Well-being, the state of the organs of vision, and, consequently, the performance and general health of a person directly depend on how bright the light is in the room.
This must be taken into account when choosing the type of lamp, its power and placement.
Let's consider what kind of documentary basis illumination standards have, what units of measurement they are characterized by, and what their meaning should be for different objects - a house, apartment, office, warehouse, production, protected facility, children's playgrounds.
Documentary basis
The level of illumination largely depends on the conditions in which a person lives and the nature of his activity. Therefore, the standards are different for different rooms. In order not to adjust the brightness of the light each time to the subjective feelings of employees, visitors and household members, there are established values, documented in SNiP and SanPiN.
SNiP
According to the requirements of Building Norms and Rules numbered 23 – 05 – 2010, lighting parameters are laid down already at the initial stage of building planning - in the drawings.
Table of illumination values for different objects according to SNiP:
| Room type | Illumination, lux (lx) |
| Office with computer equipment | 300 |
| Residential building room | 150 |
| Children's | 200 |
| Drawing office | 500 |
| Conference hall | 200 |
| Library, office | 300 |
| Corridor, staircase, hallway | 50-75 |
| Shower room, toilet, bathtub | 50 |
| Swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna | 100 |
| Pantry | 50 |
| Archive | 75 |
| Emergency, security, duty lighting | Not less than 0.5 |
| Laboratory | 300-500 |
SanPiN
Unlike SNiP, SanPiN prescribes lighting standards for an existing building. Therefore, according to its requirements, an inspection is carried out, and according to SNiP, the parameters of the object under construction are set. Thus, the brightness of the light is regulated in accordance with regulation 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03 - hygienic requirements for natural, artificial and combined lighting of public and residential premises.
Meaning of light
Human eye
Light has always been of great importance for people, since it is the visual analyzer that provides us with almost 90% of the information about the world around us. And in the conditions of computerization of society, not every person is able to maintain visual acuity at the proper level.
At the same time, you can significantly deteriorate your vision even without working at a computer for 8 hours a day. It is enough to make poor lighting in your home and you will be provided with a set of problems in just a couple of years. Just the right lighting, which is created in the house by various types of lighting fixtures, will allow you to increase your productivity, normalize the microclimate in the family and take a more effective break from work.
Directional light
Since we spend most of our time at home (of course, after work), we need to approach the lighting of the apartment as responsibly and thoughtfully as possible. After all, this is where no one can put you in to make your life better and more comfortable. Light in the house can be supplied as follows:
- directed. This lighting is created by ceiling chandeliers and wall sconces with floor lamps;
- scattered. Such light is possible from hidden backlights, which have recently become very popular. They look especially beautiful on plasterboard and suspended ceiling structures. Unlike directional lighting, diffuse lighting alone cannot independently provide the required level of light in the room. Therefore, it often acts as additional lighting.
Diffuse lighting
It is also worth noting that a room in the house such as the kitchen requires additional lighting in certain areas. It is with the kitchen that many people have problems in terms of creating proper lighting. This is due to the fact that the kitchen is often small in size and is always filled with all kinds of kitchen utensils, devices and cabinets. As a result, there are many dark and poorly lit areas. To help solve this problem:
- spotlights installed above the work area (countertop, sink, stove);
- LED cabinet lighting.
But in any case, before installing certain lighting fixtures, you need to find out what degree of illumination you need. For these purposes, you should seek help from SNiP.
Units
The internationally accepted unit of measurement of illumination is the physical quantity lux. It is equal to the luminous flux of one lumen distributed over a surface area of one square meter. Checking compliance with the standard of this parameter is carried out using a special device - a lux meter. Both the device itself, the measurement technique, and the data obtained must comply with Russian standards GOST R 54944-2012 or the interstate standard GOST 24940-96.
The measured parameters are checked according to two systems of illumination standards:
- Planes of tabletop covering or its equivalent (for libraries, classrooms, auditoriums, offices, laboratories).
- Floor surface (in relation to workshops, warehouses, street areas, staircases).
Recommendation! In order to independently bring the level of illumination in a particular room to the norm according to SNiP, it is necessary to change its area. Then multiply the resulting value by the parameter from the tabular data. For example, a children's room requires 200 lux. If it occupies 20 square meters, then the desired value will be 200 x 20 = 4000 lm. Now you can divide this number by the lumen value of one light bulb (information can be obtained from the manufacturer in watts and in lumens) and we will obtain the required number of lighting fixtures for this room.
What does SNiP say?
The main document that specifies existing standards is SNiP (building codes and regulations). So, according to this document, the following standards of illumination in lux (Lx) must be observed in an apartment and a private house:
- attic and basement passage – 20;
- toilet, shower, bath – 50;
- hall, corridor – 50;
- wardrobe – 75;
- bathhouse, swimming pool – 100;
- bedroom, kitchen – 150;
- children's - 200;
- personal office, library, utility room, room with billiards - 300.
Please note that in the bathroom you can optionally increase artificial illumination to 100 Lux, because... for applying makeup and shaving, the value specified in SNiP 05/23/2010 may not be enough
So that you understand how to convert the provided numbers into more familiar values, remember - 1 Lux is 1 Lumen/1 square meter of room. Each light bulb must indicate such a characteristic as luminous flux (in lumens, Lm). All you need to do is first calculate the standard illumination of a living space, in your case one of the rooms, then convert the value to Lumens and select the appropriate light bulbs. Let's look at the calculation technology using an example.
Workplace illumination standards
Lighting standards at different workplaces vary widely (from 70 lux in archive rooms to more than 500 lux in analytical laboratories) and are completely determined by the specifics of human activity. The luminous flux should be:
- Enough, but not excessively bright - so that if you stay indoors for a long time, there is no irritation to the eyes.
- Ensure compliance with safety regulations.
- Provide the opportunity to examine details without overstraining the visual organs.
- Create conditions for natural color rendering of objects.
- Adjustable and guideable to ensure maximum comfort in your specific work area.
What is illumination
Physics defines illumination as the number of rays of light falling on an area of a certain area. If we are talking about a workplace, then the level of illumination is measured for the room as a whole or for a specific section of it (an employee’s desk). GOST establishes illumination levels that are acceptable for certain professions. A lux meter is used for measurement.
Lighting in the workplace
Lighting standards for office premises
According to construction requirements and sanitary and hygienic rules, lighting in office premises must comply with the following standards:
- General purpose using computers – 200-300 lux.
- Large space with spontaneous placement of furniture - up to 400 lux.
- Conference rooms – 200 lux.
- Premises for drawing work - at least 500 lux.
- Utility rooms, hallways, stairs, corridors – 75-100 lux.
The given values characterize the degree of illumination of workplaces, primarily at table level, that is, at a height of about 1-0.8 meters above the floor surface.
When planning lighting in the office, we must not forget about its multifactorial nature:
- Intensity of general and local illumination systems.
- Uniformity of light scattering.
- Directions of the light flux.
- Glare formation.
- Color rendition.
- Temperature spectrum of lamps.
- Lamp pulsations.
Attention! It is important not only to comply with lighting standards in a particular room, but also to conveniently position the lamps relative to the line of sight of employees/household members. The optimal indicator is when the protective angle is at least 50 degrees. It is recommended to shield powerful lamps with special shades with frosted glass.
What are Lumen and Lux
The light intensity that a lighting device emits is an important characteristic. In the international system, candelas (Cd) are used for this purpose; its derivative is a unit of measurement that characterizes light power - Lumen (Lm). This value is indicated on the packaging of modern light sources.
Light flux depends on luminous efficiency, the latter value shows the efficiency of transformation of electricity into light. Luminous output is measured in Lm/W, to calculate the number of Lumens, you need to carry out calculations using the following formula: Lumen = Lm/W x power (W). For example, the luminous efficiency of a 100 W incandescent lamp is 15 Lm W: 100 x 15 = 1500 Lumens.
Consumers often confuse Lumens and Luxes, but there is a difference between them: the first value shows the luminous power, and the second shows the illumination. That is, Lk differs from Lm in that it shows the ratio of the luminous flux that falls on a small area of the surface to its area. To find out how much 1 Lux is equal, you need to calculate using the following formula: 1 Lux = 1 Lumen/1m².
The brightness of light in Lux is always a multiple of the light power in Lumens for each individual lamp. The larger the surface, the less the amount of light that falls on it. For example, place a 1500 Lumen incandescent lamp in the center of an opaque cube, the total area of which is 6 m² (4 sides of 1 m² each, bottom and top sides). The illumination will be: 1500 Lm/6 m² = 250 Lux.
Then this device is placed in a room with a total area of 96 m² (the area of all surfaces is taken into account). Then the illumination level will be: 1500 Lm/96 m² = 15.625 Lux.
In the second case, there is a clear lack of light, especially in the corners of the room.
The brightness of a surface depends not only on the luminous intensity, but also on the following factors:
- distance to the light bulb;
- placement of the lighting element, its rotation and tilt;
- lamp shape;
- surface curvature;
- reflective qualities of the object (for example, dark matte and mirror surfaces need to be illuminated differently).
To avoid errors when calculating illumination, it is better to use a lux meter (a device for determining the brightness of light).
Lighting standards for industrial premises
Lighting standards in production include, first of all, minimizing the harmful effects of light radiation on the visual organs of personnel. The success of the enterprise, safety and health of employees will largely depend on compliance with this rule. The specificity of compliance with SNiP and SanPiN standards for enterprises is that several different functional areas can be located under one roof.
In each of them, lighting standards must be met. Therefore, two lighting systems are used here - general and local. The first can be either natural (due to windows) or artificial, the second, as a rule, is carried out exclusively through lighting fixtures. In this case, the intensity of the required light flux in production is set by the level (from 1 to 7) of visual work and the corresponding accuracy:
- The highest - from 1.5 to 5 thousand lux.
- Very high - from 1 to 4 thousand lux.
- High – 400 – 2 thousand lux.
- Medium - 400-750 lux.
- Small – 400 lux.
- Rough - no more than 200 lux.
- Observation – 20-200 lux.
The absolute value of illumination is determined by the degree of presence of the employee and the nature of his work - from permanent work and periodic stay to simple observation of communications.
How to correctly calculate room illumination
When creating a project for lighting a residential building, they are often guided not by some strict standards, but by personal feelings. Light sources are placed so that it is sufficiently light, cozy and comfortable. Experts believe that this method is not always correct and it is better to follow the rules.
But if you still decide to set up the lighting yourself, then there are several ways to help you do it correctly.
Method No. 1. Install enough light sources to make your eyes comfortable - neither dim nor bright. To adhere to at least some calculations, you can use a simple formula: per 1 sq. m – one 25 W light bulb.
Method No. 2. Use a table that contains lighting standards in watts for residential premises. You look for the right room, the norm for it and multiply it by the number of square meters.
This table is suitable if you use regular light bulbs. If you choose halogen or fluorescent, keep in mind that the former, with the same power, provide 1.5 times more light, and the latter – 5 times.
For example, you have calculated how many light bulbs are needed for a 20 m2 bedroom. Then we multiply 12 W/m2 by the area and get 240 W. That is, for full lighting you need to buy at least two lamps with a power of 100 and 150 watts.
If we use halogen lamps, then divide 240 W by 1.5. Outputs 160 W. This means you need three halogen bulbs: two with a power of 50 W and one with a power of 60 W. The number of fluorescent lamps is calculated using the same principle. Make calculations “with a margin” if the decor and interior of the room are made in dark colors.
As lighting fixtures, you can use chandeliers as the main source of light, and floor lamps, sconces, table lamps as an additional source. You can “distribute” light bulbs of different wattages between different devices. The main thing is that the lighting is uniform.
Method number 3. Suitable for calculating illumination if LED lamps are used. First, the amount of luminous flux is calculated (in lumens, Lm), then the number of LED lamps is determined.
Lumens are calculated as follows: the standard of illumination (in Lux), the area of the room and the coefficient depending on the height of the ceiling (from 2.5 to 2.7 meters; from 1.2 to 2.7–3 meters; from 1.5 to 3– 3.5 meters; from 2 to 3.5–4 meters).
Next, using the table, we divide the number of lumens by the number of corresponding watts of the LED lamp. As a result, we determine how many LED lamps are needed.
Lighting standards for warehouse premises
According to SNiP standards, 5 categories of illumination can be used in warehouses in accordance with the place and method of storing things and the work being carried out.
| Storage method | For gas-discharge lamps, lux | For incandescent lamps, lux |
| On the floor | 75 | 50 |
| On the racks | 200 | 100 |
| Unloading/loading, sorting, transportation | 200 | 200 |
| Carrying out similar work outdoors | 5 | 5 |
| Pantry | 50 | 50 |
Open storage areas also have their own lighting standards, which are also determined by the type of cargo and how it is stored:
- Containers, timber and other heavy objects on the ground surface - 10 lux.
- Loading platforms and ramps in warehouses – 20 lux.
- Loose and bulk materials on the ground – 10 lux.
- Loading ramps – 20 lux.
How to Convert Luxes to Lumens
However, if you know the required illumination value in lux and the area of the illuminated surface, you can calculate the required luminous flux in lumens. It should be understood that the calculation will be performed with many assumptions, since it is not possible to bring the conditions for its implementation closer to physically ideal ones. When calculating, it should be assumed that:
- the light source is located in the center;
- the illumination is uniform over the entire area, which is practically impossible;
- light falls on the entire surface area at the same angle;
- the surface is illuminated from within the mental sphere supposed to surround the source.
In order to get the value in lumens, you need to multiply the standard in lux by the value of the area that needs lighting.
The floor and ceiling area will be: 10 x 10 = 100 m². Area of each wall: 4 x 10 = 40 m². Theoretically, with the assumption of uniform illumination and the location of the source, equidistant from all points of the surface, the problem is solved as follows: 300 lux x (4 x 40 + 100 + 100) m² = 300 x 360 = 108,000 lm. If this astronomical value is “translated” into ordinary 100-watt incandescent lamps, then you will only need... 72 pieces.
The practical approach will be different. There is absolutely no need to illuminate the ceiling - employee workplaces are located below. Moreover, the design of many ceiling lights makes it impossible for light to spread upward. This means you need to remove the ceiling area from the calculations:
300 lux x 260 m² = 78,000 lumens.
Modern LED ceiling lights can produce 5,000 lumens. Accordingly, 16 pieces (78,000/5000) will be required, rounded to the nearest whole number.
This number can be reduced. According to SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03, illumination is measured above the working surface, as well as at control points 1 m away from walls and light openings. It is enough to place lighting fixtures above employees’ workplaces. Mathematically reducing the geometric characteristics of the floor by 1 m on each side, we get:
300 lx x (160 + 64) m² = 300 x 224 = 67200 lm. What in the ceiling lights will be: 14 pieces, rounded to the nearest whole number.
Watch this video on YouTube
Residential lighting standards
In an apartment, house and other residential premises, lighting standards depend on the purpose and characteristics of their zone and have the following values (lx):
- Office – 250.
- Kitchen – 250.
- Children's - 200.
- Bedroom – 120.
- Hallway – 60.
- Bathroom – 250.
- Storeroom, utility room, attic, basement, staircase – 60.
The level of comfort inside the house should be maximum, and therefore it is so important to choose the right lamp for lighting, based on the following criteria:
- For an apartment, it is better to install a light source with a warm spectrum of radiation. It is provided by halogen, energy-saving and incandescent lamps.
- There is no need to use one chandelier; it is better to install several lighting fixtures. This will allow you to highlight individual areas and make the interior more expressive.
Advice! You can diversify the lighting design of your apartment and bring the illumination up to normal using spotlights, directing them at individual objects (flowers, paintings, decor).
Important nuances
Lighting devices have long become an integral part of our daily lives. When organizing a technically and ergonomically correct artificial lighting system for a living space, the following recommendations should be taken into account:
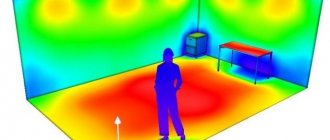
- maximum uniform illumination of the entire room. The best option here would be to use spotlights located at equal intervals throughout the ceiling;
- absence of sudden changes in lighting and its pulsation;
- pleasant light emitted by the light source;
- absence of a state of “blindness” of the entering person;
- the spectrum of light emitted by the light bulbs is pleasant to the eye;
- optimal conditions for shadow formation;
- you need to take into account the light reflectance of all surfaces of the room - ceiling, walls and floor.
Lighting design
In order to take all this into account, it is necessary to carry out qualified design for each room in the house. There are many programs for these purposes. You can also seek help from specialists in designing light levels for residential premises.
Emergency and security lighting
Emergency, duty and security lighting does not imply the creation of conditions for carrying out any visual work. Its main task is to ensure safety, security and the possibility of evacuation from the site. Depending on the purpose, standards may vary in the following categories:
- Security of the territory at night (without special equipment) – 0.5 lux at ground level or one side of a vertical plane at a height of about 0.5 meters.
- Ensuring safety - 5% of working lighting, but not less than 2 lux indoors and 1 lux outdoors.
- During evacuation - 0.5 lux inside buildings, 0.2 lux outside.
The legislative framework
All lighting standards for residential premises are enshrined in a special document SNiP 23-05-95 “Natural and artificial lighting”. This document indicates how much light is needed to illuminate certain objects.
It should be understood that SNiP 23-05-95 is a document of general significance, therefore it contains lighting standards for not only residential but also non-residential premises (for example, administrative buildings, warehouses, educational institutions, and so on). Also, when creating lighting for residential buildings, European standards can optionally be taken into account.
Children's playground lighting
In accordance with the requirements of SNiP and SanPiN, children's institutions, kindergartens, the opening and closing of the site must also have an appropriate level of illumination. The following standards exist:
- Physical playgrounds - 10 lux.
- Alleys, cycling paths – 4 lux.
- Walking paths – 1 lux.
- Game rooms – 400 lux.
- Sleeping quarters – 150 lux.
- Medical office – 200 lux.
In preschool institutions, in order to comply with lighting standards for various rooms and areas, it is better to use combined light sources.
With their help, you can easily set the required brightness and uniformity of lighting, despite a cloudy day, vegetation growing near the window, seasonal fluctuations in daylight hours, and building features.
Where to contact if a violation is detected: step-by-step instructions
There are three ways to protect your rights if there is poor lighting in your office or workshop:
- Self-defense. First you need to talk to your boss to change the conditions. There is no need to prepare any documents;
- Trade union. You need a written complaint about the dimness in the workplace. A trade union inspection does not issue any instructions, but may require the employer to change the lamps and help file a complaint;
- Labour Inspectorate. If the employer does not agree to change anything either after a personal conversation or after the demands of the trade union, then a complaint to the labor inspectorate will call him to order;
- Court. A last resort if all else fails.
Main conclusions
Lighting standards for various types of premises are strictly regulated by the rules of SNiP and SanPiN. Its value is measured in lux. When calculating it, it is necessary to take into account the area, as well as natural lighting and the uniform distribution of lamps. In production, warehouse complexes, apartments and houses, offices, guarded facilities and playgrounds, there are established standards. Their compliance ensures the safety of material assets, personnel safety, compliance with the technological process, human health and comfort.
Previous
Lamps and lampsConnection diagram and rules for installing a motion sensor for lighting automation
Next
Lamps and luminairesFull characteristics and types of halogen lamps
Artificial light
Full lighting
Today, natural lighting alone is not enough. This is the objective reality of our time. Humanity is increasingly leading an evening or nocturnal lifestyle. This is due to the fact that most of the daylight hours we are at work, while only evenings and weekends are left for family and recreation. Therefore, in order for your vacation to be complete, and communication with family and friends to bring only positive emotions, you need to make sure that optimal lighting is created in your home.
A distinctive feature of artificial lighting is the ability for a person to independently control the level of light available in each room of the house. Artificial lighting for a residential building can be created by the following types of lighting devices:
- ceiling lamps. Most often, their role is played by either one large chandelier or many spotlights;
- wall sconces;
- table lamps;
- floor lamps.
In one room, in order to comply with SNiP standards, you can use all types of lighting at once or combine only some options.
Note! For apartments and houses, the optimal choice in terms of room illumination is a combination of several options.
Thanks to the excellent range of lighting products on the market, you can use a wide variety of light sources to illuminate your home.
Sources of light
- incandescent lamps. It is for these light sources that SNiP provides basic standards (most values). Therefore, if you use other light bulbs, then you will need to make a small recalculation for the selected light source;
- halogen and metal halide lamps;
- fluorescent light bulbs;
- gas discharge lamps;
- LED
Each of the above light sources has both pros and cons. Therefore, be very careful when choosing light bulbs for your home, as not all lamps will give you the required level of illumination. All of the light sources listed above, except the incandescent light bulb, are energy-saving. Today, LED models are the undoubted leader, as they are the most economical in terms of energy consumption and have a long service life. But their disadvantage is their fairly high cost.
Accounting and accounting again
Illumination and its level must be taken into account when constructing almost any buildings and arranging street areas:
- residential and administrative buildings;
- industrial complexes;
- educational institutions;
- public service buildings, shops, etc.;
- streets, pedestrian areas, squares and tunnels;
- places for refueling and vehicle maintenance;
- public places.
Street lighting
From time to time, the standards established for certain premises are subject to some changes. For example, such changes include the use of a special design coefficient, which was introduced with the advent of modern lighting devices. This is due to the fact that in the documentation all standards are given only for incandescent lamps.
We carry out lighting calculations - example
To calculate the lighting for the kitchen, let's look at the table - it indicates that 150 Lux is required to illuminate one square meter of the kitchen. Let's start choosing lamps!
The area of our kitchen is 10 square meters. m. To find out how many lux are needed for this area, we multiply 10 meters by 150 Lux and get 1500 Lux - this is exactly the amount of light we need to get. But the power of the luminous flux is measured in Lumens - remember that one lumen is lux/sq.m. Therefore, we will need lamps with a total of 1500 Lumens.
In the table of the number of lm of various light bulbs, we select suitable light sources. 100 W incandescent lamps will please us with only 1300 lm, which means we need to choose a lamp with at least two, or even three horns. The point is that you need to “add up” the brightness a little, because surrounding factors can cause errors: dark curtains, walls in dark shades, lamp glass, etc.
A CFL (energy saving) lamp will consume less energy, so with 1500 lumens at 24 W, you need to take a 30 W lamp, taking into account external interference. An LED lamp looks most advantageous here - our ten-meter kitchen will only require a 15-16 Watt lamp.
As you can see, there is nothing complicated in independently calculating room lighting; you just need to skillfully use the necessary rules and regulations, and bright and economical light will shine in your home.
Lighting recommendations
There are several general recommendations for creating comfortable electric lighting:
It is better to choose lighting design that matches the color of the interior. The distribution of luminous flux should be uniform in bright rooms. For dark ones, it is better to use zone lighting. Sudden changes in lighting should be minimized
Each piece of furniture should be illuminated evenly. Use lamps with a color temperature that is comfortable for the eyes. When selecting lamps, it is necessary to take into account the reflection coefficient from the floor, walls, ceiling and other objects.
The following rules are often followed based on the functionality of the premises:
- The hallway is in most cases deprived of natural electric lighting. For lighting, lamps with directional light and large dispersion angles are installed.
- The living room is a multifunctional room in which general lighting is often combined with spotlights to obtain maximum functionality.
- The kitchen-living room is divided into zones; general lighting is combined with spot lighting, which has an auxiliary function.
- Bedroom – used for rest and sleep. Calm, warm colors are recommended, with the ability to regulate the light intensity using dimmers.
- A bathroom is a room in which general lighting is combined with local lighting.
Ripple coefficient: measurement features
To determine the frequency of lighting pulsation, you can use a simple and effective device - an illumination, pulsation and brightness meter.
Its functionality allows you to determine:
- brightness level of monitors and artificial lighting devices;
- room illumination level;
- pulsations of illumination of all types of monitors;
- pulsations of light waves that appear when different lamps flicker.
The operating principle of the main group of devices (pulse meter, brightness meter and lux meter) is to control the light level using a photosensor, after which the signal is converted and the result can be seen on the LCD display.
Luxmeter-Pulsemeter-Brightness meter Ecolight-02.
To determine the pulsation coefficient, you can go in two ways - conduct an independent analysis or use a computer program.
The most popular devices for calculating pulsations are “Ecolight - 01 (02)” and “Lupin”. If you need to analyze data on a computer, you can use special software - Ecolight-AP.
The main difference between devices for measuring pulsations is the quality of photocells, the type of power sources (batteries) and the level of sensitivity.
LED lamps have the maximum pulsation coefficient (sometimes this parameter can reach 100%). Incandescent and fluorescent lamps have a lower ripple factor.
For example, the former have a pulsation coefficient of no more than 25%. At the same time, the quality and price of the light source are not important, because even expensive lamps can have a high pulsation coefficient.