What is dry water?
The recipe for dry water was invented by the 3M company in the 90s of the last century. Scientifically, this liquid is called Novec. The discovery of this refrigerant was a real breakthrough. After all, it had the goal of replacing freons, which are dangerous for the ozone layer.
Today, several types of liquid are produced under the Novec brand. They differ from each other in density, boiling point and some other characteristics. But, in general, they all have quite amazing properties to one degree or another.
Principle of operation
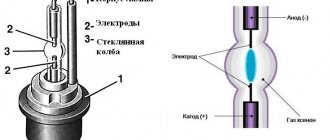
Semiconductor or rectifier diodes have a fairly simple operating principle. As we have already said, a diode is made of silicon in such a way that one end is p-type and the other end is n-type. This means that both pins have different characteristics. One has an excess of electrons, while the other has an excess of holes. Naturally, there is a region in the device in which all the electrons fill certain gaps. This means that there are no external charges. Due to the fact that this region is depleted of charge carriers and is known as the combining region.
Photo - principle of operation
Despite the fact that the connecting area is very small (often its size is several thousandths of a millimeter), current cannot flow in it in the usual way. If a voltage is applied such that the p-type area becomes positive and the n-type area becomes negative, the holes move to the negative pole and help electrons pass through the combining area. In the same way, electrons move to the positive contact and, as it were, bypass the unifying one. Despite the fact that all the particles move with different charges in different directions, they ultimately form a unidirectional current, which helps to rectify the signal and prevent voltage surges at the diode contacts.
If voltage is applied to a semiconductor diode in the opposite direction, no current will flow through it. The reason is that the holes are attracted by the negative potential, which is in the p-type region. Likewise, electrons are attracted to a positive potential that is applied to the n-type region. This causes the combining region to increase in size, making it impossible for directed particle flow to occur.
Photo - characteristics of semiconductors
Weight, viscosity, fluidity
The properties of the new Novec substance are unique. No other composition has them. It is significantly heavier than ordinary water. If, for example, you take a two-liter bottle of Novec and put it on the scale, then the needle will approach 3 kilograms. The density of the liquid is 1.5 grams per cubic centimeter.
The viscosity of dry water is two times lower than that of ordinary water. Therefore, its fluidity exceeds even the fluidity of alcohol. Hence the unusual wetting properties. If, for example, you dip two identical paper napkins in Novec and in ordinary water, you can immediately see the difference. In ordinary water, the paper will quickly become wet. In dry water, the napkin will only become slightly damp, and soon after it is removed from the liquid it will again be completely dry. It seems that this liquid substance does not wet anything. But, in fact, she is simply too mobile.
Current-voltage characteristics
The current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode depends on the material from which it is made and some parameters. For example, an ideal semiconductor rectifier or diode has the following parameters:
- Resistance for direct connection – 0 Ohm;
- Thermal potential – VG = +-0.1 V;
- In the direct section RD > rD, i.e. the direct resistance is greater than the differential resistance.
If all parameters correspond, then the following graph is obtained:
Photo - CVC of an ideal diode
This diode is used in digital electrical engineering, the laser industry, and is also used in the development of medical equipment. It is necessary for high demands on logical functions. Examples: laser diode, photodiode.
In practice, these parameters are very different from real ones. Many devices are simply not capable of operating with such high accuracy, or such requirements are not necessary. An equivalent circuit characterization of a real semiconductor demonstrates that it has serious disadvantages:
Photo - current-voltage characteristic in a real semiconductor diode
This current-voltage characteristic of a semiconductor diode indicates that during direct connection, the contacts must reach the maximum voltage. Then the semiconductor will open to allow the passage of electron charged particles. These properties also demonstrate that current will flow normally and without interruption. But until all parameters match, the diode does not conduct current. At the same time, the voltage for a silicon rectifier varies within 0.7, and for a germanium rectifier it varies within 0.3 Volts.
The operation of the device is very dependent on the level of the maximum forward current that can pass through the diode. In the diagram it is defined by ID_MAX. The device is designed in such a way that when switched on directly, it can only withstand an electric current of limited strength. Otherwise, the rectifier will overheat and burn out, like a regular LED. Different types of devices are used to control temperature. Naturally, some of them affect the conductivity, but they prolong the performance of the diode.
Another disadvantage is that when passing alternating current, the diode is not an ideal isolating device. It only works in one direction, but leakage current must always be taken into account. Its formula depends on the other parameters of the diode used. Most often, circuits designate it as IOP. A study by independent experts found that germanium transmits up to 200 µA, and silicon transmits up to 30 µA. At the same time, many imported models are limited to a leakage of 0.5 µA.
Photo - domestic diodes
All types of diodes are susceptible to voltage breakdown. This is a property of a network that is characterized by limited voltage. Any stabilizing device must withstand it (zener diode, transistor, thyristor, diode bridge and capacitor). When the external potential difference between the contacts of a rectifying semiconductor diode is significantly higher than the limited voltage, the diode becomes a conductor, reducing the resistance to a minimum in one second. The purpose of the device does not allow it to make such sharp jumps, otherwise it will distort the current-voltage characteristic.
Is it possible to mix dry and regular water?
In addition to the above amazing properties, dry water has one more feature. She easily rejects other substances. For example, in Novec, ink or paint from a felt-tip pen will not float on paper. Which is almost impossible to prevent in ordinary liquid.
You cannot even brew tea from a bag in boiling dry water. This liquid cannot dissolve the substances from the tea leaves.
Mixing regular and dry water also won’t work. You can verify this by dropping a dye, for example brilliant green, into such a mixture. You will see a clear boundary between the liquids. Zelenka will dissolve in ordinary water, and dry water will remain transparent. The same effect will occur if you try to mix Novec with alcohol.
Where to buy and how much does dry water cost?
Buying dry water is quite difficult. This can only be done by having friends who work in specific industries or in specialized online stores. For one liter you will have to pay 4 thousand rubles or more. For a barrel of 15 kilograms you will have to pay more than 2 thousand euros.
Firefighting remains Novec's main application area today. However, China is already trying to use this liquid as a coolant for cooling computer equipment. And perhaps soon the dry water recipe will also be used to cool home computer processors.
Dependence of resistance on temperature
The most common effect of current is thermal effect. As already noted in the last chapter, the mechanism of this action is the collision of electrons with the nodes of the crystal lattice, as a result of which the kinetic energy of the electrons is converted into the internal energy of the conductor.
In turn, having increased internal energy, lattice nodes begin to vibrate faster, colliding with electrons more often. That is, electrons are braked more efficiently. In other words, as the temperature of the conductor increases, its electrical resistance increases.
A simple experiment confirming this theoretical conclusion can be heating the conductor in a circuit with the lamp and measuring instruments turned on (see Fig. 3).
Rice. 3.
As the conductor warms up, the lamp will begin to shine less brightly, and the instruments will begin to show a drop in current strength.
After qualitative confirmation of the dependence of resistance on temperature, a quantitative dependence was obtained. After a series of experiments, it was found that the relative increase in resistance is directly proportional to the absolute increase in temperature:
Or:
Here: – resistance at a given temperature, – resistance at temperature ; – temperature change relative to ; – temperature coefficient of resistance. Temperature coefficient is a tabular value known for most metals. Coefficient dimension:
Since the linear dimensions of the conductors change slightly when the temperature changes, this means that the resistivity changes, and according to the same law:
Applications of Superconductivity
The use of superconductivity greatly facilitates many technical aspects of the use of electric current. Firstly, no resistance means no heating losses, which typically account for 15% of the total energy. As confirmation, we can cite the experiment of passing current through a conductor immersed in liquid helium for two years, which was interrupted only due to a lack of helium
The absence of heating and energy loss is extremely important for electric motors and electronic computers
In addition, due to the lack of resistance, extremely high currents flow in superconductors, creating strong magnetic fields, which can be used in thermonuclear fusion.
A household example of the use of superconductors is the currently existing railway network with magnetic levitation trains (Fig. 6):
Rice. 6. Magnetic levitation train
High temperature superconductors
After the discovery of superconductivity, Onnes, trying to create a superconducting electromagnet, discovered that changes in current, or magnetic fields, destroy the effect of superconductivity. Only by the middle of the twentieth century was it possible to create superconducting electromagnets.
Also an extremely important discovery was made in 1986. Materials have been discovered that exhibit superconductivity at temperatures around
Such temperatures can be achieved using liquid nitrogen, which is much cheaper than liquid helium. However, when trying to create such superconducting wires and cables, they encountered the problem of the extreme fragility of such materials, which crumble during the rolling process. At the moment, work is ongoing to solve this problem.
In the next lesson we will look at electric current in semiconductors.
Bibliography
- Tikhomirova S.A., Yavorsky B.M. Physics (basic level) - M.: Mnemosyne, 2012.
- Gendenshtein L.E., Dick Yu.I. Physics 10th grade. – M.: Ilexa, 2005.
- Myakishev G.Ya., Sinyakov A.Z., Slobodskov B.A. Physics. Electrodynamics. – M.: 2010.
Additional recommended links to Internet resources
- Storage.mstuca.ru (Source).
- Physics.ru (Source).
- Elements (Source).
Homework
- How does the resistance of metals depend on temperature? What causes this dependence?
- How many times will the resistance of a copper wire increase when the temperature increases from 200 to 300?
- Water got on the connected electric stove coil. How has the glow of the tile changed?
- *Do all metals become superconductors when cooled to low enough temperatures?