How to connect a water heater to electricity - mistakes, choice of cable, socket, machines.
For a comfortable stay in the house, when you want to constantly use hot water, and not depend on the repair schedule of monopolists who can turn off this water for an unknown number of days, many people think about purchasing a boiler. Most often, the choice falls towards a storage water heater. They come from different companies: Ariston, Drazice, Baxi, etc., shapes and designs - flat, cylindrical or elongated.
The installation of cold and hot water pipes may differ, but they are all connected to the 220V network in the same way.
Many people mistakenly believe that in order to connect the boiler, you just need to plug the plug into the socket and not worry about anything else. However, they forget that it is in the boiler that, in case of insulation failure, direct contact of electricity with a person can occur through water.
- selection of the cross-section of the supply cable (depending on the power of the boiler)
- selection of a circuit breaker for power supply to the boiler
- socket selection
If you want to connect the boiler to the old common wiring, which already has several sockets connected, be sure to make sure that it can withstand the power of the boiler. In most cases, with a power of up to 3.5 kW, wiring must be done with a 3-core copper cable VVGnG-Ls, with a cross-section of at least 2.5 mm2.
The three-core cable is required to ensure a permanent connection to ground.
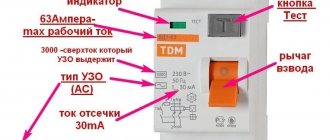
Choose a two-pole boiler connection machine. The rated current of the machine is 16A (sufficient for boiler power up to 3.5 kW).
For loads up to 2 kW, a circuit breaker with a rated current of 10 A is suitable.
If the boiler is connected from an outlet, then the outlet must have a degree of protection IP44. These are sockets for rooms with high humidity levels.
Remember that the socket in the bathroom can only be placed in certain places. And there are areas where doing this is strictly prohibited. You can read more about this in the article “Socket in the bathroom - 5 placement rules.”
If it says that this boiler can be connected in two ways
- directly
- and via the standard power cord
then you will not lose the guarantee here.
In addition, if you need to dismantle the device from the wall, if there is a plug, you will not need to call an electrician to disconnect it from the power supply. Pull out the plug, take it off, rearrange it, do whatever you want.
Powerful boilers over 3.5 kW should only be connected directly through a circuit breaker; a socket connection is not allowed here.
The cable must be routed so that there are no intersections with water pipes and places where the heater will be mounted.
It is mandatory to install an RCD - a residual current device - in the boiler supply line. Select its current one order of magnitude higher than the current of the machine.
Leakage current for RCD – 10mA or 30mA.
Why 10mA is better and not more can be understood from this sign of the effect of current on the human body:
A significant disadvantage here is that at 10mA the protection may falsely trigger. Especially if your water heater has been hanging for more than a year and such condensation and moisture often form in the places where the terminals are connected.
How can I check if this is a false positive or if the heating element itself is faulty? To do this, use a multimeter.
Turn off the power supply or pull out the plug from the socket and disconnect the standard grounding from the titanium body.
Then remove the terminal clamps from the heating element itself, and using probes, measure the resistance between the boiler body and the heating element.
If the heating element is working properly, the readings on the multimeter screen should tend to infinity, that is, they should be something like this:
In case of breakdown and damage to the heater, they will either be zero, but most often they can be several hundred or even kiloohms. In the photo below this is exactly the option
500kOhm.
Very often, in many of the latest boiler models, an RCD with a leakage current of 15 mA is already built into the cable for connecting to the outlet. In this case, it may not be necessary to install an additional leakage current protection device in the panel.
However, do not forget that such a built-in RCD will protect against leakage only if there is damage in the heater itself, but will not protect you in any way if there is a fault directly in the outlet or the supply wiring to it.
How to find these and other similar faults and what this can lead to can be found in the article “Electric shock in the bathroom. 5 reasons and what to do?”
What to do if you are not an expert in electricity and you yourself cannot or do not want to go into the electrical panel in order to install all the required protection devices there. But you still need to protect yourself.
Plug it into the existing outlet in the bathroom, and through it you plug the plug from the boiler cord.
Will the residual current device on the boiler trip if you do not have a ground connection? Will. These two systems, when working together, are designed to complement each other.
In the event of a current leak on a boiler without grounding, the protection device will only work when you directly touch the tank or the water from it (with the heating elements turned on).
Boiler connection diagram via socket:
Electrical diagram of the water heater:
Schematic diagram without socket directly from the panel:
- installing an outlet directly under the boiler itself
Sockets should be placed away from the heating device and placed above the faucets. Don't forget about the safety valve and possible leaks. The valve will operate as a last stage of protection if the thermostat fails. By the way, the thermostat needs to be checked first when the light on the panel does not light up and the heating elements do not heat up. Look at the position of the button on the element, it can be “knocked out”.
- A common mistake when connecting the device directly to an outlet is the desire to turn off the device by pulling out the plug at a time when the water has not yet warmed up and the heater is still working
If its power reaches 3.5 kW, then with such a break in the contacts, sparking may occur, with the formation of an arc. And since the bathroom is a room with high humidity, the consequences may not be predictable.
- You cannot plug in an empty boiler without water.
The heating element installed inside requires water cooling. Without it, it will simply burn out and fail. Therefore, before each switching on, check the presence of water in the boiler.
In general, it is not recommended to keep titanium without water. This reduces its service life. A full tank contains less oxygen, and therefore the risk of corrosion is reduced.
Plus, the magnesium anode, which also protects against rust formation, only works when the tank is full.
- connecting the water heater only through an RCD, or only through an automatic device
These two protection devices must duplicate each other. The RCD protects against leakage current, and a simple circuit breaker protects against overload and short circuits.
If your budget allows, then instead of these two protective elements you can install one differential automatic device; it will replace both devices.
Basic Concepts
Electric water heaters are devices in which current energy is converted into heat and then transferred to water. Conventionally, such devices can be divided into 2 groups:
- Flow-through. The water is heated in them by passing through special systems with warm plates or pipes that instantly release heat to it. Flow-type heaters are characterized by high power.
- Cumulative. These include a conventional boiler with a heating element, which consistently heats the water inside the tank.
An RCD for a water heater is a special device designed to protect against current leakage.
The principle of its operation can be described as follows:
- The device is installed directly in front of the heater itself. All the current passes through it, which powers the mechanism.
- If there is a current leak inside the heater, then the RCD catches it, after which the entire system is switched off. Its operation is ensured using special sensors and switches.
It should be noted that the RCD, in its operating principle, resembles an automatic machine, but technically it is not one. It picks up even small current fluctuations that automatic machines are unable to analyze.
Today, such mechanisms do not always provide an optimal level of safety, so the water heater must also be additionally equipped with grounding. An RCD should not be confused with a difavtomat, as these are two different designs. The first mechanism is capable of catching only current leaks, and the second is more universal: the difavtomat also reacts to short circuits, overloads and other similar problems, while “knocking out” the electricity.
Reasons for triggering
Technically, protective systems do not need to be used. However, for water heaters they are mandatory attributes. This is due to the fact that the structures are made of metal, and the water itself conducts current well. The use of water heaters without protective systems is unacceptable, as it can become a threat to human life.
The RCD is turned off for several main reasons:
- Damage to the insulation of the heating element. It is this that protects the entire system from the passage of current. Any user can safely wash their hands without fear of electrocution. However, in old or low-quality models of water heaters, this element may be damaged. Such phenomena can only be checked using special instruments.
- Leakage current. Very often the RCD is knocked out if the cable inside the boiler or the power cord itself is damaged. You need to pay attention to the fact that this can happen in almost any wire. Very often, the cable itself is damaged from the inside, after which current is supplied to the metal housing. To find the cause, very often it is necessary to disassemble the heater and analyze the situation.
- The shutdown mechanism does not work. This very often happens with cheap products from unknown companies. They may simply not turn on after several operations.
- Incorrect location of the RCD. If the device is connected in the wrong place, then it will analyze the wrong currents. If the heater breaks down, the system will not protect a person from current leakage.
How to choose?
RCDs are universal mechanisms that can be used to turn on and off various household appliances. You can select such a mechanism for an electric water heater based on some simple rules, which will be discussed below:
- The power of the RCD is selected based on the similar indicator of the household appliance that is planned to be used. For boilers with a power of no more than 2.3 kW, experts recommend installing mechanisms rated at 10 A. If this figure varies in the range of 5.5-8 kW, you should buy an RCD for 32-40 A. That is why it is so important to pay attention not only on the switch itself, but also on the connected device.
- Leakage current. This characteristic is calculated based on operating current indicators. Often 0.4 mA is taken into account at 1 A. If the RCD is installed at a remote distance, it is advisable to add another 10 µA per meter of cable. This value can be easily minimized if you install the device directly in front of the water heater itself.
- Installation method. There are several options for protective devices on the market. The most common are RCDs that can be mounted on a DIN rail. An alternative option is separate units that allow you to plug them directly into an outlet.
It should be noted that many modern manufacturers of water heaters integrate such devices into their equipment.
The elements may be located in an inconspicuous place - under the housing or inside the network cable, so it is advisable to clarify this feature before purchasing a boiler. The advantage of such a system is that the manufacturer accurately calculates all the characteristics of the RCD for a heater of a certain power.
RCDs are not complicated, but they can be classified according to several criteria. Devices are divided into the following types (depending on the type of current leakage):
- Class A. Used for alternating or pulsating electrical currents.
- Class AC. These devices are designed for AC operation only. They are one of the cheapest and simplest models and are used in many apartments.
- Class B. Universal devices for industrial use. They can be used not only for alternating current, but also for direct or rectified current.
- Sometimes manufacturers add the letter S , which indicates that the device turns off only after a certain period of time. In everyday life, there is no need to use such systems together with water heaters, so they are very rare here.
- Class G. These RCDs are similar to S, but their dwell time is much shorter.
Depending on the method of breaking the circuit, RCDs can be divided into the following groups:
- Electronic. They are relatively inexpensive devices that are used in simple systems. Experts do not recommend installing them, as they are powered from the electrical network. If the user accidentally damages the neutral wire, the device will simply fail. Another disadvantage is the relatively long response period.
- Electromechanical. Switches of this type are not powered from external electrical sources, so they are more reliable and of higher quality. The only drawback of such devices can be considered only their inflated price.
Why install a separate protective device?
Modern homes are literally filled with various equipment and household appliances, many of which are highly powerful. In this regard, the load on the electrical wiring increases significantly, and the likelihood of damage and failure of the insulation after a certain period of operation increases. As a result, the wiring through the damaged insulation is connected to the ground, and the flow of current changes its direction, that is, a current leakage occurs. When coming into contact with dangerous places, a person himself becomes a conductor and can receive serious injuries.
Modern washing machines are also among household appliances with increased energy consumption. They gain maximum power in the range of 3-3.5 kW during operation of the heating element and heating of water. If the insulation is damaged, current leakage can also reach a large value that is dangerous to human life. Therefore, experts recommend installing a separate RCD on the line supplying the washing machine. In the event of a leak, the RCD will simply turn off the network and stop supplying voltage.
To connect the RCD with the consumer into a single circuit, a serial connection is used. The principle of operation of the device is based on measuring and comparing the difference in current at the input and output. If the network is healthy, it will have a zero value. And in the event of a leak, the output current will differ downward by exactly the amount that went along the other path. When the current leakage value for which the device is installed is reached, it will instantly react and turn off the network.
Connection
You can get reliable protection against leaks using an RCD. However, to do this, you need to properly connect the device to the main network. When carrying out such operations, you should adhere to a few simple rules:
- The RCD should be connected directly in front of the boiler itself. A separate line machine is installed in front of it, and then a meter and a common input machine for the entire house. If the electric line is used only for a specific water heater, then it is permissible to change the order of the RCD and the circuit breaker. However, it is advisable to adhere to the first scheme.
- It is not advisable to place several additional sockets or connect other household appliances between the switch and the boiler. Experts recommend using separate lines for heaters. The RCD here should only control the boiler.
- Be sure to supplement the house with a common RCD that will control the entire network. If the device malfunctions, the system will be switched off by another device.
Technically, connecting an RCD is not difficult. On the body of each device there are input and output terminals. The neutral and phase wires are connected to them (using special clamps). At the output, wires are also used that already go directly to the boiler or other heater.
One of the mistakes is the use of only one machine or RCD. It should be understood that these devices complement each other, since they are responsible for different threats. They must be used in pairs.
An RCD for a water heater allows you to ensure an optimal level of safety for its operation. If you need to get a high-quality and reliable system, then the design of electrical circuits and the installation of all protective devices should be trusted only to professionals.
You will learn even more useful information about RCDs for water heaters in the following video.
How does an RCD work and why is it needed?
First, you need to understand the difference between RCDs and circuit breakers.
The machine is the main protection of the power supply network. If overcurrents occur during an overload or short circuit, the switching device will react to the excess current and turn off, cutting off the emergency section and saving the entire network from damage.
The main function of the RCD is to protect not the network, but the person and this device reacts to small values of leakage currents. How does this happen?
Our homes now have a huge number of different household appliances, and some devices have quite a lot of power. Electrical wiring does not have a lifetime; the longer it is in use, the greater the likelihood of insulation failure. Damage to the insulating layer entails the connection of the wiring to the ground, as a result, the path of the current changes, and now it flows to the ground. And in some cases, a person can become a conductor for current leakage.
More clearly about the principle of operation of the device in the video:
Modern washing machines and water heaters are considered equipment with a higher energy consumption class. They take maximum power during the period when the heating element is operating and water is being heated (about 3-3.5 kW). This is a very large load for electrical wiring, which can cause premature aging of the insulation.
Let's assume that the insulating layer breaks down in a washing machine, causing the body to become energized. By touching the machine, a person may be exposed to electricity.
To protect yourself from such a situation, you need to install an RCD for the washing machine.
If a current leak occurs to the ground, the device will turn off and stop supplying voltage.
The RCD is connected to the consumer in one circuit in series, and its operating principle is based on measuring the difference between the input and output current values. Ideally, it should be equal to zero, that is, whatever amount of current comes in is what comes out. As soon as a leak occurs, the output will have a different reading, smaller by exactly the amount of current that went along a different path. The measured difference will change accordingly. As soon as the current leakage reaches the value for which the device is designed, it will immediately react and turn off.
There are no particular difficulties in connecting the device. In the circuit, first there is a circuit breaker, after it there is an RCD, from the output contacts of which the wires go to the consumer, that is, the power outlet for the washing machine or boiler.
Why does a water heater need an RCD?
An electric boiler combines water and electric current, and with the slightest malfunction in the water heating element, this is a direct path to fire and electrical injuries. The safety of the water heater power supply must be given special attention.
With proper use, this electrical appliance will fully fulfill its service life, but if errors are made during its installation, problems may arise that lead to repairs.
The main purpose of an RCD is to break the power supply circuit of an electrical installation (its protective disconnection from the network) when a leakage current occurs. On the one hand, this protective switch prevents electric shock to a person, and on the other hand, it prevents overheating of the wire cores.
If the heating element or the cable suitable for it is suddenly damaged, then the condensate outside and the water inside the boiler turn into a natural conductive element, and when they come into contact with them or the body of the water heater, a person is hit with a leakage current.
The result is discomfort, cardiac arrhythmia and possible death. It all depends on the strength of the applied electric current in amperes.
When a powerful leakage current appears in the circuit, the wires begin to operate at extreme levels. But the cross-section of the cores is simply not designed for such loads. As a result, the wire begins to get very hot, burning through the insulation. And this inevitably leads to an increased risk of fire in the house.
Thus, it is not recommended to connect a water heater to the electrical network without an RCD.
The most common situations when RCDs are triggered are:
- damage to the wire and short circuit of the exposed wire to the boiler body;
- damage to the insulation layer in the tubular electric heating element;
- incorrect selection of parameters of the protective device;
- incorrect connection diagram of the water heater to the power supply;
- malfunction of the leakage current protection device itself.
In all these cases, in the absence of an RCD, human touch to the body of the water heater or the water heated in it is fraught with serious injury.
What is the difference between a shutdown device and a difavtomat?
Both types of devices are designed to protect against electric shock when a leakage current to ground occurs, and to disconnect the load in this case. That is, they protect us from electric shock in case of damage to the insulation, and in the case of a bathroom, in case of breakdown through moisture. However, the differential circuit breaker has one more, perhaps main, function - disconnecting the consumer when the load current exceeds the rated one for a given circuit breaker and there is a short circuit.
Differences in Features and Settings
The main characteristics of an RCD are sensitivity (minimum leakage current at which it triggers) and rated operating current. For the bathroom, you should choose devices with a sensitivity of 100 to 300 mA and a rated current equal to the current consumption of all connected electrical devices. For example, if you plan to install a washing machine in the bathroom, the operating current of the device is selected equal to 16 amperes.
The main characteristics of an AV with a differential block are the operation (shutdown) current and the differential shutdown current. There are machines with operating currents from 1 to 300 A and settings for shutdown by leakage current of 10 and 30 mA.
So, the main differences between the RCD and the automatic differential switch:
- both devices will protect us from electric shock, but the machine will also turn off the load if the power consumption exceeds the norm; the first one will simply fail during long-term operation in this case.
- the difference in leakage response currents (for AVs is much less) also limits the scope of application of both devices.
- significant difference in cost.
How to distinguish RCD from differential. machine - watch the video:
What to use to protect electrics in the bathroom
In relation to the power supply of powerful devices in the bathroom, it is more advisable to install a separate RCD unit, as a device specially designed and intended for these purposes. In addition, the high sensitivity of differential protection in an AB can provoke false alarms when connecting a washing machine, mainly due to high-frequency interference from its electronic components; by the way, this is why it is not recommended to install differential circuit breakers in the computer’s power supply circuits. The area of application of differential circuit breakers is electrical lighting circuits.
Connection diagram of the residual current device. To connect the protection device, it is necessary to have a third protective conductor in the circuit. When turned on without this wire, the device will not perform its functions.
The difference between a residual current device
It is necessary to clearly distinguish between the RCD (differential circuit breaker) and the differential circuit breaker (differential circuit breaker, differential current circuit breaker, RCBO). They have slightly different purposes, they work fundamentally differently, and their internal structure is also different.
The RCD reacts exclusively to leakage current. A difavtomat is a more complex device, part of which is a protective shutdown device. The differential circuit breaker is triggered not only by the current leaks described above, but also by short circuits and overloads in the electrical network.
In addition to the RCD, the RCBO additionally contains thermal and electromagnetic releases that respond to those same ultra-high currents and short circuits.
The main unit of the RCD is a differential transformer with three windings (input, outlet and control). The electric current passing through the protective device excites magnetic fluxes with directly opposite poles on them. In the absence of leaks, when the water heater is working properly, the sum of the currents is zero.
But if the heating element breaks down or the insulation breaks down, if a person takes hold of a bare wire (or the metal body of the boiler), then through his body the electric current will begin to flow into the ground - as a result, the sum of the currents from zero will become positive.
Then the balance in the transformer is upset and the EMF acting on the internal relay instantly opens the circuit, and the RCD is triggered.
Additional information about the differences between an RCD and a difavtomat, as well as the choice of a load disconnect switching device, is presented in this article.
Dangerous area
From the point of view of electrical safety, the bathroom is a room with a high degree of responsibility. This is due to high air humidity and the possibility of uncontrolled splashing of water.
The bathroom space is conventionally divided into zones. There are requirements for the installation of electrical installation devices and lighting by zone, as well as requirements for their design in terms of water resistance:
- in zone 0, directly in the bathtub or shower tray, it is allowed to use devices with a voltage of no more than 12 V, with the highest degree of protection from moisture;
- in zone 1 it is allowed to install water heaters protected from low pressure water jets from all sides;
- in zone 2, within 0.6 m from the edge of the bathtub or shower tray, it is allowed to install lamps with a degree of protection that allows them to be used in the presence of drops and splashes;
- in zone 3, at a distance of more than 0.6 m from a bathtub, sink or tray, it is already allowed to install 220 V sockets protected from drops and splashes.
Due to the increased risk of electrical shock in the bathroom, the requirements for the use of protective devices are quite high.
All electrical devices must be protected by residual current devices (RCDs) or differential circuit breakers, unlike other premises where protection can be organized using circuit breakers of the required rating.
Types of differential switches
RCDs installed with water heaters and other electrical appliances are divided according to the nature of the leakage current, operating current, number of phases, as well as the presence/absence of a delay and the technology of operation of the protection device.
All RCD models according to the type of leakage current are divided into three types:
- “A” – designed to be triggered by alternating and pulsating electric current;
- “AC” - inexpensive household devices that operate only from alternating current;
- “B” - industrial options, designed to work in networks with alternating, direct and rectified electric current.
If there is an “S” , then this is a device with an adjustable selective response delay. It breaks the chain only after a strictly set time, and not immediately. Such devices are used in cascade protection systems with multiple circuits. They are practically not used in everyday life.
According to the principle of circuit breaking, RCDs are:
Electromechanical models do not require separate external power and are more reliable. However, they also cost more than the latter. But, despite the high price, it is recommended to install electromechanical devices.
Electronic analogues during voltage surges reduce the efficiency of the device - in such situations their response time increases. Plus, if the neutral wire is accidentally damaged, such an RCD will simply stop working without power.
How to choose a protection device
The operating current of the RCD determines the maximum permissible load in the circuit that will pass through it. It must match the power of the water heater.
For example, if a boiler consumes up to 2.3 kW, then the protective device should be rated at 10 A. For heaters of 5.5–7 kW, a 32 A device is needed. But for boilers of 7–8 kW, a 40 A RCD is required.
The leakage current is indicated in mA (milliamps). According to electrical rules, its calculation must be made based on 0.4 mA for each Ampere of operating electric current. Plus, 10 µA per meter of wire to the water heater is added.
It is not for nothing that RCDs are recommended to be installed directly next to the boiler in order to exclude the influence of the second parameter in the calculations.
The shape and size of the protective device under consideration can be mounted on a DIN rail in a switchboard or in the form of a block with a plug in a regular socket.
There are models of water heaters on sale that initially come with RCDs built into the cable. All parameters of such protective devices are already pre-calculated for a specific boiler; they just need to be plugged into a power outlet.
Another point in choosing an RCD is the presence of natural current leaks in almost every electrical appliance. If they exist, they are indicated in the technical data sheet of the water heater.
The nominal parameters of the protection device must exceed these rating data at least three times, otherwise false alarms will constantly occur.
Among the best manufacturers of differential switches are:
- Swedish-Swiss ABB ;
- French Legrand and Schneider Electric ;
- German Siemens and AEG ;
- Russian "KEAZ" , IEK and DEKraft .
European manufacturers have slightly higher prices. At the same time, products from Russian companies are often in no way inferior in quality.
Connection diagrams for electric boilers
For a water heater, the current leakage protection device can be installed directly in the apartment (cottage) electrical panel or directly on the wall near the heating device.
The principle of the connection sequence is the same in both cases - boiler, RCD, line circuit breaker, meter and general circuit breaker. In this case, the RCD and the circuit breaker of a specific line with a socket for the water heater can be swapped, both diagrams are correct.
The domestic water heater should be connected to a separate branch from the electrical panel. Moreover, ideally there should be no sockets or other electrical appliances on it.
A boiler is a rather dangerous device. It is best if the protective device only works for him. This will both increase the safety of operating the heater and make it easier to identify problem areas throughout the wiring around the house.
If the RCD is installed next to the water heater, then the wire from the protective device to the machine in the panel will be unattended. If the insulation on it is damaged, the boiler protection device simply will not work. It won't even notice the flowing electric current.
RCD connection diagram.
There are several RCD connection schemes. All of them are used quite often in practice, and now we will consider all of these schemes.
This is the most common RCD connection diagram. In this case, the device will protect a person from electric shock throughout the entire apartment. The current rating of the RCD is one order of magnitude higher than the current rating of the input circuit breaker. If in the RCD it is 40A, then in the circuit breaker it is 32A. The current rating can be increased depending on your current consumption needs. But the rating of the RCD should always be higher.
This scheme is good because it is budget-friendly. Since it only requires one RCD. But it also has its drawbacks. When your residual current device starts tripping, it will be very difficult to determine the cause of the trip. Since one device is responsible for the entire apartment or house.
Therefore, rich people choose the following RCD connection scheme.
From this diagram it can be seen that each group of sockets or lighting is responsible for its own RCD. And in front of it there must be a circuit breaker with a high current rating. And at the input there is a so-called fire protection RCD, where the differential shutdown rating is 100 mA.
In this case, you can separately install an RCD in rooms with high levels of humidity, where a differential shutdown rating of 10 mA is recommended. And separately for sockets and lighting in rooms with a shutdown rating of 30 mA. And if an RCD trips in a separate group of sockets, then it will be easier for you to establish the reason why it tripped. And you don’t need to turn off the power to the entire apartment.
Many people once lived without an RCD and felt protected. Because we followed basic safety rules. Then they began to use such protection as grounding and life became even better. But in those days, sockets were rarely installed in bathrooms. Now they are being installed more often and the demand for RCDs has increased. Therefore, many people believe that this device must be installed in rooms with high humidity levels, such as bathrooms. And they install it not for the entire apartment, but only for one room.
From this diagram it can be seen that the RCD is installed only for the bathroom. If you have a group of sockets in the bathroom, then install an RCD with a differential shutdown rating of 30 mA, and if you have only one socket, or more, but basically only one is always working, then install an RCD with a rating of 10 mA.
Possible installation errors
Mistake #1 . In order for the RCD to work correctly, contacts between the “working zero” and “ground” are not allowed in the protected circuit. Each of these wires must have its own bus. At the same time, “grounding” is not present at all in connecting the protection device. This conductor is not connected to it anywhere.
Mistake #2 . The operating current of the RCD is selected to be the same or slightly exceed the operating current of the machine in the circuit. Only in this way can the circuit breaker protect the protective device itself from overloads.
Mistake #3 . Inexperienced electricians often install sockets and RCDs directly under the water heater. This is strictly not recommended.
Leaks from hot water titanium cannot be completely excluded, and with such a layout of sockets and other electrical appliances with exposed wires under a potential “waterfall”, tragedy is not so far away.
Mistake #4 . The water heater cannot be connected only through an RCD or one automatic circuit breaker. These devices complement, but do not duplicate each other. They protect the boiler from fundamentally different problematic situations in the electrical network.
Mistake #5 . If you choose an RCD that is too sensitive (with a low leakage current), then it will trigger too often to block the circuit. The water heater will constantly turn off. As a result, the water will not heat up normally and the boiler may fail due to continuous switching on/off.
After completing the electrical installation, it is necessary to check the functionality of the RCD. To do this, most water heaters have a “TEST” function, which simulates current leakage. If everything is connected correctly and the protection is working, then the latter will trip and de-energize the boiler.
Otherwise, you need to look at where and what is not working as expected. It is recommended to carry out such checks once a month and thereafter.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
There are few nuances in installing a residual current device, but they exist. To make it easier for you to understand these issues and choose the right device, we have made a selection of relevant videos. They describe in detail the principles of operation and diagrams for connecting an RCD to a network with a water heater.
Connecting protective devices in networks without grounding:
What is an RCD, why is it needed in everyday life (using the example of connecting a washing machine):
It is not recommended to connect the water heater to the network without an RCD. Only a protective device that monitors current leakage can protect users. There are no difficulties in installing such a device; you can connect it to the power circuit yourself by selecting the parameters for the electric current.
Do you have personal experience in selecting and connecting an RCD to a water heater? Do you want to share your accumulated knowledge or ask questions on the topic? Please leave comments and participate in discussions - the feedback form is located below.
Rules for choosing ouzo
The most frequently asked question when installing and connecting washing machines: is it necessary to install an RCD for a washing machine? The answer is simple - yes, it is necessary. After all, the washing machine itself is a fairly energy-consuming device, and also operates in an environment with high humidity, due to which it belongs to the category of increased danger. That is why the installation of an RCD is necessary when connecting washing machines to the power supply network.
In order for the washing machine to serve for many years, and its operation to be safe, it is important to choose the right residual current device. To do this, you must follow the following rules:
- Device power. The choice of RCD for a washing machine based on power is based on the rated power of the electrical network. There are single-phase and three-phase devices.
- Mains voltage. Single-phase RCDs are designed for 220 V, and three-phase RCDs are designed for 380 V.
- Current strength. The most common RCDs, which are recommended by experts, have 30 mA protection. It can be set to 10 mA, but a similar degree of protection is not required for household electrical equipment.
- Design features of the RCD. Since the washing machine has a high level of power consumption, it is better to choose a class A residual current device. It is also possible to install class AC, but this type does not always perform its function well.
- Features of the release and marking of the machine. An RCD marked “C” is suitable for the electrical network in an apartment or private house. There are also devices with digital markings; in this case, the correct choice would be a device with a C16 marker or, more rarely, a C25.
- Additional levels of protection. Some RCD models do not have a protection system in case of a break in the neutral conductor, which leads to the device ignoring current leaks.
RCD for a water heater: how to choose and why it triggers
Now we will figure out why you need an RCD in a water heater and how to choose the right one for your equipment. We will also look at the reasons why the protection may work and how to minimize the risks.
When using a water heater, a residual current device (RCD) plays an important role in protecting people from electric shocks.
There are two types of water heaters (based on the speed of heating the liquid): instantaneous and storage. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, different energy consumption and operating principles.
Both the electricity consumption and the current strength that passes through the boiler depend on how the RCD for the water heater works. Naturally, if the RCD is not available, then the health risk increases.
Safety shutdown device for water heaters
To choose the right residual current device, you should pay attention to the power of the water heating element, the current strength in the power supply network and the distance at which the plumbing system and the water heater itself are located. Reliability of operation and safety will depend on these parameters.
Let us highlight the important parameters for choosing an RCD:
- The power of the structure depends on the rated power of the power supply network. There may be single-phase and two-phase models.
- Mains voltage. Single-phase residual current devices are needed for a boiler operating from a 220 V network, three-phase for a 380 V network.
- RCD protection level. It is better to use devices with a protection level of 30 mA. It is not recommended to install the boiler without grounding.
- Place of application of the protective device. Both letter and number markings are used. For an RCD installed in an apartment or house, a unit with a C16 or C25 marker is suitable.
- Useful qualities of a protective device. Water heaters are considered devices with high electricity consumption. As a result, it is better to play it safe and choose A-group devices. Sometimes you can consider the option of a group of speakers, but it is not a fact that it will cope with a high load.
Power cord with RCD for water heater: which one to install and how to check
When using a water heater, a residual current device (RCD) plays an important role in protecting people from electric shocks.
There are two types of water heaters (based on the speed of heating the liquid): instantaneous and storage. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, different energy consumption and operating principles.
Both the electricity consumption and the current strength that passes through the boiler depend on how the RCD for the water heater works. Naturally, if the RCD is not available, then the health risk increases.
Safety shutdown device for water heaters
To choose the right residual current device, you should pay attention to the power of the water heating element, the current strength in the power supply network and the distance at which the plumbing system and the water heater itself are located. Reliability of operation and safety will depend on these parameters.
Let us highlight the important parameters for choosing an RCD:
- The power of the structure depends on the rated power of the power supply network. There may be single-phase and two-phase models.
- Mains voltage. Single-phase residual current devices are needed for a boiler operating from a 220 V network, three-phase for a 380 V network.
- RCD protection level. It is better to use devices with a protection level of 30 mA. It is not recommended to install the boiler without grounding.
- Place of application of the protective device. Both letter and number markings are used. For an RCD installed in an apartment or house, a unit with a C16 or C25 marker is suitable.
- Useful qualities of a protective device. Water heaters are considered devices with high electricity consumption. As a result, it is better to play it safe and choose A-group devices. Sometimes you can consider the option of a group of speakers, but it is not a fact that it will cope with a high load.
Which RCD to install and how to connect it
You should immediately find out that there are several options for connecting an RCD to a water heater: into an outlet or through an additional copper cable.
Connection using a socket is possible for devices with low rated power. A prerequisite is grounding in the outlet, and when installed in a bathroom, it must be resistant to moisture. Otherwise, the high-power unit will heat up the outlet and the tightness of the connection between the plug and the socket will weaken. As a result, a gap will appear in the contacts and sparks will appear.
Connection using an auxiliary copper cable, which is connected to the electrical account and has a residual current device. There is no plug with socket, and switching off is carried out using a circuit breaker. The machine will protect the water heater, and users will be protected by a protective device.
The following video clearly demonstrates how to connect an RCD.
Why does the residual current device trip?
How to check an RCD and why does an RCD trip on a water heater?
Let's try to figure it out:
- Firstly, the cause may be a violation of the integrity of the insulating layer of the heating element. This happens while the water heater is operating. Current, water and elevated temperature begin to damage the insulation of the heating element, and the liquid begins to come into contact with parts that conduct current. To check the heating element, you should remove it from the boiler tank, descale it, and also do an inspection. If there are cracks on the surface, then the insulation layer is no longer suitable and the heater should be replaced.
- Secondly, the reason may be the following - electric current leakage. This can happen due, for example, to the fact that the boiler is connected to old electrical wiring, and over time the insulation has lost its appearance due to exposed wires, and a short circuit occurs.
- Thirdly, the protective device may not be selected in accordance with voltage and power standards. Therefore, the RCD cannot handle such a load and may trip from time to time.
- Fourthly, the device itself may be faulty. For example, the release mechanism could become unusable and even with small vibrations it could turn off.
It is possible and even necessary to check the RCD on the water heater. Once a month will be enough. To start the test mode, simply press the “test” button on the device itself. The device will create an electrical leakage situation and should automatically turn off.
What happens if you discover a system failure? How to repair a cord for a water heater with an RCD? A residual current device is a complex electronic device; only an electronics engineer can repair it using the necessary spare parts. And most often the device is not repaired, but simply changed.
Review of manufacturers
You can purchase a power cord with an RCD for a water heater from many manufacturers. The choice is great. However, it is better to give preference to reliable companies that have proven themselves, such as ABB, Legrand, AEG.
Manufacturer Country Features
| ABB | Sweden-Switzerland | The company develops and produces products in the field of power engineering, electrical engineering, and information technology. It entered the market in 1988 and is a collaboration between a company from Sweden (ASEA) and a company from Switzerland (Brown, Boveri & Cie). ABB has offices in more than one hundred countries around the world. |
| Legrand | France | The products of this company are used both in residential premises and industrial facilities. Legrand concentrates on the electrical business, and therefore has high positions in many countries around the world in this industry. Leadership positions are also ensured thanks to the production culture, as well as large investments in the development and research of new materials and technologies. Legrand is a product of high European quality standards. |
| AEG | Germany | The company is aimed at producing products in the fields of mechanical engineering, electrical energy and household goods. She is over 130 years old. During (and before) World War I, AEG was the largest weapons manufacturer. |
By choosing the appropriate type of residual current device and connecting it correctly, you will extend the service life of the water heater.
teplofan.ru
Which RCD to install and how to connect it
You should immediately find out that there are several options for connecting an RCD to a water heater: into an outlet or through an additional copper cable.
Connection using a socket is possible for devices with low rated power. A prerequisite is grounding in the outlet, and when installed in a bathroom, it must be resistant to moisture. Otherwise, the high-power unit will heat up the outlet and the tightness of the connection between the plug and the socket will weaken. As a result, a gap will appear in the contacts and sparks will appear.
Connection using an auxiliary copper cable, which is connected to the electrical account and has a residual current device. There is no plug with socket, and switching off is carried out using a circuit breaker. The machine will protect the water heater, and users will be protected by a protective device.
The following video clearly demonstrates how to connect an RCD.
Review of manufacturers
You can purchase a power cord with an RCD for a water heater from many manufacturers. The choice is great. However, it is better to give preference to reliable companies that have proven themselves, such as ABB, Legrand, AEG.
| Manufacturer | A country | Peculiarities |
| ABB | Sweden-Switzerland | The company develops and produces products in the field of power engineering, electrical engineering, and information technology. It entered the market in 1988 and is a collaboration between a company from Sweden (ASEA) and a company from Switzerland (Brown, Boveri & Cie). ABB has offices in more than one hundred countries around the world. |
| Legrand | France | The products of this company are used both in residential premises and industrial facilities. Legrand concentrates on the electrical business, and therefore has high positions in many countries around the world in this industry. Leadership positions are also ensured thanks to the production culture, as well as large investments in the development and research of new materials and technologies. Legrand is a product of high European quality standards. |
| AEG | Germany | The company is aimed at producing products in the fields of mechanical engineering, electrical energy and household goods. She is over 130 years old. During (and before) World War I, AEG was the largest weapons manufacturer. |
By choosing the appropriate type of residual current device and connecting it correctly, you will extend the service life of the water heater.
Why does the residual current device trip?
How to check an RCD and why does an RCD trip on a water heater?
Let's try to figure it out:
- Firstly, the cause may be a violation of the integrity of the insulating layer of the heating element. This happens while the water heater is operating. Current, water and elevated temperature begin to damage the insulation of the heating element, and the liquid begins to come into contact with parts that conduct current. To check the heating element, you should remove it from the boiler tank, descale it, and also do an inspection. If there are cracks on the surface, then the insulation layer is no longer suitable and the heater should be replaced.
- Secondly, the reason may be the following - electric current leakage. This can happen due, for example, to the fact that the boiler is connected to old electrical wiring, and over time the insulation has lost its appearance due to exposed wires, and a short circuit occurs.
- Thirdly, the protective device may not be selected in accordance with voltage and power standards. Therefore, the RCD cannot handle such a load and may trip from time to time.
- Fourthly, the device itself may be faulty. For example, the release mechanism could become unusable and even with small vibrations it could turn off.
It is possible and even necessary to check the RCD on the water heater. Once a month will be enough. To start the test mode, simply press the “test” button on the device itself. The device will create an electrical leakage situation and should automatically turn off.
What happens if you discover a system failure? How to repair a cord for a water heater with an RCD? A residual current device is a complex electronic device; only an electronics engineer can repair it using the necessary spare parts. And most often the device is not repaired, but simply changed.
Selection of protective device
When choosing an RCD for a boiler, it is necessary to take into account its technical characteristics. The main ones include the following:
- Operating current. Determined by the power of the water heater.
- Differential current. Depends on operating current.
By working is meant the current passed through the power contacts of the protective device. It directly depends on the power of the water heater. For example, if the boiler power is 2.5 kW, then the operating current is 2500/220 = 11.4 A. It is advisable to select the RCD with a margin of operating current. In this case, a 16 A device is suitable.
The differential current (leakage) is determined from the operating current of the consumer. For a boiler with a power of 2.5 kW and a current consumption of 11.4 A, an RCD with a leakage current equal to 11.4 * 0.4 = 4.6 mA will be required. This figure is approximate. It is influenced by the length and condition of the electrical wiring. Therefore, in everyday life, residual current devices with a leakage current of 30 mA are usually installed.
Additional Information. Current leaks also exist in fully operational equipment and wires. However, their level is minimal and is about 10 μA. If the cables are old, then the leakage value increases many times. Therefore, RCDs are not recommended for use with old equipment or wiring.