Every experienced gardener knows the huge role that properly selected lighting for indoor plants plays. Along with watering and soil, light is an indispensable component on which successful growth directly depends. It is no secret that in the natural environment, some plants thrive in shaded areas, while others cannot develop without direct exposure to sunlight. At home, the situation looks similar. Let's talk in detail about how to properly make artificial lighting for indoor plants.
Decorative lighting and lighting for plant growth
A lamp for growing indoor plants is a great way to extend daylight hours. After all, many indoor flowers are of tropical origin, which means they experience a daily lack of solar energy, especially in winter. For effective plant growth, the daylight hours should be about 15 hours. Otherwise, they weaken, stop blooming and are susceptible to various diseases.
When planning the future illumination of indoor flowers, it is important not to miss the aesthetic component. The phytolight should become part of the interior, a unique decorative element. There are a huge number of lamps on sale with wall mounts of different shapes, suitable for any energy-saving lamp: CFL or LED. Depending on the size of the home flower garden, lighting can be made from several spot lights aimed directly at each green pet, or from tubular fluorescent lamps with a reflector. Using your own imagination, you can make an original LED phytolight yourself.
The most important component of growth is the light spectrum
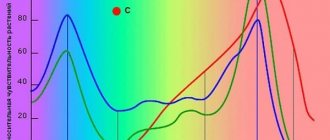
In order to understand how inhomogeneous light is from different electrical sources and the sun, you need to look at their spectral composition. The spectral characteristic is the dependence of the radiation intensity on the wavelength. The solar radiation curve is continuous throughout the visible range with a decrease in the UV and IR regions. The spectrum of artificial light sources in most cases is represented by individual pulses of different amplitudes, which as a result gives the light a certain hue.
During the experiments, it was found that for successful development, plants do not use the full spectrum, but only its individual parts. The following wavelengths are considered the most vital:
- 640–660 nm – velvety red color, necessary for all adult plants for reproductive development, as well as for strengthening the root system;
- 595–610 nm – orange for flowering and fruit ripening;
- 440–445 nm – violet color for vegetative development;
- 380–400 nm – near UV range to regulate the rate of growth and formation of proteins;
- 280–315 nm – mid-UV range to increase frost resistance.
Lighting with only the listed rays is not suitable for all plants. Each representative of the flora is unique in its “wave” preferences. This means that it is impossible to fully replace the sun's energy using lamps. But artificial lighting of plants in the morning and evening hours can significantly improve their life.
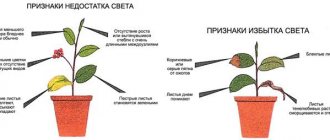
Signs of lack of light
There are a number of signs by which it is easy to identify a lack of light. You just need to take a close look at your flower and compare it with the standard. For example, find a similar view on the Internet. A clear lack of illumination manifests itself as follows. The plant slows down its growth. The new leaves are smaller and the stem becomes thinner. The lower leaves turn yellow. The flower either stops blooming completely, or the number of buds formed is less than the statistical average. It is assumed that watering, humidity and air temperature are normal.
How much light do you need?
It is impossible to give a definite answer to this question. Just as a person can live in different parts of the globe, so an indoor flower can grow on a windowsill facing north, south, west or east. Throughout its life, the plant will strive to adapt to current conditions: stretch upward due to lack of light or, conversely, expose the next blossoming bud to the sun’s rays.
By observing the appearance of the stems and leaves, the size and number of flowers, you can determine the adequacy of the lighting level. At the same time, do not forget about what stage of development the indoor flower is at: growing season, flowering, seed ripening. At each stage, it takes light from the sun of the wavelength that it needs at the moment. Therefore, when organizing additional lighting, it is important to take into account the qualitative component of the light flux.
Long-term exposure to bright light from the sun and lamps with an illumination level of more than 15 thousand lux is favored by those indoor flowers that grow in the open air in their natural habitat. These are many people's favorite crassula, geranium, kalanchoe, and begonia. Artificial lighting for plants of this type in the evening will benefit them.
Representatives of the flora that feel comfortable in illumination of 10–15 thousand lux include spathiphyllum, clivia, saintpaulia, tradescantia and dracaena. The leaves of these types of indoor flowers do not like hot sunlight, but also do not tolerate early twilight. Therefore, the ideal place for them would be a window sill with access to the west, where in the evening their leaves will receive the necessary energy from the setting sun.
So-called shade-loving plants can bloom and develop away from the window opening, being content with illumination of up to 10 thousand lux. However, this does not mean that they will die if they are placed in a brighter place. They just need less direct sunlight. These include some types of ficus and dracaena, philodendron, as well as tropical vines.
How to light with LED lamps?
Suppose you need to highlight Spathiphyllum, a flower that tolerates shadow well. According to the above classification, 5000 lux of light is enough for him, and he will live for a certain time under illumination 10 times less (500 lux). The illumination level in offices is only 500 lux; in apartments it is usually less.
Let's assume that we buy an LED lamp for illuminating seedlings that emits light at a level of 500 lumens. You can put Spathiphyllum under such an LED light bulb, and this should be enough for the flower. But there is a catch: the light bulb will not illuminate the entire plant with the same intensity, but only the top, provided that the flower is brought closer to the light bulb (no closer than 10 cm). You can illuminate a larger area, but then the light bulb needs to be installed higher.
Rule #1. The amount of light a plant receives will be inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the bulb and the pot.
If the light bulb is 2 times higher above the plant, it illuminates a larger area, but the plant receives 4 times less light! Therefore, you need to correctly calculate at what height to attach additional illumination lamps above the seedlings.
Scheme. Dependence of illumination on the distance to the light bulb
This means you will have to hang a fairly powerful LED light bulb over each pot, or just one above all the pots, but a really powerful one. Considering the current prices of lighting fixtures, this will be a large investment at first, and it is also worth using energy more efficiently:
- screw the light bulb into a fixture with a reflective lampshade (the inside of the lampshade can be covered with adhesive mirror tape),
- Use mirrors or regular aluminum foil to reflect the light towards the plants.
Rule #2. Light your plants from the top! A lamp that illuminates pots from the side or at an angle will cause the plants to grow crookedly and bend over in search of light.
Supplementary lighting for plants and artificial lighting sources
In most cases, indoor plants need additional lighting. Flowers, which at first glance have bright green succulent leaves and bloom regularly, will look even better if they are exposed to a phytolamp. If someone thinks otherwise, then he has an excellent chance to be convinced of the error of his thinking and assemble a phyto-lamp with his own hands. To extend daylight hours, various sources of artificial light are used. Let's look at each of them and figure out which light is best for plants.
Incandescent lamps
Illuminating plants with incandescent lamps is the least effective for several reasons. The emission spectrum of conventional light bulbs with a spiral is strongly red-shifted, which does not contribute to photosynthesis in any way. Low efficiency and, as a consequence, enormous heat generation drive their energy and light efficiency to zero. In addition, incandescent lamps have the shortest service life compared to other artificial light sources.
Fluorescent lamps
Tubular fluorescent or, as they are most often called, energy-saving fluorescent lamps of the T8 full spectrum type (T = 5300–6500°K) are considered the best option for illuminating indoor plants for many years.
They have earned many positive reviews due to the presence of a selective spectrum, efficiency and low heat transfer combined with reasonable cost. Companies specializing in the production of fluorescent lamps offer plant growers an improved option - a phytolamp with a selective emission spectrum. They work predominantly in the blue and red range, as can be seen from the characteristic glow. But the cost of such lamps for illuminating plants is an order of magnitude higher than their conventional counterparts.
DNAT
A sodium lamp is the most efficient light source. In terms of luminous efficiency and working life, these lamps are comparable to LEDs for plants. But they are not suitable for home use due to their excessively high brightness (more than 15 thousand lux). But in many greenhouses and conservatories, growing plants under artificial lighting is based precisely on gas-discharge lamps. Due to the fact that they emit more red light, they are installed in combination with 6500K fluorescent lamps.
LED light sources
All LED phytolights are divided into three groups:
- bicolor;
- with multispectrum;
- with full spectrum.
Bicolor or two-color lamps are based on blue (440–450 nm) and red (640–660 nm) LEDs. Their light is considered to be the most optimal for organizing illumination of any plants during the growing season. This working spectrum favors the process of photosynthesis, which leads to accelerated growth of green mass. That is why summer residents prefer blue-red LED lamps when growing vegetable seedlings on the windowsill.
LED lamps with a multispectrum have a wider application due to the expansion of the red range into the region of infrared and yellow light. They are in demand for illuminating adult plants, stimulating flowering and fruit ripening. In apartment conditions, it is better to use LED multispectrum for flowers with a dense crown.
A phytolight with a full spectrum of radiation can be used to illuminate flowers in an apartment, regardless of the type and location. This is a kind of universal artificial light source that emits over a wide range with maximums in the red and blue zones. The full spectrum LED lamp is a tandem of energy efficiency and light energy reminiscent of the action of sunlight.
Today, the creation of favorable conditions for a widespread transition to phyto-LEDs is not happening for two reasons:
- high cost of high-quality lamps for plants;
- a large number of fakes based on conventional LEDs.
Long daylight hours
The group of plants that require long daylight hours is represented by onions, radishes,
Chinese cabbage, radish, tobacco and some other types. However, when arranging additional lighting, it is necessary to take into account the properties of some light-loving plants, which exhibit undesirable qualities with additional home lighting. For example, Exhibition onion seedlings are grown to produce large bulbs within one season. But if these seedlings are subjected to additional lighting for more than 16 hours a day, this will provoke the premature formation of bulbs, which will reduce the purpose of growing seedlings to zero. Therefore, even for light-loving plants, artificially created daylight hours should not exceed 16 hours in order to avoid inhibition of the growth of green mass and premature formation of peduncles or bulbs.
What light is best for growth?
Of course, the ideal light source is solar energy. In apartments with windows facing southeast and southwest, you can grow any flowers, placing them in different parts of the room. But don’t be upset for those who only have a north-facing view from their window. Fluorescent and LED lamps for lighting plants compensate for the lack of sun rays.
Fluorescent lamps for plants are a time-tested budget option. They are suitable for those who are trying to create normal conditions for a flower with little investment. LED phytolamps are for those who want to speed things up and achieve the best results in a short time, despite the price of several thousand rubles.
Lamp power
In addition to the light spectrum, the power of the lamp is important - additional lighting must be efficient and economical.
Reference. Wattage is measured in watts and is the amount of energy consumed by the lamp. Wattage does not always correspond to the amount of light emitted.
A light-emitting diode (LED) lamp uses less energy than a compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) and can illuminate the same surface. Lamps produce the same number of lumens with different electricity consumption - LEDs are much more economical than CFL.