circuit or current leakage
Tap water is not of the best quality, and chemicals are also used when washing, all this leads to the formation of scale and deposits on the heating element. The heat transfer process is disrupted, the heating element overheats, and it shorts out. As a result, the RCD is triggered.
Washing machine water heater
Check the heater by measuring the resistance with a multimeter. To do this, you need to disconnect the wires from the contacts on the heating element, set the limit on the device to 200 Ohms. Normal resistance values are 20-50 Ohms.
Steps to take when replacing the heating element:
- the back panel is removed. If the water heater is located in front of the tank, then dismantle the control panel, then the front cover;
- the nut on the grounding bolt is unscrewed (6 turns), it is recessed inside;
- Use a screwdriver to pry up the heater and remove it;
- a new heating element is being installed.
Line filter malfunction
SMA surge protector
This element is designed to stabilize electrical voltage. Its surges in the network contribute to the breakdown of the network filter, which causes the RCD to trip. The filter should be replaced.
Some models of washing machines have a surge protector built into the electrical cord. In this case, the entire cord is replaced.
Engine
The engine may fail during prolonged use or if the tank or hose leaks. To detect a malfunction, you need to ring the engine and body of the machine using a special device.
If it breaks down, the motor is replaced with a new one or repaired. The place where a leak is found is inspected and restored.
An RCD can trip if the brushes on the motor are worn out. Then you need to disconnect the wires from the terminals and remove the old element. After installing the new brushes, turn the engine pulley by hand, but there should not be any loud noise.
Asynchronous motor SMA
Contacts and control buttons
If the washing machine has been in use for a long time, wear and oxidation of the contacts can be noticed during visual inspection. Using a multimeter, you need to test all the wiring and connectors of the unit.
To replace a damaged button, you need to disconnect the panel and electrical wiring. Remove the faulty one and install a working one.
Broken and frayed electrical wires
Scuffs often occur where the wiring comes into contact with machine parts. This occurs due to vibration during operation. A short circuit to the housing causes the RCD to trip.
Scuffs are detected by visual inspection: carbon deposits, melting, and darkening are visible on the insulation. Damaged areas are soldered and re-insulated.
Do you wash your shoes in the machine?
Oh yes! No
Features of repair and replacement of RCDs
If the machine knocks out when the boiler is turned on, there is a high probability of breakdown. You can repair a faulty RCD if you have experience, tools and parts. The optimal solution for owners is to replace the device. To determine its likelihood, a monthly check is necessary. To do this, use the button to create an artificial leak.
Nuances of repair work
The difficulty of repair lies in the lack of a circuit. Therefore, when troubleshooting problems yourself, you should be guided by the following algorithm:
- Removing sealant and screws on the body.
- Removing the fasteners with a slotted screwdriver and disassembling the device.
- Making a circuit by drawing from a printed circuit board.
- Device testing. The leakage current is simulated by applying voltage from the resistor to the amplifier. A leak is indicated by the activation of the triac and the closure of the circuit.
- Troubleshooting and assembling the device.
To protect against leaks, overloads, and short circuits, the water heater must be connected through an RCD or automatic circuit breaker.
Knocking out of the boiler safety shutdown device occurs for several reasons. You can detect the breakdown yourself. Since the RCD is not equipped with a circuit and is a complex device, it is easier to replace it than to repair it.
How to properly connect an RCD.
There are two possible connection options:
- Connection to an outlet. This connection scheme is possible for devices with low rated power. Another important condition must be the presence of grounding in this outlet, and when installed in the bathroom, it must be moisture resistant. If the device is of sufficiently high power, the socket will heat up, as a result, the tightness of the connection between the plug and the socket will become weak, a gap will appear in the contacts and sparks will occur.
- Connection via an additional copper cable connected directly to the electrical panel and equipped with an RCD. With this scheme, there is no plug and socket, and shutdown will occur through an automatic switch (machine), with the help of which the water heater will be protected, and the protection of the users directly will be entrusted to the protection device.
the circuit breaks. When choosing which one to install, two values are taken into account: the current strength (it is recommended to choose a slightly higher value than the machine) and the amount of its leakage, not exceeding 30 mA. To install a boiler, a type A or type G device is suitable. Currently, there are many manufacturers on the market, but preference should be given to more reliable ones, such as: Legrand, ABB, AEG, because you should not skimp on safety.
The main condition for the safe and reliable service of the boiler is its correct connection to the electrical network, with the least number of connecting elements. All connections must be made in rooms with minimal humidity, except for connecting the wire directly to the water heater. The best connection point is the electrical panel, where all the elements are installed.
Next, let's look at some parameters as an example:
How much space does it take on the dashboard?
It is important for owners of small shields, since the RCD is installed in tandem with the machine, and accordingly, it will take up two places. This means that the automatic rifle has primacy here.
Installation
If the machine is + RCD, then we connect the phase to the machine, then from its output we need to make a jumper to the output of the protection device. We connect the neutral wire to the protection input. If the connection is made for a differential device, then we connect phase and zero to the input terminals at once. Thus, again, the best option is this automatic machine, since the connection is very simple.
Ease of use. If the devices are separated, it is easier to find out the reason; if the RCD turns off, it means there is a current leak; the machine turns off, it means there is a voltage surge or short circuit. And if you connect a difavtomat, you will need to spend more time searching for the cause of the breakdown.
Price. The cost of these two devices is approximately the same.
Durability. Everything here will depend on the company you choose and the condition of your wiring. And yet, if a breakdown occurs in the RCD, you will most likely have to replace either it or the machine; this will be cheaper in cost than replacing the entire assembly of the machine.
As for reliability, there is an opinion that if the device is a combined type, it means that it is less reliable than individual devices. Based on the results of numerous checks and tests, there is no definite leader here.
Also watch a video about the operation of an RCD on a Termex water heater:
Basic Concepts
Electric water heaters are devices in which current energy is converted into heat and then transferred to water. Conventionally, such devices can be divided into 2 groups:
- Flow-through. The water is heated in them by passing through special systems with warm plates or pipes that instantly release heat to it. Flow-type heaters are characterized by high power.
- Cumulative. These include a conventional boiler with a heating element, which consistently heats the water inside the tank.
An RCD for a water heater is a special device designed to protect against current leakage.
The principle of its operation can be described as follows:
- The device is installed directly in front of the heater itself. All the current passes through it, which powers the mechanism.
- If there is a current leak inside the heater, then the RCD catches it, after which the entire system is switched off. Its operation is ensured using special sensors and switches.
It should be noted that the RCD, in its operating principle, resembles an automatic machine, but technically it is not one. It picks up even small current fluctuations that automatic machines are unable to analyze.
Today, such mechanisms do not always provide an optimal level of safety, so the water heater must also be additionally equipped with grounding. An RCD should not be confused with a difavtomat, as these are two different designs. The first mechanism is capable of catching only current leaks, and the second is more universal: the difavtomat also reacts to short circuits, overloads and other similar problems, while “knocking out” the electricity.
Options for checking an RCD on a water heater: why the machine knocks out and which one to choose
Electricity is a universal source of energy for practical use. You can use it to heat water. However, water is a universal conductor and it is necessary to limit contact with it using conductive elements. The RCD is just such an element. The article gives the concept of what an RCD is, why it is needed, what functions it has, how to choose and check it, why the water heater knocks out the RCD, and much more.
Residual current device
Water heaters are devices in which water is heated by current. Conventionally, they are flow-through and storage.
In the first case, water is heated by passing current through special warm plates and pipes. In the second case, a simple boiler and heating element are used, where the water is heated sequentially inside the tank. An RCD for any type of water heater is a device that prevents electrical leakage and equipment failure.
What it is
An RCD for a boiler or a residual current device is a special device whose main task is to protect the boiler from current leaks. It can be differential, starting, executive and controlling.
Note! In the first case, the RCD design contains a ferrite ring and conductor windings. In the second case - a sensitive magnetic-electric relay with direct action. In the third case - a spring wire, and in the last - a resistor.
What role does it play?
Thanks to the protective shutdown device, stable and safe operation of the entire water heater connected to the network is guaranteed. The device is placed near the heater itself. All the current powering the system flows through it. If a leak occurs inside the system, then the RCD catches it and then turns off the entire system using special sensors and switches.
It is worth pointing out that according to the principle of operation, an RCD is similar to a machine gun. It picks up even small electrical vibrations that are inaccessible to automatic machines for analysis.
Note! Today, such mechanisms do not always ensure 100% safety, so the water heater is additionally grounded. An RCD is not a automatic device. These are two different systems. The first one only catches leaks, the second one is more universal. It also reacts to short circuits, overloads and other problems.
Criterias of choice
RCDs are mechanisms that can be used in all household appliances, not only in boiler installations. You can select such a mechanism using special criteria:
- Power;
- Current readings;
- Installation method.
You can also choose an RCD based on price, manufacturer, brand, and reviews from users. As for power, the RCD must have the same power as the water heater or household appliance that is planned to be connected to the equipment. For boilers, the RCD should have a power of about 10 Amperes (with 2-3 kilowatts of boiler power).
In terms of current, this characteristic is calculated based on the total operating current. As a rule, 0.4 microamps per amp is taken into account. Based on the installation method, it is better to give preference to devices that can be attached to a DIN rail. As an alternative, devices should be selected in the form of separate units. Moreover, they can be placed anywhere.
Which to choose
The RCD must be selected depending on the cut-off current, rated current, differential current, current of the product itself, in addition to the selection criteria given above. For an apartment where the electrical network is single-phase at 220 Volts, you need to connect an appropriate single-phase device. With a stable mains voltage of 380 Volts, a three-phase device is required.
There are some important points to consider:
- The cutoff current must exceed the current line by 25% where the device is planned to be installed.
- The rated electric current must be higher than what is in the cutoff. Typically it ranges from 16 to 100 Amps.
- The differential current must correspond to the rated value. The optimal limit is 30 Amps.
Note! When choosing, you must also look at the type of electric current for which the product is designed. It can be variable, variable with constant, for any type and with a shutdown delay.
Kinds
An RCD is not a complexly designed device, but it is classified according to several criteria. Devices come in A, AC, B and G classes. Also, depending on the method of breaking the electrical circuit, the RCD can be electronic or electromechanical. The following is a description of each type.
The purpose of devices of class A is alternating or pulsating electric current, class AC is alternating. Class B devices are devices for industrial purposes. They work with both alternating and direct rectified current. AC class devices are most often used in ordinary apartments.
Sometimes the letter S is added to the classes, indicating that the device will turn off after some time. Such systems are not used in everyday life, therefore such designations are only on industrial equipment. Class G devices are similar to S class, but have a shorter exposure time.
As for the classification into electronic and electromechanical units, in the first case these are inexpensive devices used at home and in simple systems. Professional electricians say there is no need to install them because they are powered only from the mains. If the neutral wire is damaged, the device will simply break. In addition, it has a long response period.
Electromechanical devices are not powered solely from the electrical network. These are more reliable and high-quality units. The only drawback is their overpriced.
Wire with RCD
An RCD on a wire is a very easy-to-use system that can be connected in different ways.
Connection options
There are four options for connecting an RCD:
- In a three-phase network with grounding;
- Connection without grounding to a single-phase two-wire network.
For each option, the corresponding diagram is presented in the figures above.
It is worth noting that to check the operation of the equipment, it is necessary to connect automatic cut-offs and press the test button. If everything works properly, the equipment will function for many years.
Reasons for triggering
In answer to the question why the machine knocks out when the boiler is turned on, it is worth noting that the device reacts as a result of configuration, connection to the circuit, current load and insulation breakdown. The trigger can be both false and true. The task is to disconnect the circuit from the voltage supply during current leaks, if there is any malfunction in the electrical equipment.
Note! The RCD is triggered falsely due to a malfunction of the equipment itself, incorrect connection, sticking of the test button, broken lever, current leakage, damaged or missing grounding and exposure of a person to current influence.
Why does it turn off when turned on?
An RCD on a water heater can turn off due to insulating damage to the heating element, current leakage, lack of operation of the shutdown mechanism and incorrect location of the device. It is worth noting that if the insulation on the device is damaged, further operation of the equipment cannot be continued.
Most often, the RCD is knocked out due to a damaged water heater cable or the power cord itself. It is important that the cable can be damaged from the inside and often disassembling the heater is necessary to find such a reason.
Note! If the shutdown mechanism does not work, it should be noted that this phenomenon occurs on cheap products of unknown origin. They may simply not be turned on after several operations occur.
Selecting a protection device
How to remove, replace and check a water heater heating element
Based on the above characteristics, an RCD is selected, but do not forget to take into account the conditions of the bathroom (high humidity).
Give preference to type “A” devices, which respond to alternating and direct current. Despite the fact that sinusoidal alternating current flows in our electrical network, modern household appliances are equipped with special power supplies based on electronic semiconductor elements. Due to this, the AC sinusoid in the power supply is converted into a pulsed half-cycle. And if the leak is of this nature, then a cheaper “AC” type device will not react to it and will not work.
Carefully consider the passports for the washing machine and water heater when you are planning to buy an RCD.
It is for equipment installed in the bathroom that manufacturers indicate the type of device required, most often it is “A”.
Some differential circuit breakers have an additional block in their design, with the help of which consumers are disconnected in the event of a break in the neutral wire in the network.
For household appliances in bathrooms, it is recommended to install an RCD with a rated differential current of 10 mA. According to the time-current characteristic parameter, type “C” is preferable.
If you are not sure that you can choose a protective device yourself, then go shopping at retail chains that have a good reputation. Qualified sales consultants will provide you with the necessary assistance, tell you which manufacturer to choose, and select the appropriate device according to your financial capabilities.