The effect of electric current on the human body
Current, unlike other hazardous media, is colorless, odorless, and invisible.
Electric current has the following types of effects on the human body: thermal, electrolytic, biological. Let's look at each of these impacts in more detail.
The thermal effect consists of burns to areas of the body, heating of blood vessels and nerve endings. This type of action is also called thermal. Because thermal energy obtained from electrical energy creates burns.
Electrolytic exposure leads to the decomposition of blood and other fluids in the body through the process of electrolysis, which causes disturbances in the physico-chemical composition of these fluids. The essence of the damage comes down to the molecular level - thickening of the blood, changes in the charge of proteins, steam and gas formation in the body.
The biological effect of electric current on the body is accompanied by irritation and excitation of organs. This causes spasms and contractions.
In the case of the heart and lungs, this effect can be fatal due to the cessation of respiratory and cardiac function.
Biological effects cause mechanical damage to human organs and joints. Mechanical damage can also be caused by a person falling from a height due to exposure to electric current.
Biological and mechanical effects
The degree of damage can vary and leaves its mark on living tissue. Current can leave thermal, electrolytic, mechanical and biological “imprints”. Usually it is the last 2 categories that are distinguished.
The mechanical, or as it is also called dynamic, effect of electric current is determined by the delamination and rupture of various tissues. This affects mainly muscle and lung tissue, and the walls of blood vessels in the circulatory system. This happens under the influence of an electrodynamic effect, as well as the instantaneous explosive formation of steam from superheated tissue fluid and blood.
The biological effect of electric current on the human body can be understood by the activation of living tissues and a change in their functionality. Additionally, there is a disruption of internal bioelectric processes, which up to this point were proceeding normally. This work directly affects viable functions. The biological effects of current in this interpretation are considered to be of a very dangerous type.
Additional Information ! Determining the type of exposure can help guide the treatment process.
Thermal - gives itself away as burns in certain areas of the body. Blood vessels, nerve endings, heart, brain and other organs are heated to very high temperatures. Such overheating causes serious disorders of tissue functions. Organic fluid decomposes, namely lymph, blood, and cellular fluid.
Thermal damage
This is accompanied by significant disturbances in body fluids and its physical properties. Many changes occur in the chemical composition.
What reasons influence the consequences after an electric shock?
There are several routes for current to travel through the body. Depending on this scheme, an electrocardiogram is determined, which determines the sign of coronary insufficiency, and morphological studies show the presence of a sign of myocardial infarction.
Note ! Such data are confirmed by numerous clinical observations and analyses.
A person who has suffered an electrical injury, even if he feels normal, cannot be left without medical supervision. The victim should be hospitalized for 3 days under the category of “potentially seriously ill.”
Disruption of body systems
Even after a long-standing incident, there were cases when the victim began to develop diabetes, thyroid disease and reproductive system disease. Diseases such as allergies, persistent negative changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and autonomic-endocrine disorders may also occur.
Cases of delayed complications have been recorded in history. These were mainly mental problems (schizophrenia, psychoneuroses). For several years (months) after the event, some people developed cataracts. Victims who have been in an electrical circuit often experience unexpected bleeding even at the time of treatment.
People whose work involves electric current develop the following chronic diseases:
- Super early arteriosclerosis.
- Endarteritis.
- Disorders of the autonomic system.
The consequences of old electrical injuries in most cases appear many years after the incident. It turns out that the effect of electric current is not without its consequences. This often leads to decreased ability to work, suppressed body functions, and the acquisition of chronic diseases.
This essence of the effect of electric current on the human body has statistical indications. In the first month, 30% of victims already experience results; in 15%, this occurs after six months.
Electrical safety, the dangers of electricity
So why is electricity dangerous for the human body? There are two main reasons here. This is a simple mechanical damage to tissue, and in addition, an effect on the human nervous system, leading to very serious consequences.
From the history of the development of electricity, it is known that the Italian doctor Luigi Galvani used dissected frogs in his experiments, because there were no electrical measuring instruments at that time. A weak electric current passed through the nerve endings caused the muscles of the frog's legs to contract. Now this phenomenon has been studied quite well, and everyone knows that not only frog legs, but all human muscles, including the heart, contract from electrical impulses generated by the central nervous system. A person has his own electricity, very low-power, but sufficient to control the entire body, all its organs.
If a person comes into contact with a bare live conductor, two dangerous situations are possible. Firstly, it has an effect on the nervous system. As mentioned above, the human body is controlled by weak electrical impulses. If an electric current from an external source passes through human tissue, the body reacts to it as if it were electrical signals from its central nervous system. But external signals can turn out to be much stronger than internal ones, they can simply be “drowned out”, so they cause erratic, convulsive contraction of muscles that come into a state of constant tension and cannot be relaxed. In such cases they say that electric current attracts.
Threshold palpable, non-releasing and fibrillation currents
The degree of danger of electric current affecting a person depends on its value. An electric current that causes tangible irritation when passing through the human body is called tangible current , and the smallest value of this current is called threshold tangible current .
A person begins to feel the impact of a small current passing through him: on average, about 1.1 mA with alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz and about 6 mA with direct current. This effect with alternating current is manifested by mild itching and slight tingling (tingling), and with direct current, a feeling of heating of the skin in the area touching the current-carrying part.
A threshold perceptible current cannot cause injury to a person, but prolonged (several minutes) passage of this current through a person can adversely affect his health. In addition, a noticeable current can become an indirect cause of an accident, since a person, having felt the effects of electric current, loses confidence in his safety and may perform incorrect actions. Unexpected exposure to significant current is especially dangerous when working near live parts at height and in other similar conditions.
An electric current that, when passing through a person, causes irresistible convulsive contractions of the muscles of the arm in which the conductor is clamped is called non-releasing current , and its smallest value is the threshold non-releasing current . Threshold non-releasing currents are different for men, women and children. Their approximate average values are: for men - 16 mA at 50 Hz and 80 mA at constant current, for women - 11 and 50 mA, respectively, for children - 8 and 40 mA.
Fibrillation current is an electrical current that causes fibrillation of the heart as it passes through the body. Its smallest value is called threshold fibrillation current . An electric current of 50 mA or more at 50 Hz, passing through the human body, spreads its irritating effect to the muscles of the heart, thereby causing it to contract chaotically and stop.
At a frequency of 50 Hz, fibrillation currents range from 50 mA to 5 A, and the average value of the threshold fibrillation current can be considered 300 mA. A current greater than 5 A, either alternating or direct, causes immediate cardiac arrest, bypassing the state of fibrillation.
The basis for organizing the safe operation of electrical installations is high technical literacy and conscious discipline of maintenance personnel, who are obliged to strictly observe special organizational and technical measures, rules and regulations for safe work in existing electrical installations, as well as techniques and sequence of operational operations.
Electric current from 0.5 to 1.5 mA
A person will definitely feel the impact of the passing current if its strength is 0.6-1.5 mA. This indicator is determined by the threshold perceptible type. It does not pose a significant danger. A person without the help of others can interrupt contact with a source of electric current.
Minor indicators
This is a slight effect of electric current, which is manifested by a slight tingling or tingling sensation.
Power 15 mA
With a current strength of 10-15 mA, a person is no longer able to take his hand off the electrical wires or break the circuit. Such a current is conventionally called “non-releasing current”. This value provokes contraction of the muscles of the hand and forearm. The pain is significant. As a result, the victim cannot throw away the wire. The duration of this action may cause changes in the body.
Power above 25mA
A current of 50 mA provokes damage to the respiratory and circulatory system. At 100 mA, cardiac fibrillation occurs - the organ stops its work, blood circulation stops.
Electricity
The electrolytic effect of current on the human body is expressed in the form of sudden cardiac arrest and respiratory paralysis.
Dangerous voltage
First of all, we note that it is a mistake to think about the presence of dangerous and non-hazardous electric current - any impact is negative, only the degree of harm differs. The reason why one person will suffer less and another will suffer more is due to internal resistance. It also depends on the thickness of the skin, the humidity level of the room in which the contact occurred, and the human body, as well as the path of the current.
And this needs to be given special attention, because the most dangerous current flow for human life is either through the leg and head, or through the arm and head. This is because the current passes through the heart, brain and lungs. And if the DC or AC voltage is high, then in worst cases it causes cardiac or respiratory arrest.
It has been established that direct current is slightly safer for humans than alternating current if everything happens within networks up to 500 V. And as soon as the voltage begins to rise, the danger to humans grows along with it.
However, this is not all, because it is also important to consider the network frequency. If we take 500 Hz for consideration, then it is somewhat safer than industrial 50 Hz. This is due to the fact that with increasing frequency, the Skin Effect gradually appears, the essence of which is the passage of current along the surface of the conductor, due to which the internal organs are not affected.
The final value of the danger of current for a person is time. If you are exposed to direct or alternating current for a long time, the damage will be higher than a short-term shock. And, although here you also need to take into account the strength of the current in order to give a definite answer, the less time under influence, the better.
Causes of Electrical Damage
Many causes of electrical injuries are very banal - absent-mindedness of the victim himself. Damage occurs as a result of incorrect current supply and power surges. The reason may be poor insulation or direct contact with electrical installations without first disconnecting.
The causes of electric shock can be systematized as follows:
- technical - faulty equipment;
- organizational - safety precautions are not followed;
- psychophysiological - severe fatigue, inattention.
Most injuries occur at work. As a result of examining each case, it was noted that people are more often injured at the end and beginning of a work shift. Electric shocks often occur during workers' morning shifts. At the end of work, attentiveness decreases and severe fatigue develops. But the frequency of morning injuries is explained by the peculiarity of the work order: most work with electrical installations occurs at the beginning of the shift.
Types of electric shock
Electrical injury is an injury caused by exposure to an electric current or electric arc. This variety of effects of electric current on the body often leads to various electrical injuries, which come down to two types:
- Local electrical injuries, when local damage to the body occurs;
- General electrical injuries, so-called electric shocks, when the entire body is affected due to disruption of the normal functioning of vital organs and systems.
Local electrical injury is a pronounced local violation of the integrity of body tissues caused by exposure to electric current or electric arc. The danger of local electrical injuries and the complexity of their treatment depend on the location, nature and extent of tissue damage, as well as on the body’s response to this damage. As a rule, local electrical injuries are cured, and the victim’s ability to work is fully or partially restored.
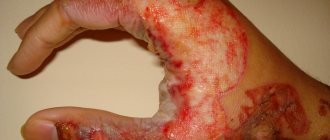
Typical local electrical injuries are electrical burns, electrical marks, skin metallization, mechanical damage and electroophthalmia.
- Electrical burns are divided into current (contact) and arc.
- Electrical marks , also called current signs or electrical marks, are sharply defined spots of gray or pale yellow color on the surface of the body of a person who has been exposed to an electric current.
- Metallization of the skin is the penetration into the upper layers of the skin of the smallest particles of metal melted under the action of an electric arc.
- Mechanical damage is in most cases the result of sharp involuntary convulsive muscle contractions under the influence of current passing through the human body. As a result, ruptures of tendons, skin, blood vessels and nerve tissue, and joint dislocations can occur. Of course, injuries caused by falling from a height, bruises on objects, etc. are not considered electrical injuries. as a result of exposure to current.
- Electroophthalmia (from the Greek ophthalmos - eye) is an inflammation of the outer membranes of the eyes - the cornea and conjunctiva (the mucous membrane covering the eyeball), resulting from exposure to a powerful stream of ultraviolet rays, which are vigorously absorbed by the body's cells and cause chemical changes in them. Such irradiation is possible in the presence of an electric arc, which is a source of intense radiation not only of visible light, but also of ultraviolet and infrared rays.
- Electric shock is the excitation of living tissues of the body by an electric current flowing through it, manifested in involuntary convulsive contractions of various muscles of the body.
The outcome of the effect of electric current on the human body depends on a number of factors, including the value and duration of the current passing through the body, the type and frequency of the current, as well as the individual properties of the person. An electric shock, even if it does not lead to death, can cause serious disorders in the body that appear immediately or after a certain time.
As a result of an electric shock, cardiovascular diseases (cardiac arrhythmia, angina, blood pressure disorders, etc.), as well as nervous diseases (neurosis, endocrine disorders, etc.) may arise or worsen.
Electric shock
Electric shock is an extreme reaction of the body to the effects of electric current; during shock, severe disorders of all organs and systems develop. At first, excitement develops when a person does not feel pain and seems to be fine, but there is no need to rejoice because then inhibition sets in when the nervous system “switches off”, blood pressure drops and the pulse becomes frequent, consciousness is depressed, the person does not respond to external stimuli .
The state of shock can last, depending on the functional capabilities of the body, from several minutes and last several days. After a critical period, gradual recovery or death may occur. It all depends on the treatment performed and first aid provided correctly.
By type of contact
Damages may be:
- contact - there is direct contact of electricity with the human body, the current directly passes through its tissues,
- non-contact or arc - injury occurs when a person is exposed to an electric arc; as such, the passage of current through the body does not occur,
- mixed - the impact of both traumatic factors is combined.
By type of receipt
Depending on the method of receipt, electrical burns are divided as follows:
- household - a person receives them at home. Most often they are mild and do not pose a serious threat to life,
- natural - lightning burns are considered the most dangerous, few people survive after them,
- industrial ones are among the most serious, since enterprises use enormous voltage current.
Outcome of electric shock
Situations are different, so the outcome of an electric shock varies. When receiving a strong electric shock, problems with blood circulation and breathing are caused. Severe cases are characterized by cardiac fibrillation: the heart muscles twitch chaotically. In fact, the heart stops functioning normally, so in such a situation, prompt medical intervention is required.
Often, electric shock has a force of up to 1000 V. Burns occur if the force exceeds 1 A. The most common reason is a person’s failure to comply with safety regulations. The element through which electricity passes is located close to the human body, resulting in a spark discharge resulting in varying degrees of burns. When accidentally receiving a spark discharge, the current in contact with the body heats the tissue to 60 degrees Celsius. The protein begins to coagulate, and subsequently a burn appears on the affected area. Electrical burns are dangerous because they are quite difficult to cure.
Electric shock can have different consequences
Degrees of electrical burns
There are several degrees of severity of electrical damage to a person:
- First. The mildest, accompanied by slight redness and swelling of the skin. After properly provided first aid, treatment can be continued at home.
- Second. Involves deeper tissue damage with the formation of blisters. The victim feels severe pain. Treatment usually takes place at home, but under the supervision of a doctor.
- Third. It is characterized by skin necrosis and the formation of blisters with bloody contents. If, after opening the blisters, the red wound surface is exposed, this indicates a favorable prognosis with adequate therapy. If the skin becomes dark and does not hurt, we can assume complete tissue death with no prospect of recovery.
- Fourth. Necrosis occurs of both the skin itself and subcutaneous fatty tissue, muscles, and bone tissue. In this case, only emergency medical intervention will save a person’s life.
Physical impact
First aid for electric shock.
This is primarily thermal damage. The heat generated when electric current passes through a conductor (in this case, the human body) depends on the resistance of this conductor. This value for dry human skin is approximately 1000 Ohms, which is quite enough to cause burns of varying severity (this, of course, depends on the current strength and does not mean that contact of electricity with wet skin is preferable).
The resistance drops sharply, and the electrical discharge penetrates further into the human body, having a stronger effect on the internal organs.
Physical effects also include eye damage from electric arc flashes or short circuits. Harsh ultraviolet light can seriously burn the retina of the eye, causing short-term or permanent blindness, inversion of color vision, etc.
Classification of premises in relation to the danger of electric shock
Depending on certain conditions that increase the danger of exposure to electric current on a person, different rooms have different degrees of danger of electric shock - some are greater, others are less. In accordance with the Electrical Installation Rules, premises with respect to the danger of electric shock to people are classified as follows:
1. Premises without increased danger , in which there are no conditions that create increased or special danger. In such rooms, the relative air humidity is less than 60%, there is no high temperature, conductive dust, chemically active or organic environment, conductive floors, and the possibility of simultaneous contact with the metal structures of buildings, apparatus, mechanisms and metal casings of electrical equipment.
2. Premises with increased danger , characterized by the presence of one of the following conditions creating an increased danger:
- dampness (relative humidity more than 75%) or conductive dust;
- conductive floors (metal, earthen, reinforced concrete, brick, etc.);
- high temperature (temperature constantly or periodically (more than one day) exceeds 35°C);
- the possibility of simultaneous human contact with metal structures of buildings connected to the ground, with technological devices, mechanisms, etc., on the one hand, and with metal casings of electrical equipment (exposed conductive parts) on the other.
3. Particularly dangerous premises , characterized by the presence of one of the following conditions creating a particular danger:
- special dampness (relative air humidity is close to 100% - the ceiling, walls, floor and objects in the room are covered with moisture);
- chemically active or organic environment (rooms containing aggressive vapors, gases, liquids, deposits and mold that destroy insulation and live parts of electrical equipment);
- two or more high-risk conditions at the same time.
In terms of the danger of electric shock to people, the territory of open electrical installations is equated to especially dangerous premises.
Natural phenomena dangerous to the network
Another dangerous factor for household equipment is the so-called overvoltage, which is caused by lightning discharges and internal processes of electrical networks. Usually this type of danger is undeservedly forgotten when installing protective equipment in an electrical panel, and meanwhile, overvoltages caused by lightning discharges often cause not only malfunctions of electrical and, especially, electronic equipment, but also put this equipment out of action, which requires owners of expensive repairs. What is the reason for such phenomena? The answer lies in the school physics course. Let's imagine a building whose power supply is carried out via an overhead power line (OHL). During a thunderstorm, a lightning discharge spreads electromagnetic oscillations around itself, which induce voltage in the overhead line conductors. Then, through the wires, the induced voltage enters the network of our home and affects the equipment connected to the network.
Considering that the voltage of a lightning discharge can reach a million volts, a voltage is induced in the network, sometimes reaching several thousand volts and lasting thousandths of a second. Of course, equipment, especially those containing electronic components, is not able to withstand such overvoltages without consequences. At best, this will cause a malfunction, but most often with such impacts we are talking about equipment failure. However, you can protect yourself from such dangers with the help of surge protection devices (SPDs) or, as they are also called, surge arresters (SPDs). Installed in an electrical panel, they are able to limit the surge voltage to safe values, thereby protecting the equipment connected to the network. Modern SPDs are able to protect the electrical network at home even if a lightning strike strikes directly into the power line wire. Such devices are available in the Acti 9 line of surge protectors manufactured by Schneider Electric.
So, we have looked at all types of dangers that may await us when using electrical energy. However, if you choose and install security devices correctly, you can protect our home and ourselves and make it safe and comfortable.
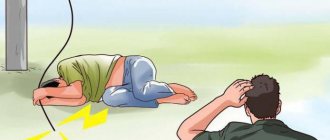
First aid rules
To properly provide first aid to the victim, you need to adhere to the following algorithm:
- It is very important to stop the impact of the traumatic factor as quickly as possible. It is necessary to open the circuit by unplugging the plug from the socket, moving the electrical wire away with a wooden object, or simply dragging the person away from the power source. At the same time, it is important to take care of your own safety. It is strictly forbidden to step on water or touch the victim with bare hands .
- If the person is conscious, you need to ask him in detail about his state of health and immediately call an ambulance.
- If the victim has lost consciousness, it is necessary to check for signs of life - breathing, pulse. If they are absent, you should immediately begin resuscitation measures - chest compressions and artificial ventilation.
- The person's torso should be higher than the head. It is advisable to place a cushion of clothing, a blanket or any other available materials under your feet.
- Before doctors arrive, you should carefully examine the victim’s body for visible injuries.
- It is advisable to find places of burns - entrance and exit zones. They must be covered with a sterile bandage to prevent infection.
Electrical network overload
Another type of accident in the electrical network, in which the current in the circuit exceeds the permissible limit for the elements of the electrical network. This is no less dangerous, because despite the lower currents, it lasts longer and can lead to heating of electrical structures and, ultimately, to a fire. Unfortunately, overload is one of the most common phenomena and it occurs, as a rule, through the fault of people themselves. Many people are familiar with the situation when there are not enough sockets in the house. In this case, they act simply - they use devices such as extension cords with several sockets, but this does not take into account that the total current consumption in a given section of the electrical circuit may exceed the permissible limit, say, for the outlet to which the extension cord is connected. The result is predictable - the outlet will begin to heat up and, if this section of the circuit is not turned off, will eventually ignite, which can lead to a fire. This is why overload protection is absolutely necessary in the electrical network.
At the moment, the functions of protection against overload and short circuit are performed by devices called circuit breakers. These are compact devices that combine protective properties with a number of additional functions. For example, in the Acti 9 series circuit breakers from Schneider Electric, you can use additional contacts to monitor the on/off state and timely detect the moment of emergency shutdown. This is convenient if we are talking about a country house. The owner will undoubtedly feel much calmer about the safety of his property if he has the opportunity to control the situation remotely.