It is difficult to imagine the modern world without machines and mechanisms powered by electricity. The quality of its presentation is also improving. For example, aluminum conductors were replaced with copper ones, and non-flammable insulation was invented. Production facilities began to be divided into zones based on fire safety principles. The idea is simple: a fire that starts in one zone cannot spread to another. The need for qualified specialists who keep up with the times is growing at the same speed. What should an electrician know?
No. 3 Green electricians.
Students
are all those who are having the most fun right now. On the one hand, they are stressed by teachers in classes and sessions, but on the other hand, they know much more theoretically than even experienced electricians. Unfortunately, this is temporary until the time comes to forget a lot. When you put them in the workplace for the first time, all knowledge will turn into a lot of questions and side effects.
Lovers
- these are electricians who, seeing no point in higher education institutions, decided to conquer this science on their own. To some extent, we all were them once. Some started with amateur radio, others with covens, but in the end time put everyone in their place.
Dumaly
- This is a special type of electrician. Due to great faith in their abilities, but at the same time knowing nothing about electricity, such people can truly surprise. Fortunately for them, they completely lack the instinct of self-preservation, but in return they have some kind of amulet. They constantly come across emergencies and incidents, but somehow they always manage to escape unscathed. In a word, they can be called “extreme” in the field of electricity.
Electrician education: how to get it?
To learn to become an electrician, you need to graduate from high school and then enter a higher or secondary specialized educational institution. The directions and names of the courses can be very different, but the profile must be related to electricity in one way or another. In this case, of course, the practical component of training, as well as an extensive safety course, is of great importance.
Professional retraining for another specialty is also possible, subject to the required clearance.
Specialty: electrical power engineering and electrical engineering
What job should graduates who have received this specialty work in? Professions related to power engineering and electrical engineering are in great demand. Specialists who have received education in one of the professions related to this field will find employment in the following industries:
- at various industrial enterprises;
- in design and scientific organizations;
- at nuclear, thermal and hydroelectric power plants;
- in the coal industry;
- in construction.
The responsibilities of a specialist in this profile may include:
- design of electrical power systems and networks;
- development of schemes;
- control of installation and maintenance of electrical networks;
- selection and diagnostics of equipment;
- monitoring the safety and operating condition of equipment;
- troubleshooting repair work;
- introduction of the latest technologies.
Energy management involves scientifically based management of energy resources. Experts in the field of energy management strive to reduce energy costs by optimizing the operation of the energy complex
This is very important for modern enterprises
The specialist must have analytical abilities and a technical mindset, have computer literacy and programming skills, be able to read drawings, engineering diagrams and draw up technical documentation.
These specialists have large energy capacities in their hands, and the slightest negligence can lead to disaster.
Therefore, a responsible attitude to the performance of duties, attentiveness and punctuality is very important.
Electrotechnologies are various technological processes, common to which is the use of electricity for processing materials, electric welding processes, electrophysical and electrochemical processes, ion exchange technologies.
Electrical engineering is the specialty of designers of microelectronic circuits, devices, and applications. Computer-aided design, microprocessors, integrated circuits are their professional areas.
An electrician can conduct research in the electrical field, work in scientific institutes and laboratories, develop new methods for generating energy from renewable sources and methods of energy storage. In industrial enterprises there is the opportunity to work as a specialist in electricity and energy.
Who are electricians and what do they do?
To begin with, it should be said that such a profession as “electrician” does not exist. In official documents there are several categories of workers associated with electricity:
- Electricians;
- Electricians;
- Electricians.
At the same time, for example, an electrician is a very broad specialty, including 44 separate narrow specializations. The situation is exactly the same with the profession of electrician - there are 12 directions.
One way or another, all these people deal with electrical devices and infrastructure. Therefore, working as an electrician generally involves several areas of activity:
- repair and replacement of electrical equipment;
- diagnostics of the condition and monitoring of the operation of electrical devices;
- repair and maintenance of infrastructure facilities (substations, power lines, power plants).
The responsibilities of an electrician can thus be outlined in several points:
- Laying cables (including high-voltage) and repairing breaks in networks;
- Installation of electrical equipment for various purposes - from transformers to plugs in electrical panels and replacement of meters;
- Testing and diagnostics of new electrical equipment and devices;
- Participation in commissioning works at large facilities (substations, power plants);
- Inspection trips to facilities and checking electrical equipment for safety, wear, performance, issuing conclusions;
- Training of personnel in electrical safety rules (position of safety engineer).
Photo source pvproductions/freepik
Results of mastering the program
By studying in this profile, you will learn to create your own optoelectronic devices, understand the devices of lasers, as well as their applications in various industries (industry, construction, biology, medicine, etc.). The main emphasis in training will be on solar energy and laser technologies. During the learning process, students have the opportunity to actively engage in scientific work in the following areas:
Solar energy:
- Development of robotic systems using solar panels
- Development of solar energy complexes
- Quantum dot synthesis
- Synthesis and application of nanomaterials (fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, graphene, etc.)
- Development of liquid crystal optical devices and systems
- Development of new types of photoelectric devices and devices (LEDs, photodiodes, photoresistors, photoelectric multipliers, etc.)
Laser technology:
- Spectroscopy
- Development of 3D laser scanners
- Lidar technologies
- Laser cleaning and restoration of works of art
- The quantum physics
- Application of lasers in industry (laser welding, cutting)
- Biophotonics
- Laser medicine
By studying in this area, you will also gain basic knowledge in such software packages as:
- Comsol
- Zemax
- SciLab
- MatLab
You will also be given the opportunity to undergo scientific/industrial practice at the Physics and Technology University named after. Ioffe. Work in the laboratory named after. Zh.I. Alferova.
Requirements for personal and professional qualities of an electrician
The profession of electricians is a potentially dangerous activity, especially when working with networks and equipment under high voltage. Therefore, for specialists in the field of electrical installation, certain personal qualities are not just a formal requirement, but also a vital condition. Among these qualities and characteristics are:
Accuracy Attention to detail Responsibility in matters of compliance with work technologies and safety precautions Excellent memory Technical mindset Ability to quickly make decisions when eliminating breakdowns and emergency situations Good eyesight
Electrician training
If you enroll after 9th grade, you can receive a diploma in 4 years . After 11th grade, studying at a university will take almost 3 years. You can choose any educational institution where there is a specialty “Electrical power and electrical engineering” and the corresponding faculty.
The most prestigious universities include:
- Moscow State University named after Bauman. Power engineering.
- LETI im. Lenin in St. Petersburg. Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Automation.
- Omsk State Technical University. Energy Institute.
- Kazan State Power Plant. Institute of Electric Power and Electronics.
- UrFU named after Yeltsin in Yekaterinburg. UralENIN.
ATTENTION There is also a distance learning form - online courses, but it does not involve practice. After training, you will first have to be an intern, and only then will you have the opportunity to work full-time.
How to increase the category of an electrician from 3 to 4?
Bgau
» Other »
Loading…
Question for experts: I am interested in the conditions for assigning the next rank... Well, for example, what knowledge should an employee know... and in general, what is required to increase the level????
Best answers
There are unified states. tariff qualification directory of professions and industries. Depending on the industry and the nature of the work, the discharge grid is used. As a rule, 3-5 digits are used in industry. they are assigned by the certification commission created at the enterprise. BUT always make sure when you assign that the nature of the work corresponds to the work being completed.
An electrician with category 3 will screw in the light bulbs, and category 5 already meets deeper requirements FOR EXAMPLE for category 5 - adjustment, repair and regulation of critical, particularly complex, experimental circuits of technological equipment, complex electrical circuits of automatic lines, as well as responsible and experimental electrical machines, electrical devices, electrical appliances and electrical circuits of unique and precision metalworking equipment; - maintenance, adjustment and regulation of electrical recording and electronic devices; - maintenance and adjustment of ignitron welding machines with electronics, ultrasonic, electronic, electric pulse installations, especially complex distance protections, automatic transfer switching devices, and also complex circuits using semiconductor installations on transistor and logical elements; - checking the accuracy classes of instrument transformers; - performing work on repair, installation and dismantling of cable lines in special pipelines filled with oil or gas under pressure; - complex epoxy terminations in high-voltage cables networks, as well as installation of couplings between copper and aluminum cables; - comprehensive testing of electric motors, electrical devices and transformers of various capacities after major repairs; - preparation of repaired electrical equipment for commissioning; - studies the operating conditions of devices, identifies the causes of premature wear, takes measures to their prevention and elimination;— instructs workers using these devices on the rules of their operation and measures to prevent occupational injuries;— takes part in eliminating malfunctions in the operation of devices, their repair, installation and adjustment, electrical measurements and testing;— masters and implements progressive methods of maintenance, repair, installation and other work on the assigned type of devices; - takes part in the development of measures to improve the reliability, quality of operation of assigned technical equipment, in the development and modernization of existing devices; - participates in the preparation of requests for materials, spare parts, tools and ensures their economical and rational use; - performs work on repair, assembly and regulation of particularly complex, critical and experimental electrical machines, electrical devices and electrical appliances; - carries out comprehensive tests of electric motors, electrical devices and transformers of various capacities after major repairs;
— Prepares repaired electrical equipment for commissioning;
The rank is assigned based on certification. The procedure for conducting certification is specified in the “Regulations on personnel certification.” This Regulation is developed and approved at each enterprise.
Qualification requirements are usually indicated in the job description; if there is none, then qualification requirements and work experience can be found in the Unified Tariff and Qualification Handbook (UTKS).
Our own training centers in the Russian Federation and laboratories: + certification + advanced training + distance learning throughout Russia for any profession website: komi.ekcroskom
Social networks, page: sm/idpromresurs
Answers from experts
Without secondary education 6 months. in the previous group with secondary education 3 months with secondary electrical and higher technical education 3 months
with higher electrical and technical education 2 months
in accordance with Interindustry rules on labor protection (safety rules) during the operation of electrical installations (POT R M-016-2001, RD 153-34.0-03.150-00)
What does time have to do with it, you need knowledge, education, a desire to work, at one time I passed this stage in two weeks.
yes, at least a week if there is a recommendation from management
A few words about self-taught people
A novice electrician can independently become a highly qualified specialist only if certain conditions are met. To do this, first of all, you will need the help of a professional who will agree to take on a novice electrician as an auxiliary worker at the initial stage of training. A situation can be considered ideal if he pays some amount for the work (most often a purely symbolic amount).
A novice electrician with the rank of a student mastering mastery lessons is entrusted with only the simplest and “dirtiest” operations such as:
- gating walls for wiring;
- drilling mounting holes;
- laying wires and simple connections.
If a novice electrician has a strong desire to become a professional, he will have to strictly follow the instructions of the mentor and immediately complete all the tasks received from him. In addition, you should carefully observe all his actions and, if possible, try to copy them.
Educational articles on our website will help a novice electrician achieve certain success in mastering the profession he or she likes. To begin with, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the “Installation of electrical wiring” section. In addition, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the first steps in electrical engineering using the literature we have selected and listed below. After studying these books, the future master will be able to advance one more step along the path of mastering his favorite subject.
Electrical Engineer
Electricians who graduate from technical universities receive engineering qualifications. Specialists are trained in the following areas:
- electrical equipment and electrical technologies in the agro-industrial complex;
- electrical equipment of cars and tractors;
- management of energy resources of enterprises;
- electrical equipment of aircraft;
- production of power equipment;
- power supply and cable networks;
- electrical power systems and networks;
- relay protection and automation of electrical power systems;
- power supply
Jobs for electrical engineers are opening in construction, transport, medicine, agriculture, medicine, IT sector and defense sector. The work of these specialists may involve both the design and maintenance of electrical networks inside buildings, as well as the development of electrical equipment, the creation of reliable and efficient electrical circuit boards.
Watch this video on YouTube
Job Responsibilities
The specific list of responsibilities of an electrical engineer varies significantly depending on the area of activity of the organization. In general it looks something like this:
- Understand regulatory documents and be able to quickly find the necessary information.
- Accept and participate in the implementation of design decisions.
- Perform calculations of power and energy consumption at the facility.
- Prepare requests for the purchase of equipment and components for it.
- Organize acceptance, assembly and testing of machine tools, pumps, engines and other devices.
- Monitor the safety of electrical installations.
- Draw up acts for decommissioning equipment that has exhausted its service life.
- Monitor energy consumption at the enterprise. Suggest optimization measures.
- Observe electrical safety precautions. Instruct employees on the correct and safe use of electrical installations.
- Identify the causes of breakdowns and failures at the enterprise. Propose to management measures to eliminate them.
Knowledge and skills of an electrical engineer
An electrical engineer organizes the work of line personnel and ensures document flow. To make rational decisions, he must have an understanding of physical processes, an excellent understanding of electrical equipment, and be able to read and draw up single-line and other electrical diagrams of varying levels of complexity. The main tools of this specialist include a computer with access to information and reference databases, as well as programs for drawing up technical and commercial documentation: Electrician, Splan, AutoCAD, MsOffice and others. Beginners without experience are usually expected to have knowledge of the structure of household electrical networks and relay automation, and a basic understanding of electronics.
Among the personal qualities inherent in an electrical engineer are responsibility, attentiveness, good memory, and developed logical thinking. Having a personal car and willingness to travel will also be pluses when applying for this position.
How many electrical safety groups are there and the principles for assigning them
What is instrumentation and automation and what do service specialists do: mechanics and instrumentation and automation engineer
What is ASKUE and where is it used?
What is a surge protector, what is it for and where is it used?
What is a contactor: purpose, principle of operation, types, connection diagrams
What does IP protection mean - explanation, table, examples of use
Electrical Basics
The work of an electrician requires a large amount of knowledge. Elementary course: “Electrics for Beginners” provides the opportunity to study:
- basic concepts and quantities used in electrical engineering;
- symbols used in electrical circuits;
- materials and their electrical conductivity;
- marking of cables, electrical circuits and wires;
- methods for calculating the cross-section of cables and wires;
- methods for obtaining contacts and other connections;
- rules for constructing a grounding system and protection of electrical installations;
- methods of connecting generators and engines;
- procedure for protecting against overloads of electrical circuits;
- existing types of electrical wiring and methods of its installation;
- basic safety precautions when carrying out electrical installation work;
- rules for providing first aid in case of electric shock.
So, what does a novice electrician need to know? The basics of electricity are the basic foundation of the future electrician. But besides this, it is necessary to have a good command of the basics of applied mechanics, automation and electrical engineering.
Electrician
The main task of an electrician is to maintain the performance and normal functioning of electrical systems for domestic and industrial purposes. Persons who have received education in this specialty are required in housing maintenance services, repair shops, factories and factories.
They are the ones who deal with such problems as: replacing sockets, installing switches, energy meters, ceiling and wall lamps. In addition, the acquired knowledge and experience in repairing electronic devices gives them the ability to identify and replace damaged components in electric ovens, televisions, players, audio speakers and other equipment. Employers often add responsibilities for wiring, setup and subsequent maintenance of power equipment.
Job responsibilities
According to standard instructions typical for most enterprises, an electrician must:
- Conduct routine equipment checks and maintain entrusted equipment in serviceable condition.
- Adjust electrical appliances and switch functional modes.
- Ensure timely repairs of networks and equipment.
- Comply with all labor safety requirements when working with electricity.
- Use personal protective equipment and wear company uniform.
- Store the working tool in proper condition and promptly report its loss or breakage.
- Regularly, at least once every 2 years, undergo a professional medical examination.
- Install and dismantle power and signal cables.
- Provide instructions on safe handling of electrical networks and industrial equipment.
- Provide first aid to victims of electric shock.
Electrician qualification requirements
An electrician is one of the company's line personnel and usually works under the supervision of a chief engineer or other responsible person. The position mainly involves working with your hands, albeit under conditions of constant health risk. The passage of current through the body can cause burns, damage to the nervous system, or even death.
However, in most cases, an electrician works according to already developed instructions and projects, and therefore he is not required to have the same deep knowledge as an electrical engineer. The voltage that an employee encounters does not exceed 1000 V, so for work it is enough to obtain group 3 electrical safety clearance. Higher or secondary technical education is not a prerequisite for occupying a vacancy; to start a career at an earlier age, you can complete a vocational school or courses.
Electricians performing the tasks of electricians are subject to higher demands. They must have experience in managing power systems, have a good knowledge of electrophysics, understand the principles of current action, and understand the design of power electrical equipment.
Main tool
The necessary equipment for an electrician's work is divided into four categories:
- hand tool;
- power tools;
- measuring instruments;
- consumables and accessories.
A set of hand tools is individual for each electrician. But there is the necessary basis. Having completed training as an electrician, the young specialist will be familiar with how to work with pliers (nippers), a mounting or utility knife, a set of screwdrivers and wrenches, a hammer, a chisel, a construction tape measure, a stripper and an electric soldering iron.
If electrical installation work requires more serious intervention, then you will definitely need a hammer drill with an adapter chuck and a set of attachments, a grinder for cutting steel angles for a grounding system or laying grooves under cables. You will also need an electric drill, which can work as a screwdriver if necessary.
As follows from the course “Electricians for Beginners”, measuring instruments today perform many functions and they are necessary in work. One of the main ones is a tester for the presence of a phase in the electrical network. It looks like a screwdriver, but the body is not durable, since the device has a different purpose. More information can be read from a universal multimeter. In addition to basic measurements, it is able to check the correctness of installed equipment or laid networks. Current clamps make it possible to connect without interrupting the network and take measurements.
Auxiliary devices are not included in the list of mandatory ones, but they greatly facilitate the work of a specialist. This could be a stepladder, a carrier, an autonomous light source, markers, construction pencils, levels, calipers, etc.
Automatic protection systems
The power grid carries 2 types of threats:
- The power of household wiring is sufficient to ignite materials used in finishing premises. A short circuit in the network leads to an uncontrolled increase in current strength and ignition. It is impossible to reduce the likelihood of such a situation to zero, but it is reduced by introducing a circuit breaker into the circuit. When the current parameters increase, the device plate is deformed, a spring is released, which opens the contacts. The machine does not respond to starting current pulses.
- The neutral wire is connected to the ground, the phase wire is energized in relation to it. A current arises between such a conductor and grounded objects. There is practically no risk of injury to a person by electricity generated between 2 network cables. However, under certain conditions of current flow, electrical injury becomes fatal. Automatic protection systems ensure that current enters one wire and leaves through the other. When voltage appears between the phase and a grounded object, for example, a human body, the RCD de-energizes the network.
Required Tools
To eliminate breakdowns and install devices, a technician needs special equipment. A specialist must be able to not only connect wires and replace broken devices. He has to make holes in the walls to run wires and dismantle old, worn-out networks.
An experienced electrician has with him:
- rubber dielectric gloves, their integrity is checked before each work;
- glasses;
- Phillips screwdrivers, straight, different sizes;
- a screwdriver with a set of attachments or a cordless screwdriver;
- pliers or pliers;
- platypuses;
- round nose pliers;
- side cutters;
- nylon ties for connecting a bundle of wires;
- calipers;
- electrical installation knives, used for stripping wires;
- screw terminal blocks;
- alloy of tin and lead;
- soldering iron with nozzles;
- spanners;
- indicator screwdriver;
- multimeter;
- drill;
- perforator;
- wall chaser
When installing electrical networks and inserting devices, specific types of tools may be needed. Before work, it is necessary to check the integrity of dielectric gloves. The face and eyes must be protected with mounting glasses. We must not forget about the rules of personal safety.
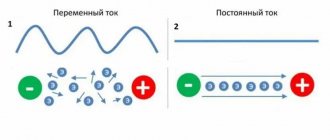
Variable and constant quantities
When electricity was just in its infancy, consumers were supplied with direct current. However, it turned out that the standard value of 220 volts is almost impossible to transmit over a long distance.
On the other hand, you cannot supply thousands of volts - firstly, it is dangerous, and secondly, it is difficult and expensive to manufacture devices operating at such a high voltage. As a result, it was decided to convert the voltage - 10 volts reaches the city, and 220 volts reaches the houses. The conversion takes place using a transformer.
As for the voltage frequency, it is 50 Hertz. This means that the voltage changes its state 50 times per minute. It starts from zero and rises to 310 volts, then drops to zero, then to -310 volts and rises to zero again. All work proceeds in a cyclical manner. In such cases, the voltage in the network is 220 volts - why not 310 will be discussed later. Abroad there are different parameters - 220, 127 and 110 volts, and the frequency can be 60 hertz.
Basic current quantities
When an electric current occurs in a circuit, a constant charge transfer occurs through the cross section of the conductor. The amount of charge transferred in a certain unit of time is called current , measured in amperes .
In order to create and maintain the movement of charged particles, it is necessary to have a force applied to them in a certain direction. If this action stops, the flow of electric current also stops. This force is called the electric field; it is also known as electric field strength. It is this that causes a potential difference or voltage at the ends of the conductor and gives impetus to the movement of charged particles. To measure this value, a special unit is used - volt . There is a certain relationship between the basic quantities, reflected in Ohm's law, which will be discussed in detail.
The most important characteristic of a conductor directly related to electric current is resistance , measured in ohms . This value is a kind of resistance of the conductor to the flow of electric current in it. As a result of the influence of resistance, the conductor heats up. As the length of the conductor increases and its cross-section decreases, the resistance value increases. A value of 1 ohm occurs when the potential difference in the conductor is 1 V and the current is 1 A.
Advantages of being an electrician
The advantages of this specialty include the possibility of additional income, for example, in carrying out all kinds of electrical work in the housing sector. It is possible to combine work in several enterprises when only preventive or emergency maintenance is required.
The great advantage of the specialty is its huge demand in the labor market.
From large enterprises to small enterprises and individual businesses, electricians are required everywhere. Accordingly, the salary is higher than that of other working specialists.
The national average in 2012 was 37 thousand rubles. With such a profession you will not be left without work at any period in the life of society.
Career growth and development
To become an electrical engineer, you need to obtain a college degree. The same applies to those who want to work as an electrical engineer, electromechanic or high-level specialist. The difference between them is small. In other cases, higher education is not required.
- Profession of a lawyer: specifics of activity, what qualities a specialist should have
Therefore, for people who have received specialized secondary education or are working from scratch, there is an opportunity to improve their qualifications and thereby increase their salaries.
For those who already have a higher education, there is always a chance to improve their rank.
This way you can get a job as a production manager or manager of an enterprise or workshop.
Safety precautions
When working with electrical networks or devices, observe the following rules:
- Before operating or repairing equipment, read the instructions. The safety section specifies unacceptable actions that can lead to short circuits and electric shock.
- The devices must be de-energized. After this, the condition of the wire insulation is assessed. If damage is detected, bare areas are covered with electrical tape.
- If it is impossible to de-energize the electrical network, work in dielectric gloves, shoes with rubber soles and special glasses.
- Access to switchboards and electrical installations is prohibited for novice specialists.
- Do not touch stripped wires with your hands. To find the phase, multimeters, indicator screwdrivers and other tools are used.
Required level of knowledge
Electrical basics are the bare minimum that an electrician needs to work. Here are a few categories that a modern electrician must have information about.
- Direct purpose of the device or mechanism that needs repair.
- Frequent problems that occur with a specific device.
- Rules for operating a non-working mechanism or device,
- Basics of safety precautions when carrying out electrical work.
If there is a need to repair the wiring, the electrician must know and present its diagram in detail, and also be able to diagnose the causes of failure.
General labor protection requirements.
2.1. Electrical personnel at least 18 years of age who have passed a medical examination, industrial training, knowledge testing in the qualification commission of the enterprise with the assignment of an electrical safety group (II-IV) and who have received a certificate of knowledge testing as an operational repair worker are allowed to work independently as an electrician in servicing electrical equipment. personnel.
2.2. Before being allowed to work independently, an electrician must pass:
- training in professional training programs;
- initial training at the workplace;
- testing knowledge of instructions: on labor protection;
- to provide first aid to victims of industrial accidents;
- on the use of protective equipment necessary for the safe performance of work;
- on fire safety;
2.3. Admission to independent work is issued by appropriate order.
2.4. In the future, the electrician must go through:
- repeated training at the workplace at least once every three months;
- periodic testing of knowledge on the Rules for the Technical Operation of Consumer Electrical Installations (PTEEP) and the Interindustry Rules for Labor Protection (Safety Rules) during the Operation of Electrical Installations (POT RM - 016 - 2001) for the electrical safety group at least once every 12 months;
- medical examination at least once every 24 months.
2.5. When performing official duties, you must have with you a certificate of knowledge testing on PTEEP and POT RM - 016 - 2001.
2.6. An electrician must know and follow the Internal Regulations.
2.7. While working, an electrician may be exposed to the following dangerous and harmful production factors:
- accidental contact with live parts that are energized;
- electric arc and combustion products;
- rotating parts of machines and mechanisms not protected by guards;
- work at height;
- increased noise level (more than 85 dBA).
2.8. The electrician must be provided with special clothing, safety shoes and other personal protective equipment in accordance with approved standards and must use them during the work.
2.9. Keep the workplace clean. Do not allow it to be cluttered with parts, materials, waste, or foreign objects. Wiping materials (rags) should be stored in metal boxes with appropriate labels.
2.10. Fuels and lubricants should be stored in specially designated rooms.
2.11. Smoking on the territory and in production premises is permitted only in specially designated areas.
2.12. An electrician must know where fire extinguishing equipment is located and be able to use it.
2.13. If you feel unwell, you must report to the energy specialist or administration.
2.14. Do not allow the presence of unauthorized persons in electrical rooms.
2.15. The electrician must know the location of the first aid kit.
2.16. In the event of an accident, you must immediately seek medical help and notify the power engineer or administration.
2.17. The electrician must immediately notify the energy sector or administration of any noticed shortcomings or malfunctions of the equipment.
2.18. An electrician must be trained in how to free a person caught under voltage from the action of electric current and provide him with first aid, and must also provide first aid in other accidents.
2.19. The electrician is responsible for the correct, technically competent operation of electrical equipment located in the electrical panel room, its safety, exemplary maintenance and prompt action on incoming signals.
2.20. The electrician is responsible in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for failure to comply with the rules of this Instruction, PTEEP, POT RM - 016 - 2001, Internal Regulations, as well as for incorrect actions that led to an accident, damage to equipment, or an accident.
Advantages and disadvantages
With increasing qualifications and obtaining a higher rank, wages increase. And this is a tangible incentive. To improve the level of qualifications, various training courses are held for electricians.
The most difficult part of working as an electrician is correctly identifying the fault.
Any field of activity has its own advantages and disadvantages that arise in its process. The advantages of being an electrician are:
- Opportunity to earn additional income.
- Combination is also possible, that is, the implementation of the work process at several enterprises.
- This profession is one of the most in demand.
Negative features are:
- High danger during work.
- There are also times when it is necessary to work at height.
- Salary depends on qualifications and location of activity.
Professions related to electricity
The list of tasks that workers and engineers have to solve when setting up new networks and maintaining old ones in proper condition is very extensive. There is a specialization that allows you to train professionals in a realistic time frame, i.e. during their studies at colleges and universities.
- Electrician. Responsible for servicing electrical equipment and maintaining internal networks in working order. Sets up and repairs household appliances, communication systems, lighting fixtures, replaces sockets and switches.
- Electrician. Specializes in repair work of power supply and low-current systems. Serves lighting panels, low-voltage electric motors, pumps, landline telephones, etc.
- Electrician. Lays internal and external networks, installs and repairs equipment related to the power supply of various objects and territories. Mounts and adjusts transformers, punches holes for laying cables.
- Electrician Creates electrical wiring outside and inside the building, marks and secures cables. Reads diagrams, installs street lighting poles and overhead lines.
- Electrical Engineer. Designs electrical networks in residential and industrial buildings, calculates planned electricity consumption, selects lighting equipment, panel models, etc. Provides acceptance, storage and decommissioning of electrical installations.
- Energy Engineer. Designs electrical, heat and gas networks. Selects and purchases the necessary equipment. Checks automation and relay protection. Monitors loads on the power system. Optimizes energy costs.
Where to start learning?
The first thing you need to become an electrician is to master the appropriate amount of knowledge. You must learn to navigate basic electrical quantities, operating principles of elementary circuits, and radio components. You also need to understand the laws of electric current flow, voltage transmission, etc.
In relation to the chosen profession, it is necessary to study the relevant literature or take a course according to the educational institution’s program.
University, technical school, college
If you decide to become an experienced electrician, then training at a specialized institution will not hurt you. Today, many universities, technical schools and colleges provide vocational education for electricians in various areas.
Let's look at the features of training courses for each of them:
- Higher educational institutions will require about 4 to 5 years of training from a beginning electrician. Compared to other types of institutions for training electricians, they provide a minimal practical base, but they prepare good specialists with deep theoretical knowledge in the electrical field. An important criterion is obtaining an 11th grade education or having a professional one that excludes such a need.
- Technical school represents the golden mean in terms of theoretical and practical skills that an electrician receives after graduation. Of course, the theory is not studied in such a detailed manner, but this is more than enough to produce competent electricians. Training can be carried out either after 9th grade for 4 years, or after 11th grade for 3 years.
- College or school - prepares the working professions of electricians; as a rule, the theoretical part here is kept to a minimum, maximum emphasis is placed on acquiring practical skills. An electrician's license can be obtained fairly quickly - from 1 to 3 years.
The above training options provide the opportunity for both paid and free education. As a result, you receive a diploma or certificate of appropriate qualifications, and some institutions even take care of the employment of their graduates.
Of course, not all offers will exceed the average salary, but this will be an excellent platform for practical consolidation of knowledge. A significant disadvantage is the rather lengthy process to become an electrician.
Courses
Professional courses for electricians have become especially popular in the modern world, where the constant development of the labor market creates constant demand. Thanks to this, you can become an electrician in such special courses in 2 to 8 weeks. Training can take place both online and offline, which greatly simplifies the process of mastering the profession of an electrician. Depending on the specific course, you can take it either from a textbook or through webinars or conferences.
The disadvantage of training in courses is that the amount of information is rather small; a novice electrician receives exposure to the basics of electrical engineering and narrowly focused practical recommendations. Which he will be able to test directly in independent practice. In addition, courses are always offered on a paid basis.
A significant advantage is much greater freedom - to obtain a certificate, you can not leave another job or study and master the profession of an electrician in parallel. Also during the courses you will get a summary of what concerns a specific type of activity.
Self-study
If none of the above methods suits you, you can become an electrician yourself by studying the information you are interested in in the literature or on the Internet. Having joined the ranks of home craftsmen, you are unlikely to be able to perform any complex work, but installing wiring in an apartment or installing simple household equipment will be a clear and easily implemented task for you.
To become an experienced self-study specialist, you will still need the help of a qualified specialist. It is advisable to work with practitioners, if there is an opportunity to be hired as an electrician’s assistant, at least for a nominal fee - this would be an ideal option.
At the initial stage, an apprentice electrician will be entrusted with the simplest operations (shaping walls, drilling holes, laying wires, well, bring it - give it), here it is important to carefully complete all the tasks and watch what your mentor is doing.
Wall chipping
After some time, you will be able to repeat the same work yourself without any problems.