When using batteries at any facility, especially in uninterruptible power supply systems, their condition must be monitored and checked regularly. In this material we will look at the main parameters of the battery, and also consider what devices and how to monitor and test them!
The main task when checking the condition of any battery is to find out whether it has sufficient capacity and can provide the characteristics declared by the manufacturer for the required time. However, only a few basic parameters are determined directly by measuring instruments - voltage, current. In serviced batteries, you can also measure the density of the electrolyte. Measurements can be taken repeatedly, recording changes in values over time. All other parameters and characteristics are not measured directly, but are derived using a method developed by the manufacturer, and it depends on the type of battery, the manufacturer’s recommendations, and the type of connected load. It is necessary to take into account that many dependencies characterizing the operation of the battery are nonlinear. Other factors may also play a role, such as temperature.
When performing short-term measurements using even the most advanced techniques, testing is not accurate quantitative, but qualitative. The only reliable way to measure the capacity of a battery is to completely discharge it over many hours, carefully recording the parameters during the entire process. But it is not always possible to use such a lengthy procedure in practice, especially if there are a lot of batteries. However, short-term evaluation measurements are sufficient to distinguish a working battery from a worn-out one that has lost capacity, and to replace the battery in a timely manner.
Measurements using a load fork
The structure of the simplest load fork is shown in the diagram:
The device is equipped with a voltmeter, parallel to which a high-power load resistor is installed, and has two probes. In older models, voltmeters are analog; newer models are usually equipped with an LCD display and a digital voltmeter. There are load forks with a complicated circuit, using several load spirals (replaceable resistances), designed for different voltage measurement ranges, intended for testing acid or alkaline batteries. There are even plugs that are used to test individual battery banks. In addition to a voltmeter, advanced devices may include an ammeter.
The data obtained from measurements must also be compared with the parameters declared by the manufacturers for a given type of battery and a given resistance.
Leakage current
If the above measurements are not so difficult to understand and remember the steps, then you need to move on to the question of how to check the capacity of a car battery for current leakage. This is an indicator on which the volume of the battery capacity itself, and therefore its “life”, directly depends.
The level of self-discharge allowed for a battery at rest is specified in its technical documentation. However, it is worth knowing that alkaline types of batteries have the highest level!
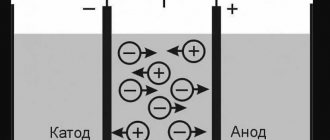
Any leak implies a break or poor sealing in the battery power circuit. And if the measurements revealed a leakage level much higher than the technically permissible level, then the battery will discharge even faster. But not only battery discharge can become a problem, since poor insulation of individual sections of the power circuit can lead to a short circuit or fire!
To test the level of battery current leakage, the multimeter is switched to the appropriate mode, and the voltage indicator is set to 10 Amps. The multimeter is connected in this way: the red wire is connected to the positive terminal, and the black wire is disconnected completely.
The leakage indicator is determined as follows: if nothing is displayed on the device monitor, it means that the test of the car battery capacity was successful, there is no leakage! If there are any indications, then it is urgent to check the entire on-board system.
Measurements using special devices, battery analyzer testers
Devices Pendant
A fundamental development of the idea of a load fork can be considered the family of digital testers Kulon (Kulon-12/6f, Kulon-12m, Kulon-12n and others) for checking the condition of lead-acid batteries, as well as other similar devices. They allow you to quickly measure voltage, approximately determine the battery capacity without a test discharge, and store several hundred and sometimes thousands of measurements in memory.
Pendant devices are powered by a battery, which is used for measurements. The included wires with alligator clips have parts insulated from each other, which provides a four-clamp connection to the battery and eliminates the influence of resistance at the terminal connection points on the readings of the device. According to the developer, the device analyzes the battery's response to a test signal of a special shape, while the measured parameter is approximately proportional to the active surface area of the battery plates and, thus, characterizes its capacity. In fact, the accuracy of the readings depends on the reliability of the methodology developed by the manufacturer.
Battery capacity - the electrical charge delivered by a fully charged battery - is measured in ampere-hours and is the product of the discharge current and time. To accurately determine the capacity, it is necessary to discharge the battery (a long process, many hours), constantly recording the amount of charge given by the battery. In this case, the relative capacity of the battery varies nonlinearly depending on time. For example, for a battery type LCL-12V33AP, the relative capacity changes over time as follows:
| Discharge time, hours | Relative capacity, % |
| 0,1 | 37 |
| 1,3 | 48 |
| 0,7 | 53 |
| 1,9 | 76 |
| 4,2 | 84 |
| 9,2 | 92 |
| 20 | 100 |
The Coulomb device uses a quick measurement to approximately determine the capacity of a fully charged battery . It is not intended to assess the state of charge of the battery; all measurements must be carried out on a fully charged battery. The device briefly emits a test signal, records the response from the battery, and after a few seconds gives the approximate battery capacity in ampere-hours. At the same time, the measured voltage is displayed on the screen. The obtained values can be stored in the device’s memory.
The manufacturer emphasizes that the device is not a precision meter, but allows you to estimate the capacity of a lead acid battery, especially if the user has independently calibrated the device using a battery of the same type as the one being tested, but with a known capacity. The calibration procedure is described in detail in the instructions for the device.
PITE testers
The next type of device for testing batteries is PITE testers: Kongter BT-3915 model for measuring the internal resistance of batteries.
Control is carried out using a color touch screen, but the main control buttons are located on the keyboard at the bottom of the case. The device can test batteries with a capacity of 5 to 6000 Ah, with battery cells of 1.2 V, 2 V, 6 V and 12 V. The voltage measurement range is from 0.000 V to 16 V, resistance is from 0.00 to 100 mOhm. The device allows you to set the type of batteries being tested, measure voltage and resistance (model 3915) or voltage and conductivity (model 3918), and based on them, judge whether the battery capacity corresponds to that declared by the manufacturer or not. In this case, the Capacity parameter (battery capacity) is displayed as a percentage.
The device interface allows you to carry out both single and sequential measurements (up to 254 measurements in each sequence, the total number of results is more than 3000), which is convenient when testing a large number of batteries of the same type (in the latter case, the results are saved automatically, in addition to the data, a serial number is also recorded in them measurements). Depending on the settings, the device can use its own criteria or user-specified values to produce a result (Good, Pass, Warning or Failed status). Test results can be transferred to a computer via USB port for viewing and subsequent preparation of reports.
Fluke Analyzers
A deeper development of the same idea is the Fluke Battery Analyzer 500 series (BT 510, BT 520, BT 521), which allows you to measure and store voltage, internal resistance of a stationary battery, negative terminal temperature, and discharge voltage. With additional accessories, other parameters can be measured and stored in memory. Tests can be carried out both in individual measurement mode and in sequential mode; using custom profiles. It is possible to set threshold values for various parameters. The built-in USB port allows you to transfer collected records (up to 999 records of each type) to a computer for reporting using the included Analyze Software.
The probes of the device have a special design: the internal spring-loaded contact is designed to measure current, the external one is designed to measure voltage. When pressure is applied to the stylus, the inner tip moves inward so that both contacts of each stylus touch the surface at the same time. As a result, the same probes allow you to organize both 2-wire and 4-wire connections to the battery poles (the latter is necessary for Kelvin measurements).
- The device allows you to measure the following parameters:
- Internal battery resistance (measurement takes less than 3 s).
- Battery voltage (performed simultaneously with internal resistance measurement)
- Negative terminal temperature (there is an IR sensor next to the black tip on the BTL21 Interactive Test Probe)
- Discharge voltage (determined several times during discharge or during load test)
It is also possible to measure ripple voltage, measure AC and DC current (if current clamps and an adapter are available), and perform the functions of a multimeter. Fluke analyzers can use the BTL21 Interactive Test Probe with a built-in temperature sensor. A wide variety of additional accessories are compatible with the devices (current clamps, extension cords of different sizes, removable flashlight, etc.).
Although the device has rich functionality, the key stage in determining the condition of the battery remains the comparison of the measured indicators with those calculated or specified by the manufacturer for this specific type of battery. The Fluke Battery Analyzer 500 Series is convenient for bulk battery inspection. The sequential mode and profile system allow you to perform the necessary measurements one after another, the results are memorized by the device and stored in an ordered form, sequentially numbered and divided into groups. But the device does not have the function of directly or indirectly measuring the battery capacity in ampere-hours - if only because for batteries of different types today it is hardly possible to develop a single accurate method for such determination.
All of the devices listed above, although they differ from each other in size, belong to the portable class. A separate group includes stationary complexes for testing batteries, which can conduct quick tests with determination of internal resistance, monitor all parameters, including active and reactive components of resistance, control the discharge/charge process, etc. Such complexes are more likely addressed to research laboratories, industrial battery manufacturers and developers of new equipment than end users.
How to restore battery capacity?
To ensure the operability of all vehicle components, it is not enough to know how to determine capacity. Motorists should explore ways to restore charge.
Preparation
Before restoring the charge and capacity of the battery, the power source is inspected. Electrolytic leaks are removed from the body. Conductive terminals are cleaned of dust, dirt and oxides.
The contaminated electrolytic composition is drained. It is also mandatory to wash the tanks and cans that are included in the composition.
Lead plates are checked. If the integrity of the elements is compromised, it is not worth restoring the charge. After all, these actions will not bring any results.
Control training cycle
Carry out to reduce the effect of sulfation and restore charge. What is the essence of this cycle? So, the battery is charged and discharged 2–4 times.
To control the process use:
- Hydrometer. With its help, the density of the electrolytic composition is controlled.
- Bulb. With its help they create a certain load.
- Voltmeter or multimeter. Such devices are used to estimate current, voltage, and other parameters.
The frequency and duration of charging is set individually.
Multiple charging
Between charging and discharging cycles, breaks of 12–16 hours are established. The charging time is 7–8 hours. A more precise period is set taking into account the current strength, rated capacity, and other parameters.
A break between cycles is necessary to ensure that there is a uniform potential on the surface of the lead plates.
The number of restoration processes reaches 4–5. During this period, the degree of density of the electrolytic composition increases. If the density has increased excessively, the electrolytic composition is diluted. For this purpose, distilled water is used.
Chemicals
The essence of this technique is to pour sodium solution into the power source. This is done after draining the distilled water and washing the housing. The special solution is poured 2-3 times.
Monitoring the capacity of a car battery helps extend its service life. After all, even minor deviations provoke a rapid discharge, destruction of lead plates, and the formation of oxides. Every motorist can easily choose a way to check this indicator that is ideal.
Full discharge/charge
Today, complete discharging and charging is the only direct and most reliable way to determine the battery capacity. Specialized battery discharge/charge monitoring devices (UKRZ) allow deep discharge and subsequent full charging of the battery with constant capacity monitoring. However, this procedure takes a very long time: 15-17-20-24 hours, sometimes more than a day, depending on the capacity and current state of the battery. Although the method gives the most accurate results, its use is limited due to the time required.
Measuring internal battery resistance
Using this circuit, you can measure the internal resistance of the battery. It can be roughly represented as a resistor connected to the battery terminals from the inside.
To increase accuracy, you need to take a more powerful load so that the current is at least 50 amperes (and preferably 100 or more). For this, a “battery” of lamps with a total power of at least P=U*I=12*50=600 watts is suitable. If you get more, the measurement will be more accurate. Instead of lamps, you can use a resistor made, for example, from a spiral for an iron or electric stove. You just need to accurately measure its resistance. Two measurements are made:
- at idle, record the voltage at the battery terminals E;
- under load, measure the current I and voltage at the terminals U.
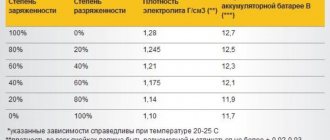
Electrolyte density measurement
In serviced batteries, to determine their condition, you can measure the density of the electrolyte, since there is a direct relationship between this parameter and the battery capacity. The density of the electrolyte can change due to various reasons, which are also interrelated (frequent deep battery discharge, sulfation, suboptimal electrolyte density, evaporation and leakage of the solution, etc.). The battery begins to discharge faster and releases less charge. It is necessary to understand that the density of the electrolyte, even in a working battery in ideal condition, is not a constant; it changes with temperature and the degree of charge of the battery. Moreover, for different regions, the recommended electrolyte density differs depending on typical climatic conditions.
The results of density measurements with a hydrometer can be compared with the following diagram for acid batteries.
Depending on whether the density of the electrolyte is greater or less than the required one (and deviations in either direction are harmful for the battery), you can partially or completely replace the electrolyte, add distilled water or a solution of the required concentration, making sure to ensure stirring. As with all previously described methods of checking the condition of the battery, the key is to compare the measured values with the battery manufacturer's recommendations and follow all prescribed maintenance procedures.
Control discharge technique
To check the battery with a multimeter using the test discharge method, the load is first calculated. It should be equal to the strength of the discharge current. This parameter is recorded in the technical documentation that comes with the power source.
How to check the battery capacity if the passport is missing? The data is easy to find on the manufacturer's website.
The multimeter remains connected until the current drops to 50-60%. The value that was obtained is compared with that stated in the technical data sheet. If they differ significantly, it is recommended to replace the power supply.
Checking other parameters of the car power supply
A modern multimeter is multifunctional. With its help, not only the residual capacity of the battery is measured.