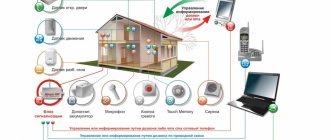
Types of products
The purpose of power wires is to transmit electricity to residential buildings, public organizations, and industries. Products are classified according to the parameters and characteristics of cables, internal wires, sheaths, etc.
External (external) protection from precipitation and changes in weather conditions in electrical wiring cables can be armored or unarmored. The control cable differs from the power wire in less strength, because has no reinforcement.
Based on the design of the current-carrying cores, products are divided into single-core cables or cables with 2-5 wires (multi-core).
Classification by voltage strength divides cables into those intended to operate under pressure:
- low;
- average;
- high.
Products differ in total mass and weight of individual elements (insulation, cores, screens).
Popular and in demand power cable designs include the following types:
- PPV;
- APPV;
- VVG;
- PVS;
- VBBShv;
- NUM;
- KG.
The PPV cable consists of a copper core (three-core), protected by a layer of polyvinyl chloride. The products are used for indoor lighting. Products must be attached statically.
APPV wire is made mainly of aluminum alloys; material runs along the length of the wire.
The core of the VVG cable consists of copper and has 1-4 cores. The protective coating consists of PVC. The cables are used to conduct lighting lines in residential and public complexes with different temperatures and air humidity.
Copper in the PVA wire ensures the plasticity of the structure. Depending on the thickness of the product, 2-5 twists of the rod parts are allowed. Wires are used in household appliances, lighting systems, and adapters.
VBBShV cables provide up to 5 twists of cores. The products are used in the construction of power lines. The products are distinguished by their strength and durability.
The NUM wire has an outer sheath of non-flammable material and 2-4 internal cores. The wires are optimal for electrical wiring. The advantage of the products is their resistance to deformation; the design can withstand temperature changes from -50 to +50°C.
What is the cable cross-section?
Regulates the requirements for the cross-section of the power cable, regardless of the material - PUE (Electrical Installation Rules). The reliability of the facility’s operation and fire safety depend on the correctness of the calculation. If you overload even an armored power cable that is well protected from mechanical damage, the minimum that will happen is that the automation will turn off. In extreme cases, overheating, insulation melting, smoke and fire occur.
Calculations should be made based on the total power of electrical appliances that will be used in everyday life. In production, they usually install a cable with a large “margin” so that if the current consumption sharply increases, there will be no downtime due to automation shutdowns. The formula for 220V networks looks like this:
Current = Power / 220.
In a three-phase 380V network, a different option is used:
Current = Power / (1.732 * 220)
Then the cross section is determined based on the value of the maximum current. It is calculated by the diameter of a single core using the formula for the area of a circle:
Section = 3.14 * wire diameter
If we are talking about a multi-wire power cable, it is enough to get the value of one line. In the case of a single core, there are no difficulties with the calculation; it is enough to measure its diameter using a caliper. The cross-section of a multi-core cable is determined by adding the cross-section of all cores. Here you cannot do without passport characteristics.
Table 1. Current permissible for a cable with a copper core in the open air
| Current, A | Power at 220V, W | Power at 380V, W | Section, mm2 |
| 1 | 0,22 | 0,66 | 0,5 |
| 2 | 0,44 | 1,30 | 0,5 |
| 3 | 0,66 | 1,97 | 0,75 |
| 4 | 0,88 | 2,63 | 0,75 |
| 5 | 1,10 | 3,30 | 1,0 |
| 6 | 1,32 | 3,90 | 1,0 |
| 10 | 2,20 | 6,60 | 1,5 |
| 16 | 3,52 | 10,50 | 1,5 |
| 25 | 5,50 | 16,45 | 2,5 |
| 35 | 7,70 | 23,03 | 4,0 |
| 42 | 9,20 | 27,60 | 6,0 |
| 55 | 12,10 | 36,19 | 10 |
| 75 | 16,50 | 49,36 | 16 |
| 95 | 20,90 | 62,52 | 25 |
| 120 | 26,40 | 78,98 | 35 |
| 145 | 31,90 | 95,43 | 50 |
| 180 | 39,60 | 118,40 | 70 |
| 220 | 48,40 | 144,70 | 95 |
| 260 | 57,20 | 171,10 | 120 |
| 305 | 67,10 | 200,70 | 150 |
| 350 | 77,00 | 230,30 | 185 |
When installing the power cable under the finishing, in the plaster, higher heating should be taken into account due to the lack of cooling by the surrounding air. To compensate for this, a section with a higher load capacity is taken. There are also generally accepted standards. For example, in housing, 2.5 mm copper cable is used for sockets, and 1.5 mm for lighting.
The concept of a core in electrical wiring
The structure of power cables includes plastic conductors made of metal alloys. The core can be single-wire or multi-wire. The configuration of the element’s cross-section varies (flat, sector). An important characteristic is the cross-sectional area of the core.
Current-carrying and neutral grounding conductors
The conductors, in accordance with their purpose, can be conductive or grounding (zero).
The conductor is the main element in the cable. The core may contain 1-5 wires. The shape of the elements according to the standards is round, segmented or sector-type. Products are standardized by section type and diameter.
Zero cores are used for uneven loads in the electrical network. Grounding threads have a small cross-section and are placed in the center of the wire. The elements ensure safe operation.
Core insulation
The cores in the wires must be insulated with a special coating.
The following are used as protective raw materials:
- paper;
- rubber;
- plastic.
Paper insulation involves applying layers to the conductors and impregnating the raw materials with a fire-resistant compound. The products are used on equipment operating under high voltage.
The insulating rubber coating is plastic, strong, durable. Cores with a rubber sheath are used in cables for connection to devices that are moved during operation. It is necessary to take into account the sensitivity of rubber to sub-zero temperatures. To prevent deformation, the cores are supplemented with a polyvinyl chloride coating.
The insulating layer made of plastic (polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride) is inexpensive, reliable, has high insulation, and a long shelf life.
Single-core and stranded
The power cable design includes wires:
- single-core;
- stranded.
A single-core wire includes 1 current conductor. The products are used in public buildings and residential complexes to supply electricity. In industrial premises, single-core wires are used to output electricity from generators to the general network.
Stranded wires consist of several intertwined wires. To increase ductility, a thread is pulled between the strands. The products are vibration-resistant, flexible, and are designed for connecting household appliances.
Main differences from wire
The term “cable” in everyday life often intersects with the concept of “wire”. Visually there is not much difference, except that cable products are characterized by the presence of several cores. If you remove the protective sheath from a power cable, you will end up with several single conductors (wires). Here is the difference between the two terms. Both pass electricity without problems. The main thing is that the characteristics match the voltage and power consumption.
Peculiarities:
- the brand of copper (aluminum) power cable contains information about the material of the cores, their quantity, and insulation method;
- two-, three- and five-wire options are common, designed for 220, 380V, but under different operating conditions;
- permissible power depends on the cross-section of the core and the material from which it is made;
- Regardless of the purpose, the distance between power cables is maintained up to 100 m.
They increase mechanical strength by including a steel core in the design. Usually no current passes through it, it serves as an “amplifier”, as in the case of a separately suspended wire. This option is often used in laying temporary power supply lines: along the ground or supports, through water barriers.
Single wire strands are used only for urgent repairs. The cable, depending on the number of conductors under general insulation, is used in domestic and industrial conditions. Thus, five-core ones are suitable for connecting to a three-phase 380V network (three phases, zero, ground). Three-core ones are used for European-quality renovation of residential and office premises, where the power of devices is supplied from a single-phase 220V line.
Core material
For the manufacture of cores, different types of raw materials are used (alloys of aluminum, copper, steel). Combined compositions and synthetic core materials are acceptable. To transmit optical signals, the wires are made of plastic or glass. Nichrome cores are used to dissipate thermal energy.
Copper
Copper cores, in accordance with manufacturing technology, are produced either ductile or rigid. The diameter of single-wire elements is 16-95 mm², multi-wire - 25-800 mm². Cores with a rigid structure have a round cross-section. Copper alloys are effective, reliable, durable, but have a high price.
Classification of cables and wires: photo features
- At the very beginning of the marking there are 4 or 3 letters. If the first letter is A, then an aluminum core is used. If there is no letter A, then the wire is copper.
- The next letter indicates the insulation material of the entire cable. B – vinyl (polyvinyl chloride), R – rubber.
- Then comes a letter indicating the insulation of each core. The decoding is the same as for cable insulation.
- The third (or fourth) letter indicates the features of the outer shell. A – asphalt shell, B – armored properties, D – bare, unprotected cable.
- Capital letters may be followed by small letters “ng”. They mean that the cable is non-flammable. Shv indicates that the outer cover is a PVC hose, Shp is a polyethylene hose.
Screens, fillers and shells
The design of a power cable includes the required layers between the insulation:
- screens;
- fillers;
- shells;
- protective coatings.
Screens are designed to protect outer layers from electromagnetic influence. The elements are made of foil and paper treated with a special compound.
Fillers are made in the form of bundles of plastic, rubber, and paper tapes. The elements allow you to adjust the tightness of the junction of parts of the structure. The compositions make the product airtight, resistant to mechanical stress, and give it the required shape.
Sheaths are designed to protect the surfaces of the wire. Parts of the structure are made of alloys of aluminum, lead, non-flammable plastic and rubber. Surfaces can be smooth or corrugated. Sheaths prevent deformation of the wire from the action of water and acid-base compounds.
The final components of the design are protective covers (cushion, armored cover). Armor made of galvanized strips and wires gives the product strength.
Cable marking
Marking helps to select a power cable without precise measurements. Its use is regulated by GOST 18690-82. If the standard is observed, products from different manufacturers are identical in all characteristics (within tolerances). Color and letter markings of power cables are used. The first type of designation simplifies the identification of a conductor for phase, neutral, and grounding.
Color options:
- yellow - phase A (L1);
- green - phase B (L2);
- red - phase C (L3);
- blue - zero bus;
- inclined yellow (green) stripes - grounding.
Compliance with such rules reduces the risks of incorrect connections and simplifies electrical repairs without a diagram. Just before installation, you still have to choose the brand of power cable. On price tags and packaging, a letter designation is used.
Labeling rules:
- 1st position - material from which the cores are made:
- A - denotes aluminum;
- absence of a letter - copper.
- B - polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
- P - polyethylene;
- PV - cross-linked polyethylene;
- PS - self-extinguishing polyethylene;
- R - rubber;
- G - bare wire;
- F - fluoroplastic;
- C - film insulation;
- KG - flexible cable.
- A - aluminum;
- C—lead;
- P - polyethylene;
- B - polyvinyl chloride;
- R - rubber.
- BS - lead;
- BBG – steel profiled tape;
- BB - two steel strips;
- K - steel wire covered with metal tape;
- D - steel braid of two wires;
- P - flat steel wire.
- G - waterproofing;
- E - shielding;
- N - non-flammable composition.
The choice depends on the application. The marking does not affect the permissible voltage of the power cable (the cross-section plays a role here). For example, the VVG marking means that there is waterproofing and double PVC braiding.
Electrical wiring insulation
The power cable sheath is designed to isolate products from the external elements of the building. The coating must not conduct current.
The main types of cable insulation are represented by coatings:
- from impregnated paper;
- made of durable rubber;
- made of polyvinyl chloride;
- made of polyethylene.
Polystyrene, fluoroplastic, magnesium oxide, etc. can be used as insulation.
The designs of cables covered with paper sheets with a sheath of aluminum and lead are optimal for transmitting electrical energy with a voltage of 35 kV (GOST 18410-73). Aluminum coated insulation materials are not recommended for production sites where caustic solutions are used. Lead-coated insulation protects against aggressive alkaline environments.
Cables with external rubber insulation are suitable for installation of electrical networks with direct voltage up to 10 kV. Wires are used in routes with different levels of electrical wiring (GOST 433-73). The products are highly hygroscopic and plastic. The wire structure is equipped with durable steel armor that prevents deformation.
Cables with polyvinyl chloride insulation are designed for electrical wiring with a rated voltage of 0.66-6 kV (GOST 16442-80). The materials are budget-friendly and flexible. When using additives, the composition becomes resistant to sub-zero or elevated temperatures.
What is a cable
The term “cable” comes from the word Capulum, which is translated from Latin as “arcanum”. It is a structure of several conductors (cores) insulated from each other, which are placed with a protective sheath along the entire length of the power cable. The insulation may consist of a polymer material, fabric, specially impregnated paper and an outer steel shell to provide mechanical strength.
Structural elements and the type of insulating material are selected based on the purpose of the cable products.
Thus, copper armored power cable is suitable for laying in the ground. Its design provides sufficient protection against accidental damage during road work, as a result of exposure to animals and insects. If you take a power cable with polyvinyl chloride insulation, its scope of application is limited to rooms where the risk of mechanical damage is lower.
Life time
The cable service life is regulated by state standards (GOST 16442-80, GOST 18410-73, etc.), divided into actual and warranty.
The product warranty is issued by the manufacturer for a period calculated from the start of use of the design. The procedure is valid if the buyer complies with the rules of transportation, installation, and operation. The warranty on wires with plastic insulation is at least 5 years. Cables with paper insulation are guaranteed for up to 4.5 years.
The cable shelf life represents the actual period of use of the structure up to the technical parameters permitted by the standard. The actual duration and period of operation for cables with plastic insulation is about 25 years. Wires insulated with impregnated paper can be used for up to 30 years.
Lighting wires and cords (Table 47)
Table 47. Technical characteristics of lighting wires and cords
| Group, product brand | Cross-section of current-carrying conductors, mm2 | Number of conductors | Operating voltage, V | Climatic performance | Notes |
| SHVVP | 0,5; 0,75 | 2; 3 | Up to 450/750 | U, T, UHL | — |
| Ball screw | 2 | ||||
| ShVP-2 | 0,35; 0,5; 0,75 | 2 | |||
| ShVL | 0,5: 0,75 | 2; 3 | |||
| PVS | 0,75; 1,0; 1,5; 2,5; 4,0 | 2; 3; 4; 5 | |||
| ShVO | 0,5; 0,75; 1; 1,5 | 2 | 380 | UHL | Flexible cord with cross-linked polyethylene insulation, PVC sheathed, braided made of threads for connecting heating devices |
| ShVO | 0,75; 1; 1,5 | 2; 3 | 380 | UHL | Same |
| PUNP | 1; 1,5; 2,5; 4; 6 | 2; 3; 4 | 250 | U | The shell is black. Upon request, the casing can be made in any color |
| PUGNP | 0,75; 1; 1,5; 2,5; 4; 6 | 2 |
Power wire PVS
PVS cables (vinyl insulated connecting wire) consist of flexible multi-core insulated conductors of small or medium cross-section, twisted together and covered with a polyvinyl chloride sheath. The number of current-carrying conductors varies from 2 to 5; there are wires with or without a grounding conductor. They can withstand temperature fluctuations from minus 40 to plus 40 degrees Celsius. When laid alone, the cable does not propagate combustion, the heating limit is 70 degrees. Rated voltage 380-660 volts, test voltage 2000 volts. Widely used as a conductor for connecting low-power equipment to the network.
Definition
Power cable - in a broad sense, is a cable for transmitting electrical energy, connecting consumers to power from distribution boards of industrial and municipal facilities. It is traditionally accepted that a wire for connecting lighting devices with a cross-section of less than 1.5 sq. mm is lighting, and a cable for connecting more powerful devices is power (this also does not include speaker wire for an amplifier, network wire for a computer, television) .
In some cases, the lighting wire is also called the supply wire. For example, when connecting powerful lighting devices. It is also fair to call twisted pair power cable for retro wiring.