LED lighting is very popular among our compatriots. And it’s absolutely no coincidence! It allows you to create a soft, pleasant light and significantly saves energy costs. At the wiring planning stage, it is advisable to calculate the number of LED lamps required to illuminate the areas. How to calculate the illumination of a room? You will learn about this in detail from our article.
Why do you need to calculate illumination?
The calculation of the number of lamps and the choice of their power is made in order to create comfort for a person under artificial lighting conditions. The fact is that excessively bright light or, on the contrary, its lack forces our eyes to strain. Frequent eye strain leads to vision loss. In addition, scientists have proven that poor lighting negatively affects the psycho-emotional state of the human body.
The ideal light for our eyes comes from natural light sources (morning, afternoon and evening light). The key task of designing lighting systems is to create conditions under which artificial light in the room will be as close as possible to natural light.
The results of the conversion of electrical energy into electromagnetic radiation are perceived by our visual organ as light. SNiP contains rules according to which lighting devices are selected for various types of premises.
Nuances of room lighting
To illuminate rooms, they are guided by the area of the room, the chosen layout of lamps (for example, with a chandelier and LED spotlights) and the power of the lighting fixtures. The light should be evenly distributed throughout the apartment or office.
Recommendations of regulatory documentation on lamps for public buildings
- SP 52.13330 “Natural and artificial lighting. Updated edition of SNiP 23-05. 95*":
7.23 In public buildings, as a rule, a general lighting system should be used. It is allowed to use a combined lighting system in administrative buildings where visual work of A-B categories is performed (for example, offices, workrooms, reading rooms of libraries and archives, etc.).
4.29 The choice of the type of luminaires should be made taking into account the nature of their light distribution, economic efficiency and environmental conditions.
4.33 In rooms with light ceilings of administrative and educational buildings, to reduce brightness contrasts in the field of view, as a rule, lamps should be used that direct at least 10-15% of the luminous flux they emit to the upper hemisphere.
4.34 To create the highest level of vertical illumination in a lighting installation for general uniform illumination, luminaires with luminous intensity curves of types L, D and M (semi-wide, cosine and uniform) should be used.
4.37 Lighting of rooms equipped with displays should be done with direct-light fluorescent lamps, which have limited brightness in the zone from 50 to 90° from the vertical (luminaires with non-luminous sides and screening grilles or prismatic diffusers). (Like a four-lamp raster lamp built into Armstrong ceilings),
- SP 31.110-2003 “Design and installation of electrical installations of residential and public buildings”:
4.22 To increase the energy efficiency of lighting installations, as a rule, discharge light sources should be included in projects.
Why LEDs?
A few years ago, many of our compatriots began to use energy-saving fluorescent lamps with E14 and E27 sockets. But now the turn has come for more efficient devices - LEDs, which demonstrate lower energy consumption (compared to incandescent lamps - 10 times, compared to fluorescent lighting devices - 3 times).
Advantages of LEDs
The undeniable advantages of LED lamps have made them popular all over the world. Such lamps are many times more effective than conventional incandescent lamps and devices emitting fluorescent light.
Advantages of LED lamps:
- energy saving;
- creating light as close to daylight as possible;
- Possibility of use both indoors and outdoors (street lighting);
- higher voltage swing - lamps will operate in the range from 80 to 230 Volts;
- increased service life - up to 25 years;
- environmentally friendly, since they do not emit harmful substances into the air;
- the ability to control the backlight using a remote control;
- silent operation unlike fluorescent lamps.
The disadvantages of such lighting devices can be considered the increased price and low color rendering index, reaching 85-90%.
Practical recommendations
It is accepted by hygienic standards that in rooms in which a person works (or is simply constantly present), the illumination should be at least two hundred lux. Moreover, such illumination should reach a maximum on the working surface (usually the value taken is 0.8 meters from the floor). Also, the efficiency of propagation of lamp rays can be affected by the height of the room; the higher it is, the further the light source is from the plane of the table. If the ceilings in the office are high, a correction factor of 1.5 must be introduced into the calculation, which increases the total number of lamps, since the luminous flux of the required intensity simply does not reach the workers’ places. Therefore, it is logical that for rooms with larger internal space, more lamps should be used. As an option, in this case you can use lamps with long suspension wires. They are easily adjustable to any ceiling height - very convenient. And the light hits exactly where it should. To illuminate the work area, it is preferable to choose linear models; they will evenly illuminate the entire surface.
As for the choice of the lamps themselves and the lamps for them, for general lighting it is best to give preference to models such as the popular raster lamps. Today they are equipped with economical and very bright LED systems. They provide a soft and even background, do not flicker or fade during operation as much as fluorescent ones.
Raster lighting
It is advisable to choose lamps that shine in the sunny yellow or neutral white spectrum. Due to the minimal difference from natural insolation, they provide the least visual fatigue and highly efficient work of personnel.
What parameters are taken into account when calculating illumination with LED lamps?
How to calculate the number of lamps? To do this, use a special formula, the final result of which will depend on individual parameters. Let's take a closer look at what factors will affect the calculation.
Lighting standards
Each type of room has its own lighting standards. For example, in a production workshop where high-precision work is performed, more light is required than in a hallway or bathroom.
Lighting standards depending on the type of room
| Room type | Light, in suites |
| office | 300-500 |
| conference hall | 200 |
| kitchen, bedroom, guest room | 150 |
| hallway, pantry, bathroom | 50 |
| children's | 200 |
| library or office | 300 |
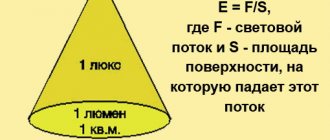
The given lighting standards are expressed in Lux. Lux is a unit created to compare the light of a device with 1 sq. m. area. That is, light of 1 Lux corresponds to a luminosity of 1 Lumen per 1 sq. m. premises.
Room type
SNiP standards will always indicate the type of room for which you need to select a lighting device. Of course, brighter light is created in office spaces, the library and the children's room. Corridors, staircases, and bathrooms do not require increased brightness of lamps.
Room parameters
To perform the calculations, you will need to know the area of the room. It is calculated using a formula known to us from school: S = a*b, where S is the area of the room (m2), a is the length of the room (m), b is the width (m).
In addition, the correction factor is taken into account. It is formed taking into account the height of the ceiling. The higher the wall, the more light will be scattered on the way to illuminating the work surfaces and floor.
Correction factor
| Ceiling height, m | Coefficient |
| up to 2.7 | 1 |
| 2,7-3 | 1,2 |
| 3-3,5 | 1,5 |
| 3,5-4,5 | 2 |
Power of LED lamps
This parameter is selected after calculating the lighting. The correct choice of lighting equipment power will ensure comfortable living conditions in the room.
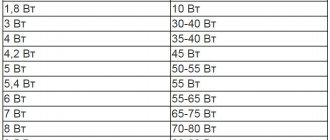
What to do if the manufacturer does not indicate the luminosity of LED lamps? Refer to the following table.
Correspondence of power to luminous flux
| Power, Watt | Luminous flux value, Lumen |
| 3-4 | 250-300 |
| 4-6 | 300-450 |
| 6-8 | 450-600 |
| 8-10 | 600-900 |
| 10-12 | 900-1100 |
| 12-14 | 1100-1250 |
| 14-16 | 1250-1400 |
Type of luminaire being calculated
There are several types of LED lamps: spot, industrial, ceiling, street. The formula for calculating the illumination of each of them has its own differences.
Calculation algorithm
Calculating the luminous flux is quite simple. The formula involves only 3 components, which are multiplied among themselves.
It is enough to multiply 3 parameters:
- Lighting standards.
- Room area.
- Correction factor.
An example of calculating room illumination
It is necessary to choose an LED lamp for a kitchen of 15 square meters. m with a ceiling height of 2.6 m. What power will the lighting fixture have?
Calculation
The kitchen lighting standard is 150 Lux. Then the luminous flux will be: 150*15*1= 2250 Lumens.
Based on the table of power to luminous flux, we select the number of light bulbs and their power. For example, you can purchase 2 lamps with a power of 12 W each or 4 lamps with 8 W each.
As you can see, illumination is calculated using a completely simple formula!
Modern office lighting: LED panels versus fluorescent lighting
Let's start the comparison with lighting calculations. For calculations you need to know the following parameters:
- room size;
- ceiling height;
- color of walls, ceilings and floors;
- accepted reflection coefficients;
- accepted lighting standards;
- illumination pulsation coefficient;
- safety factor.
The first 4 parameters can be obtained from the room drawings.
We select illumination standards according to SP 52.13330.2011. If you cannot determine the illumination standard, then more complete data should be found in SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03.
For office premises, the normalized pulsation coefficient in accordance with SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03 is no more than 10%, and if computer work is carried out in the premises, this value is no more than 5%.
Safety factor (SP31.110):
- discharge lamps 1.4;
- LED light sources 1.1.
Two methods for calculating the number of luminaires
There are 2 ways to determine the number of lamps for normal room lighting:
- By electrical power.
- By luminous power.
The first option is considered simple, but not so accurate. In the second case, they resort to a similar calculation algorithm, but lumens are used in the formula.
Electric power calculation method
How many watts per square meter? The norm is 20 W*m. sq. To calculate illumination, use the following formula: S*N/W, where S is the area of the room, N is the lighting rate, W is the electrical power of the lamp.
Example
There is a children's room with an area of 17 sq. m. This type of premises is equipped with LED lamps with a power of 60 W. How many lighting fixtures will be needed to create comfortable living conditions for a child?
Calculation of lamps:
17*20 = 340 W
340/60 = 5.6 lamps.
Electricians recommend rounding up. Therefore, you need to buy 6 LED lamps.
Calculation method based on luminous power
Calculation in lumens is a more accurate option when selecting lighting fixtures. The sequence of actions is similar to the algorithm for calculating electrical power. The only difference is that they use Lumens, not Watts.
For example, for a corridor of 10 square meters. m. will require 500 Lumens (10 sq. m. * 50 Lux). If you plan to use devices with a light output of 300 Lumens, then you will need to buy 2 lamps (500/300 = 1.7).
Illumination norms and standards
It is not the employee himself or his employer who determines what the correct lighting for the workplace should be.
The standards are regulated by regulations, which set the permissible brightness level in Lux. Regulations:
- SNiP - building codes and rules for lighting design;
- SanPiN - sanitary rules and regulations, which include all occupational hygiene, including light hygiene;
- GOST R 55710-2013 - regulates lighting standards inside buildings.
The level of light varies depending on the type of work being performed. Types of production are divided into high-precision, medium-precision, and low-precision labor. The lighting used in high-precision manufacturing workplaces differs from that in low-precision workplaces. Below are the brightness standards depending on the required accuracy:
- highest accuracy - 5000 Lux;
- very high - 4000 Lux;
- high - 2000 Lux;
- medium - 750 Lux;
- small - 400 Lux;
- rough - 200 Lx.
The table shows lighting standards depending on the type of office space:
| Room | Standards, according to SNiP |
| Office with computers | 200-300 Lux |
| Server room | 400 Lux |
| Operations or cash room | 400 Lux |
| Large open-plan office | 400 Lux |
| Visitor's room | 300 Lx |
| Cabinet for drawing work | 500 Lux |
| Photocopying room | 300 Lx |
| Conference hall | 200 Lx |
| Flights of stairs and escalators | 50-100 Lux |
| Hall, corridor, vestibule | 50-75 Lux |
| Archive | 75 Lux |
| Pantry | 50 Lx |
How to choose LED lamps for a room?
LED lighting of premises should be guided by the following indicators:
- Scattering of light.
- Colorful temperature.
- The amount of luminous flux.
For example, when choosing matte light, soft diffused lighting is achieved (suitable for an office and small areas), while transparent light distribution is more relevant for large rooms. Warm light is more suitable for the lounge area, neutral white for illuminating work surfaces, and cold light for illuminating warehouses.
Types of spotlights
There are many options for spot lighting. Spotlights can be overhead (attached to walls or ceilings) or recessed. Depending on the type of adjustment, there are rotary and non-rotating devices, downlights, stops, gimbal LEDs and retractable devices.
How to calculate LED strip lighting?
LED strip is designed to decorate a room. The calculation method is based on the intensity of the luminous flux per 1 linear. m. tape. Of course, you can choose high-power LEDs. But they are more suitable for street lighting - facades, neon signs and billboards. For home decoration, 6.5-24 W lamps are sufficient.
Optimal workplace lighting - how to calculate it
To determine the illumination coefficient, you need to apply the following formula:
KO = Luminous flux (Watt)/room area (sq.m.)
In proportion to the increase in area, the efficiency of the light flux decreases.
Organizing a comfortable workplace
Uniform lighting is an important requirement for the workplace. This is important to ensure eye comfort during work, because otherwise, vision will have to constantly adapt to changes in the type of lighting. Adaptation occurs as the size of the pupil, the amount of photosensitive substance, etc. changes.
If you go from a very light room to complete darkness, the eye will take a long time to fully adapt (more than an hour), the reverse process will take 15 minutes.
It is important to know! The smaller the difference between the illumination of the zones, the faster the adaptation occurs, the less harmful it is to vision.
An example of improper lighting is the backlighting of a document on a table and the lack of lighting for a monitor or books, which you also have to look at regularly. The frequent need to adapt causes fatigue and eye strain.
Recommendations for organizing a place of work:
- position facing the window or left side for right-handers, right side for left-handers;
- the location of the lamp is in the same way, above the workplace outside the prohibited angle of 45 degrees;
- avoiding blinding of the eyes by the rays of the lamp reflected from the working surface, legs, base of the lamp.
Visual comfort factors
When decorating the interior of office premises, it is important to take into account the color scheme of the walls, because it affects people differently. It is best to choose pastel colors, as well as greenish and yellow shades that are pleasing to the eye. There are other factors of visual comfort:
- suitable brightness;
- homogeneity of light;
- no glare or flicker;
- desired contrast.
Glare, or strong glare, is bad for the eyes - the property of bright surfaces to worsen contrast and disrupt visual comfort. Light fluctuations also cause eye fatigue; they greatly reduce labor productivity, so they are also unacceptable.
Selecting lamps for workplace lighting
LED lamps are ideal for the eyes. In addition, they are economical, last a long time, consume little electricity with excellent efficiency. Halogen lamps are less preferable, although their color reproduction is also quite good. The downside is that they are very hot and cannot be used in any lighting devices. Fluorescent lamps are also used in production, but the light from them is less suitable for the eyes and is unnatural.
By choosing the right lamp and positioning it correctly, you can be sure of maintaining eye health.
Proper lighting of the production area
By type, industrial lighting of a room (like any other) is divided into natural and artificial.
Natural light is the most valuable: the human eye is most adapted to it. It enters the building through windows and other transparent building structures (for example, aeration skylights).
Daylight
Types of artificial lighting:
- general;
- local;
- combined.
Local lighting is not used by itself; it is used only in combination with general lighting. A suitable lighting device can be portable or stationary. The light spot from it does not even illuminate the areas adjacent to it.
Combined building illumination method
Combined - required when workers perform high-precision operations that do not allow the appearance of sharp shadows from any objects.
Only combined lighting can ensure compliance with safety standards at the enterprise
General - organized in workshops with the same type of work (for example, in foundries). There are cases when combined lighting is simply not possible to organize.
The established illumination for workplaces with minor work corresponds to 500 Lux, gradually decreasing to 50 Lux in various storage areas.
For maximum efficiency, you can illuminate technical or street areas with devices with motion sensors to turn on the lights.