Brands and scope
Each cable product has a certain flexibility class. Flexibility is the value of the cable (wire), which determines the minimum bending radius. Even for the installation of stationary equipment, conductors must be bent during installation. Bending at an angle close to 900 already requires sufficient flexibility. This parameter has a class from 1 to 6 and is regulated by GOST 22483. It is important what material the cores of the product are made of: copper or aluminum.
Attention! Cables with aluminum conductors do not have a flexibility class higher than 3. This is due to the fact that aluminum is fragile and has fluidity. Therefore, conductors having a multi-core copper structure represent a family of flexible power cables.
Flexibility table by class
Depending on the scope of application, cables are divided into brands. Marking codes usually include letter indices that indicate the specific application.
Application area depending on type
Marking
Wires and cables are marked with letters.
First letter. Core material: A – aluminum, copper – no letter.
Second letter. In the wire designation: P - wire (PP - flat wire), K - control, M-mounting, MG - mounting with flexible conductor, P(U) or Ш - installation, in the cable designation the sheath material.
Third letter. In the designation of wire and cable - core insulation material: V or VR - polyvinyl chloride (PVC), P - polyethylene, R - rubber, N or NR - nayrite (non-flammable rubber), F - folded (metal) sheath, K - nylon, L - varnished, ME - enameled, O - polyamide silk braid, W - polyamide silk insulation, S - fiberglass, E - shielded, G - with a flexible core, T - with a supporting cable.
The rubber insulation of the wire can be protected by sheaths: B - polyvinyl chloride, N - nayrite. The letters B and H are placed after the designation of the wire insulation material.
Fourth letter. Design features. A - asphalted, B - armored tapes, G - flexible (wire), without protective cover (power cable), K - armored with round wires, O - braided, T - for installation in pipes.
In addition to letter designations, brands of wires, cables and cords contain digital designations: the first digit is the number of cores, the second digit is the cross-sectional area, the third is the rated voltage of the network. The absence of the first digit means that the cable or wire is single-core. The cross-sectional areas of the cores are standardized. The values of the cross-sectional areas of the wires are selected depending on the current strength, the material of the cores, and laying conditions (cooling).
The designation of cords must include the letter Ш.
Designation examples:
PPV 2x1.5-380 – copper wire, with PVC insulation, flat, two-core, core cross-sectional area 1.5 mm, voltage 380 V.
VVG 4x2.5-380 - cable with copper conductors, in PVC insulation, in a PVC sheath, without protective cover, 4-core, with a core cross-sectional area of 2.5 mm, for a voltage of 380 V.
Designs and operating conditions
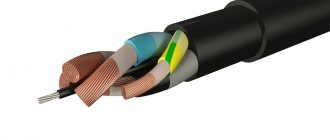
The structure of any power cable is a set of elements and components, including:
- conductor – core (one or more);
- individual core insulation;
- general insulation of the block, which includes all conductors;
- fillers (interblock) of empty spaces and inserts to prevent sticking of insulation layers;
- outer shell;
- protective armor (if necessary).
Flexible cable
Power cables can be used in different conditions and external influences. Depending on the operating conditions, a number of requirements are imposed on cable products, including:
- increased flexibility;
- permissible ambient temperature;
- reduced flammability of insulation;
- absence of toxic emissions during smoldering or combustion and a halogen-free set of components included in the insulation;
- the presence of armor or other protective layer.
The last point does not apply to power flexible cables, the insulation of the cores and outer sheath of which is made of rubber of special compounds.
Important! A flexible power cable (KSG), which has rubber insulation, for example, KGN, is resistant to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Long-term operation in the sun affects the properties of the insulating sheath: it hardens, bursts, and, accordingly, the service life of the entire cable decreases.
Preferred operating conditions depending on type
DESIGN
The conductor is copper, stranded, round, class 5 flexibility in accordance with GOST 22483.
Insulation – insulating rubber.
Twisting - insulated cores of 2, 3, 4 and 5-core cables are twisted into a core.
The sheath is made of hose rubber for KG cables, for KG-HL cables - of hose rubber in a cold-resistant design.
- Cable brands
- Characteristics
- Nomenclature
- Cable brands
- Characteristics
- Nomenclature
Core cross-section
In order to determine the cross-section of the wire, you need to know its diameter. To do this, use a special tool - a caliper or micrometer.
Flexible cable channel
Diameter and cross-section are not the same thing. Since a round conductor has a circle in its cross-section, the cross-section S, measured in mm2, is calculated using the formula. The formula for calculating S is:
S = (π/4)*D2, where:
- D – diameter of an individual conductor (core), mm;
- π – 3.14.
The total cross-section of the cable (sq. mm) is the result of the summation of the individual cross-sections of all conductors included in it. So, for electrical power cables:
Stotal = S1 + S2 +…+Sn,
Where:
- Stotal – total cross-sectional value;
- S1, S2, …, Sn – transverse dimensions for each element.
This rule is valid for cores consisting of individual wires. To find out S in this case, it is necessary to add up the cross sections of all the wires. When measuring with a caliper, it is recommended to rotate the object and take at least three measurements, and then calculate the arithmetic average of the obtained values. This measure is due to the fact that the conductor is not perfectly round, and it is worth eliminating the error.
Interesting. To calculate S of non-circular conductors, for example, segmented, it is worth using tables for calculating the S sector of an electrical conductor.
In the case of flexible wires, the core is always multi-wire and has an almost round shape.
Table of cross-sections of copper conductors
Types and designation of wires
Electrical wire is slightly less reliable than cable and is used at low voltages and low current. An alphanumeric code is also used to indicate product characteristics.
Classification
Conductor classification is related to purpose and configuration.
Flat - The strands inside the wire are arranged in the same plane, so that the conductor appears flat rather than round. The most popular brands of wires are as follows:
- PBPP - a protected version with copper single-wire conductors, used for connecting sockets and lamps;
- PBPPg – has great flexibility, can be bent during installation;
- APUNP is a wire with aluminum single-wire conductors in a protective sheath.
- PPV – 2–3 single-wire copper cores with PVC insulation, does not burn and is resistant to alkalis and acids;
- APPV - analogue with aluminum conductors.
Single-core – conductor with 1 core. The following are popular:
- APVA - aluminum conductor with a cross-section from 2.5 to 16 square meters. mm;
- PV1 - with a copper core and the same cross-section, but can also be stranded;
- PV3 is a multi-wire core, very flexible.
- PVS - model with 2–5 stranded copper cores for work with a voltage of 380 V;
- SHVVP - 2-3 core copper wire, used to power lamps and low-power electrical appliances.
Cord wires are not suitable for installation in walls. Under such conditions, the shell collapses after 3–4 years.
Marking
The wire markings are mostly alphabetic and similar to the code for cables. If the first letter is “A”, then the wire has aluminum cores. If not, then copper. There are other similarities.
Thickness of insulation and sheaths for cables of brands KG, KG-HL, KG-T, KGN, KPG, KPGS, KPGSN, mm
The insulation is designed to prevent short circuits inside the cable and electric shock to a person from the outside of the product.
There is such a thing as electrical breakdown of insulation. With increasing voltage and current passing through the conductor, it is necessary to increase the thickness of the insulating layer. Rubber protection in its electrical characteristics is noticeably behind plastic or paper (impregnated) protection. Over time or under the influence of external factors, rubber undergoes destruction through the process of oxidation. Simply put, its structure at the molecular level is destroyed under the influence of oxygen, light, temperature, etc. Because of this, rubber-coated cables are not suitable for high voltages (maximum 35 kV).
By the way! A number of foreign manufacturers practice producing cable products for voltages of 66 and 110 thousand volts using ethylene propylene rubber for insulation.
To eliminate electrical breakdown associated with the destruction of the rubber layer by ozone, rubbers based on butyl and ethylene propylene are needed. Ozone is formed in air inclusions as a result of ionization. Both bases have a linear molecular structure, with butyl rubber having a small number of double molecular bonds and ethylene propylene rubber having none at all.
Table of insulation thickness values for individual brands
How to decipher the markings of domestic manufacturers
Every person, when planning to purchase wires and cables, is faced with the difficult task of choosing. This happens because the wire markings indicated on the insulation look like a code. Knowing what the letters and numbers that are indicated on the insulation of electrical products mean, you can easily go to the store and buy the product you need.
Let's look at examples of markings, with explanations, so that you can buy products for electrical wiring that meet the technical specifications. Old wiring today cannot cope with connecting new household equipment.
Power cables are marked as follows:
- A - this letter tells you what metal the conductor is made of. If you see the letter A in the first place of the marking code, then the current-carrying wire is made of aluminum. When the core is made of electrical copper, there will be no letter in the first place;
- AA - in the first two positions informs the buyer - aluminum core in an aluminum shell;
- B – informs about the presence of armor made of 2 steel plates with anti-corrosion protection;
- Bng - armored, does not burn;
- B - the symbol can be indicated in the first position, it states that it is insulated with polyvinyl chloride;
- B – the symbol may appear in the second position; in this case, it informs about the presence of a second layer of polyvinyl chloride in the cable;
- G - the symbol can be indicated at the end of the alphabetic part of the code; it indicates that the wire is bare, without additional protection;
- K - the letter informs that the cable armor is made of round steel wire. At a summer cottage, the wiring can be chewed by rabbits and other wild animals; for this purpose, there are cables covered with armor;
- Shv – the presence of a pressed PVC hose on the armor;
- Shp - a layer of pressed hose on the armor, made of polyethylene;
- P – rubber layer;
- NR - rubber, does not burn;
- PS is a self-extinguishing polyethylene, which is important in fire-hazardous areas;
- PV – vulcanized polyethylene;
- ng – symbols indicating that the cable does not burn itself and does not support combustion in the group;
- LS – Low Smoke – emits little smoke;
- ng – LS – does not burn, does not emit smoke;
- FR – increased fire resistance, presence of mica-containing plate;
- FRLS – low smoke, fire resistant;
- Ш - sometimes there is such a marking, meaning a cord.
It should be noted that only the first letter A indicates the metal of the core. If it is not marked, then the core is made of copper. All other letters indicate the material of insulation, protective shells and their properties, such as resistance to fire, the ability to self-extinguish, and not emit a large volume of toxic smoke. If such a cable is laid in a group of others, it does not support combustion. In the marking code this is marked in small letters ng.
The control cable is marked as follows:
- A - the symbol placed in the first position states that the wire is aluminum, when A is missing, the wire is copper;
- B – in the second position, without A – in the first, indicates that the insulation is PVC;
- B – in the third position, when there is no A – in the second, indicates an additional layer of PVC;
- P – polyethylene;
- PS – self-extinguishing polyethylene;
- G – no additional protection;
- R – rubber.
All symbols except A indicate layers of protection. Where there is high dampness and temperature, for example in a bathhouse, protection is needed from rubber or self-extinguishing polyethylene.
Markings specific to installation:
- M – in the first position, denotes the installation wire;
- G – many wires, if there is no symbol, one wire;
- B – PVC;
- PV-1, PV-3 – PVC layer, numbers 1 and 3 indicate the degree of flexibility;
- PVA – PVC, wire for connection;
- SHVVP – flat cord, two layers of vinyl;
- PUNP – universal flat wire;
- PUGNP – universal flat wires, high flexibility. They are laid indoors, for household equipment and street lamps.
Colors of cores for cables of brands KG, KG-HL, KG-T, KGN, KPG, KPGS, KPGSN
During the production of cable products, the manufacturer performs color marking of the core insulation. When deciphering the color code, you should take into account the presence or absence of the ground conductor, which is intended for connecting the equipment to be connected to the power supply with this cable.
In the absence of a grounding conductor, the colors of the insulating coating are as follows:
- 3 conductors: a – blue; b – black; c – brown;
- 4 wires: a – blue; b – black; c – brown, d – black or brown;
- 5 cores: a – blue; b – black; c – brown, d – black or brown; e – black or brown.
The presence of a grounding conductor makes the following changes to the insulation colors:
- 3 conductors: a – green-yellow; b – blue; c – brown;
- 4 wires: a – green-yellow; b – blue; c – black; d – brown;
- 5 cores: a – green-yellow; b – blue; c – black; d – brown, e – black or brown.
Some manufacturers highlight only the green-yellow conductor in color, the rest have the same color. GOST indicates that colors should be easily distinguishable and even when painting only the top layer, they should be applied quite firmly. The color of the shell is not regulated, but manufacturers stick to black.
Coloring of insulation of flexible current conductors
Color coding of wires and cables
Color marking of cables and wires is also used, in accordance with GOST 28763. It is carried out along the entire length of the wiring or at the ends. So, according to GOST standards, grounding is always a yellow-green wire, the neutral and middle conductor are marked in blue. And for the phase they use white, red and other permitted shades. Allowed colors and combinations are shown in the table.
It is prohibited to use yellow and green separately for marking. The yellow-green combination is used only to indicate grounding.
Insulation and sheath thickness for KOG-1 cables, mm
The insulated cable KOG-1 has a rubber layer, which in the range of nominal conductor sections from 10 to 150 mm2 remains the same and equal to 4 mm. The outer diameter of the product increases only due to the difference in the thickness of the waist screen, as well as other screens.
Table of sheath and insulation thickness values for KOG-1
Telephone cables and wires
Telephone wires are divided into 2 main types. The first ones are intended for laying several (up to 400) subscriber lines. The second type is used for wiring in a separate apartment or house.
TPPep: 1 - core; 2 — polyethylene insulation; 3 - core; 4 - fastening winding; 5 - waist insulation; 6 - screen
TPPep is the main type of cable for laying telephone lines designed for a large number of subscribers. The cable consists of two wires twisted into pairs. TPG made of soft copper wire, cross-section 0.4 or 0.5 mm², covered with polyethylene insulation. In some types of cable, pairs are combined into groups of 5 or 10 pairs. The outer shell is also polyethylene or vinyl. The letters “e” and “p” in the name stand for film screen.
There are varieties of cable armored with tapes, or filled, in which the space between the sheath and the cores is occupied by a hydrophobic seal. In a word, this is a cable for telephone communication in an apartment building; it is intended for installation in almost all conditions: underground, in cable ducts or by air. To conduct a telephone line to an individual subscriber and distribute it indoors, the following types of telephone wires are used.
Telephone wire TRV
TRV - single or double pair telephone distribution wire . This is a flat wire with a divided base, a copper core, single-wire, with a cross-section of 0.4 or 0.5 mm². Number of cores - 2 or 4. PVC insulation. Designed for conducting telephone lines indoors. Operates at temperatures from –10 to +40 °C. Humidity should not exceed 80% at a temperature of +30 °C.
TRP wire
TRP - the characteristics are the same as TRV. The only difference is the insulation; for TRP it is made of polyethylene. Compared to expansion valves, the wire is more resistant to the external environment and can be laid outside buildings.
Wire SHTLP
ShTLP is a telephone flat cord with copper stranded conductors. The core insulation is made of polyethylene. Insulated TPGs are covered with a PVC sheath. Number of cores - 2 or 4, cross-section - from 0.08 to 0.12 mm². Used for conducting lines indoors and in telephone sets. Highly flexible wire.
Wire PRPPM
PRPPM is a flat wire with a dividing base and single-wire copper conductors with insulation and a polyethylene sheath. There is a modification of PRPVM, the shell of which is made of PVC. Number of cores - 2, core cross-section - 0.9 or 1.2 mm². It is used when laying a telephone line outdoors, on aerial supports, in the ground and along the walls of buildings. Resistant to temperature influences, operating conditions - from –60 to +60 °C.
Thickness of structural elements KSHVGT-10
For a given type of cable, starting from S = 25 mm2 and up to S = 150 mm2, this parameter changes uncritically.
Thickness of elements included in the structure of KShVGT-10
Speaking about the structure, it is worth paying attention to the decoding of the abbreviation of this conductor, it reads like this:
- cable – K;
- mine – Ш;
- high-strength - B;
- flexible – G;
- heat resistant – T;
- number 10 – indicates the value of the rated voltage Unom.
Among other things, the Electrical Installation Rules (ELR) regulate certain requirements for the electrical characteristics of cables.
Special types of cables and wires
For the installation of electrical systems in places where the conditions are very different from usual, special cables are used that have increased resistance to the external environment. Such places include baths, ovens and cellars. In general, anywhere where it is too hot, humid or cold and there is also a possibility of mechanical damage. It is clear that PVS or VVG cannot be installed in such places, not to mention PUNP or ShVVP.
Wire RKGM
RKGM - power installation single-core wire of increased heat resistance, flexible . Copper core, multi-wire, cross-section - from 0.75 to 120 mm². Insulation made of silicone rubber, fiberglass shell impregnated with heat-resistant enamel or varnish. This wire is designed for rated voltage up to 660 V and frequency up to 400 Hz. Resistant to vibration, high humidity (up to 100% at a temperature of +35 °C), heat-resistant (operating temperature range - from –60 to +180 °C). In addition, the wire is protected from the harmful effects of varnishes, solvents and fungal mold. An ideal conductor for rooms with high temperatures (boiler rooms and furnaces), suitable for electrical installations in baths, saunas, and oven connections.
PNSV wire
PNSV - single-core heating wire . TPZh single-wire steel, blued or galvanized steel. Core cross-section - 1.2; 1.4; 2 and 3 mm². PVC or polyethylene insulation. Rated voltage - up to 380 V, frequency - 50 Hz. The wire is heat-resistant: the operating temperature range is from –50 to +80 °C, it is resistant to alkalis and moisture-resistant (tolerates immersion in water). It is used as a heating element: in domestic conditions, heated floors are installed using PNSV.
Runway wire
Runway - single-core copper wire . The core is multi-wire, enclosed in polyethylene insulation, the sheath is also made of polyethylene or PVC. Core cross-section - from 1.2 to 25 mm². Rated voltage - 380 or 660 V, frequency - 50 Hz. The wire is resistant to pressure changes. Operating temperature range – from –40 to +80 °C. It is used for motors of artesian wells immersed in water under high pressure conditions.
LED cable
LED cable is a very interesting option for power cable. Under the transparent outer shell along the power TPG there are additional wires with LEDs of different colors connected in series. They are located at a distance of 2 cm from each other and burn with a constant, fairly strong light. Such a cable performs not only decorative functions, although it can be used to create entire light paintings. In addition to aesthetic purposes, it is very convenient for connecting to portable electrical mechanisms. Most often, LED cables are used to connect stage equipment. It is useful because if it breaks, you don’t have to look for the damage site: the diodes in this area will stop glowing. Manufactures such cables. In addition to power wires, there are computer glowing cables. With the help of such wires you can create very interesting design solutions, turning the cable into a lighting element.
Electroluminescent cable
In addition to LED cables, there are electroluminescent cables . They glow evenly along their entire length. Using such cables you can create luminous inscriptions and even entire paintings. This is an excellent alternative to the flexible neon tubes that these designer decorations are usually made from. In addition, electroluminescent cable is cheaper than neon tubes and is not limited in length.
These articles may also be of interest to you:
- Wire routing
- Wire connection methods
- Wire characteristics
- What are cables, wires and cords made of?
What else would you like to read?
Tags: Antenna cables, Types of cables, Cables for information transmission, cable, flexible cable, Computer cables, Flat wire, Wires, LED cable, power cable, Special types of cables and wires, Telephone cables and wires, Electroluminescent cable
Electrical Requirements
Even in order to connect a subwoofer for playing music in a personal vehicle with a four-core flexible conductor, you cannot take any one that comes to hand. A number of technical conditions must be met. For example, to supply “plus” from a battery, you need a conductor with a cross-section larger than for connecting sound speakers to an amplifier.
Important! The main thing is that the cables during manufacture comply with the parameters declared by the manufacturer.
This is strictly monitored by GOST 31947-2012, which explains the following points:
- resistance of cores to direct current, Ohm/km (GOST 22483);
- insulated conductors must undergo increased voltage values, according to category EI-2 (GOST 23286);
- Cable products should not lose their properties when exposed to a current with a frequency of 50 Hz, lasting up to 5 minutes, which belongs to the EI-1 category (GOST 23286), and a voltage of 2.5 kV and 2 kV for wires and cables, respectively.
Requirements for the electrical parameters of the CSG
MAIN TECHNICAL AND OPERATIONAL CHARACTERISTICS
| Ambient temperature during operation: — for cables of the KG brand — for cables of the KG-HL brand | from -40ºС to +50 ºС from -60ºС to +50 ºС |
| Cables with a nominal core cross-section of 6 mm2 or more must be resistant to repeated bending at an angle of ±π/2 rad with a nominal tensile force of 49 N (5.0 kgf) | |
| Maximum long-term permissible operating temperature of the cores | +75 ºС |
| Cables with a cross-section of main cores up to 4 mm2 inclusive must be resistant to repeated bending through a system of rollers under current load and withstand bending cycles of at least -30,000 | |
| Service life, not less | 4 years |
| Warranty life of the cable from the moment of commissioning | 6 months |
| Cable storage conditions | cable storage conditions in terms of exposure to climatic factors must comply with group 8 of GOST 15150 |
Cable weights
This is one of the important indicators (kg/km). Its cost depends on how many kg of copper are used for each kilometer of the product.
Attention! The number of cores, cross-sectional size, insulation thickness - all these parameters increase the weight of the product.
You can track the mass of the cable of interest per linear kilometer using tables.
Cable weight table per km
Flexible power cables can be used for different needs, but only a properly selected conductor will not fail at the critical moment. Letter and number markings are only the first guideline for the right choice. Knowledge of design features, electrical and physical properties will help not only find the required cable, but also save money.
Cables for information transmission
In addition to electricity, cables transmit information signals. Recently, many new types of information conductors have appeared. If 10–15 years ago there were only telephone and antenna cables, now with the development of computer technology there are many more types of information conductors. Most of them are too specialized and are of interest only to narrowly specialized specialists. For a home craftsman, it is enough to know and be able to use only a few types. We will consider them.
RG-6 coaxial cable
Antenna cables . Today, RG-6, RG-59, RG-58 or Russian analogues of the RK 75 series are most often used. RG-6 is a coaxial cable for transmitting high-frequency signals for electronic equipment, television or radio. It consists of a central copper core with a cross-section of 1 mm², surrounding polyethylene foam insulation, an aluminum foil screen, an outer conductor of tinned copper braid and a PVC sheath. Widely used for transmitting cable and satellite television signals. It has many technical characteristics regarding transmitting signal frequency, resistance, shielding, etc.
Cable RK 75
For example, the designation in the name of the cable RK 75 means that the conductor resistance is 75 Ohms. This information is intended for specialists. In short, we can say that this cable is ideal for transmitting a video signal from an antenna or video camera to a receiver (TV) and distributing the video signal to several sources.
Coaxial cable with lug
RG brand cables come in many varieties and differ from each other in certain characteristics, such as conductor resistance, resistance to temperature and shock loads, signal decay time, type of screen, etc.
Sectional view of cable RK 75
Computer cables . They are used to build computer networks. The cable with which computers connect to the Internet or to each other is exactly what is known to all computer scientists - twisted pair . Consists of one or more pairs of wires intertwined in pairs, which is done in order to improve signal reception or transmission.
twisted pair
Each conductor is enclosed in PVC or propylene insulation. The outer shell is also made of PVC. The cable can be additionally equipped with a waterproof polypropylene sheath.
Twisted pair section
There is a breaking thread in the twisted pair design. With its help, the outer sheath can be easily removed from the cable, opening access to the conductive wires. Depending on the type of cable, various protection options are possible:
- UTP, or unprotected, without a common shield for pairs of wires;
- FTP, or foil, with an aluminum foil screen;
- STP, or secure, with a common shield made of copper mesh, in addition, each twisted pair is surrounded by a separate shield;
- S/FTP, or foil, shielded with a common foil shield, in addition, each pair is additionally enclosed in a shield.
RJ-45 tip for connecting to a computer
In addition, twisted pair cables are divided into categories based on the number of pairs combined into one cable. The most common type used for computer networks is the CAT5e category. It consists of 4 pairs of wires of different colors. Data transfer speed - up to 1 Gb/s when using all pairs. You can see such a cable used as a telephone wire of category CAT1 or CAT2, that is, consisting of 1 or 2 pairs of wires.
Twisted pair with a connector for connecting to a computer, protected by a PVC sheath
Cable PVMR-8
The PVMR-8 cable is used to connect to the electrical network and power supplies of special high-power industrial equipment.
It is used in alternating, pulsed, and direct current circuits with operating voltage ratings of 8 kV, 12 kV, 16 kV, since its core is twisted from strong copper wires. Order
To comply with operating conditions, a special coating of the outer layer is used, such wires include RK 50-7-28, the explanation of which is presented below:
- The first two letters indicate that this type belongs to radio frequency cables.
- 50 indicates resistance.
- 7 is used to determine the insulation diameter.
- The last two digits indicate the heat resistance category and the development number in order.